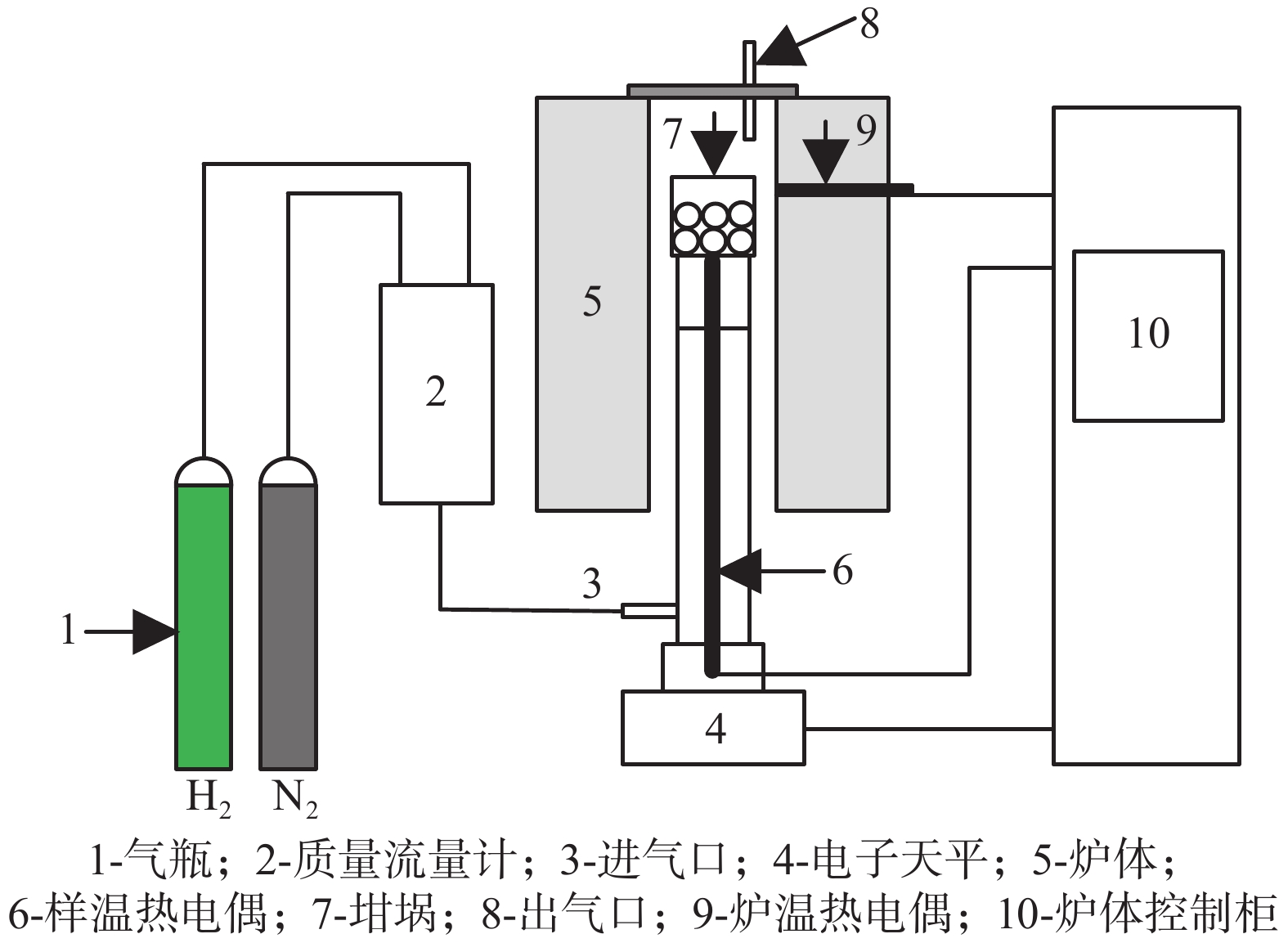
Experimental study on hydrogen-carbon synergistic reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite
-
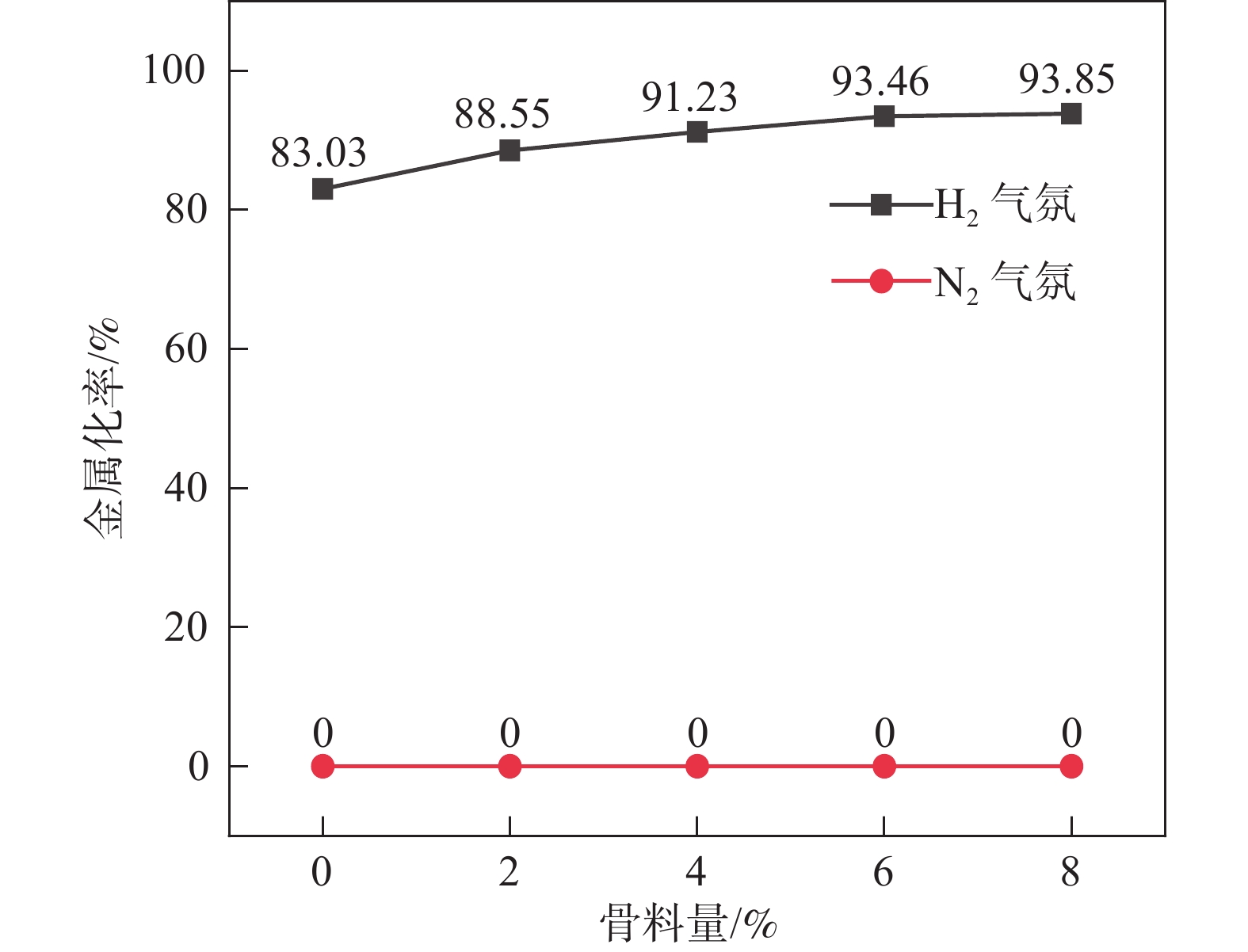
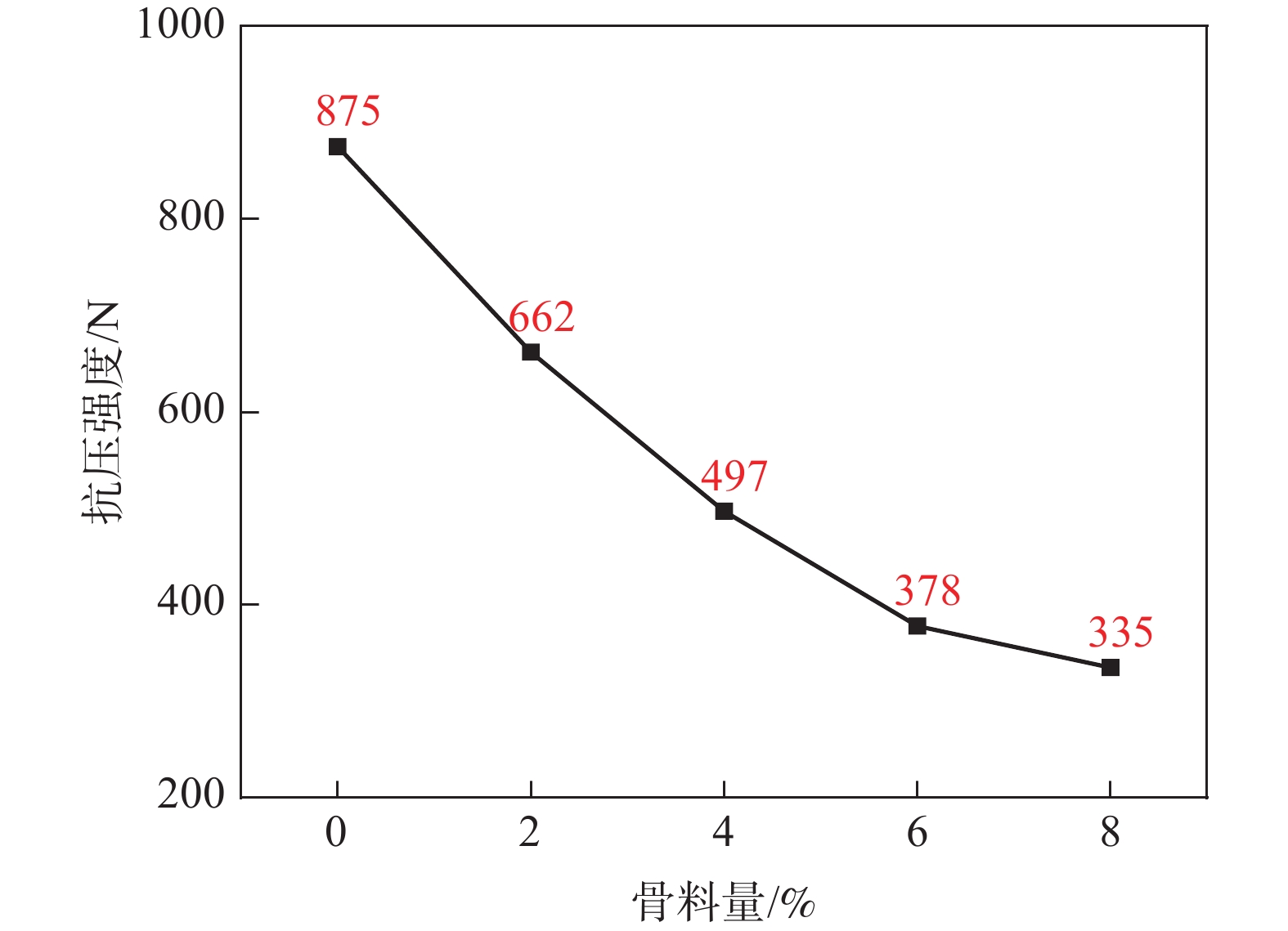
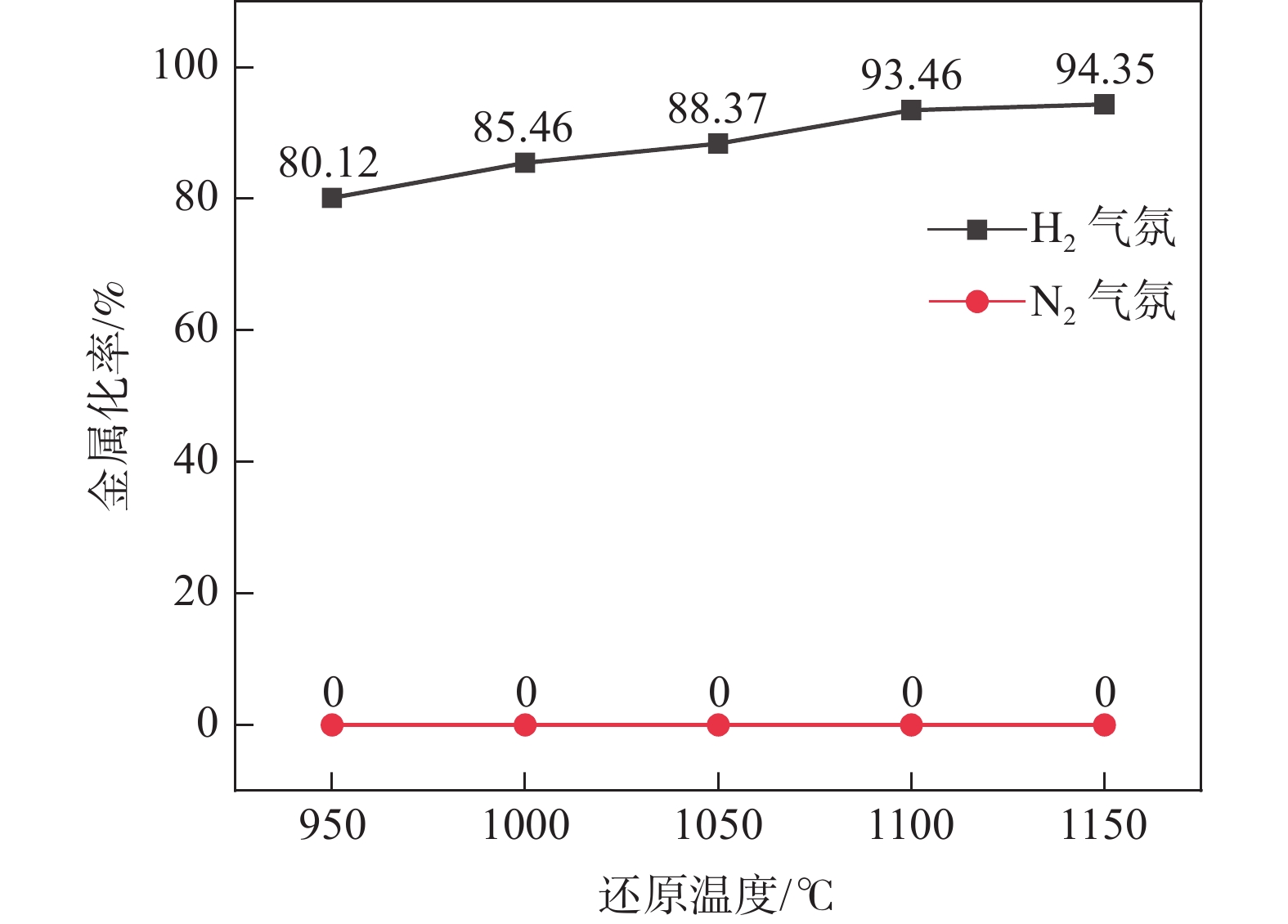
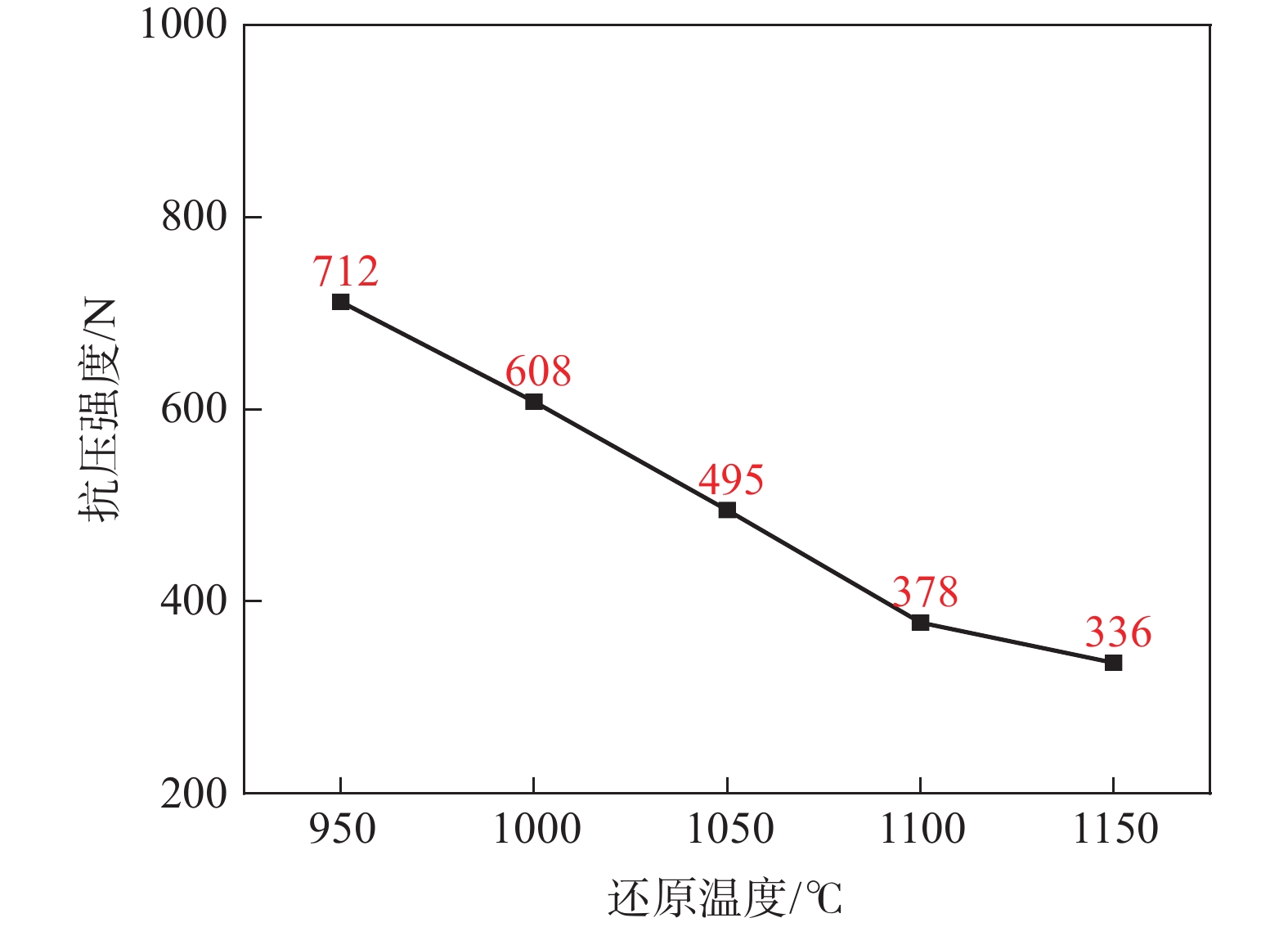
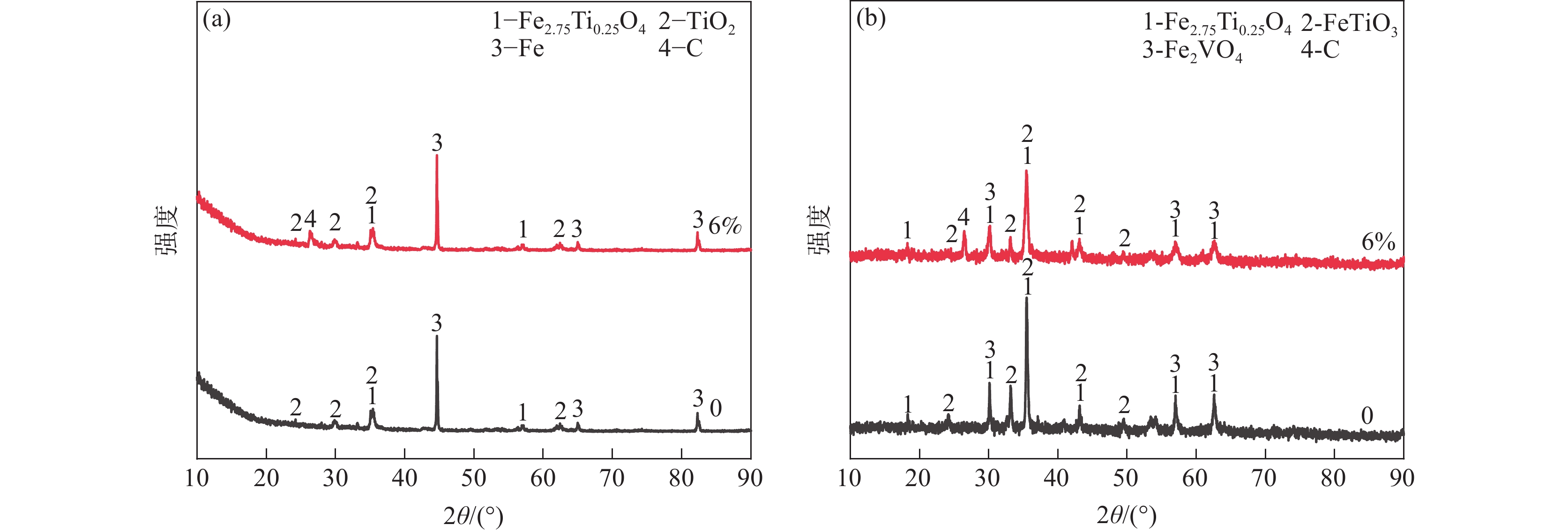
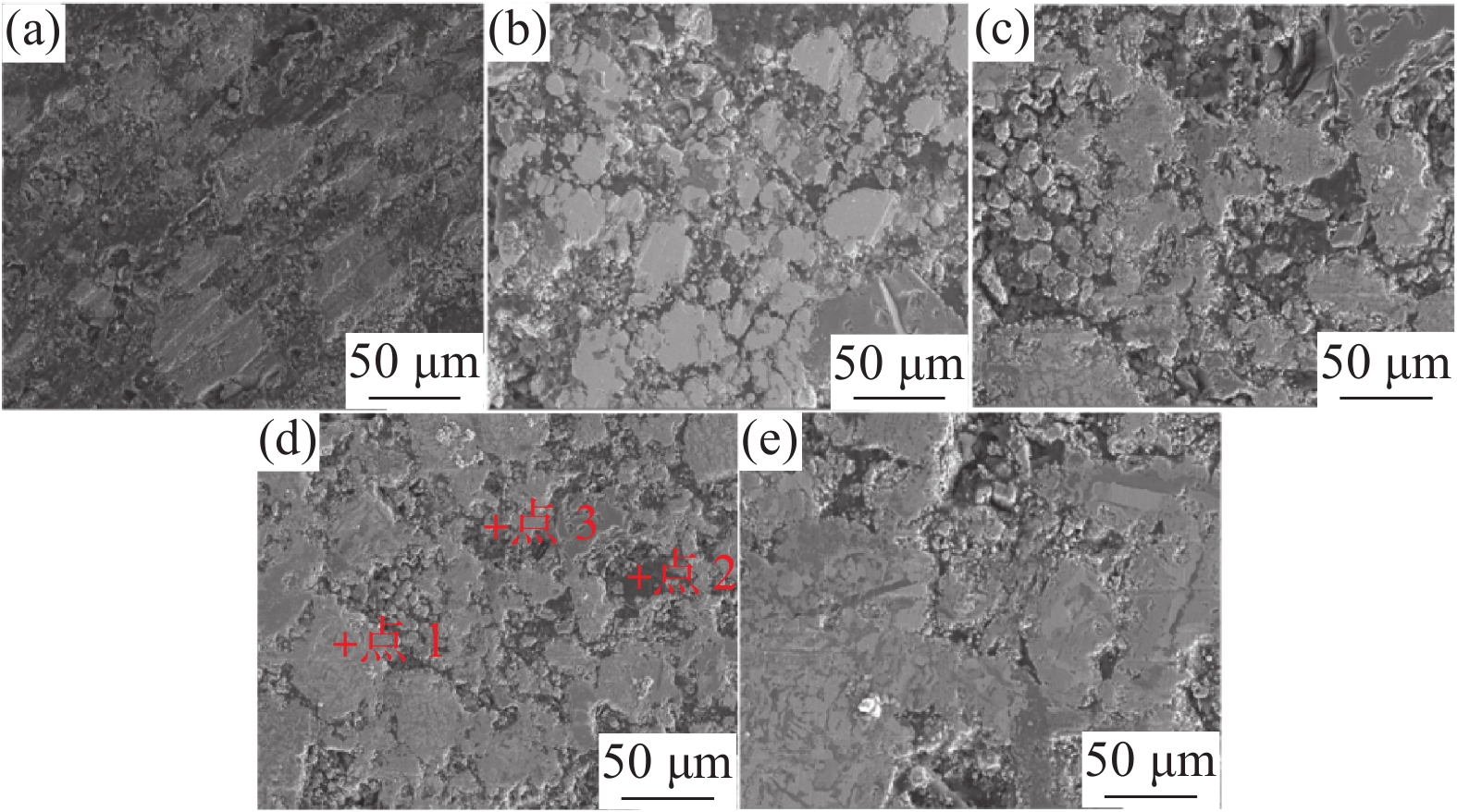
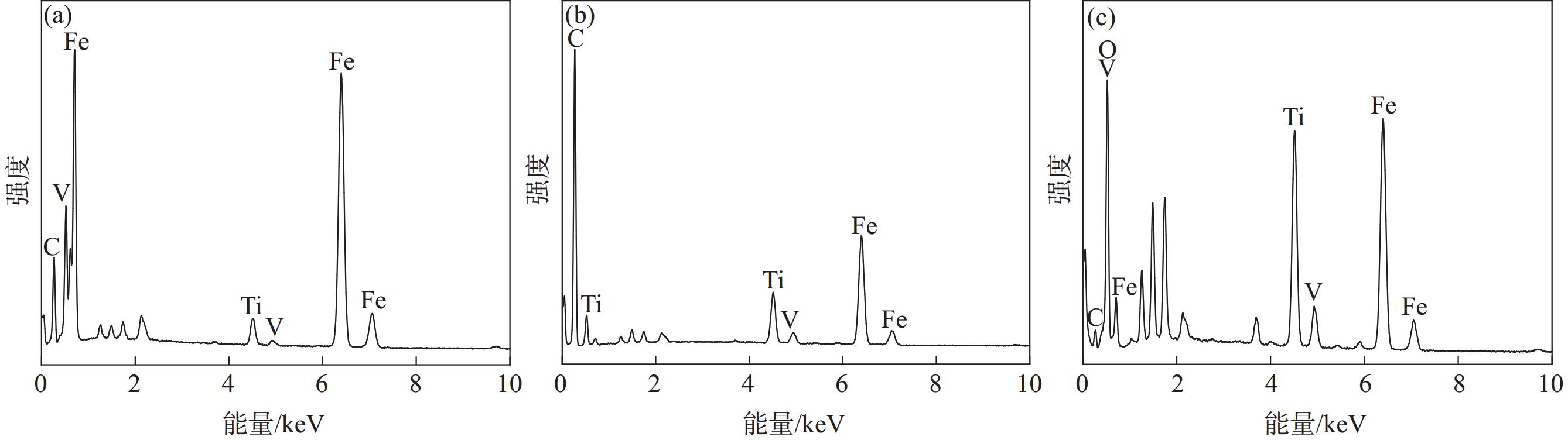
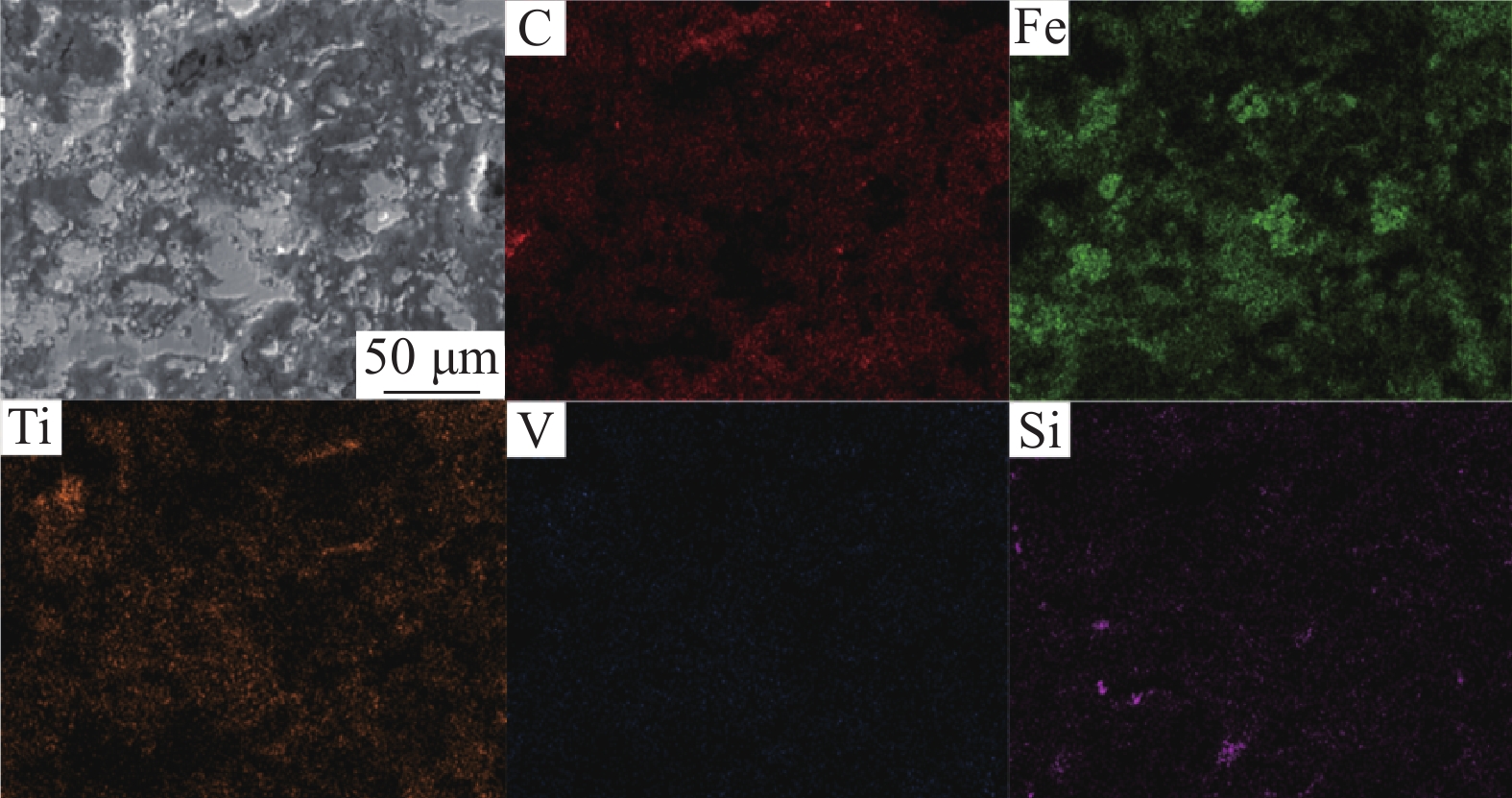
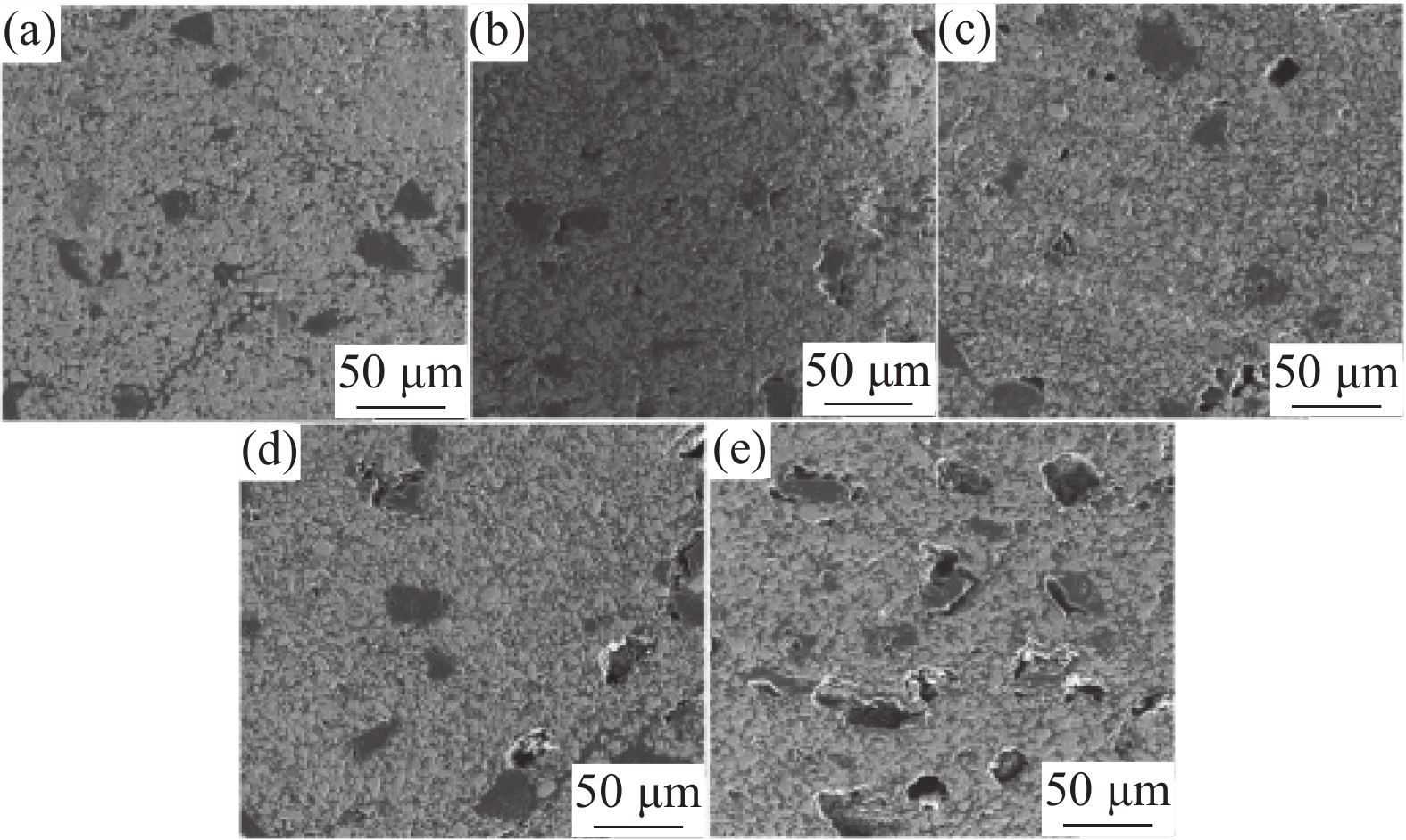
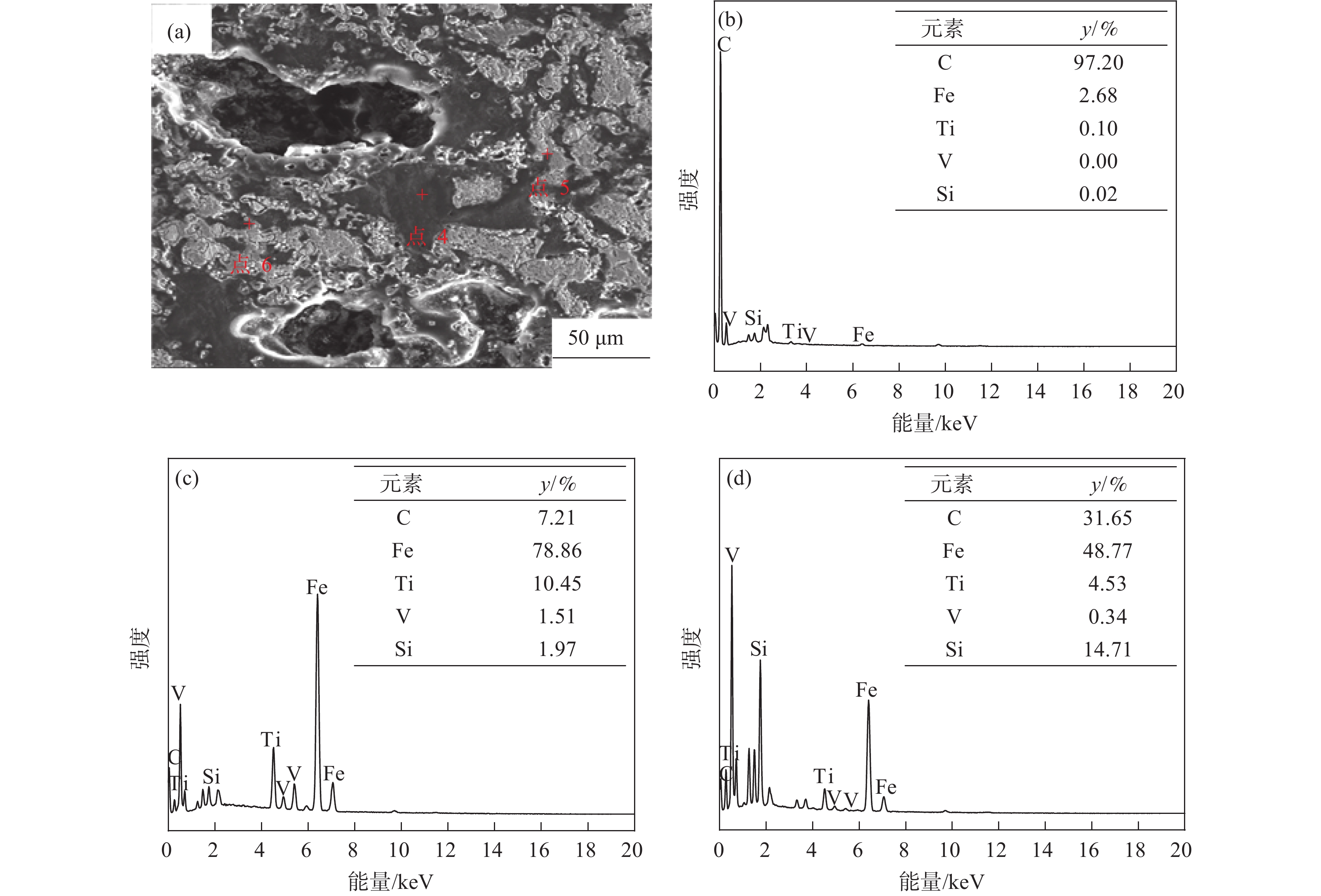
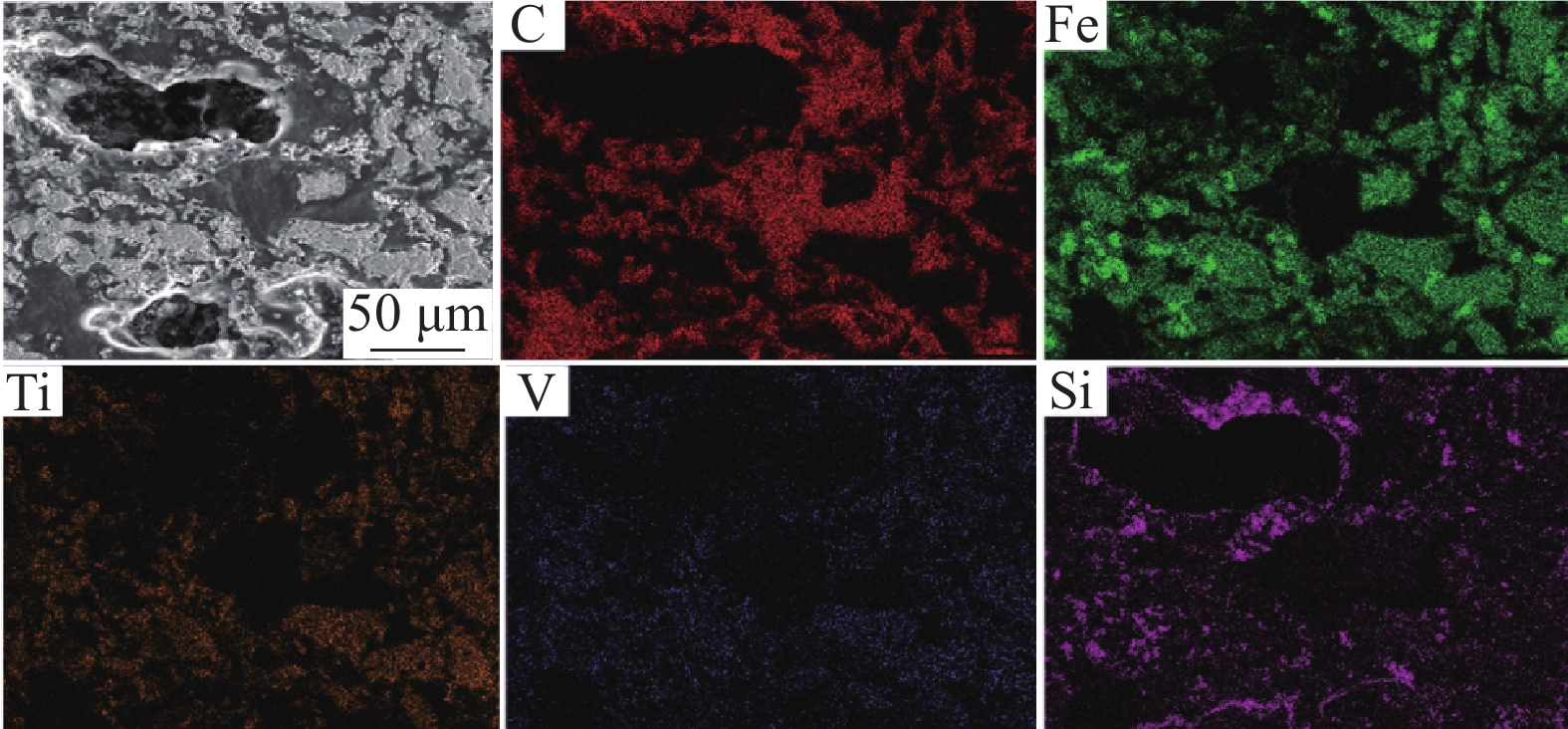
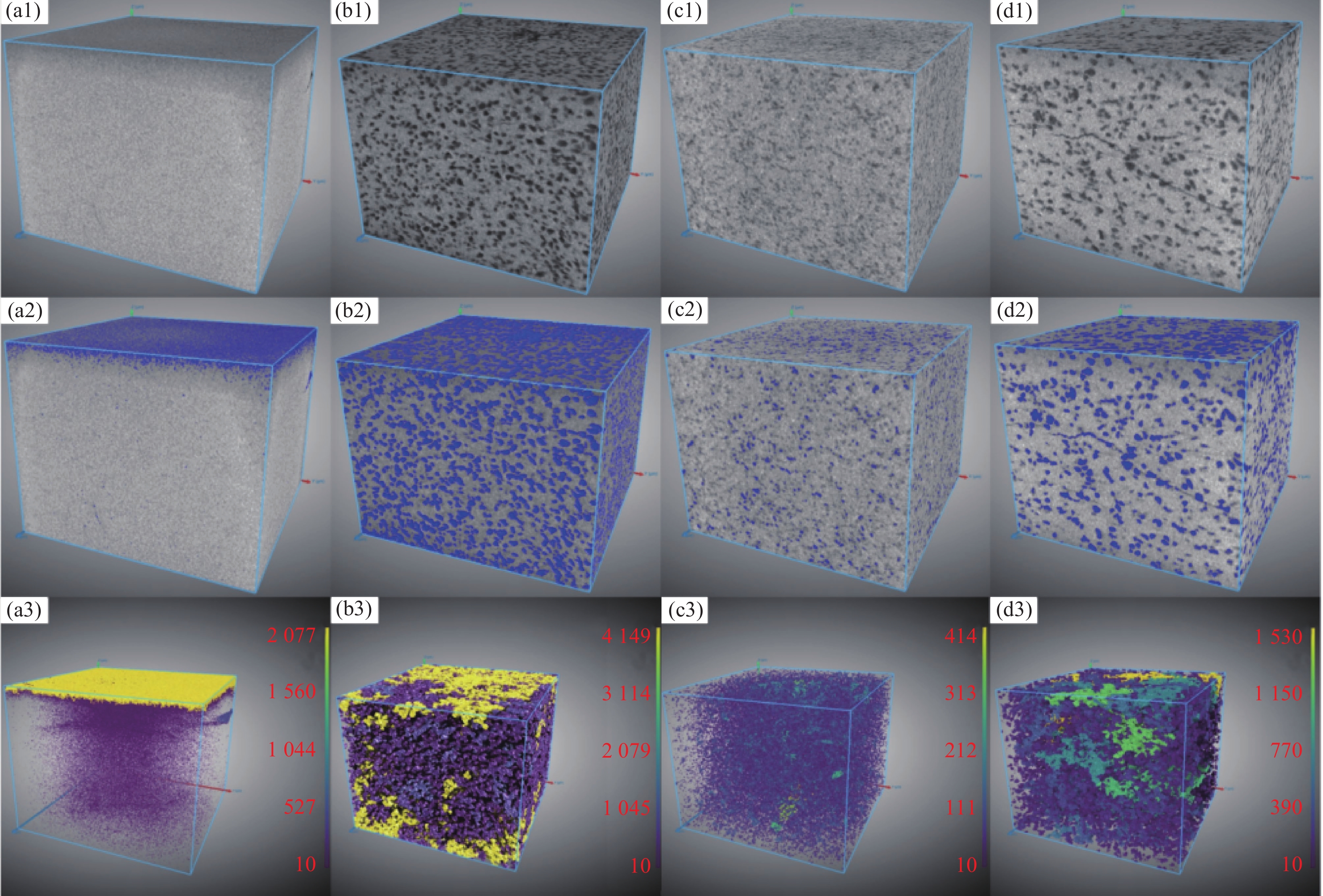
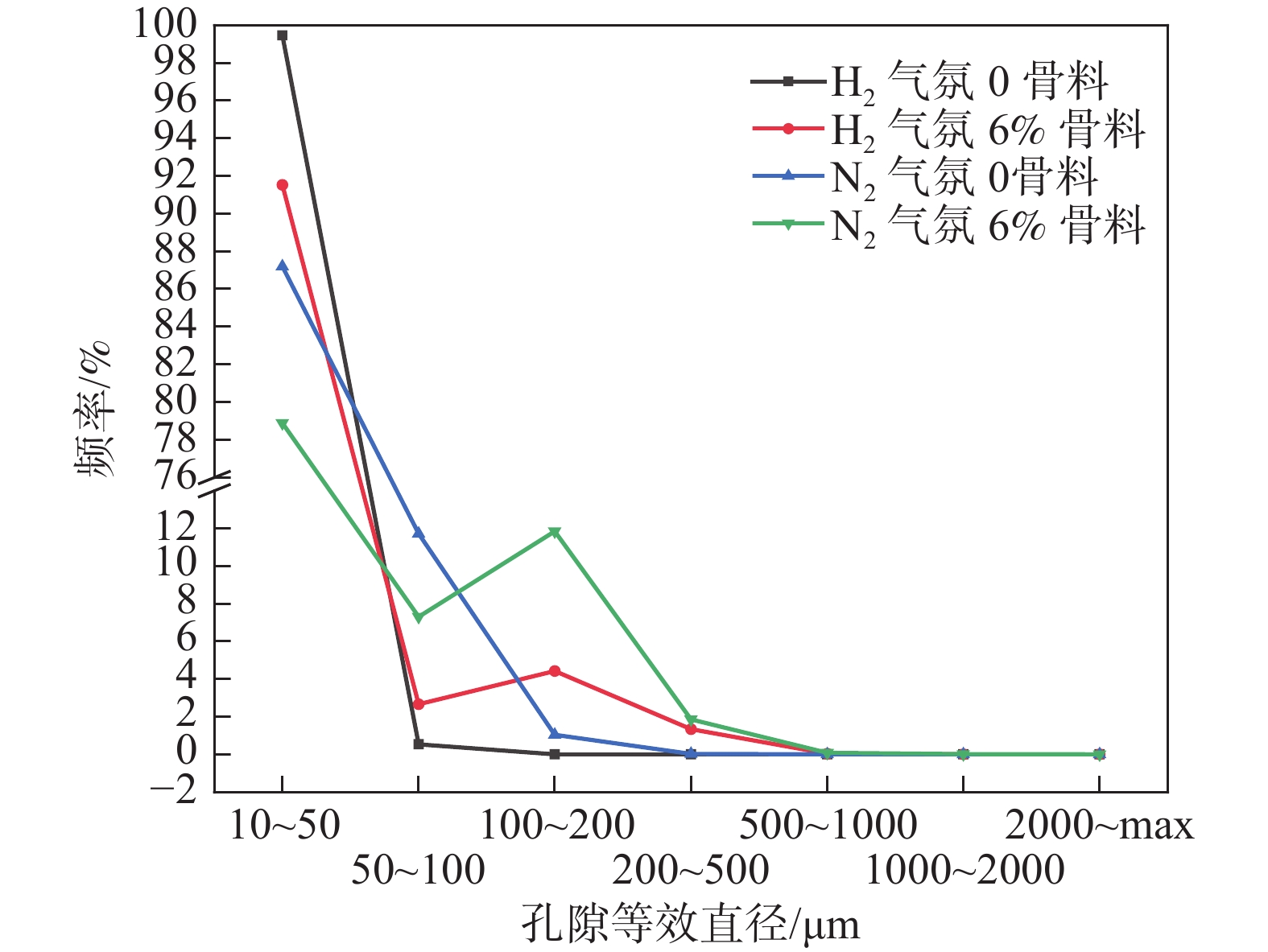
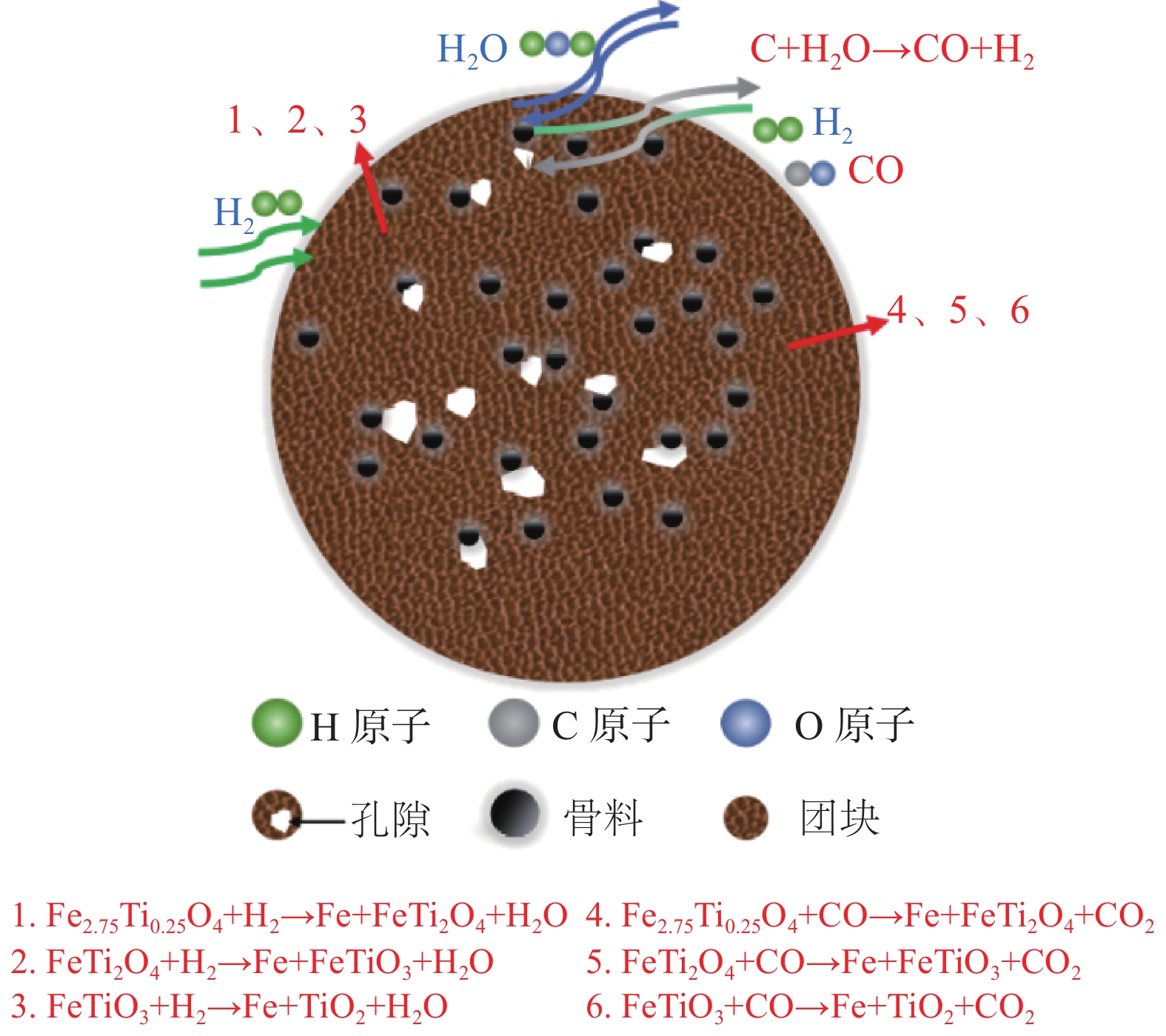
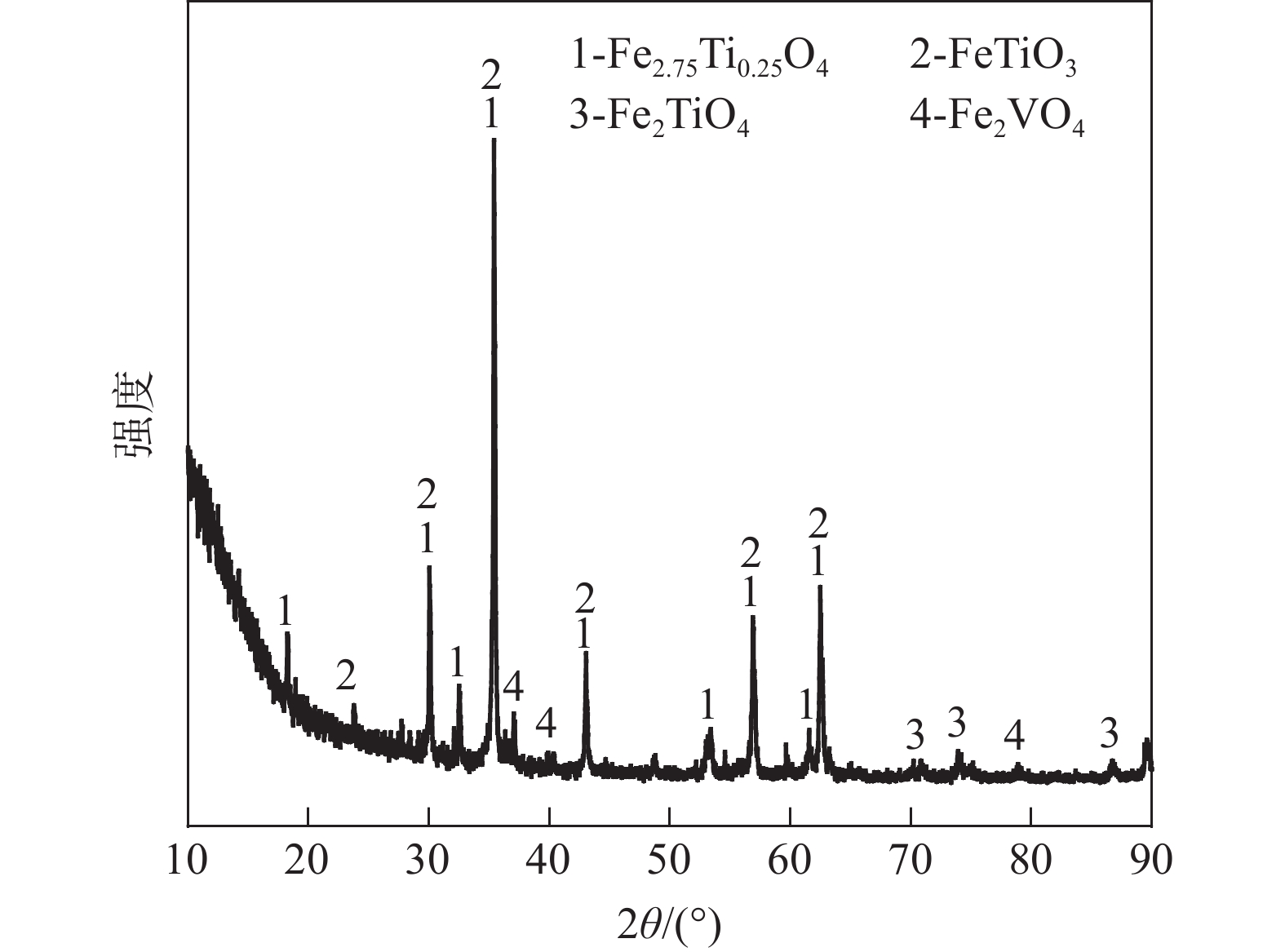
摘要: 采用钒钛磁铁矿精矿粉内配兰炭骨料与氢气进行协同还原的方式,探究了骨料量和还原温度对钒钛磁铁矿气基还原金属化率以及抗压强度的影响,并运用X射线衍射(XRD)、扫描电镜(SEM)以及X射线计算机断层扫描(XCT)方法分析了还原产物物相、微观形貌以及孔隙结构变化。结果表明,在氢气气氛下内配兰炭还原可显著提升钒钛磁铁矿的还原效果;在氮气气氛下,兰炭并未将钒钛磁铁矿还原。内配兰炭的钒钛磁铁矿还原后,金属铁的XRD衍射峰增强,而碳的衍射峰降低。在内配兰炭还原后的试样表面,兰炭颗粒保存较好且附近孔隙较多,内嵌兰炭提高了试样内部的孔隙数量并增大了孔径,促进还原气体深入试样参与还原,从而提高了钒钛磁铁矿还原效果。Abstract: The study explored the effects of aggregate quantity and reduction temperature on the gas-based reduction metallization rate and compressive strength of vanadium-titanium magnetite through a synergistic reduction method using vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate powder internally mixed with semi-coke aggregate and hydrogen. X-ray diffraction (XRD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and X-ray computed tomography (XCT) were employed to analyze the phase composition, micro-morphology, and pore structure changes of the reduced products. The results indicated that the reduction effect of vanadium-titanium magnetite was significantly enhanced when reduced with internally mixed semi-coke in hydrogen atmosphere. In contrast, no reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite was observed with semi-coke in a nitrogen atmosphere. After the reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite mixed with semi-coke, the XRD diffraction peaks of metallic iron were intensified, while the semi-coke diffraction peaks were decreased. On the surface of the samples after reduction with semi-coke, the semi-coke particles remained relatively intact, with numerous pores in their vicinity. The embedded semi-coke increased the number of pores within the samples and enlarged the pore diameters, facilitating the penetration of reducing gases into the samples for reduction, thus enhancing the reduction effect of vanadium-titanium magnetite.
-
表 1 钒钛磁铁精矿化学成分
Table 1. The composition of vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrates
% TFe FeO TiO2 V2O5 SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO Cr2O3 55.00 32.13 9.50 0.73 4.20 4.10 0.84 3.30 0.68 -
[1] LUO L G, PANG J M, LI X, et al. Experiment on separation of iron and titanium by reduction-grinding process of vanadium titanomagnetite[J]. Iron and Steel, 2024,59(8):13-18, 49. (罗林根, 庞建明, 李新, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿还原-磨选工艺分离铁钛试验[J]. 钢铁, 2024,59(8):13-18, 49.LUO L G, PANG J M, LI X, et al. Experiment on separation of iron and titanium by reduction-grinding process of vanadium titanomagnetite[J]. Iron and Steel, 2024, 59(8): 13-18, 49. [2] WANG X Y, ZHAO H Q, QI Y H, et al. Research and development of direct reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. China Metallurgy, 2024,34(2):1-8, 51. (王新宇, 赵海泉, 齐渊洪, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿直接还原的研究与发展[J]. 中国冶金, 2024,34(2):1-8, 51.WANG X Y, ZHAO H Q, QI Y H, et al. Research and development of direct reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. China Metallurgy, 2024, 34(2): 1-8, 51. [3] YANG S P, HE S H, WANG M, et al. Optimization experiment of coal-based reduction smelting and vanadium recovery of vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2024,48(7):989-998. (杨双平, 何少红, 王苗, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿煤基还原熔分及钒回收率优化试验[J]. 稀有金属, 2024,48(7):989-998.YANG S P, HE S H, WANG M, et al. Optimization experiment of coal-based reduction smelting and vanadium recovery of vanadium-titanium magnetite[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2024, 48(7): 989-998. [4] YUAN Y P, ZHOU Y Q, HONG L K, et al. Experimental study on reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite with hydrogen and biomass[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(1):113-118. (袁艺旁, 周玉青, 洪陆阔, 等. 氢气协同生物质还原钒钛磁铁矿试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(1):113-118. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.01.017YUAN Y P, ZHOU Y Q, HONG L K, et al. Experimental study on reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite with hydrogen and biomass[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(1): 113-118. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2022.01.017 [5] HOU P, YU W Z, BAI C G, et al. Viscous flow properties and influencing factors of vanadium titanium magnetite smelting iron[J]. Iron and Steel, 2022,57(1):57-65. (侯飘, 余文轴, 白晨光, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿冶炼铁水的黏流性能及其影响因素[J]. 钢铁, 2022,57(1):57-65.HOU P, YU W Z, BAI C G, et al. Viscous flow properties and influencing factors of vanadium titanium magnetite smelting iron[J]. Iron and Steel, 2022, 57(1): 57-65. [6] TONG S, AI L Q, HONG L K, et al. Metallurgical effect of microwave-hydrogen synergistic reduction for vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. China Metallurgy, 2023,33(11):48-54. (佟帅, 艾立群, 洪陆阔, 等. 微波-氢气协同还原钒钛磁铁矿精矿的冶金效果[J]. 中国冶金, 2023,33(11):48-54.TONG S, AI L Q, HONG L K, et al. Metallurgical effect of microwave-hydrogen synergistic reduction for vanadium-titanium magnetite concentrate[J]. China Metallurgy, 2023, 33(11): 48-54. [7] JI C Q, YANG Y H, XU L, et al. Comprehensive utilization of associated sulfur resources of Panxi vanadium titanium magnetite and its significance for low-carbon development[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2023(4):19-26. (冀成庆, 杨耀辉, 徐璐, 等. 攀西钒钛磁铁矿伴生硫资源综合利用及其低碳发展意义[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2023(4):19-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2023.04.003JI C Q, YANG Y H, XU L, et al. Comprehensive utilization of associated sulfur resources of Panxi vanadium titanium magnetite and its significance for low-carbon development[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2023(4): 19-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2023.04.003 [8] CHU M S, TANG Y, LIU Z G, et al. Present situation and progress of comprehensive utilization for high chromium vanadium bearing titanomagnetite[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2017,29(5):335-344. (储满生, 唐珏, 柳政根, 等. 高铬型钒钛磁铁矿综合利用现状及进展[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2017,29(5):335-344.CHU M S, TANG Y, LIU Z G, et al. Present situation and progress of comprehensive utilization for high chromium vanadium bearing titanomagnetite[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2017, 29(5): 335-344. [9] HU T, LÜ X W, BAI C G, et al. Reduction behavior of Panzhihua titanomagnetite concentrates with coal[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2013,44(2):252-260. doi: 10.1007/s11663-012-9783-7 [10] HUANG Z C, JIANG X, YI L Y, et al. Effects of biomass on reduction of vanadium bearing titanomagnetite and process enhancement[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021,56(1):12-20. (黄柱成, 姜雄, 易凌云, 等. 生物质对钒钛磁铁矿还原行为影响及过程强化[J]. 钢铁, 2021,56(1):12-20.HUANG Z C, JIANG X, YI L Y, et al. Effects of biomass on reduction of vanadium bearing titanomagnetite and process enhancement[J]. Iron and Steel, 2021, 56(1): 12-20. [11] ZHAO T, YU S W, WEN J, et al. Study on microwave enhanced direct reduction process of vanadium titanomagnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021,42(4):105-110. (赵涛, 余少武, 温靖, 等. 微波强化钒钛磁铁矿直接还原过程研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2021,42(4):105-110. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.04.018ZHAO T, YU S W, WEN J, et al. Study on microwave enhanced direct reduction process of vanadium titanomagnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2021, 42(4): 105-110. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2021.04.018 [12] LÜ Q, TANG Q, SUN Y Q, et al. Relationship between blast furnace slag properties of vanadiumtitano-magnetite and reduction of vanadium oxide[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016,37(6):1-4. (吕庆, 唐琦, 孙艳芹, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿高炉冶炼的炉渣性质与钒氧化物还原关系[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(6):1-4. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.06.001LÜ Q, TANG Q, SUN Y Q, et al. Relationship between blast furnace slag properties of vanadiumtitano-magnetite and reduction of vanadium oxide[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2016, 37(6): 1-4. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.06.001 [13] WANG J L, DAI X, ZHANG W, et al. Advances of non-blast furnace flash iron making researches[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020,55(4):100-105. (汪金良, 戴曦, 张伟, 等. 非高炉闪速炼铁研究进展[J]. 钢铁, 2020,55(4):100-105.WANG J L, DAI X, ZHANG W, et al. Advances of non-blast furnace flash iron making researches[J]. Iron and Steel, 2020, 55(4): 100-105. [14] ZHANG F, ZHAO P C, NIU M, et al. The survey of key technologies in hydrogen energy storage[J]. Int J Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41: 14535-14552. [15] NIGEL P B, JAMES J B. Hydrogen for a net-zero carbon world[J]. Engineering, 2023,29(10):8-10. [16] PAN C C, PANG J M. Development trace and application prospect of hydrogen metallurgy technology[J]. China Metallurgy, 2021,31(9):73-77. (潘聪超, 庞建明. 氢冶金技术的发展溯源与应用前景[J]. 中国冶金, 2021,31(9):73-77.PAN C C, PANG J M. Development trace and application prospect of hydrogen metallurgy technology[J]. China Metallurgy, 2021, 31(9): 73-77. [17] GAO H, GUO L, GAO J T, et al. In-situ research on the H2 based reduction process of high-phosphorous iron ore[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2015,37(10):1284-1290. (高晗, 郭磊, 高金涛, 等. 高磷矿氢气还原过程的原位研究[J]. 工程科学学报, 2015,37(10):1284-1290.GAO H, GUO L, GAO J T, et al. In-situ research on the H2 based reduction process of high-phosphorous iron ore[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2015, 37(10): 1284-1290. [18] ZANG F L, HUANG R, XU B J, et al. Reduction of Guizhou oolite hematite by hydrogen[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2016,28(11):23-28. (张伏龙, 黄润, 徐本军, 等. 贵州鲕状赤铁矿的氢气还原行为[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2016,28(11):23-28.ZANG F L, HUANG R, XU B J, et al. Reduction of Guizhou oolite hematite by hydrogen[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2016, 28(11): 23-28. [19] LI W, FU G Q, CHU M S, et al. Influence of Cr2O3 addition on the gas-based direct reduction behavior of Hongge vanadium titanomagnetite pellet with simulated shaft furnace gases[J]. ISIJ International, 2018,58(4):604-611. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2017-544 [20] YU H, ZHOU J C, LI X P, et al. Reconstruction optimization of gas based shaftfurnace direct reduction ironmaking process[J]. China Metallurgy, 2021,31(1):31-35. (于恒, 周继程, 郦秀萍, 等. 气基竖炉直接还原炼铁流程重构优化[J]. 中国冶金, 2021,31(1):31-35.YU H, ZHOU J C, LI X P, et al. Reconstruction optimization of gas based shaftfurnace direct reduction ironmaking process[J]. China Metallurgy, 2021, 31(1): 31-35. [21] SUN H Y, ZHU Q S, LI H Z. The technical state and development trend of the direct reduction of titanomagnetite by fluidized bed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2018,18(6):1146-1159. (孙昊延, 朱庆山, 李洪钟. 钒钛磁铁矿流态化直接还原技术现状与发展趋势[J]. 过程工程学报, 2018,18(6):1146-1159. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.218275SUN H Y, ZHU Q S, LI H Z. The technical state and development trend of the direct reduction of titanomagnetite by fluidized bed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2018, 18(6): 1146-1159. doi: 10.12034/j.issn.1009-606X.218275 [22] ZENG R Q, WANG N, LI W, et al. Influence of SiO2 on the gas-based direct reduction behavior of Hongge vanadium titanomagnetite pellet by hydrogen-rich gases[J]. Powder Technology, 2021,386:90-97. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2021.03.019 [23] WANG Z H, CHEN S Y, CHEN L, et al. Enhancing iron and titanium recovery efficiency via coal-based direct reduction of vanadium-titanium magnetite raw ore[J/OL]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 1-32 [2024-10-14]. [24] GAO Y C, HAO S J, JIANG W F, et al. Non-isothermal reduction kinetics of carbon-coated vanadium-titanium magnetite powder[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023,44(1):111-118. (高一策, 郝素菊, 蒋武锋, 等. 碳包覆钒钛磁铁矿粉非等温还原动力学[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023,44(1):111-118. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.01.019GAO Y C, HAO S J, JIANG W F, et al. Non-isothermal reduction kinetics of carbon-coated vanadium-titanium magnetite powder[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2023, 44(1): 111-118. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2023.01.019 [25] ZHENG P. Research on direct reduction of vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Non-ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2018,34(2):35-38. (郑鹏. 钒钛磁铁矿直接还原特性的研究[J]. 有色矿冶, 2018,34(2):35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2018.02.009ZHENG P. Research on direct reduction of vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Non-ferrous Mining and Metallurgy, 2018, 34(2): 35-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-967X.2018.02.009 [26] SHI X F, XU H J, ZHANG Y Y, et al. The experimental study on direct reduction of shaft furnace based gas of vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015,36(1):52. (师学峰, 徐红军, 张颖异, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿气基竖炉直接还原试验研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2015,36(1):52.SHI X F, XU H J, ZHANG Y Y, et al. The experimental study on direct reduction of shaft furnace based gas of vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2015, 36(1): 52. [27] DAI W L, XING X D, MIAO H S, et al. Experiment on gas-based reduction of aggregate in vanadium-titanium magnetite ore[J]. China Metallurgy, 2024,34(5):37-44. (代文林, 邢相栋, 苗红生, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿内配骨料气基还原试验[J]. 中国冶金, 2024,34(5):37-44.DAI W L, XING X D, MIAO H S, et al. Experiment on gas-based reduction of aggregate in vanadium-titanium magnetite ore[J]. China Metallurgy, 2024, 34(5): 37-44. -





 下载:
下载: