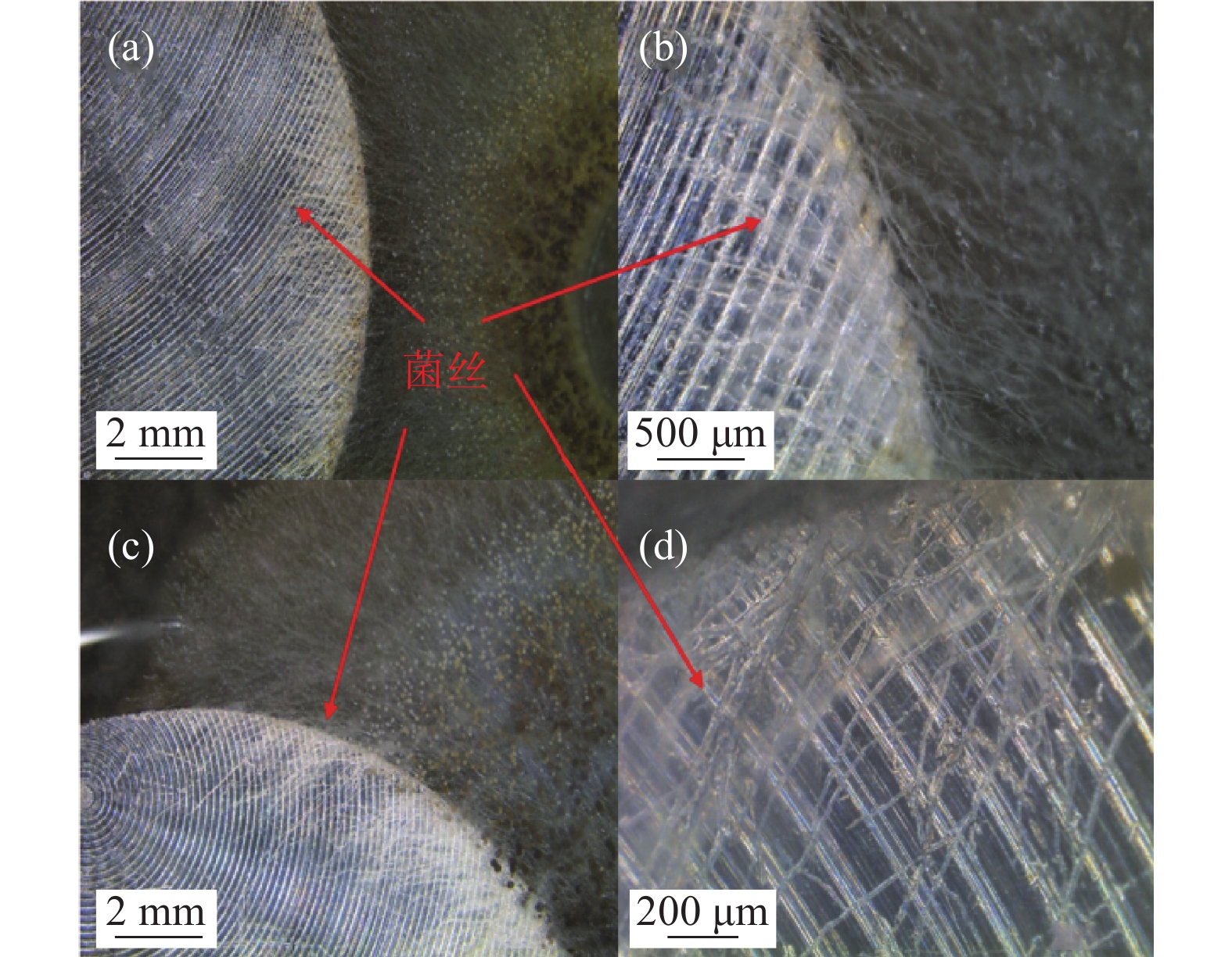
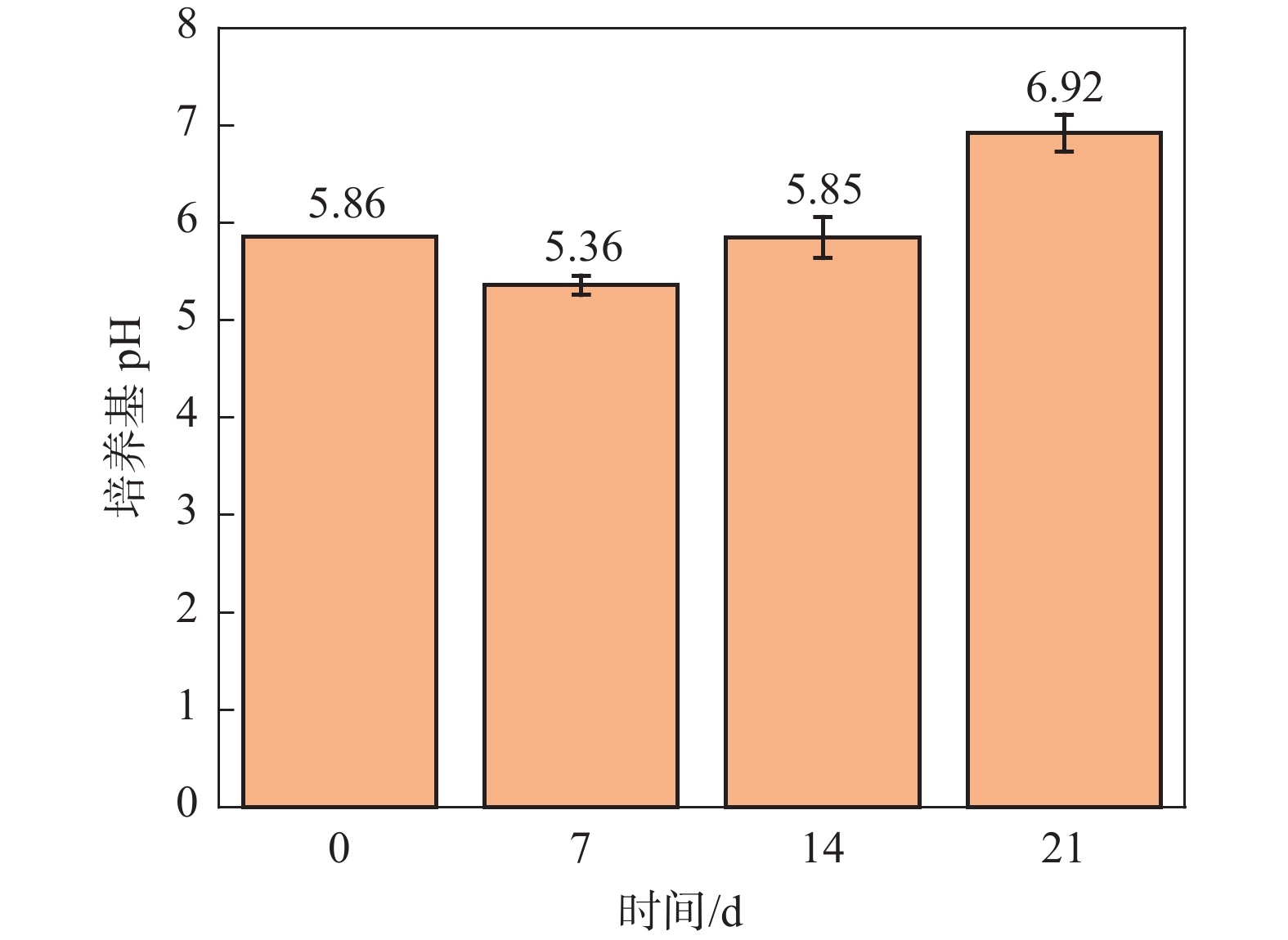
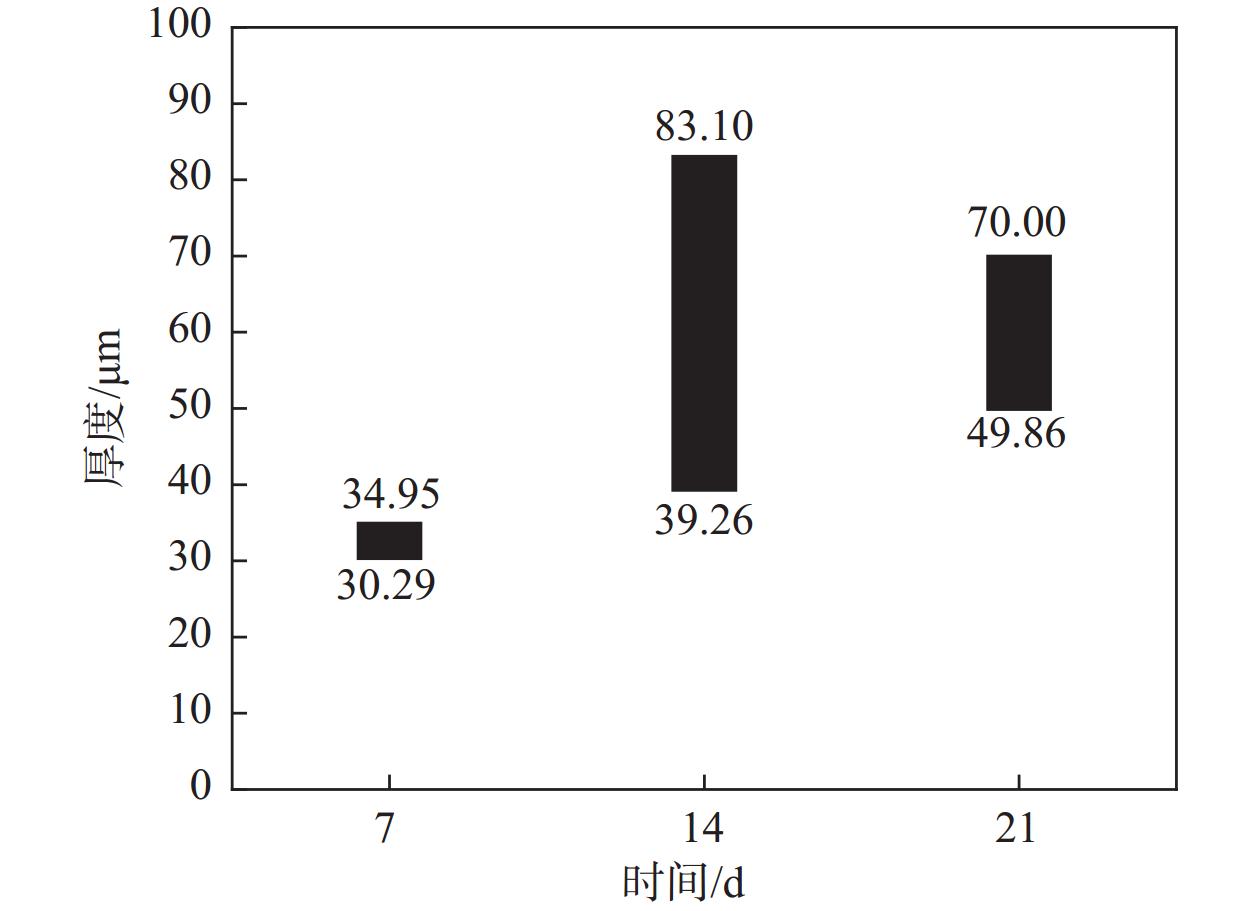
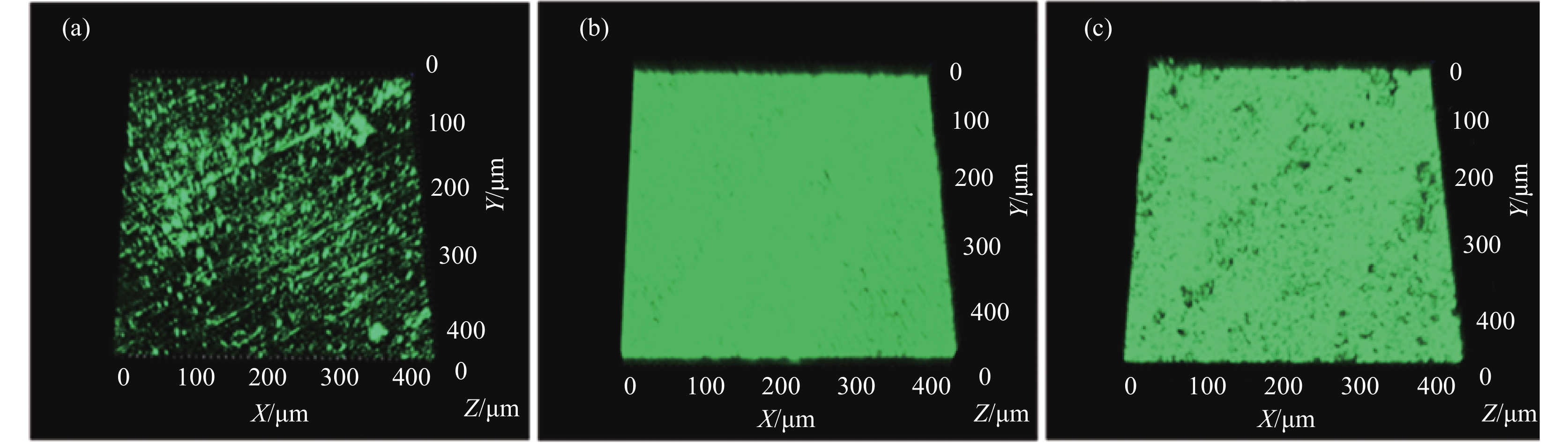
Effect of Aspergillus niger on the corrosion of industrially pure titanium
-
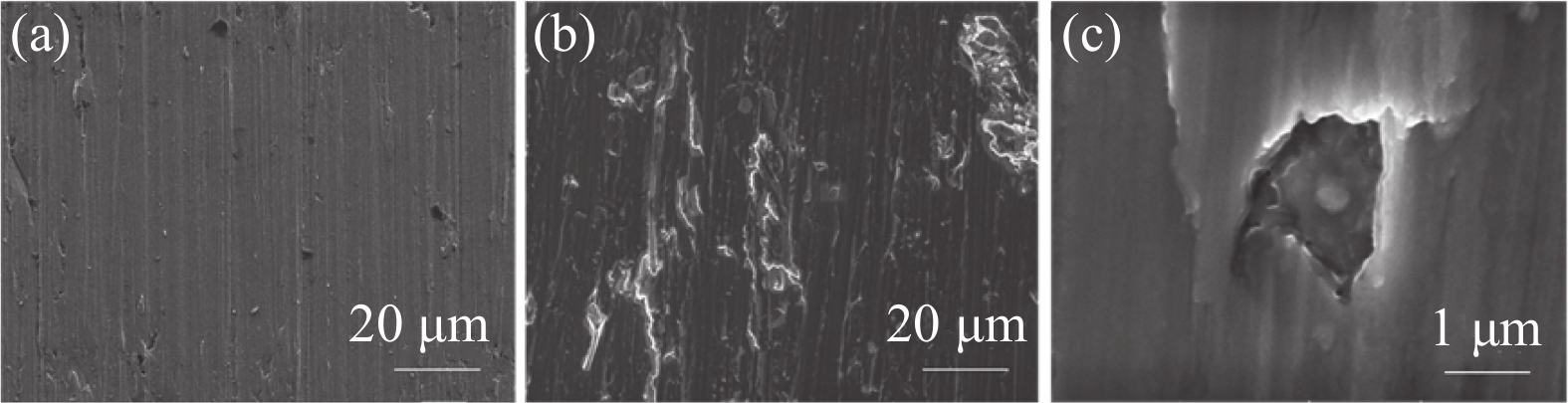
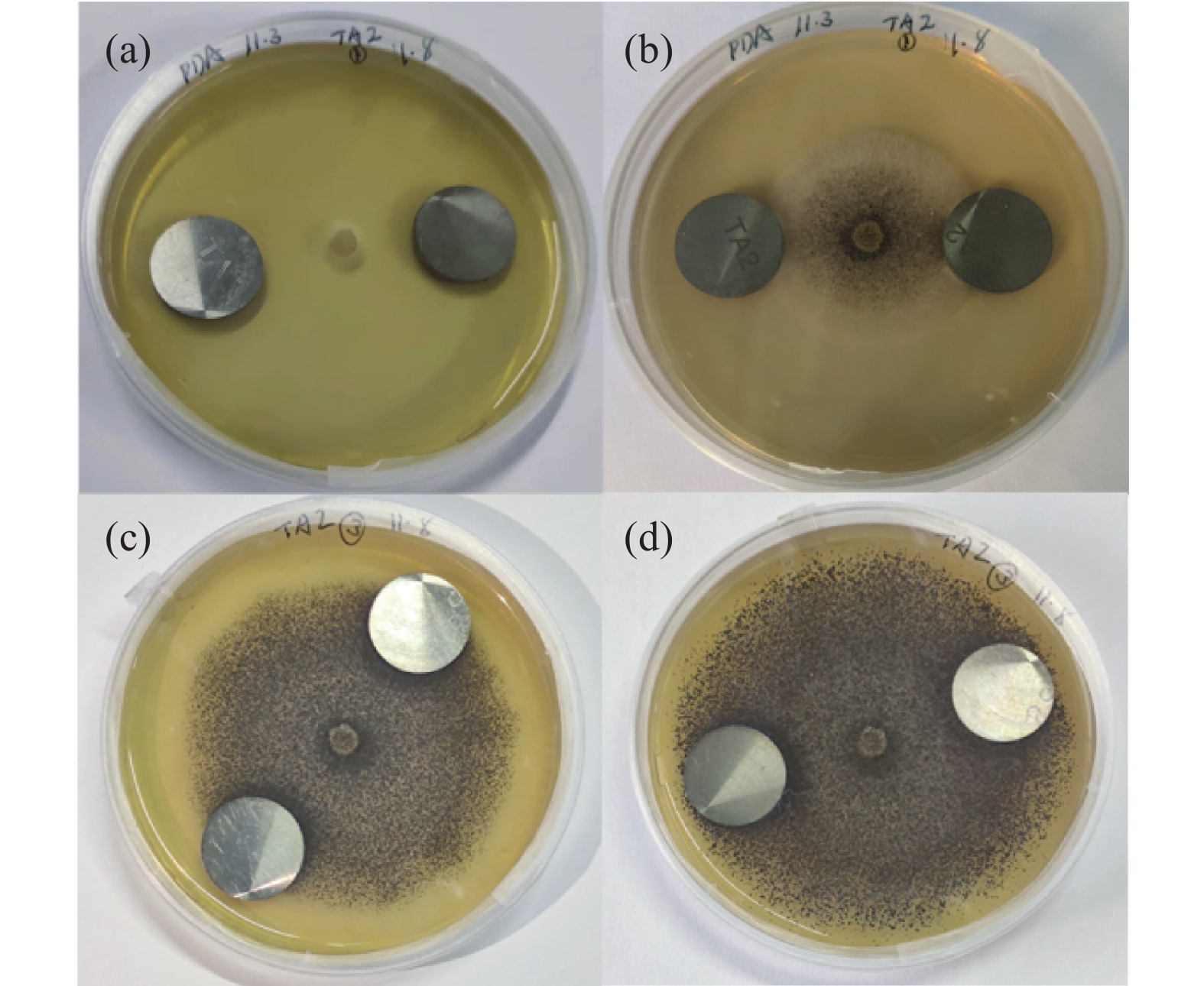
摘要: 选取黑曲霉菌为典型微生物,研究其对工业纯钛TA2腐蚀行为的影响,采用表面分析技术(激光共聚焦显微镜及扫描电子显微镜),结合电化学分析方法(电化学阻抗谱和动电位极化曲线),研究了工业纯钛TA2在黑曲霉菌富集环境下的耐腐蚀特性。研究发现黑曲霉菌在TA2表面的附着生长改变了钛片的电化学特征,其耐腐蚀性随浸泡时间的增加先增强后减弱,生物膜在一定时间周期内可提高耐蚀性能。生物膜越厚,其耐腐蚀性能越好。尽管如此,在黑曲霉菌液浸泡21 d后,钛片表面仍观察到极少量的点蚀坑,预示出现了霉菌腐蚀。Abstract: The study investigated the influence of Aspergillus niger on the corrosion behavior of industrial pure titanium TA2. Surface analysis techniques, including laser confocal microscopy and scanning electron microscopy, were employed alongside electrochemical analysis methods such as electrochemical impedance spectroscopy and potentiodynamic polarization curves to examine the corrosion resistance of TA2 in the presence of Aspergillus niger biofilms. The findings revealed that the adherence and growth of Aspergillus niger on the TA2 surface modified the electrochemical properties of the titanium, with its corrosion resistance initially improving and then declining over time. The biofilm enhanced corrosion resistance within a specific timeframe, and a thicker biofilm correlated with better resistance. However, after 21 days of immersion in the Aspergillus niger solution, minor pitting was observed on the titanium surface, indicating the initiation of microbial-induced corrosion.
-
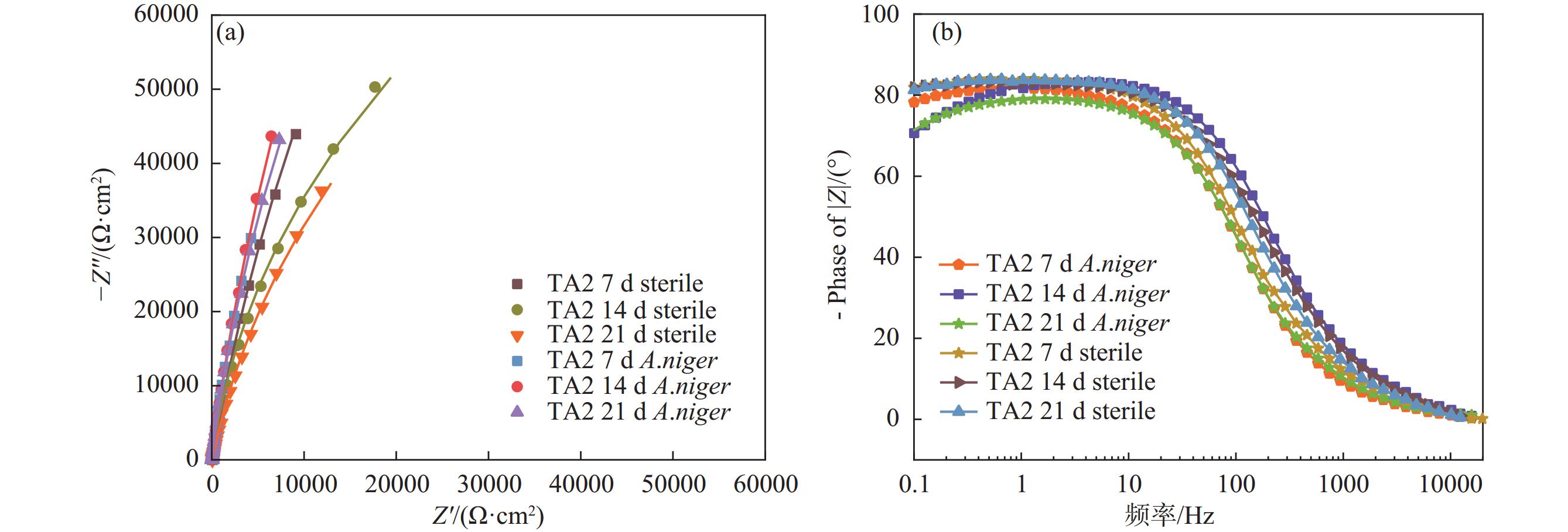
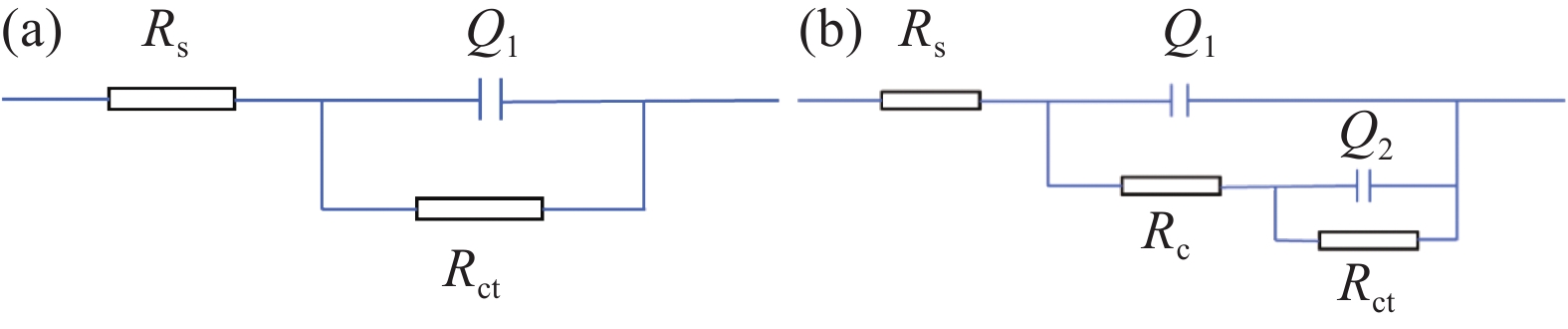
表 1 拟合参数
Table 1. Fitting parameter table
TA2 t/d $ R_{\mathrm{S}} $/(Ω·cm2) ${Q_1}$×105/(Ω−1·Sn·cm−2) ${n_1}$ ${R_c}$/(Ω·cm2) ${Q_2}$×105/(Ω−1·Sn·cm−2) ${n_2}$ $ R_{\mathrm{ct}} $/(kΩ·cm2) 不含菌(Sterile) 7 65.68 3.36 0.92 265300 14 34.98 2.63 0.93 326000 21 64.04 3.68 0.90 223900 A.niger 7 30.13 2.08 0.98 22.23 2.99 0.92 572370 14 25.07 3.07 0.93 78.17 0.3984 0.99 886780 21 27.70 2.86 0.93 58.6 0.602 0.98 579350 表 2 浸泡于PDB培养基和黑曲霉菌液中的钛片的动电位极化拟合数据
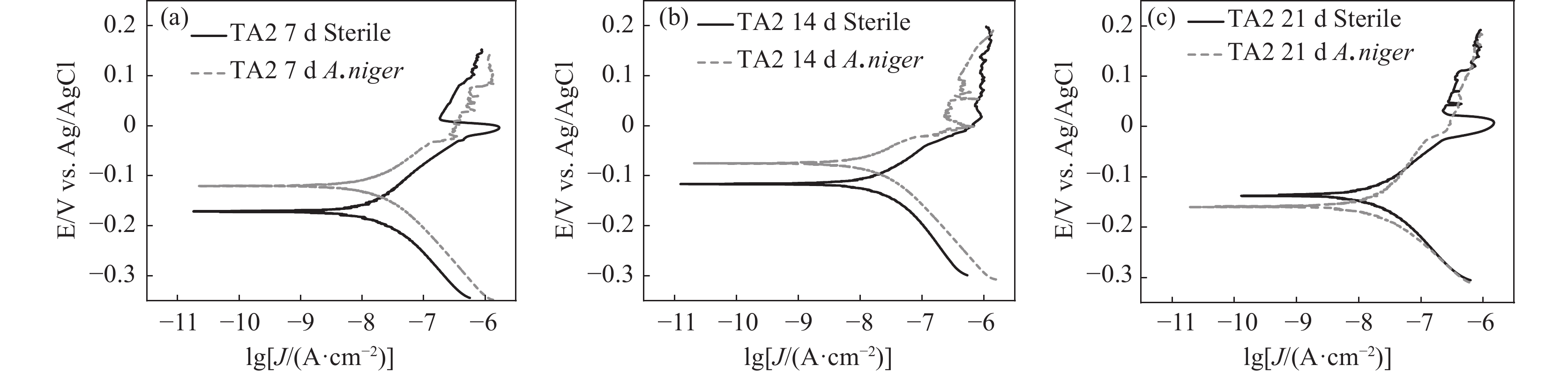
Table 2. Potentiodynamic polarization fitting data of titanium sheets immersed in PDB medium and Aspergillus niger solution
时间/d icorr×108/(A·cm−2) Ecorr/V |βa|/(mV·deg−1) |βc|/(mV·deg−1) Aspergillus niger 7 1.27 −0.120 237.91 126.66 14 1.93 −0.075 78.81 124.88 21 1.16 −0.162 147.36 126.66 PDB培养基 7 1.30 −0.171 78.75 79.90 14 2.09 −0.117 113.83 131.39 21 2.23 −0.138 117.12 124.80 -
[1] SUN J, QI Y J, LIU H, et al. Research progress on tribo-corrosion of titanium and titanium alloys in seawater environment[J]. Materials Protection, 2020,53(1):151-156. (孙静, 齐元甲, 刘辉, 等. 海洋环境下钛及钛合金的腐蚀磨损研究进展[J]. 材料保护, 2020,53(1):151-156.SUN J, QI Y J, LIU H, et al. Research progress on tribo-corrosion of titanium and titanium alloys in seawater environment[J]. Materials Protection, 2020, 53(1): 151-156. [2] DONG Y C, FANG Z G, CHANG H, et al. Service performance of titanium alloy in marine environment[J]. Materials China, 2020,39(3):185-190. (董月成, 方志刚, 常辉, 等. 海洋环境下钛合金主要服役性能研究[J]. 中国材料进展, 2020,39(3):185-190. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.201909015DONG Y C, FANG Z G, CHANG H, et al. Service performance of titanium alloy in marine environment[J]. Materials China, 2020, 39(3): 185-190. doi: 10.7502/j.issn.1674-3962.201909015 [3] LI J Q, ZHANG D Y, CHEN X B, et al. Laser directed energy deposited, ultrafine-grained functional titanium-copper alloys tailored for marine environments: Antibacterial and anti-microbial corrosion studies[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2023,166:21-33. [4] JIANG C M, YANG S X, GUO D, et al. Simulated microgravity accelerates alloy corrosion by aspergillus sp. via the enhanced production of organic acids[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 2022,88(19):1-16. [5] DENG C, ZHAO Z X, HU H S, et al. Comparisons of I− and Cl− concentrations on the corrosion behavior of TA4 titanium alloy in azeotropic acetic acid solutions[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2022,2368(1):012009. doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/2368/1/012009 [6] SAN N O, NAZIR H, DÖNMEZ G. Evaluation of microbiologically influenced corrosion inhibition on Ni-Co alloy coatings by aeromonas salmonicida and clavibacter michiganensis[J]. Corrosion Science, 2012,65:113-118. doi: 10.1016/j.corsci.2012.08.009 [7] ZHANG D, WU J J. Research progress on the mechanisms of microbiologically influenced corrosion in marine environment[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2020,51(4):821-828. (张盾, 吴佳佳. 海洋环境微生物腐蚀机理研究进展[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 2020,51(4):821-828. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20200300061ZHANG D, WU J J. Research progress on the mechanisms of microbiologically influenced corrosion in marine environment[J]. Oceanologia et Limnologia Sinica, 2020, 51(4): 821-828. doi: 10.11693/hyhz20200300061 [8] VICTORIA S N, SHARMA A, MANIVANNAN R. Metal corrosion induced by microbial activity-Mechanism and control options[J]. Journal of the Indian Chemical Society, 2021,98(6):100083. doi: 10.1016/j.jics.2021.100083 [9] JIA R, YANG D Q, XU D K, et al. Electron transfer mediators accelerated the microbiologically influence corrosion against carbon steel by nitrate reducing Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm[J]. Bioelectrochemistry, 2017,118:38-46. doi: 10.1016/j.bioelechem.2017.06.013 [10] LI Z D, BI Z Y. Effects of environmental conditions such as temperature, salinity and pH on mold growth[J]. Asian Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2019,2(4):33-38. (李卓地, 毕振云. 温度、盐度及pH等环境条件对霉菌生长的影响[J]. 亚洲临床医学杂志, 2019,2(4):33-38.LI Z D, BI Z Y. Effects of environmental conditions such as temperature, salinity and pH on mold growth[J]. Asian Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2019, 2(4): 33-38. [11] LIU S D, KONG W X, WANG J. Investigation of typical marine mould corrosion environment-A case study of “Dong Fang Hong 2”[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2016,44(21):141-143. (刘士栋, 孔维轩, 王佳. 典型海洋霉菌腐蚀环境调查-以“东方红2”为例[J]. 广州化工, 2016,44(21):141-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2016.21.050LIU S D, KONG W X, WANG J. Investigation of typical marine mould corrosion environment-A case study of “Dong Fang Hong 2”[J]. Guangzhou Chemical Industry, 2016, 44(21): 141-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9677.2016.21.050 [12] KHAN M S, LI Z, YANG K, et al. Microbiologically influenced corrosion of titanium caused by aerobic marine bacterium Pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019,35(1):216-222. [13] ZHANG Y X, CHEN C Y, LIU H W, et al. Research progress on mildew induced corrosion of Al-alloy[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2021,41(1):13-21. (张雨轩, 陈翠颖, 刘宏伟, 等. 铝合金霉菌腐蚀研究进展[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2021,41(1):13-21.ZHANG Y X, CHEN C Y, LIU H W, et al. Research progress on mildew induced corrosion of Al-alloy[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection, 2021, 41(1): 13-21. [14] TIAN F, BAI X Q, HE X Y, et al. Research progress on microbiological induced corrosion of metallic materials under ocean environment[J]. Surface Technology, 2018,47(8):182-196. (田丰, 白秀琴, 贺小燕, 等. 海洋环境下金属材料微生物腐蚀研究进展[J]. 表面技术, 2018,47(8):182-196.TIAN F, BAI X Q, HE X Y, et al. Research progress on microbiological induced corrosion of metallic materials under ocean environment[J]. Surface Technology, 2018, 47(8): 182-196. [15] CHEN J N. The study on microbiologically influenced corrosion behavior and mechanism of hull structure material 907 steel in seawater[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Science (Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019. (陈菊娜. 船体结构材料907钢在海水中微生物腐蚀行为及机理研究[D]. 青岛: 中国科学院大学(中国科学院海洋研究所), 2019.CHEN J N. The study on microbiologically influenced corrosion behavior and mechanism of hull structure material 907 steel in seawater[D]. Qingdao: University of Chinese Academy of Science (Institute of Oceanology, Chinese Academy of Sciences), 2019. -





 下载:
下载: