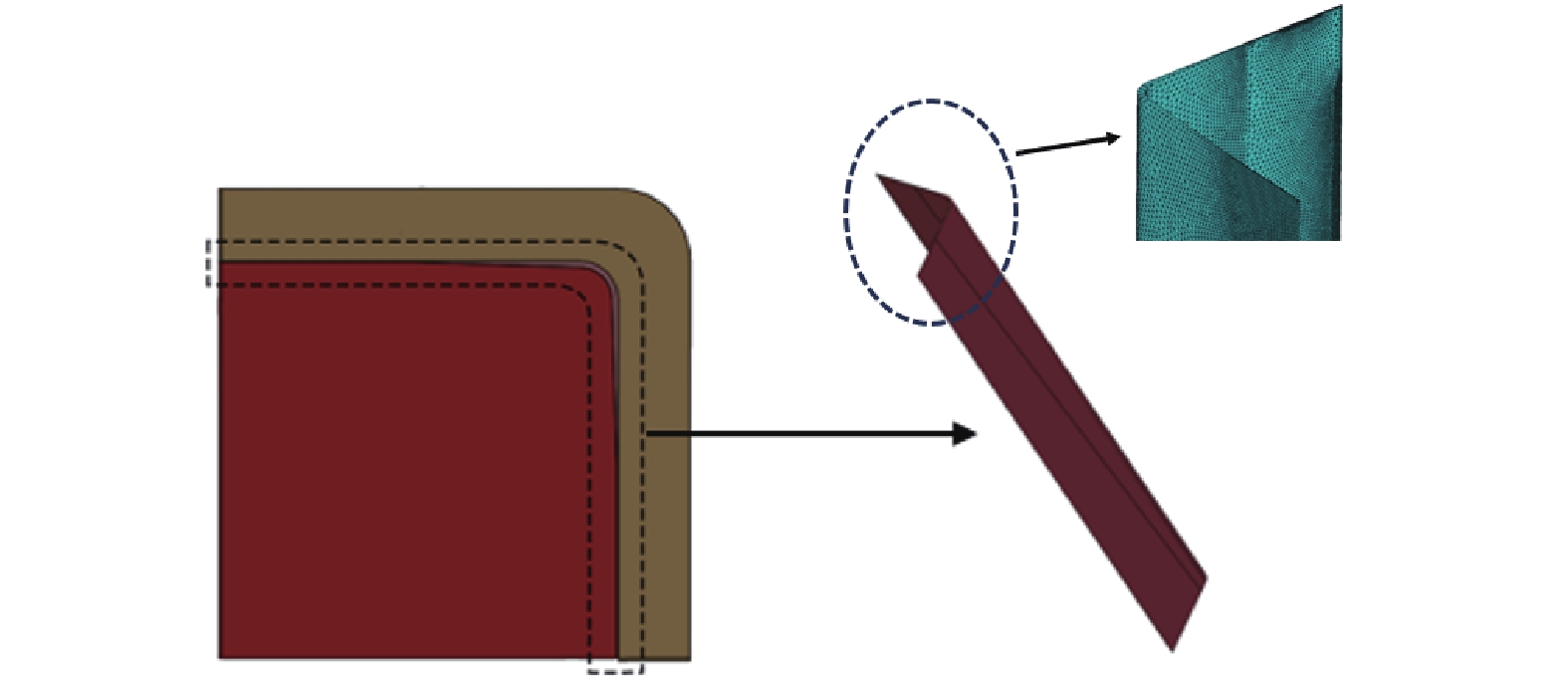
Numerical simulation of slag film distribution in protective slag of ER70-Ti steel crystalliser
-
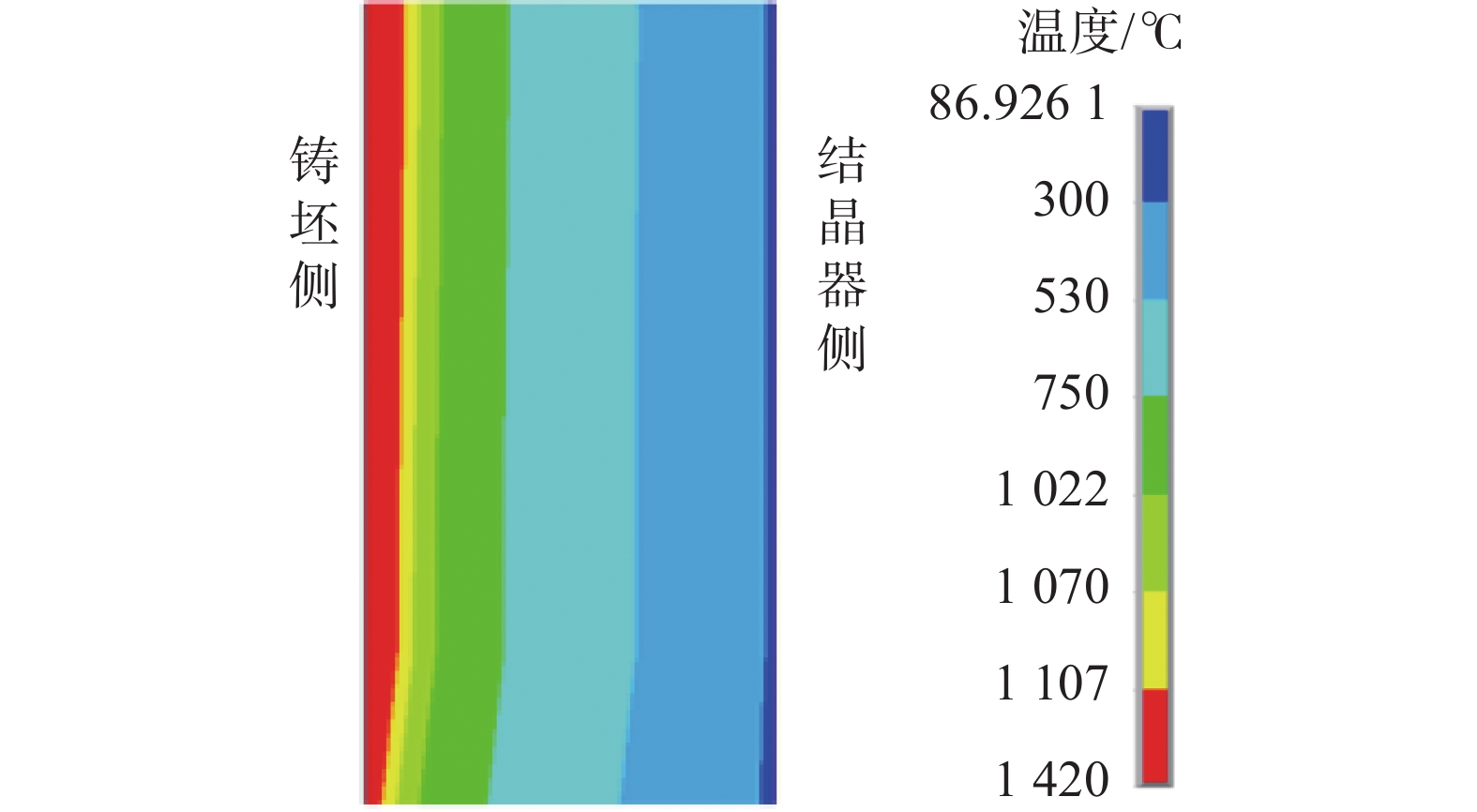
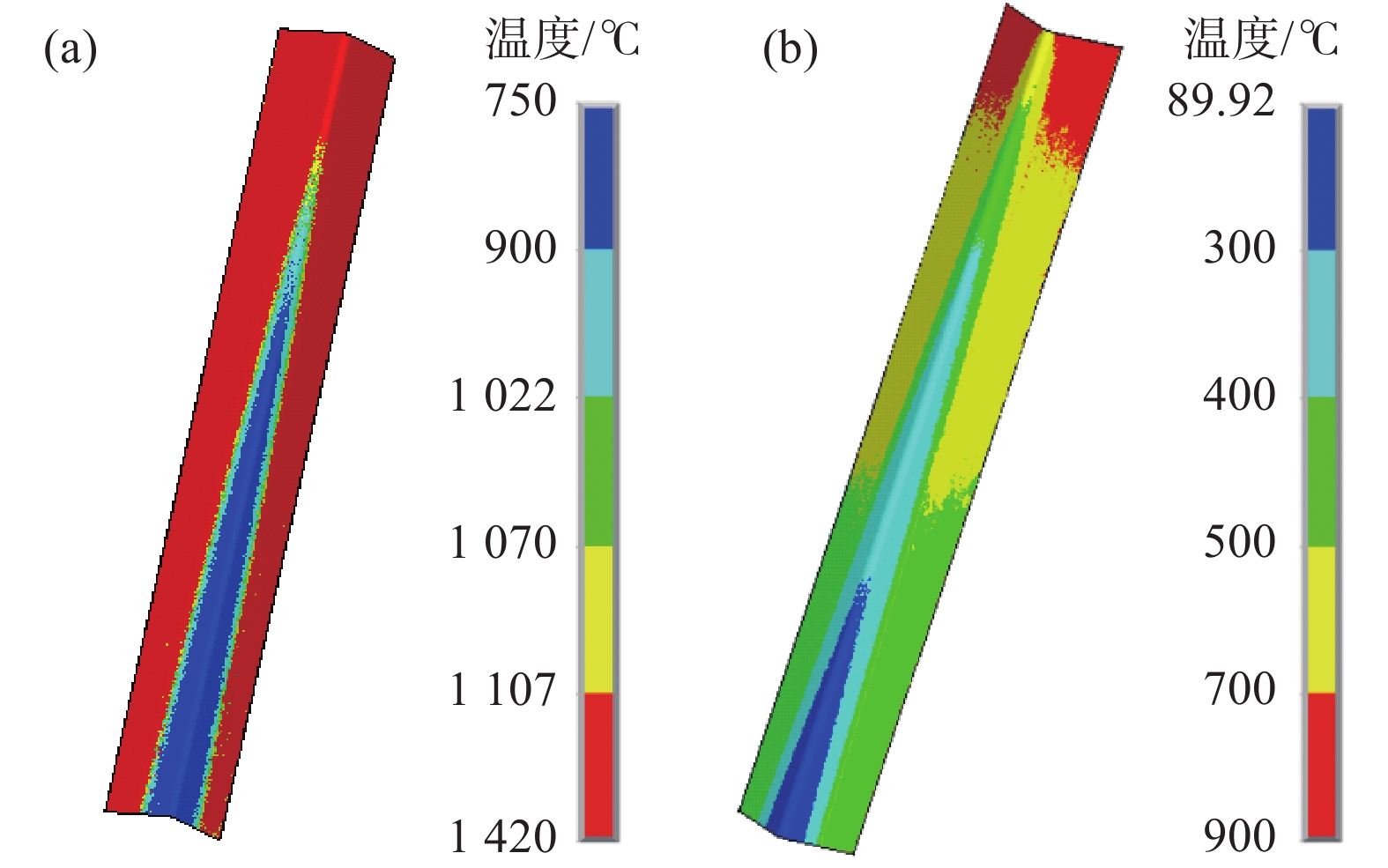
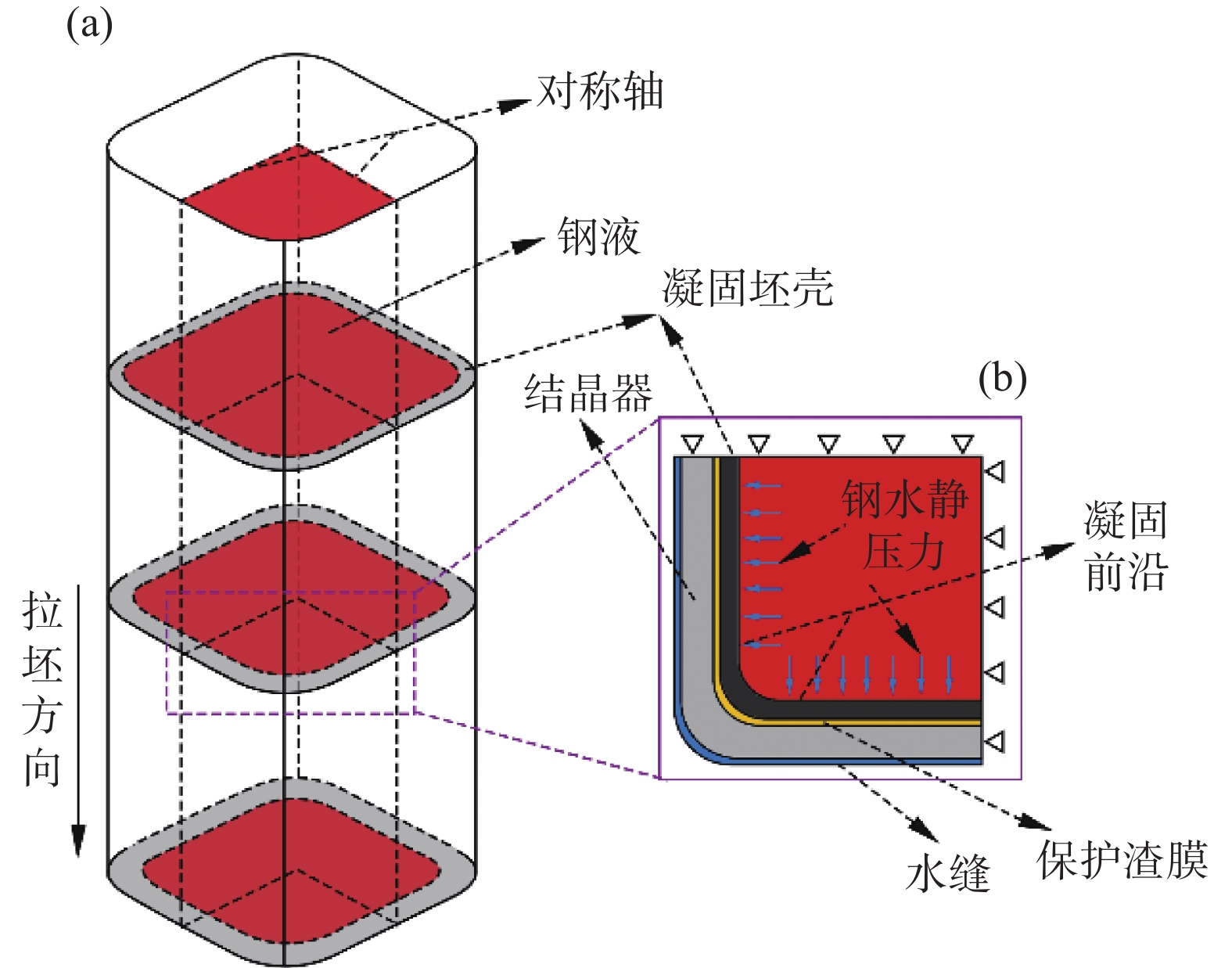
摘要: CaO-Al2O3-TiO2基专用保护渣有效解决了ER70-Ti钢生产中的钢渣界面反应严重的难题,但是否能形成合理结构的液/固渣膜,对于进一步提升铸坯质量意义重大。文中利用有限元软件建立了ER70-Ti钢连铸结晶器传热模型及渣膜传热模型,分析了结晶器内液/固渣膜沿拉坯方向的不均匀分布,并探讨了拉速、浇注温度等工艺参数对液态渣膜分布的影响。结果表明:在结晶器出口处,铸坯侧的渣膜温度范围为777.87~
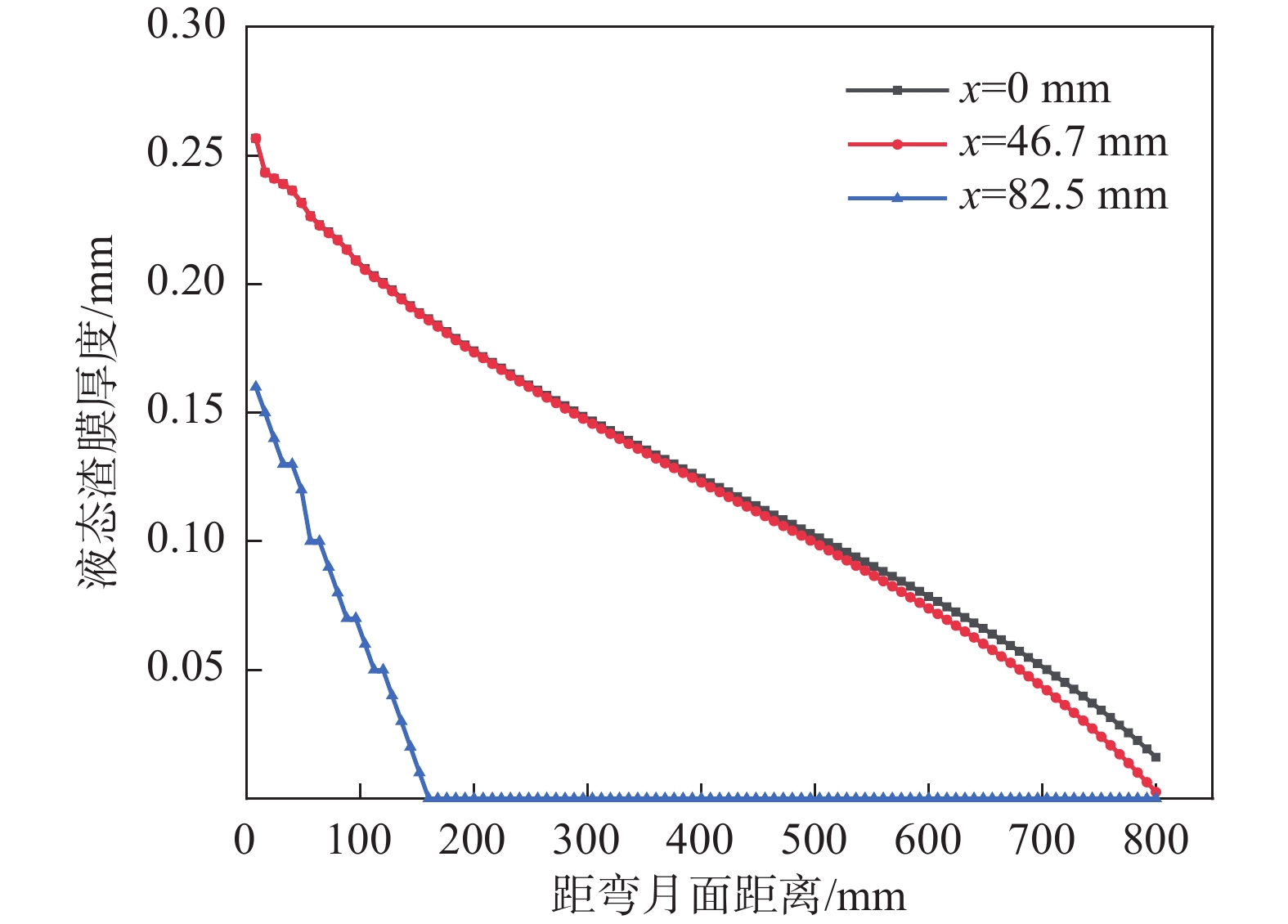
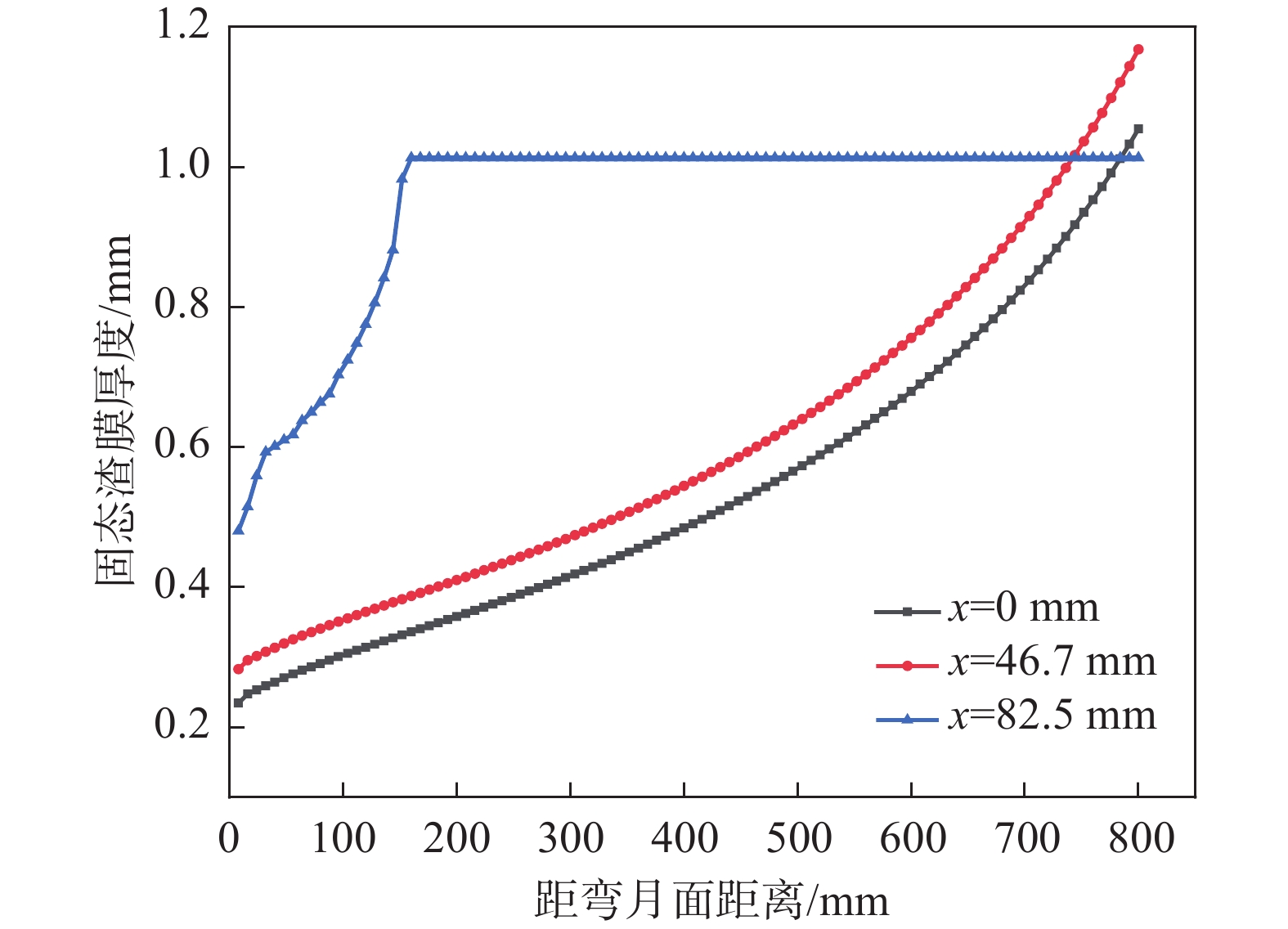
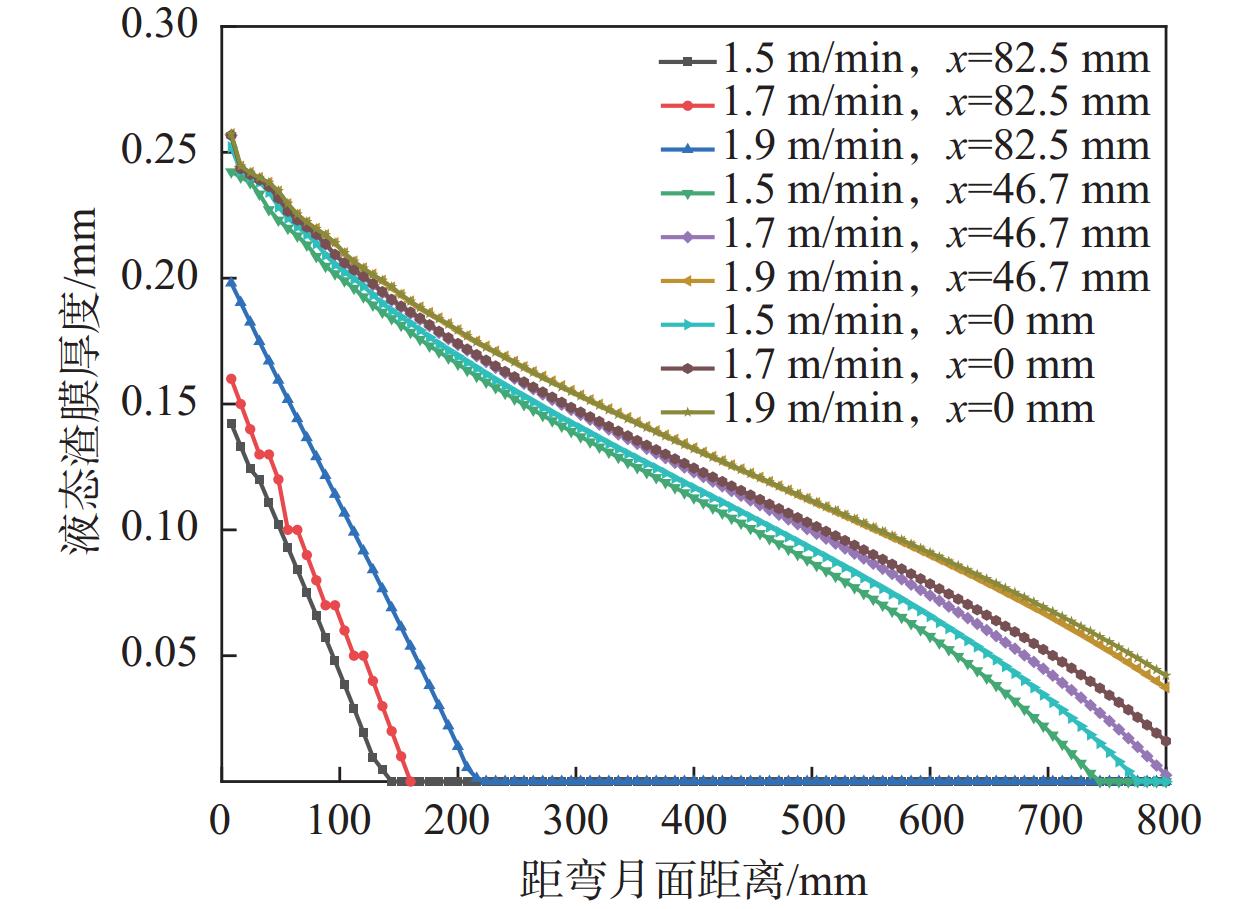
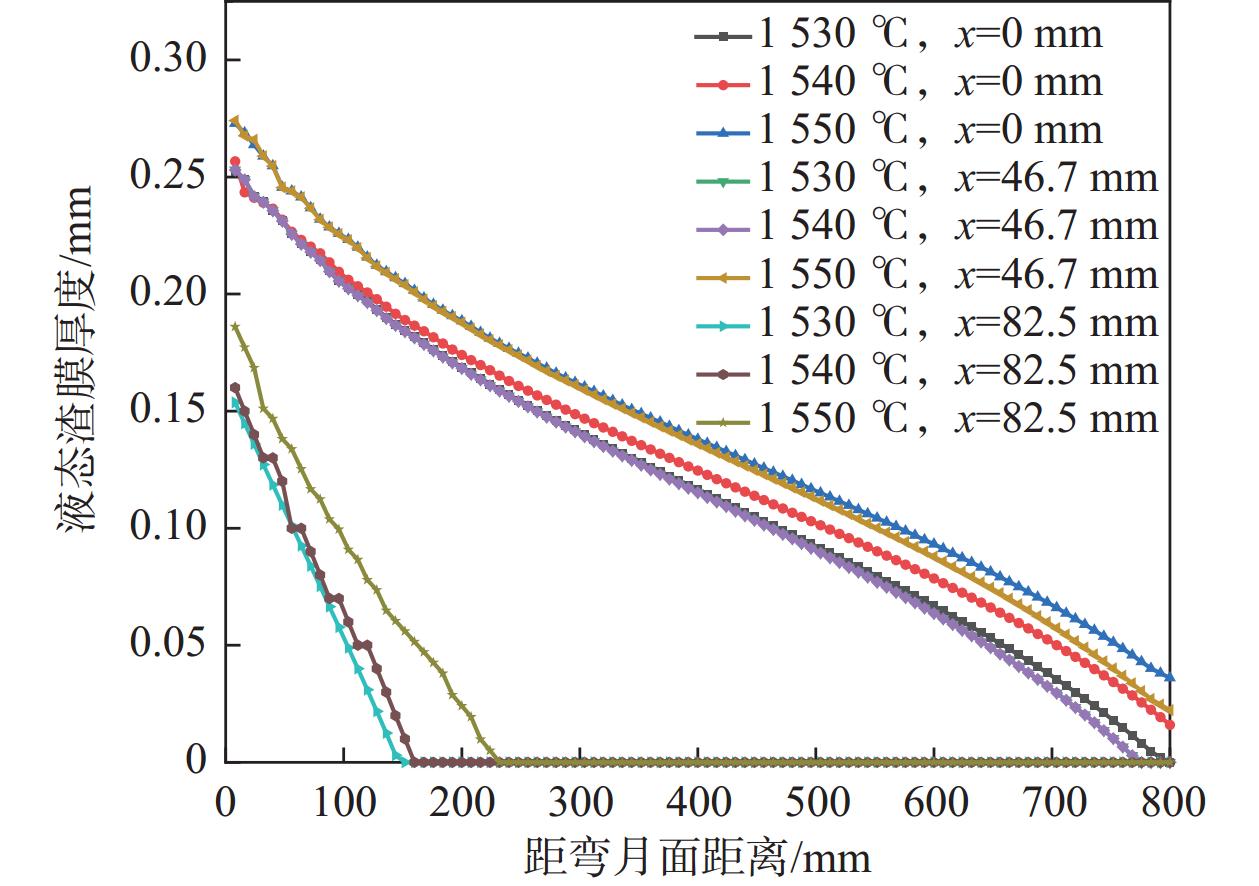
1113.3 ℃;结晶器侧渣膜温度较低,为89.92~450.54 ℃。沿拉坯方向,液态渣膜的厚度逐渐减小,而固态渣膜厚度逐渐增加,最大厚度可达1.168 mm。进一步分析发现,拉速的提高有利于增大液态渣膜的厚度,拉速每提高0.2 m/min,液态润滑区的长度平均可延长40 mm。当浇注温度从1530 ℃升高到1550 ℃时,表面中心处液态渣膜厚度从0.252 mm增加到0.272 mm,结晶器出口处液态渣膜厚度从0 mm增加到0.036 mm。Abstract: The CaO-Al2O3-TiO2-based protective slag effectively solves the problem of serious slag interface reaction in the production of ER70-Ti steel, but it is still unknown whether a liquid/solid slag film with reasonable structure can be formed. In this study, the finite element software was used to establish a heat transfer model and a slag film heat transfer model for ER70-Ti steel, to analyse the changes of liquid/solid slag film in the crystallizer and to explore the influence of process parameters on the distribution of liquid slag film. The results show that the temperature of the slag film on the billet side ranges from 777.87 to1113.3 ℃ at the exit of the mould; the temperature of the slag film on the mould side is lower, ranging from 89.92 to 450.54 ℃. Along the direction of billet drawing, the thickness of liquid slag film decreases gradually, while the solid slag film thickens gradually, and the maximum thickness is up to 1.168 mm. The increase of drawing speed is conducive to the increase of the thickness of liquid slag film, and every increase of the drawing speed by 0.2 m/min, the liquid lubrication zone can be lengthened by an average of 40 mm. When the pouring temperature is increased from1530 to1550 ℃, the thickness of the liquid slag film at the centre of the surface increases from 0.252 to 0.272 mm, and the liquid slag film thickness at the outlet of the crystalliser increased from 0 to 0.036 mm. -
表 1 ER70-Ti钢成分
Table 1. ER70-Ti steel composition
% C Si Mn S P Ni Mo Cr Ti 0.07~0.09 0.48~0.58 1.58~1.68 ≤0.008 ≤0.01 0.8~0.9 0.38~0.39 0.18~0.28 0.09~0.12 表 2 保护渣的物性参数
Table 2. Physical parameters of protective slag
熔化
温度/℃黏度/
(Pa·s)热阻/
(W·m−2·℃−1)密度/
(kg·m−3)导热系数/
(W·m−1·K−1)1 070 0.37 1.34 1 500 1.45 -
[1] LIU Y Y, CHEN Z Y, JIN T N, et al. Current status and outlook of the development of high temperature titanium alloys at 600 ℃[J]. Materials Herald, 2018,32(11):1863-1869. (刘莹莹, 陈子勇, 金头男, 等. 600 ℃高温钛合金发展现状与展望[J]. 材料导报, 2018,32(11):1863-1869. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.11.013LIU Y Y, CHEN Z Y, JIN T N, et al. Current status and outlook of the development of high temperature titanium alloys at 600 ℃[J]. Materials Herald, 2018, 32(11): 1863-1869. doi: 10.11896/j.issn.1005-023X.2018.11.013 [2] WANG X J, JIN H B, ZHU L G, et al. Influence of titanium content in steel on slag-gold reaction in continuous casting mould[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020,55(12):46-55. (王杏娟, 靳贺斌, 朱立光, 等. 钢中钛含量对连铸结晶器内渣金反应的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2020,55(12):46-55.WANG X J, JIN H B, ZHU L G, et al. Influence of titanium content in steel on slag-gold reaction in continuous casting mould[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020, 55(12): 46-55. [3] ZHU L G, ZHANG X S, LIU Z X, et al. Analysis and control of transverse cracks on the surface of ER70-Ti steel casting billets[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020,41(3):166-171. (朱立光, 张晓仕, 刘增勋, 等. ER70-Ti钢铸坯表面横向裂纹分析及控制[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2020,41(3):166-171. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.03.029ZHU L G, ZHANG X S, LIU Z X, et al. Analysis and control of transverse cracks on the surface of ER70-Ti steel casting billets[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2020, 41(3): 166-171. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2020.03.029 [4] WANG X J, WANG Y, ZHU L G, et al. Composition design of low reactivity continuous casting slag for high titanium steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(4):134-141. (王杏娟, 王宇, 朱立光, 等. 高钛钢专用低反应性连铸保护渣成分设计[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(4):134-141. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.04.021WANG X J, WANG Y, ZHU L G, et al. Composition design of low reactivity continuous casting slag for high titanium steel[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(4): 134-141. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.04.021 [5] PIAO Z L, WANG X J, ZHANG C J, et al. Behaviour of steel-slag interface reaction in continuous casting crystallizer of high titanium steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2022,57(3):61-70. (朴占龙, 王杏娟, 张彩军, 等. 高钛钢连铸结晶器内钢-渣界面反应行为[J]. 钢铁, 2022,57(3):61-70.PIAO Z L, WANG X J, ZHANG C J, et al. Behaviour of steel-slag interface reaction in continuous casting crystallizer of high titanium steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 2022, 57(3): 61-70. [6] PIAO Z L. Development and metallurgical characterisation of CaO-Al2O3-TiO2 based protective slag for high titanium steel [D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2021. (朴占龙. CaO-Al2O3-TiO2基高钛钢用保护渣开发及冶金特性研究[D]. 北京: 北京科技大学, 2021.PIAO Z L. Development and metallurgical characterisation of CaO-Al2O3-TiO2 based protective slag for high titanium steel [D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology Beijing, 2021. [7] MENG Y, THOMAS B G. Heat-transfer and solidification model of continuous slab casting: CON1D[J]. Metallurgical and materials transactions B, 2003,34:685-705. [8] SARASWAT R, MAIJER D M. The effect of mould flux properties on thermo-mechanical behaviour during billet continuous casting[J]. ISIJ international, 1999,47(1):95-104. [9] HAN H N, LEE J E, YEO T J. A finite element model for 2-dimensional slice of cast strand[J]. ISIJ international, 1999,39(5):445-454. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.39.445 [10] CAI Z Z, ZHU M Y. Study on thermal behaviour of steel solidification process in slab continuous casting mould Ⅰ. Mathematical modelling[J]. Journal of Metals, 2011,47(6):669-675. (蔡兆镇, 朱苗勇. 板坯连铸结晶器内钢凝固过程热行为研究Ⅰ. 数学模型[J]. 金属学报, 2011,47(6):669-675.CAI Z Z, ZHU M Y. Study on thermal behaviour of steel solidification process in slab continuous casting mould Ⅰ. Mathematical modelling[J]. Journal of Metals, 2011, 47(6): 669-675. [11] NIU Z Y, CAI Z Z, ZHU M Y. Dynamic distributions of mold flux and air gap in slab continuous casting mold[J]. ISIJ International, 2019,59(2):283-292. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2018-609 [12] YANG J, CHEN D F, LONG M J, et al. An approach for modelling slag infiltration and heat transfer in continuous casting mold for high Mn–high Al steel[J]. Metals, 2019,10(1):51. doi: 10.3390/met10010051 [13] SHAO K K. Research on cavity design of new billet continuous casting mould [D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2018. (邵凯凯. 新型方坯连铸结晶器腔形设计研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2018.SHAO K K. Research on cavity design of new billet continuous casting mould [D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2018. [14] SAVAGE J, PRITCHARD W H. The problem of rupture of the billet in the continuous casting of steel[J]. Journal of the Iron and Steel Institute, 1954,178(3):269-277. [15] HU P H. Study on numerical calculation of protective slag slag film/air gap and its thermal resistance in crystalliser[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018. (胡鹏宏. 结晶器保护渣渣膜/气隙及其热阻数值计算研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2018.HU P H. Study on numerical calculation of protective slag slag film/air gap and its thermal resistance in crystalliser[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2018. -





 下载:
下载: