Hot deformation behavior and processing maps of wrought TC21 titanium alloy
-
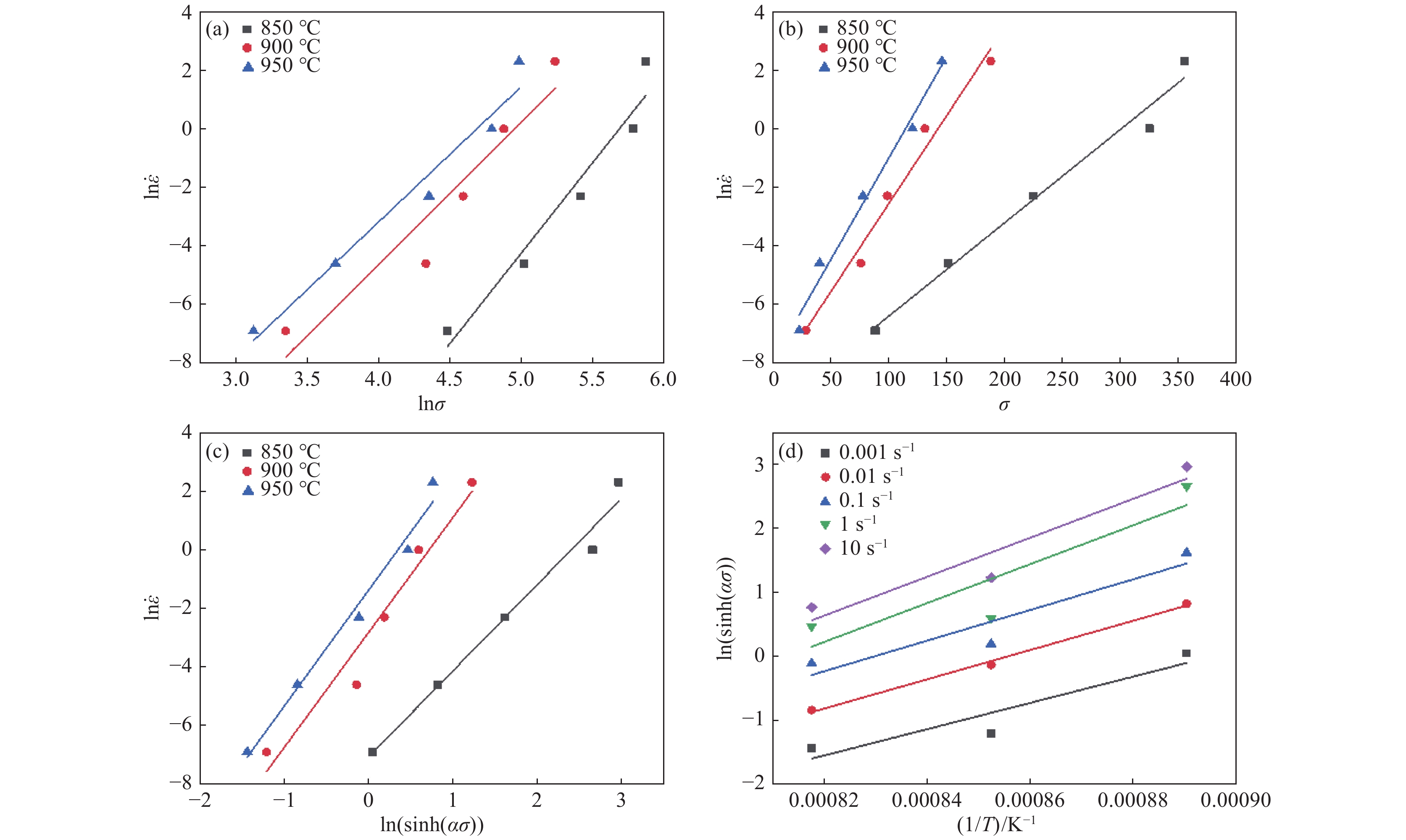
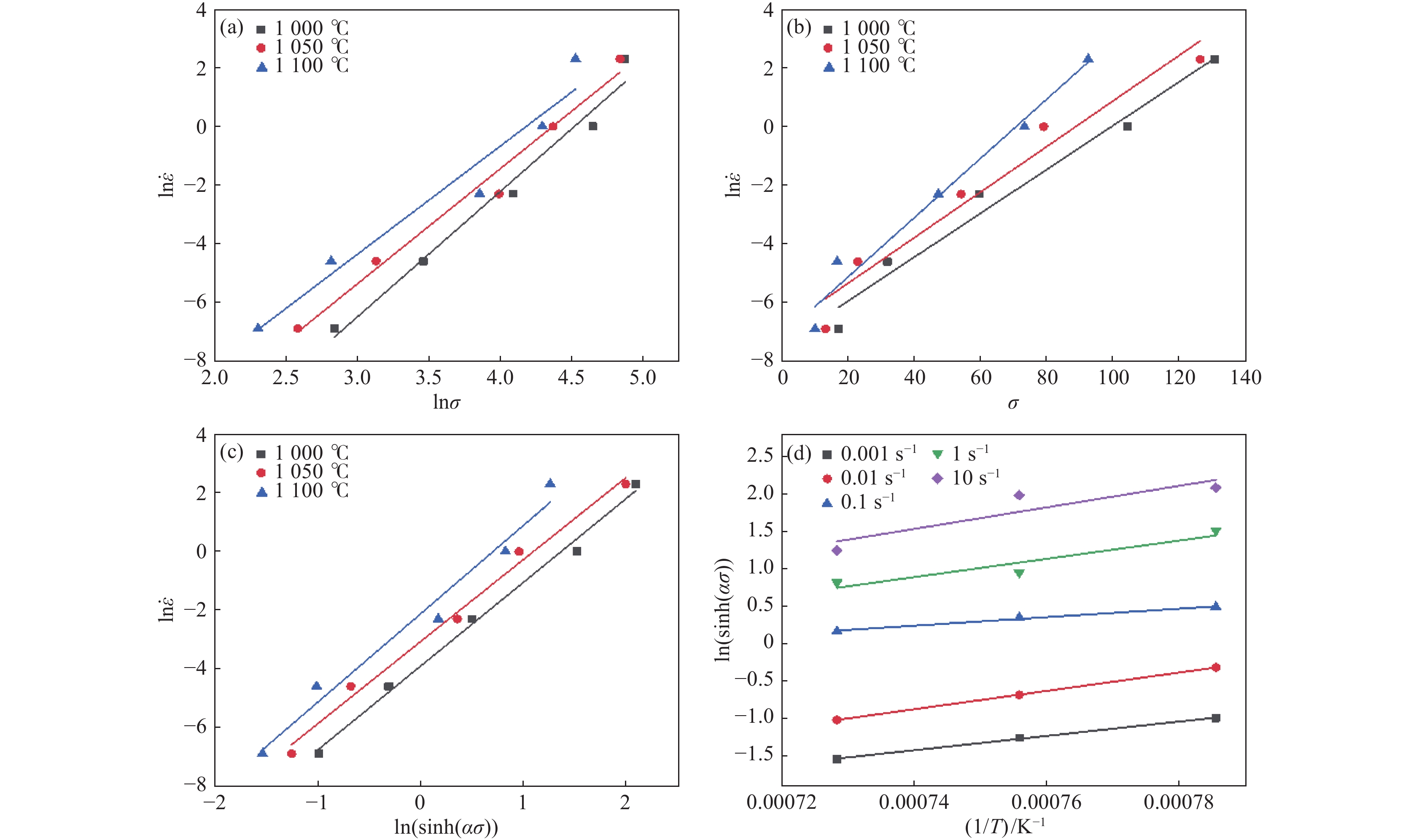
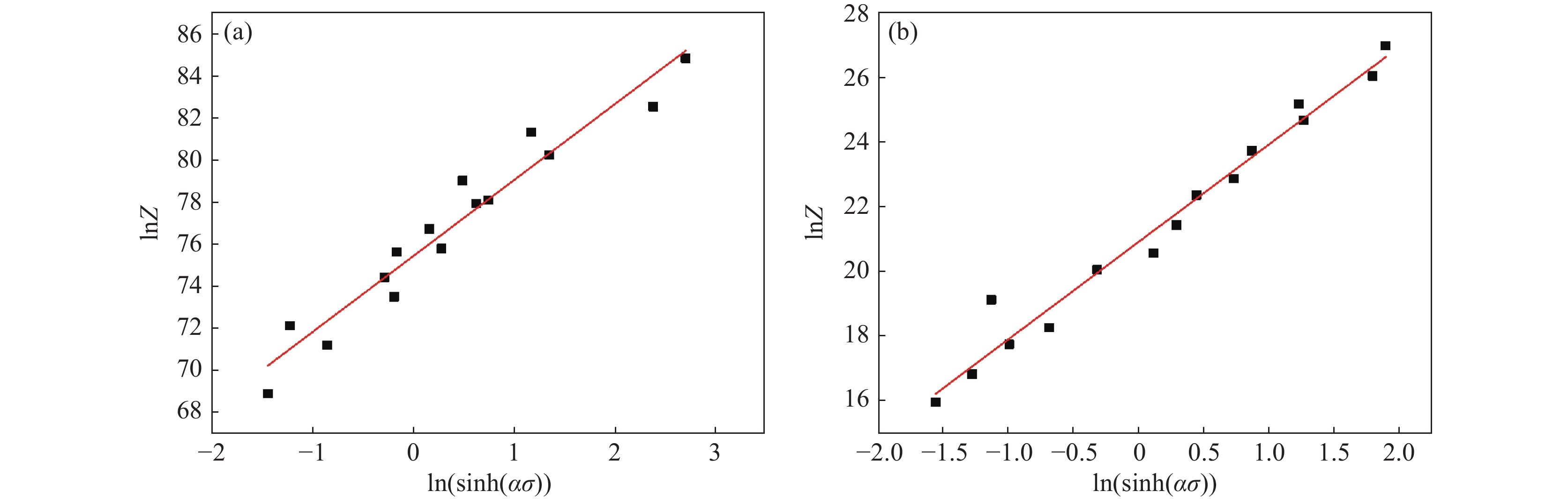
摘要: 采用热模拟试验机开展了高温热变形试验,得到锻态TC21钛合金在850~1 100 ℃、应变速率0.001~10 s−1变形参数下的应力应变曲线,分析了压应力状态下,变形温度和应变速率对流变应力的影响,基于Arrhenius双曲正弦函数建立了本构关系,绘制了0.1~0.6不同应变下的热加工图,总结出锻态合金热变形的参数范围。结果表明:变形参数对流变应力的影响较大,当变形温度升高时,流变应力降低,当应变速率降低时,流变应力降低;两相区和单相区变形激活能分别为770.86 kJ/mol和261.00 kJ/mol;随着应变量增加,热加工图中失稳区逐渐扩大,合适的热加工区域为变形温度900~1 100 ℃,应变速率0.005~0.153 s−1。试验结果可为TC21合金热加工工艺参数制定提供理论支撑。Abstract: The high-temperature thermal deformation test was carried out by thermal simulation testing machine, and the stress-strain curves of wrought TC21 titanium alloy at temperature 850-1100℃ and strain rate 0.001-10 s−1 were obtained. The effects of deformation temperature and strain rate on the flow stress in the compressive stress state were analyzed, and the intrinsic relationship was established based on the Arrhenius hyperbolic sinusoidal function. The thermal processing diagrams under different true strains from 0.1 to 0.6 were plotted, so that the range of parameters suitable for thermal deformation of wrought alloys was summarized. The results indicate that the flow stress of wrought TC21 alloy is greatly affected by deformation parameters, which decreases with the increase of deformation temperature and increases with the increase of strain rate. The activation energy of TC21 alloy in the α+β two-phase region and β single-phase region is 770.86 kJ/mol and 261.00 kJ/mol, respectively. As true strain increases the destabilization zone becomes larger in the thermal processing map and the suitable hot working region is deformation temperature of 900-1100℃, and strain rate of 0.005-0.153 s−1. The test results can provide theoretical support for the formulation of TC21 alloy hot working parameters.
-
Key words:
- TC21 titanium alloy /
- hot deformation /
- constitutive equations /
- thermal processing map
-
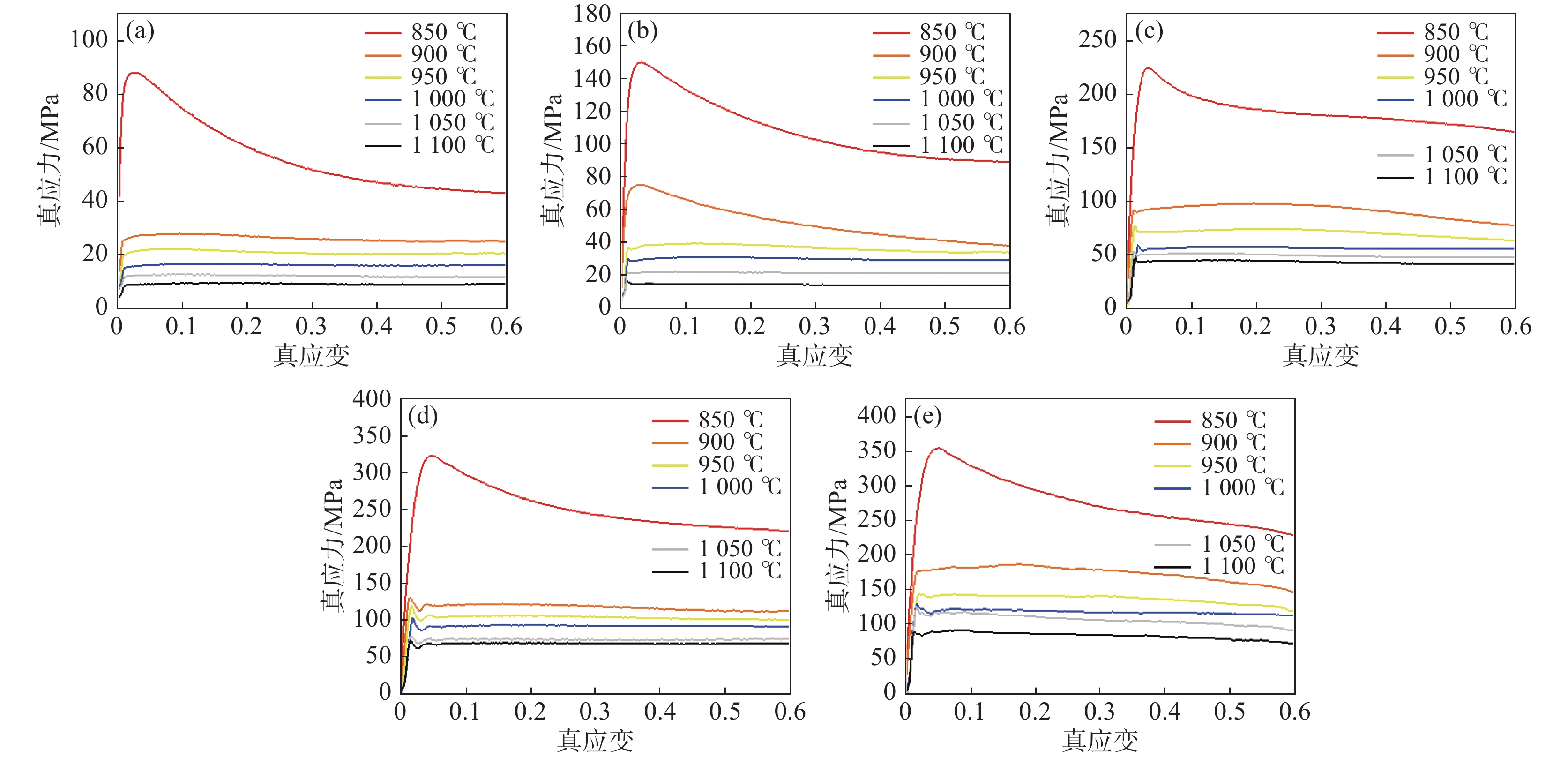
图 2 不同变形条件下TC21真应力-真应变曲线
Figure 2. True stress-strain curves of TC21 alloy under different deformation conditions
(a)$ \mathop \varepsilon \limits^ \cdot $=0.001 s−1;(b)$ \mathop \varepsilon \limits^ \cdot $=0.01 s−1;(c)$ \mathop \varepsilon \limits^ \cdot $=0.1 s−1;(d)$ \mathop \varepsilon \limits^ \cdot $=1 s−1;(e)$ \mathop \varepsilon \limits^ \cdot $=10 s−1
表 1 TC21合金的实测化学成分
Table 1. Chemical composition of TC21 alloy
% Al Sn Zr Mo Nb Cr Ti 6.20 2.03 2.02 2.91 1.96 1.52 Bal. -
[1] ZHU Z S, WANG X N, TONG L, et al. Research and application of damage tolerance titanium alloys for aeronautical use[J]. Materials China, 2010,29(5):14-17. (朱知寿, 王新南, 童路, 等. 航空用损伤容限型钛合金研究与应用[J]. 中国材料进展, 2010,29(5):14-17.ZHU Z S, WANG X N, TONG L, et al. Research and application of damage tolerance titanium alloys for aeronautical use[J]. Materials China, 2010, 29(5): 14-17. [2] ZHU Z S. Research and development of advanced new type titanium alloys for aeronautical applications[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2012(1):5-9. (朱知寿. 航空结构用新型高性能钛合金材料技术研究与发展[J]. 航空科学技术, 2012(1):5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5453.2012.01.002ZHU Z S. Research and development of advanced new type titanium alloys for aeronautical applications[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2012(1): 5-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5453.2012.01.002 [3] MA S J, WU X R, LIU J Z, et al. Influence of microstructures on mechanical properties for TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2006,26(5):22-25. (马少俊, 吴学仁, 刘建中, 等. TC21钛合金的微观组织对力学性能的影响[J]. 航空材料学报, 2006,26(5):22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.05.006MA S J, WU X R, LIU J Z, et al. Influence of microstructures on mechanical properties for TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Aeronautical Materials, 2006, 26(5): 22-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5053.2006.05.006 [4] NINGF Y Q, LUO X, LIA H Q, et al. Competition between dynamic recovery and recrystallization during hot deformation for TC18 titanium alloy[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2015,635:77-85. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2015.03.071 [5] JONAS J J, ARANAS C, FALL A, et al. Transformation softening in three titanium alloys[J]. Materials & Design, 2017,113:305-310. [6] FENG F, ZENG W D, ZHU Y C, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of as-cast TC21 alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(2): 251-255. 2012, 41(2): 251-255. ) (冯菲, 曾卫东, 朱艳春, 等. 铸态TC21钛合金高温热变形行为及加工图[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2012, 41(2): 251-255. 2012, 41(2): 251-255.FENG F, ZENG W D, ZHU Y C, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing map of as-cast TC21 alloy[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2012, 41(2): 251-255. 2012, 41(2): 251-255. ) [7] TAO C, CUI X, OUYANG D L, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental study on hot compression process of TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2023,30(8):195-201. (陶成, 崔霞, 欧阳德来, 等. TC21钛合金热压缩工艺数值模拟与实验研究[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2023,30(8):195-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2023.08.023TAO C, CUI X, OUYANG D L, et al. Numerical simulation and experimental study on hot compression process of TC21 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2023, 30(8): 195-201. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2012.2023.08.023 [8] PENG L, JIANG J, LUO X F, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing maps of TA18 titanium alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(6): 45-50. (彭力 , 江健, 罗小峰, 等. TA18钛合金热变形行为及热加工图研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022, 43(6): 45-50.PENG L, JIANG J, LUO X F, et al. Hot deformation behavior and processing maps of TA18 titanium alloy[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(6): 45-50. [9] ZHANG S M, LIN B C, XIN S W, et al. Hot deformation behavior of metastable β-titanium alloy Ti-1500[J]. Hot Treatment of Metals, 2023,48(5):158-165. (张书铭, 林博超, 辛社伟, 等. 亚稳β钛合金Ti-1500热变形行为[J]. 金属热处理, 2023,48(5):158-165.ZHANG S M, LIN B C, XIN S W, et al. Hot deformation behavior of metastable β-titanium alloy Ti-1500[J]. Hot Treatment of Metals, 2023, 48(5): 158-165. [10] ZHANG X M, CAO F Y, YUE H Y, et al. Establishment of constitutive equations of TC11 alloy during hot deformation[J], Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2013, 42(5): 937-941. (张雪敏, 曹福洋, 岳红彦, 等. TC11钛合金热变形本构方程的建立[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2013, 42(5): 937-941.ZHANG X M, CAO F Y, YUE H Y, et al. Establishment of constitutive equations of TC11 alloy during hot deformation[J], Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2013, 42(5): 937-941. [11] LÜ Z D. Study of hot deformation behavior and heat treatment for near β-Ti alloy with high strength and toughness[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2020. (吕智丹. 高强韧近β钛合金热变形行为及热处理研究[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学, 2020.LÜ Z D. Study of hot deformation behavior and heat treatment for near β-Ti alloy with high strength and toughness[D]. Taiyuan: Taiyuan University of Technology, 2020. [12] YIN B Q, XU S, XIAO N M, et al. Thermal deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of near α Ti60 titanium alloy[J], Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2022, 29(8): 193-202. (尹宝琴, 徐帅, 肖纳敏, 等. Ti60近α钛合金的热变形行为和组织演化[J]. 塑性工程学报, 2022, 29(8): 193-202.YIN B Q, XU S, XIAO N M, et al. Thermal deformation behavior and microstructure evolution of near α Ti60 titanium alloy[J], Journal of Plasticity Engineering, 2022, 29(8): 193-202. [13] LIN Y C, XIA Y C, CHEN X M, et al. Constitutive descriptions for hot compressed 2124-T851 aluminum alloy over a wide range of temperature and strain rate[J]. Computational Materials Science, 2010,50(1):227-233. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2010.08.003 [14] LI L, ZHOU J, DUSZCZYK J. Determination of a constitutive relationship for AZ31B magnesium alloy and validation through comparison between simulated and real extrusion[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2006,172(3):372-380. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.09.021 [15] JONAS J J, SELLARS C M, TEGART W J M. Strength and structure under hot-working. conditions[J]. Metallurgical Reviews, 1969,14(1):1-24. doi: 10.1179/mtlr.1969.14.1.1 [16] ZENER C, HOLLOM J H. Effect of strain rate upon plastic flow of steel[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 1944,15(1):22-32. doi: 10.1063/1.1707363 [17] PRASAD Y V R K, GEGEL H L, DORAIVELU S M, et al. Modeling of dynamic material behavior in hot deformation: Forging of Ti6242[J]. Metallurgical Transactions A, 1984,15(10):1883-1892. doi: 10.1007/BF02664902 [18] PRASAD Y V R K, SESHACHARYULU T. Processing maps for hot working of titanium alloys[J]. Material Science and Engineering A, 1998,243(1-2):82-88. doi: 10.1016/S0921-5093(97)00782-X [19] PRASAD Y V R K. Processing maps: a status report[J]. Journal of Engineering and Performance, 2003,12(6):638-645. [20] ROBI P S, DIXIT U S. Application of neural networks in generating processing map for hot working[J]. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003,142:289-294. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00579-X -





 下载:
下载: