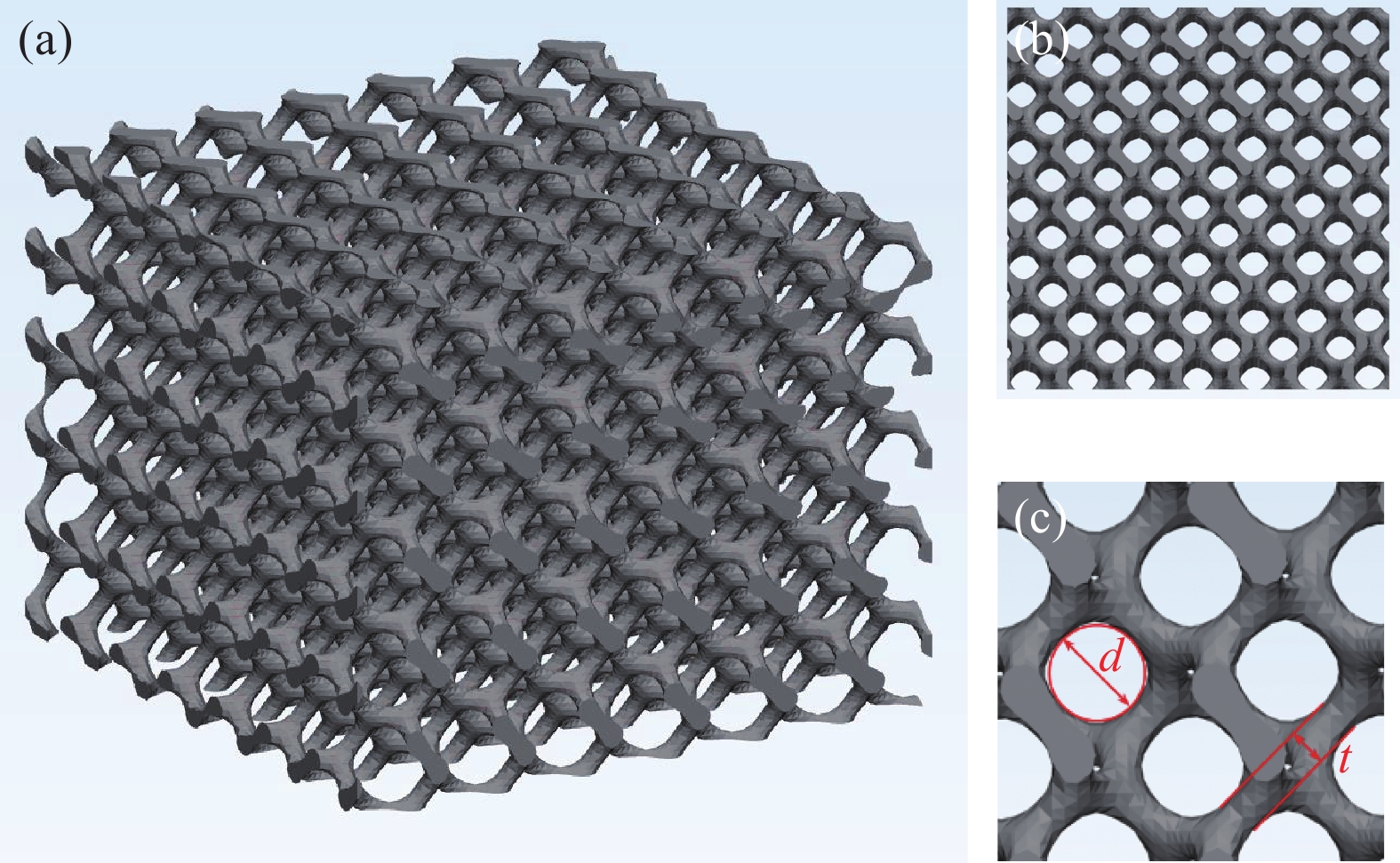
Effect of SLM process parameters and pickling treatment on the porous structure of TC4 titanium alloy
-
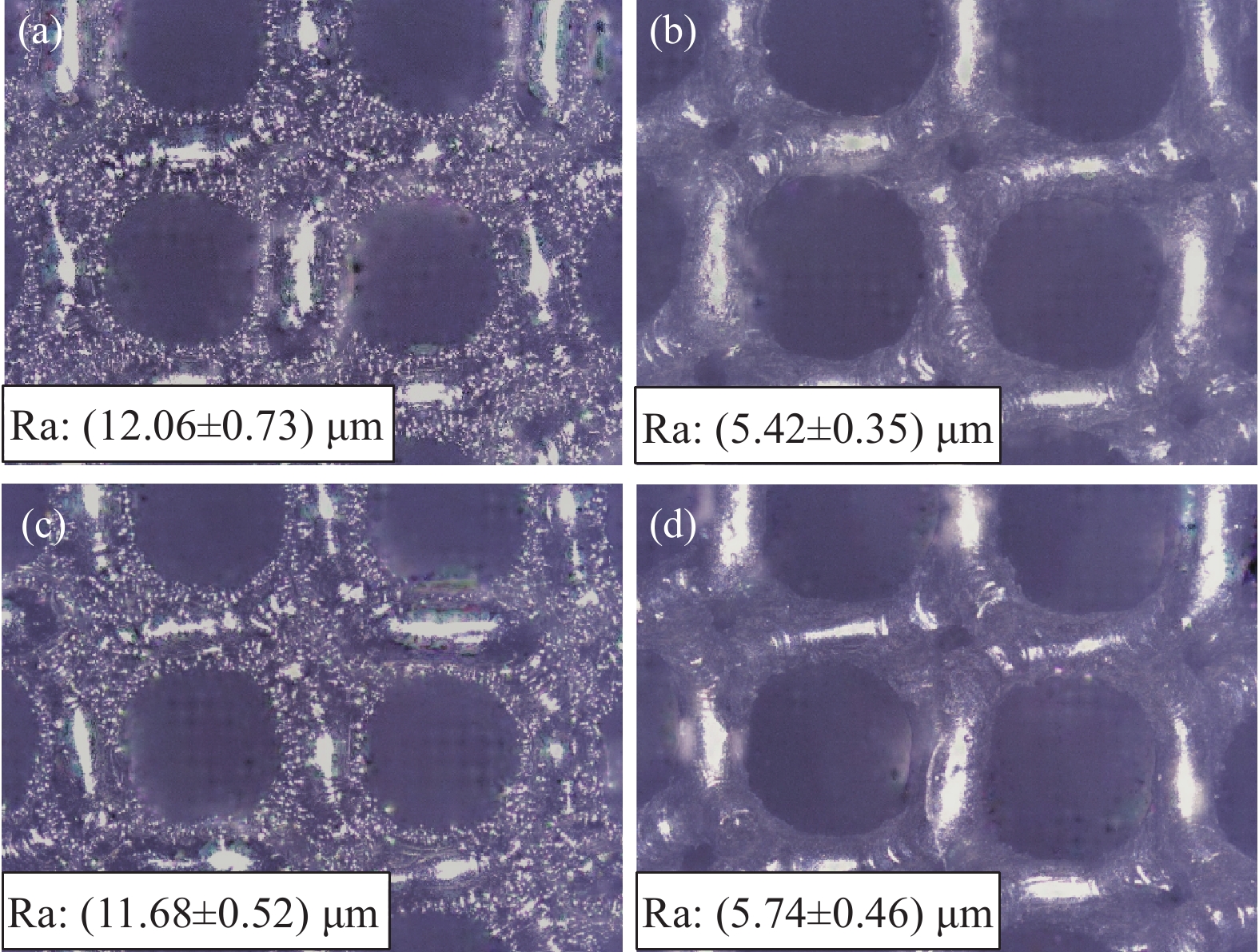
摘要: 基于TC4钛合金三周期极小曲面(TPMS)多孔结构和激光功率P、扫描速度v及扫描间距h水平差异设计三因素三水平正交试验,一方面通过极差和方差分析研究激光选区熔化制造(SLM)工艺参数对TC4钛合金多孔结构尺寸精度、质量和力学强度的影响规律;另一方面对钛合金多孔结构进行HF酸洗处理,研究酸洗工艺对多孔结构参数和力学性能的影响。结果表明:TPMS多孔结构的实体尺寸和质量与SLM工艺能量密度E呈正相关;TPMS多孔结构的力学强度受SLM工艺参数影响较小,优化SLM工艺参数应以3D打印多孔结构尺寸、质量精度控制为主导;酸洗处理可以改善TPMS多孔结构表面粗糙度,提高结构尺寸、质量精度;此外,酸洗处理促使TPMS多孔结构的弹性模量更接近天然松质骨的力学性能。Abstract: Based on the three-period minimal surface (TPMS) porous structure of TC4 titanium alloy and the horizontal differences of laser power P, scanning speed v and scanning distance h, a three-factor and three-level orthogonal experiment was designed. On the one hand, the influences of laser selective melting manufacturing (SLM) process parameters on the dimensional accuracy, mass and mechanical strength of TC4 titanium alloy porous structure were studied through range and variance analysis. On the other hand, the porous structure of titanium alloy was treated by HF pickling, the influences of pickling process on the parameters and mechanical properties of porous structure was studied. The results show that the physical size and mass of TPMS porous structure are positively correlated with the energy density E of SLM process. The mechanical strength of TPMS porous structure is less affected by SLM process parameters, and the optimization of SLM process parameters should be based on the accuracy control of size and mass parameters of 3D printed porous structure. Pickling treatment can improve the surface roughness of TPMS porous structure, enhance the size and mass accuracy of TPMS porous structure. In addition, pickling treatment makes the elastic modulus of TPMS porous structure closer to the mechanical properties of natural cancellous bone.
-
Key words:
- SLM process parameters /
- TC4 alloy /
- TPMS porous structure /
- pickling /
- dimensional accuracy /
- mechanical property
-
表 1 TC4合金粉末主要成分
Table 1. Main components of TC4 alloy powder
% Al V Fe C N H O Ti 6.0700 3.9600 0.0360 0.0060 0.0240 0.0025 0.0760 Bal. 表 2 SLM工艺参数水平表
Table 2. Level table of SLM processing parameters
工艺水平 扫描速度v
/(mm·s−1)激光功率P
/W扫描间距h
/mm1 1000 150 0.1 2 1250 200 0.14 3 1500 250 0.18 表 3 SLM工艺参数正交试验因素水平表
Table 3. Orthogonal test factor level table of SLM processing parameters
样品
编号扫描速度v
/(mm·s−1)激光功率P
/W扫描间距h
/mm能量密度E
/(J·mm−3)① 1000 150 0.1 50 ② 1000 200 0.14 47.6 ③ 1000 250 0.18 46.3 ④ 1250 150 0.14 28.6 ⑤ 1250 200 0.18 29.6 ⑥ 1250 250 0.1 66.7 ⑦ 1500 150 0.18 18.5 ⑧ 1500 200 0.1 44.4 ⑨ 1500 250 0.14 39.7 表 4 多孔样品尺寸/质量正交试验结果统计表
Table 4. Statistics of orthogonal test results of size/mass of scaffolds
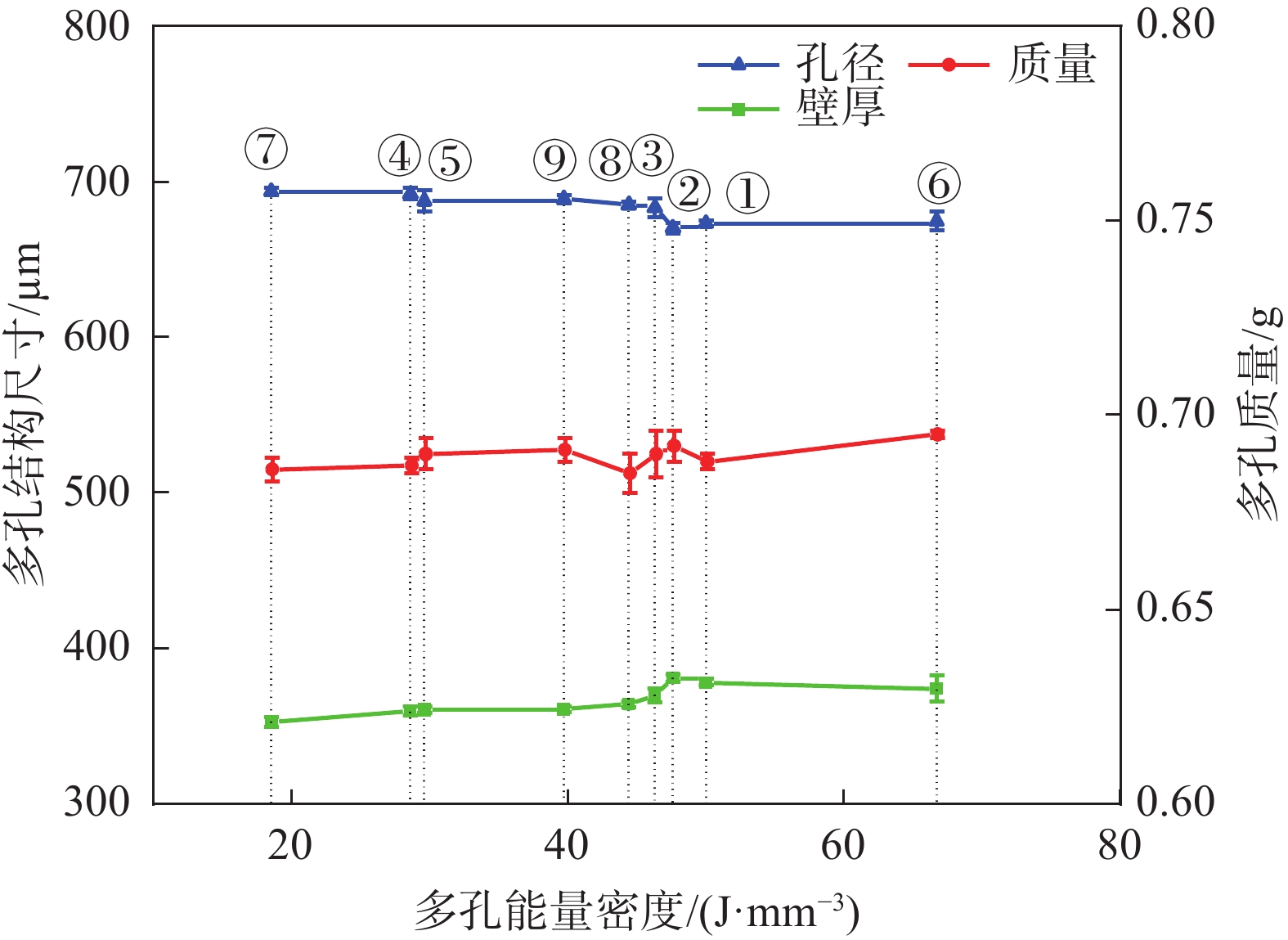
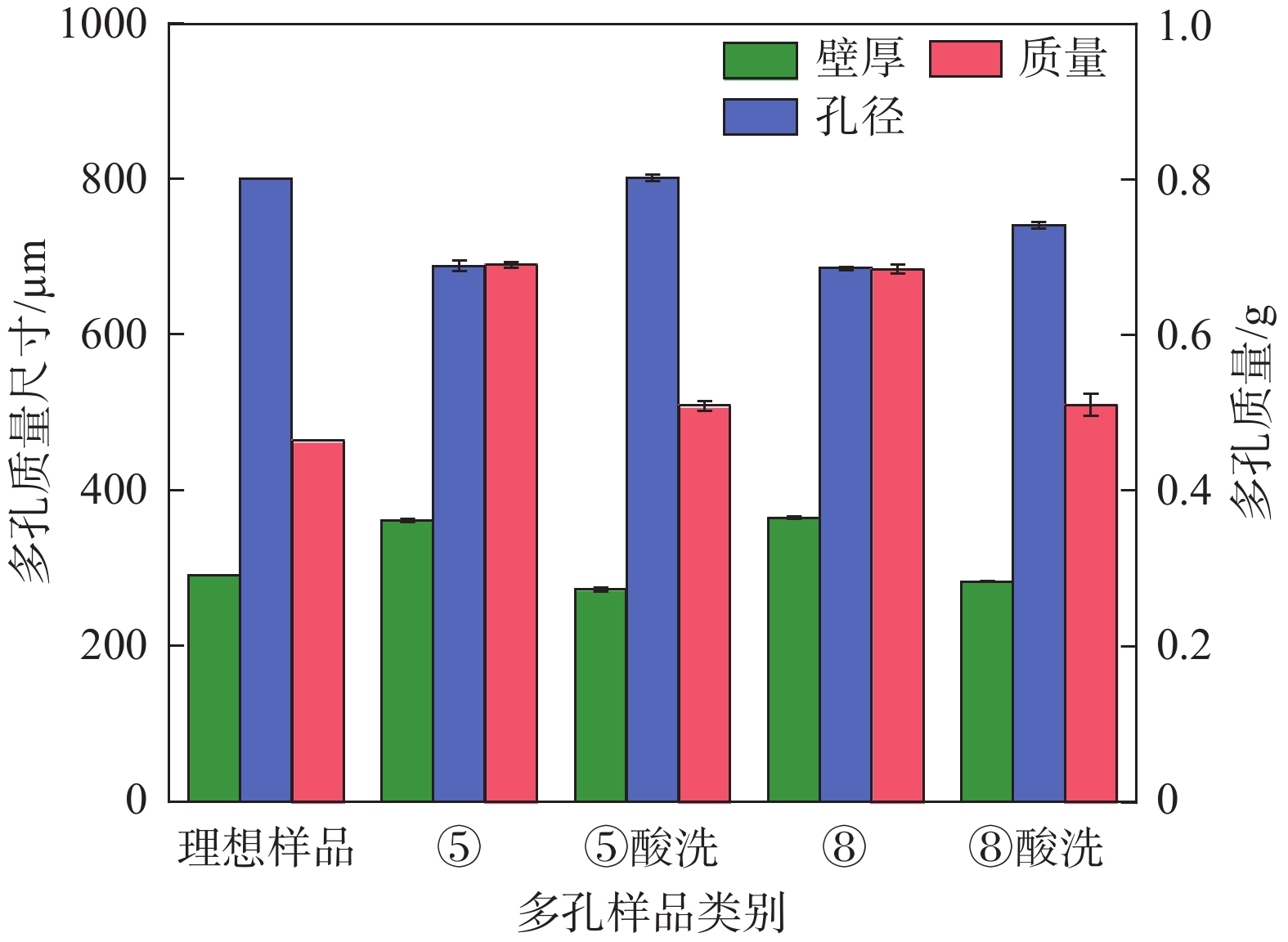
统计项 工艺水平 扫描速度v-测量参数 激光功率P-测量参数 扫描间距h-测量参数 壁厚/µm 孔径/µm 质量/g 壁厚/µm 孔径/µm 质量/g 壁厚/µm 孔径/µm 质量/g K 1 1128.48 2026.64 2.070 1090.39 2059.16 2.061 1116.26 2033.06 2.067 2 1094.25 2054.63 2.071 1105.58 2043.09 2.067 1101.25 2051.44 2.070 3 1077.71 2067.74 2.062 1104.47 2046.77 2.076 1082.93 2064.52 2.066 Kavg 1 376.16 675.55 0.690 363.46 686.39 0.687 372.09 677.69 0.689 2 364.75 684.88 0.690 368.53 681.03 0.689 367.08 683.81 0.690 3 359.24 689.25 0.687 368.16 682.26 0.692 360.98 688.17 0.689 最佳水平 3 3 3 1 2 1 3 3 3 极值R 16.92 13.70 0.003 5.06 5.36 0.005 11.11 10.49 0.001 F检验 36.58 15.88 2.07 3.91 2.56 4.16 15.20 9.00 0.30 显著性 *** *** ns * ns * *** ** ns 水平数量 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 样品重复数 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 3 表注:K为单一工艺参数变量同水平下所有样品测量结果总和,Kavg为K值除以样品数的均值,最佳水平根据优化原则选取,极值R为各不同水平Kavg间的最大差值。显著性评价:***为p<0.001、**为0.001<p<0.01、*为0.01<p<0.05、ns为p>0.05。 表 5 多孔样品尺寸/质量试验因素的交互效应
Table 5. Interaction effect of test factors of porous sample in size/mass
交互项 壁厚 孔径 质量 扫描速度*激光功率 *** *** ns 扫描速度*扫描间距 * ns * 激光功率*扫描间距 *** *** ns 扫描速度*激光功率*扫描间距 ns ** ns 显著性评价:***为p<0.001、**为0.001<p<0.01、*为0.01<p<0.05、ns为p>0.05。 表 6 多孔样品力学强度正交试验结果统计
Table 6. Statistics of orthogonal test results of mechanical properties of TPMS scaffolds
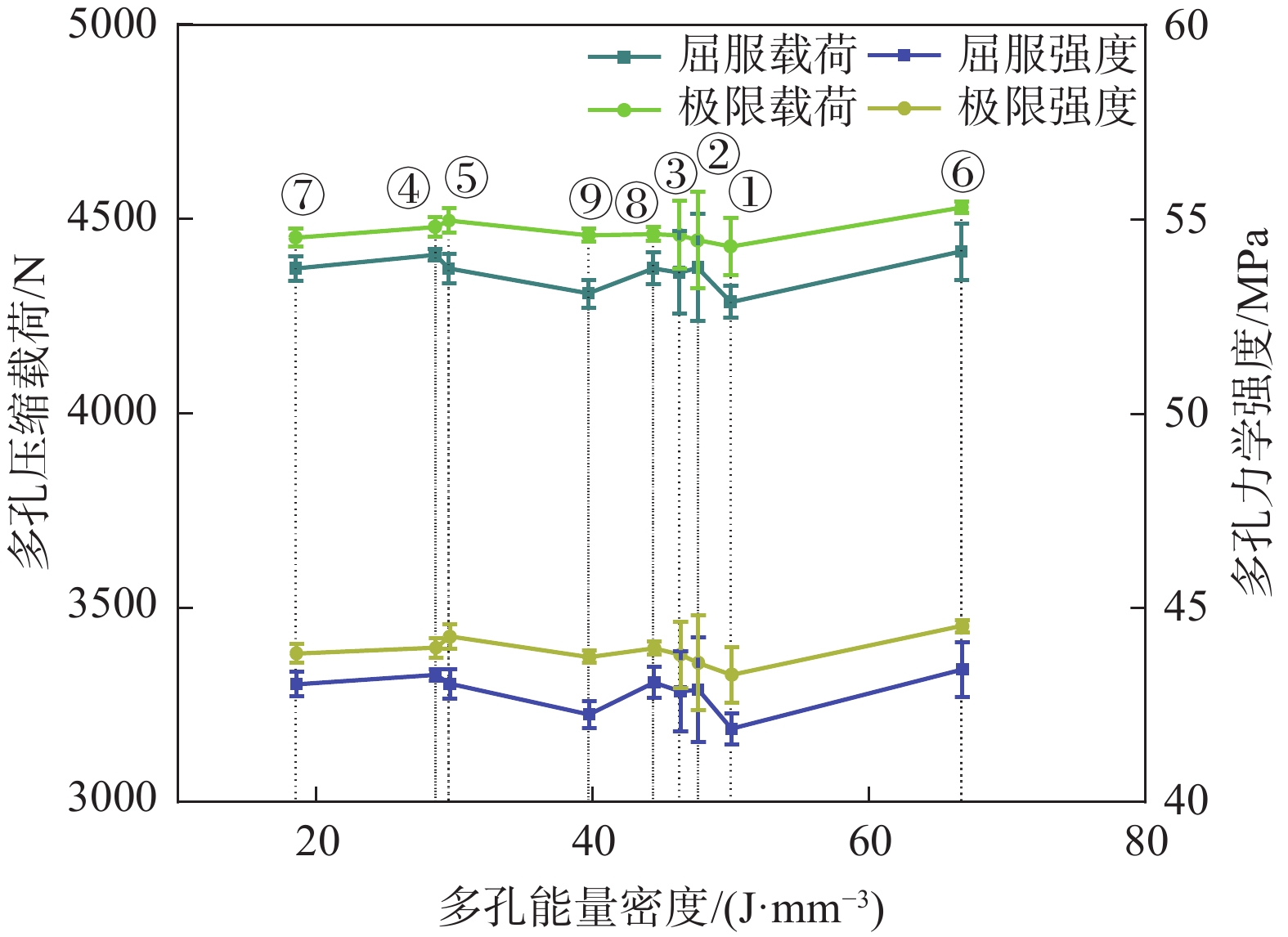
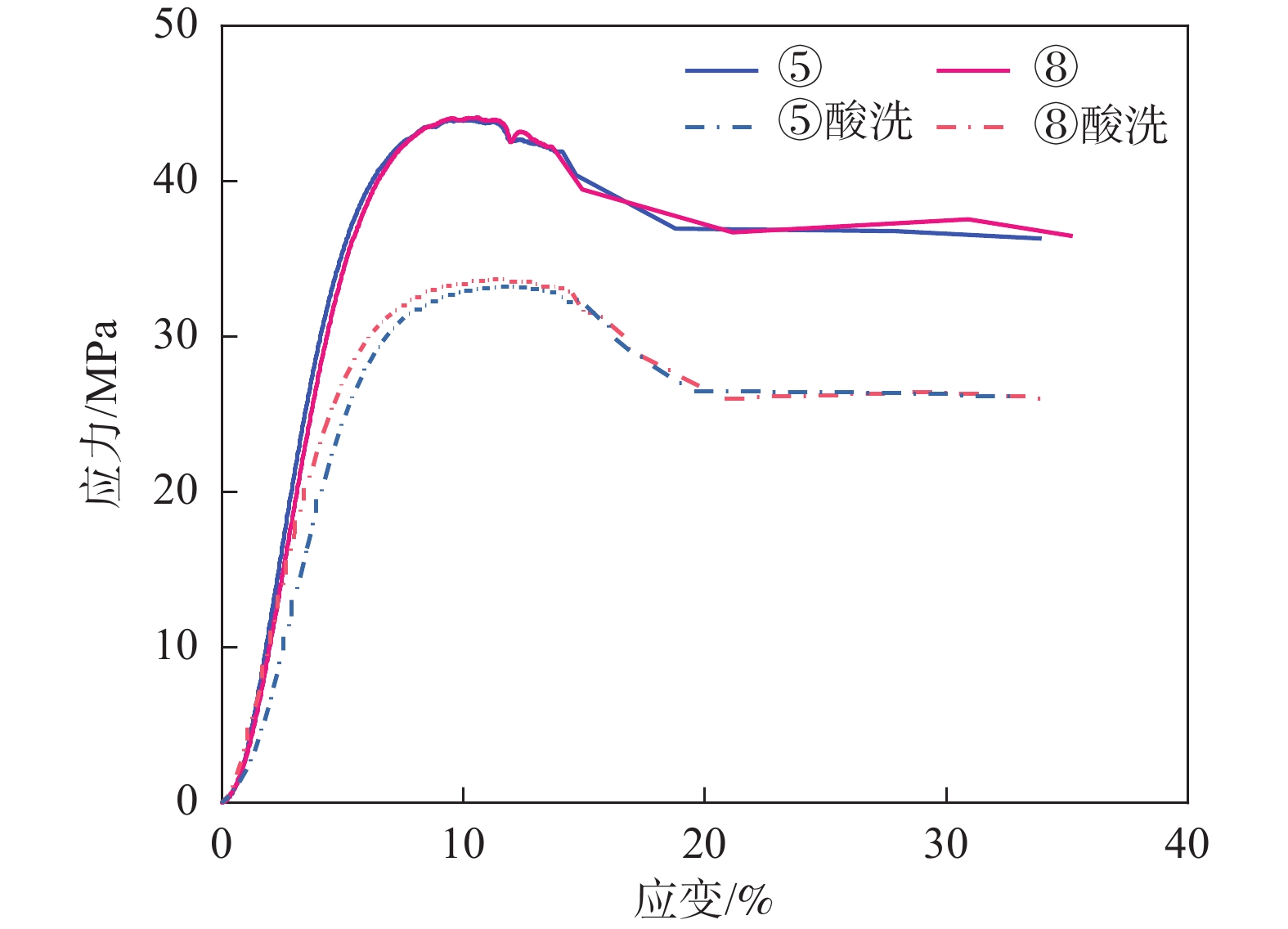
统计项 工艺水平 扫描速度v-力学强度 激光功率P-力学强度 扫描间距h-力学强度 屈服强度/MPa 极限强度/MPa 屈服强度/MPa 极限强度/MPa 屈服强度/MPa 极限强度/MPa K 1 129.25 130.69 128.23 131.10 128.41 131.79 2 130.13 132.79 129.06 131.84 128.46 131.33 3 129.37 131.55 128.55 132.09 128.97 131.91 Kavg 1 43.08 43.56 42.74 43.70 42.80 43.93 2 43.38 44.26 43.02 43.95 42.82 43.78 3 43.12 43.85 42.85 44.03 42.99 43.97 最佳水平 2 2 2 3 3 3 极值R 0.29 0.41 0.28 0.33 0.19 0.20 F检验 2.03 3.53 0.32 0.84 0.18 0.31 显著性 ns ** ns ns ns ns 水平数量 3 3 3 3 3 3 样品重复数 3 3 3 3 3 3 表注:K为单一工艺参数变量同水平下所有样品测量结果总和,Kavg为K值除以样品数的均值,最佳水平根据优化原则选取,极值R为各不同水平Kavg间的最大差值。显著性评价:***为p<0.001、**为0.001<p<0.01、*为0.01<p<0.05、ns为p>0.05。 -
[1] LIU J Q, LIU J, TANG Y J, et al. Research progress in titanium alloy in the field of orthopaedic implants[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2021,49(8):11-25. (刘剑桥, 刘佳, 唐毓金, 等. 钛合金在骨科植入领域的研究进展[J]. 材料工程, 2021,49(8):11-25.LIU J Q, LIU J, TANG Y J, et al. Research progress in titanium alloy in the field of orthopaedic implants[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering, 2021, 49(8): 11-25. [2] XU R W, ZHANG Z J, LIU Q Y, et al. The forming deviation, mechanical properties and compression failure of porous structures fabricated by laser melting were analyzed[J]. Transactions of The China Welding Institution, 2022,43(10):49-56, I0006. (徐榕蔚, 张振杰, 刘清原, 等. 选区激光熔化制备多孔结构的成形偏差及力学性能与压缩失效分析[J]. 焊接学报, 2022,43(10):49-56,I0006.XU R W, ZHANG Z J, LIU Q Y, et al. The forming deviation, mechanical properties and compression failure of porous structures fabricated by laser melting were analyzed[J]. Transactions of The China Welding Institution, 2022, 43(10): 49-56, I0006. [3] LI S J, LI X K, HOU W T, et al. Fabrication of open-cellular(porous) titanium alloy implants: osseointegration, vascularization and preliminary human trials[J]. Science China Materials, 2018,61(4):525-536. doi: 10.1007/s40843-017-9063-6 [4] LI X, GAO R N, XIONG Y Z, et al. Fabrication and characterization of porous titanium based on TPMS structure[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020,49(1):325-330. (李祥, 高芮宁, 熊胤泽, 等. 基于TPMS结构的多孔钛制备与表征[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2020,49(1):325-330.LI X, GAO R N, XIONG Y Z, et al. Fabrication and characterization of porous titanium based on TPMS structure[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020, 49(1): 325-330. [5] GU D D, ZHANG H M, CHEN H Y, et al. Laser additive manufacturing of high-performance metallic aerospace components[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020,47(5):24-47. (顾冬冬, 张红梅, 陈洪宇, 等. 航空航天高性能金属材料构件激光增材制造[J]. 中国激光, 2020,47(5):24-47. doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0500002GU D D, ZHANG H M, CHEN H Y, et al. Laser additive manufacturing of high-performance metallic aerospace components[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5): 24-47. doi: 10.3788/CJL202047.0500002 [6] SUN J, ZHU X G, LI P, et al. Effect of laser bulk energy density on densification behavior of TC4 titanium alloy by SLM[J]. Materials For Mechanical Engineering, 2020,44(1):51-56. (孙靖, 朱小刚, 李鹏, 等. 激光体能量密度对激光选区熔化成形TC4钛合金致密化行为的影响[J]. 机械工程材料, 2020,44(1):51-56.SUN J, ZHU X G, LI P, et al. Effect of laser bulk energy density on densification behavior of TC4 titanium alloy by SLM[J]. Materials For Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 44(1): 51-56. [7] YANG L J, LI Y H, ZHU Y Y, et al. Study on the influence of process parameters on the densification and surface hardness of TC4 titanium alloy formed parts by selective laser melting[J]. Applied Laser, 2022,42(4):55-62. (杨立军, 李翼虎, 朱阳洋, 等. 激光选区熔化制造工艺参数对TC4钛合金成型件致密度和硬度的影响规律[J]. 应用激光, 2022,42(4):55-62.YANG L J, LI Y H, ZHU Y Y, et al. Study on the influence of process parameters on the densification and surface hardness of TC4 titanium alloy formed parts by selective laser melting[J]. Applied Laser, 2022, 42(4): 55-62. [8] YANG Y C, RONG Y Z, WANG X, et al. Simulative and experimental study on basal sintering process of TC4 powder via selective laser melting[J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering, 2022(12):19-26. (杨寅晨, 荣远卓, 王翔, 等. TC4粉末选区激光熔化基础烧结工艺仿真与试验研究[J]. 现代制造工程, 2022(12):19-26.YANG Y C, RONG Y Z, WANG X, et al. Simulative and experimental study on basal sintering process of TC4 powder via selective laser melting[J]. Modern Manufacturing Engineering, 2022(12): 19-26. [9] YAN T Q, CHEN B Q, LIANG J Y, et al. Quality optimization of TC4 alloy fabrication via selective laser melting[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022,59(17):317-325. (闫泰起, 陈冰清, 梁家誉, 等. 激光选区熔化TC4钛合金成形质量优化研究[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2022,59(17):317-325.YAN T Q, CHEN B Q, LIANG J Y, et al. Quality optimization of TC4 alloy fabrication via selective laser melting[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2022, 59(17): 317-325. [10] LU Y C, SUN Z G, GUO Y H, et al. Compression performance of TC4 titanium alloy lattice structures manufactured by selective laser melting[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020,49(6):2067-2075. (卢毅晨, 孙中刚, 郭艳华, 等. 激光选区熔化TC4钛合金点阵结构的压缩性能[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2020,49(6):2067-2075.LU Y C, SUN Z G, GUO Y H, et al. Compression performance of TC4 titanium alloy lattice structures manufactured by selective laser melting[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2020, 49(6): 2067-2075. [11] WANG J, ZENG S J, WEI Q T, et al. Process optimization of selective laser melting for Ti6Al4V gradient porous structure[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2023,15(9):17-27 (王靖, 曾寿金, 魏青天, 等. 选区激光熔化Ti6Al4V梯度多孔结构工艺优化[J]. 精密成形工程, 2023,15(9):17-27.WANG J, ZENG S J, WEI Q T, et al. Process optimization of selective laser melting for Ti6Al4V gradient porous structure[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2023, 15(9): 17-27 [12] DANG X A, JIAO X L, YANG L J. Effect of SLM technology process parameters on tissue defects of porous scaffolds[J]. Applied Laser, 2020,40(6):998-1004. (党新安, 焦晓龙, 杨立军. 激光选区熔化工艺参数对成形多孔支架表面质量的影响研究[J]. 应用激光, 2020,40(6):998-1004.DANG X A, JIAO X L, YANG L J. Effect of SLM technology process parameters on tissue defects of porous scaffolds[J]. Applied Laser, 2020, 40(6): 998-1004. [13] CHEN J, FU G S, CHEN H L, et al. Influence of selective laser melting forming process on microstructure of porous TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Materials For Mechanical Engineering, 2023,47(11):96-103,110. (陈健, 傅高升, 陈鸿玲, 等. 选区激光熔化成形工艺对多孔TC4钛合金显微组织的影响[J]. 机械工程材料, 2023,47(11):96-103,110.CHEN J, FU G S, CHEN H L, et al. Influence of selective laser melting forming process on microstructure of porous TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Materials For Mechanical Engineering, 2023, 47(11): 96-103,110. [14] SHI Z L, WANG W, LU X L, et al. Parametric porous structure design with TPMS for bone tissue[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2024,400(6):265-270. (石志良, 王伟, 卢小龙, 等. TPMS骨组织多孔结构参数化设计方法研究[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2024,400(6):265-270.SHI Z L, WANG W, LU X L, et al. Parametric porous structure design with TPMS for bone tissue[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2024, 400(6): 265-270. [15] WANG Z L, LIAO B, LIU Y S, et al. Influence of structural parameters of 3D-printed triply periodic minimal surface gyroid porous scaffolds on compression performance, cell response, and bone regeneration[J]. Journal of biomedical materials research. Part B, Applied biomaterials, 2024(1):112. [16] JI Q. Study on toxicity of TC4 porous scaffold to mouse fibroblasts and mouse embryonic fibroblasts[D]. Zunyi: Zunyi Medical University, 2021. (纪琦. TC4多孔支架对小鼠成纤维细胞及小鼠胚胎成纤维细胞毒性研究[D]. 遵义: 遵义医科大学, 2021.JI Q. Study on toxicity of TC4 porous scaffold to mouse fibroblasts and mouse embryonic fibroblasts[D]. Zunyi: Zunyi Medical University, 2021. [17] ZHENG F, CHENG T Y, ZHANG Q Y. Pickling technology of titanium and titanium alloy[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2009,37(3):26-28. (郑锋, 程挺宇, 张巧云. 钛及钛合金的酸洗技术[J]. 稀有金属与硬质合金, 2009,37(3):26-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0536.2009.03.008ZHENG F, CHENG T Y, ZHANG Q Y. Pickling technology of titanium and titanium alloy[J]. Rare Metals and Cemented Carbides, 2009, 37(3): 26-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0536.2009.03.008 [18] ZHANG J G, HUANG D Y, HU F L, et al. Mechanical properties of Ti6Al4V alloy with porous structure prepared by selective laser melting[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2022,51(10):3619-3625. [19] XU G S, KOU H C, LIU X L, et al. Influence of different solution media on microstructure and mechanical properties of porous titanium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014,43(S1):377-381. (徐广胜, 寇宏超, 刘向宏, 等. 不同介质溶液对多孔钛微观结构和力学性能的影响[J]. 稀有金属材料与工程, 2014,43(S1):377-381.XU G S, KOU H C, LIU X L, et al. Influence of different solution media on microstructure and mechanical properties of porous titanium[J]. Rare Metal Materials and Engineering, 2014, 43(S1): 377-381. [20] OUYANG J, YANG G T, ZHOU W Z, et al. Biomechanical characters of human lumar vertebral trabecular bone[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 1997,16(4):289-293,309. (欧阳钧, 杨桂通, 吴文周, 等. 人体腰椎松质骨的生物力学性质[J]. 中国生物医学工程学报, 1997,16(4):289-293,309.OUYANG J, YANG G T, ZHOU W Z, et al. Biomechanical characters of human lumar vertebral trabecular bone[J]. Chinese Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 1997, 16(4): 289-293,309. -





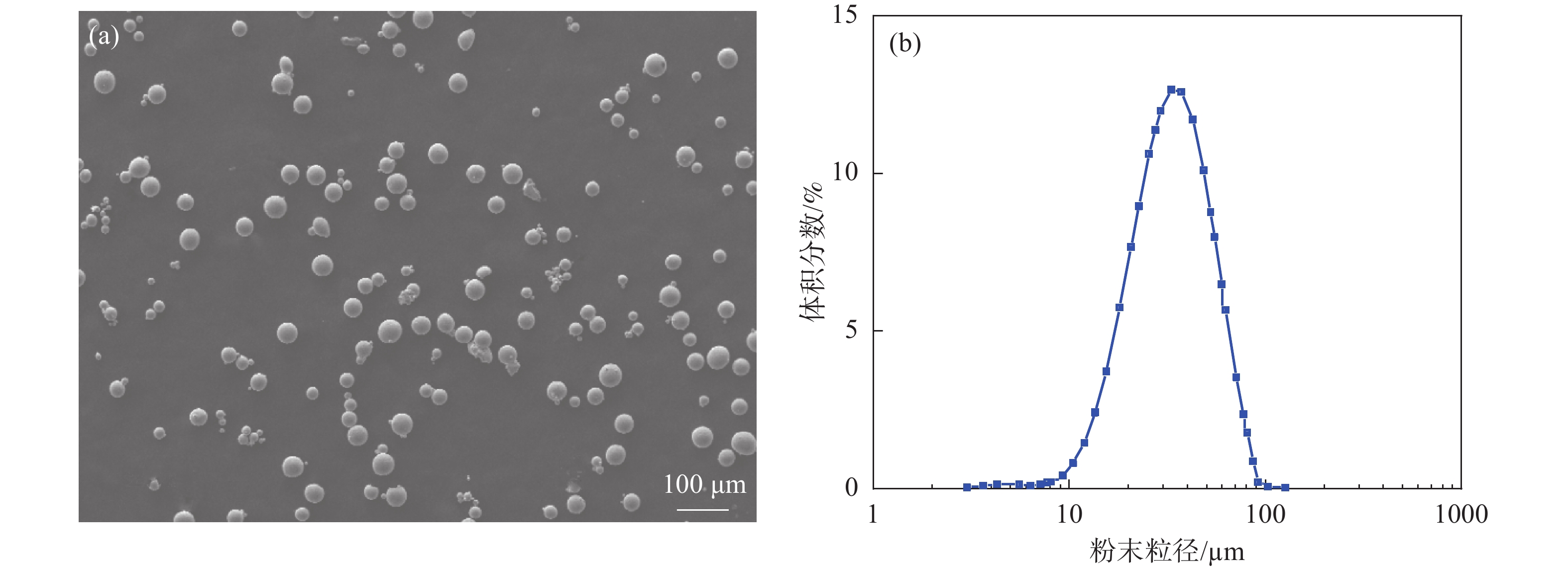
 下载:
下载: