Modification of inclusions in Ni-Al maraging steels by rare earths
-
摘要: 钢中的非金属夹杂物对超高强度钢的塑韧性具有重要的影响。在Fe-Ni-Al系马氏体时效钢中加入稀土La、Ce元素,通过扫描电子显微镜及能谱仪(SEM-EDS)与电子探针(EPMA)分析结合FactSage热力学计算,研究了不同稀土元素对钢中非金属夹杂物的变质机理。结果表明,马氏体时效钢中加入稀土元素后形成了含稀土的RE-O-S和RE-Al-O,抑制了Al2S3的形成,对AlN夹杂物的形成没有明显影响,夹杂物经稀土改性后形状由条状和不规则的几何形状转变为接近球状。热力学计算结果表明,添加稀土元素后,钢液中可能形成的夹杂物热力学稳定性大致为REAlO3→Al2O3→稀土硫化物→AlN。加入稀土后,在高温熔融态下钢液中RE2O3和Al2O3就已稳定存在,并且随着冷却温度的降低,钢中的夹杂物按REAlO3→RE2O2S→RES的顺序逐渐析出,且稀土La和Ce的夹杂物演化路径基本相同。Abstract: Non-metallic inclusions in steel have an important influence on the ductility and toughness of ultra-high strength steels. In this paper, rare earth La and Ce elements were added to Fe-Ni-Al system martensitic aging steel, and the metamorphic mechanism of non-metallic inclusions in steel with different rare earth elements was investigated by scanning electron microscopy, energy spectrometry (SEM-EDS) and electron probe (EPMA) analyses combined with FactSage thermodynamic calculations. The results showed that the addition of rare earth elements to martensitic ageing steel resulted in the formation of rare earth-containing RE-O-S and RE-Al-O, which inhibited the formation of Al2S3 and had no significant effect on the formation of AlN inclusions, and the shape of the inclusions was transformed from a strip-like and irregular geometry to a near-spherical shape after the modification of the inclusions by rare earths. Thermodynamic calculations showed that after the addition of rare earth elements, the thermodynamic stability of inclusions in the steel might be formed roughly as REAlO3 → Al2O3 → rare earth sulfides → AlN. After the addition of rare earths, the RE2O3 and Al2O3 had been stable in the high-temperature molten state of the liquid steel, and with the lowering of the cooling temperature inclusions formed in the order of REAlO3 → RE2O2S → RES, and the inclusions of rare-earth La and Ce showed basically the same evolutionary path.
-
0. 引言
马氏体时效钢是一种超高强度钢,具有极高的强度和良好的韧性,在飞机、航空航天和模具工业中得到了广泛的应用[1-2]。产生这些有益的机械性能是由于马氏体微观结构在时效热处理时形成了高密度金属间析出物。由于Fe-Ni-Al系马氏体时效钢可以通过析出β’-NiAl或Ni3Al[3-6],通常均匀分布在整个基体[7-8],且NiAl相的沉淀动力学非常快,是循环加热过程中的理想产物[9],故Fe-Ni-Al系马氏体时效钢成为研究热点。
钢中的非金属夹杂物是钢中的天然组分,对钢材的质量和性能有着至关重要的影响。夹杂物的大小和分布直接影响了钢材质量,研究表明[10-11],夹杂物与基体的基本物理性质相差较大,甚至完全不同,如硬度、塑性、热膨胀系数。因此,在夹杂物形成的位置,破坏了钢材的显微结构和物理特性,使钢基体变得不连续,影响了其性能和使用寿命。随着对稀土元素的深入研究及其开发利用,许多研究者研究了添加稀土对改善钢性能的作用,其中稀土元素在钢材中的重要应用之一就是净化钢液[12-16],已有学者表明[17-19],稀土元素具有较强的化学活性及与硫、氧很强的亲和力,能够有效地降低夹杂物的尺寸和数量,有效改善夹杂物的形貌,细化晶粒尺寸,提高钢材的质量和性能。然而目前对马氏体时效钢的研究主要集中在热处理后对钢材性能提升方面,对马氏体时效钢铸态组织及夹杂物的影响还鲜有报道。
笔者在借鉴前人研究结果的基础上,基于Fe-Ni-Al系马氏体时效钢基本成分,通过加入不同组分的稀土元素,利用扫描电子显微镜和电子探针分析了不同稀土元素对钢中的非金属夹杂物的形貌和尺寸变化,运用热力学理论计算,研究了不同稀土元素对马氏体时效钢中铸态夹杂的生成与变质的影响机理,这对稀土元素变质钢中夹杂物的行为研究及高性能稀土马氏体时效钢的研制具有重要的理论与实际意义。
1. 试验方法
基于Fe-Ni-Al系马氏体时效钢制备试验用钢,并在钢中分别加入La、Ce作为对照组,采用25 kg真空感应炉冶炼,浇铸成截面尺寸为75 mm×100 mm的铸坯。利用直读光谱仪、氧氮氢分析仪、碳硫分析仪测定铸坯化学成分,如表1所示。用电火花钼丝切割机在铸坯上切取出尺寸为15 mm×10 mm×5 mm的三种试样,磨光,确保表面无划痕,清洁无污渍。利用扫描电子显微镜(ZEISS sigma300),结合能谱仪(Oxford60)及场发射电子探针(JXA-iHP200 F)对夹杂物的形貌、尺寸和元素分布进行分析。利用全自动非金属夹杂物扫描系统(OPTON-OTS),对钢中的非金属夹杂物的数量及其组成成分进行分类统计。
表 1 试验钢化学成分Table 1. Chemical compositions of experimental steels% 样本 C Ni Al Mo Nb B O N S La Ce Fe 1 # 0.039 19.157 2.342 3.886 0.657 0.017 0.0018 0.011 0.0033 Bal 2 # 0.049 19.735 2.338 3.133 0.646 0.016 0.0011 0.012 0.0021 0.019 Bal 3 # 0.046 19.109 2.641 3.262 0.675 0.018 0.0010 0.010 0.0020 0.018 Bal 同时,利用FactSage8.1热力学软件中的Equilib模块,选用FToxid、FTmisc和FSstel数据库对稀土元素改性钢中非金属夹杂物的演化机理和过程进行模拟。
2. 试验结果
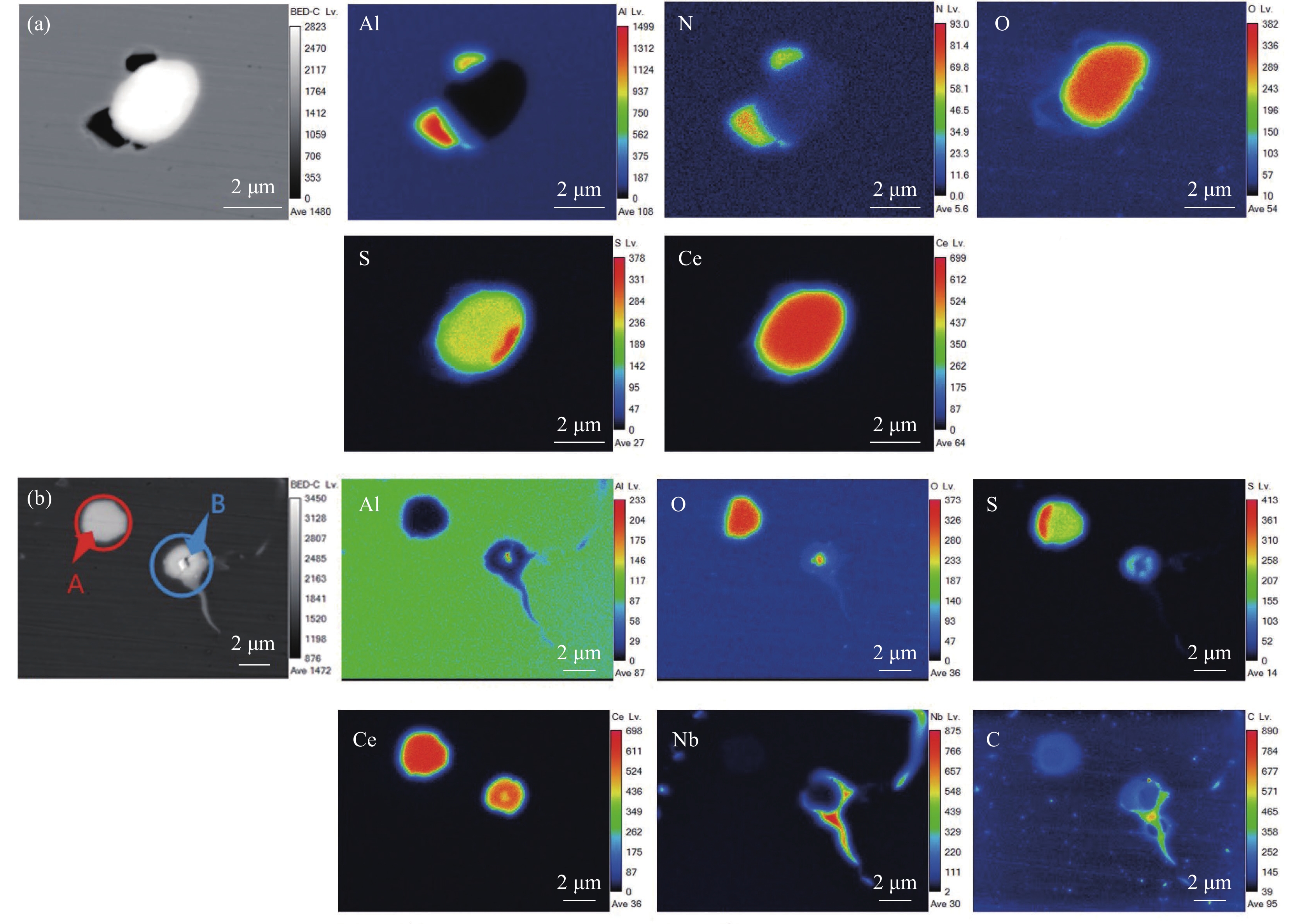
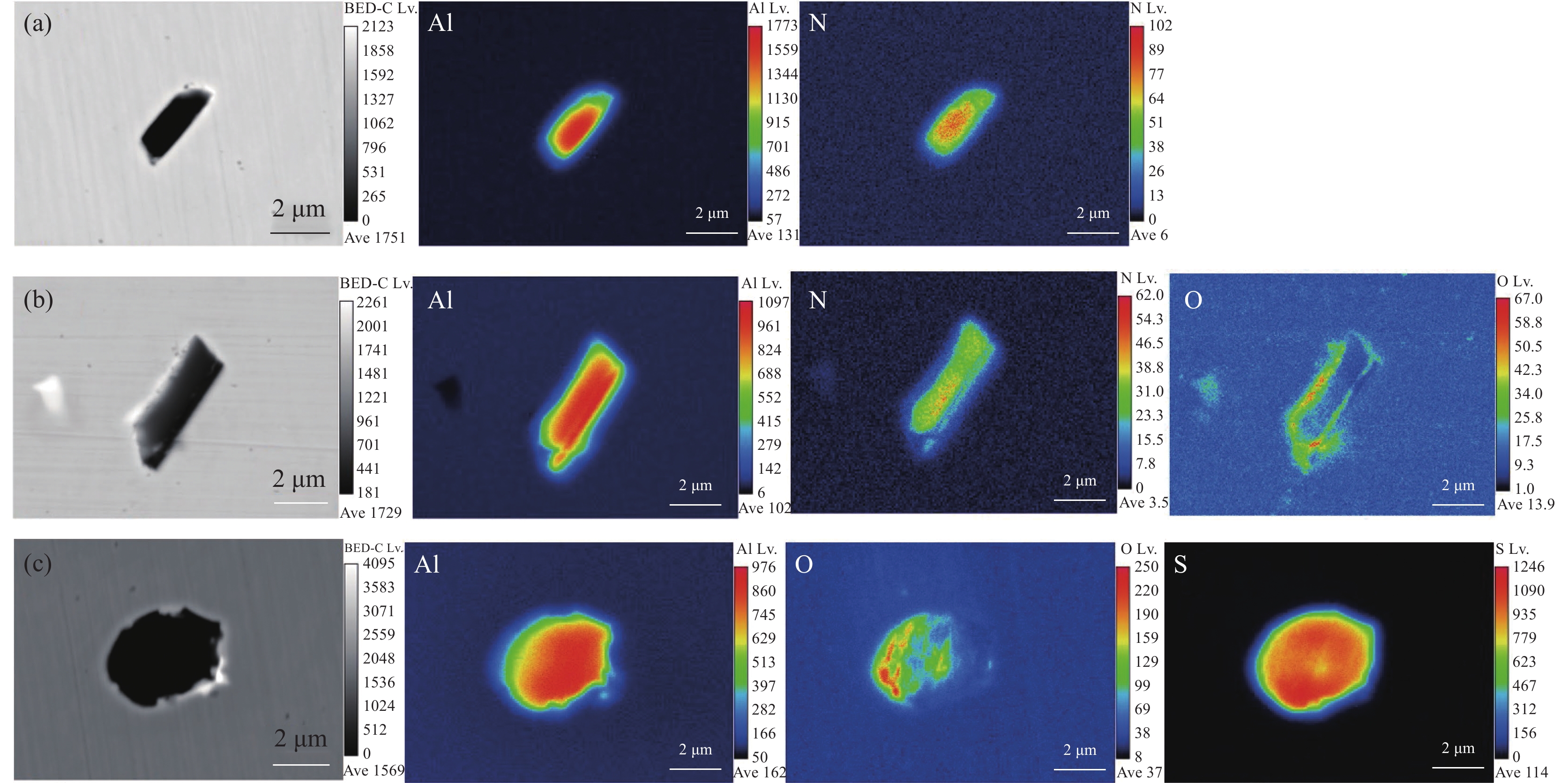
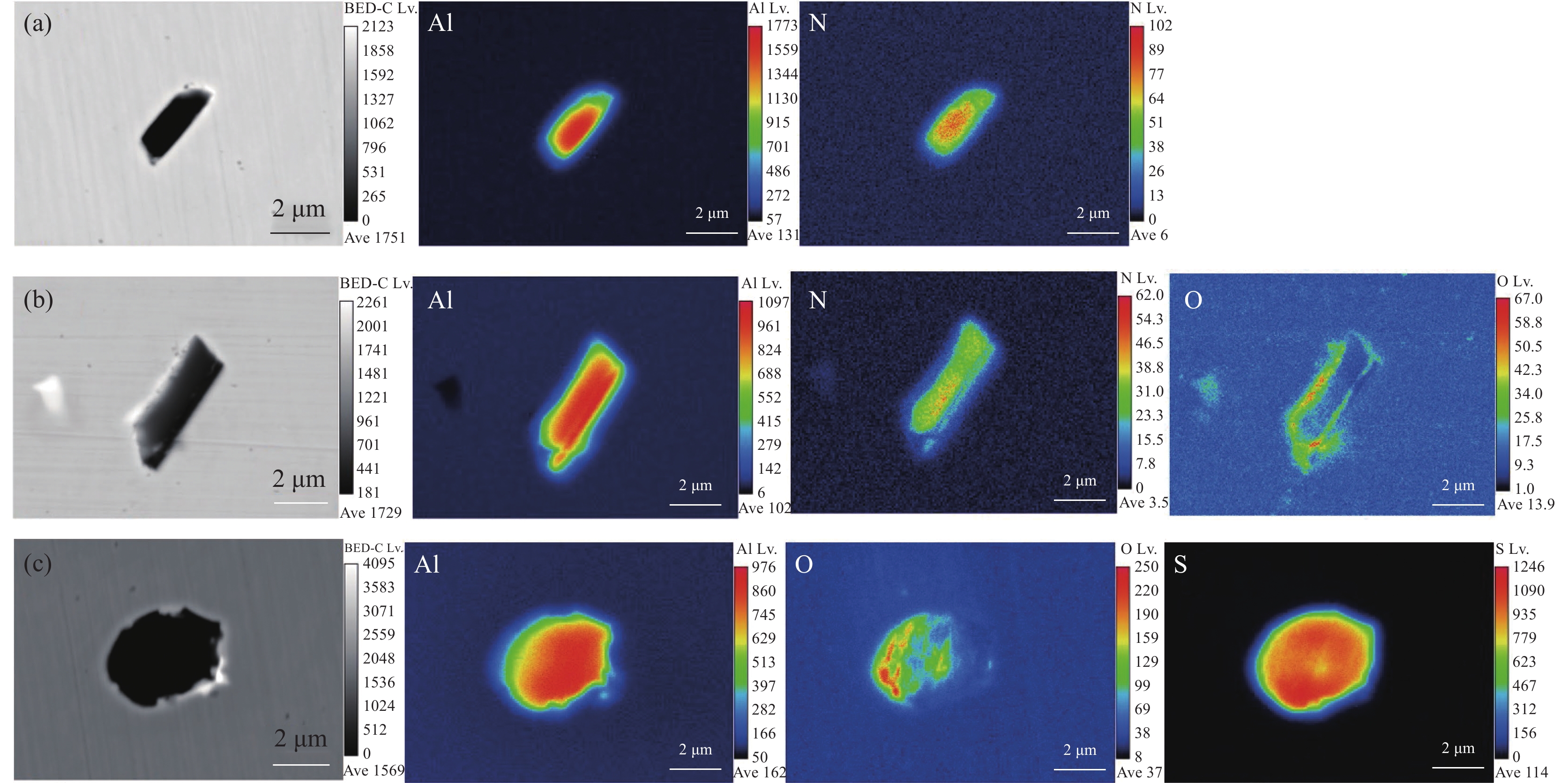
图1~3为试验钢中的夹杂物EPMA图。由图1可以看出,夹杂物主要分为三类,第一类为Al-N组成的长条状的AlN夹杂物;第二类由AlN为形核中心向外生长,在边缘位置有[O]的富集:第三类以Al-S为芯部,O在芯部附近偏聚成长,形成了Al2O3-Al2S3复合夹杂物。
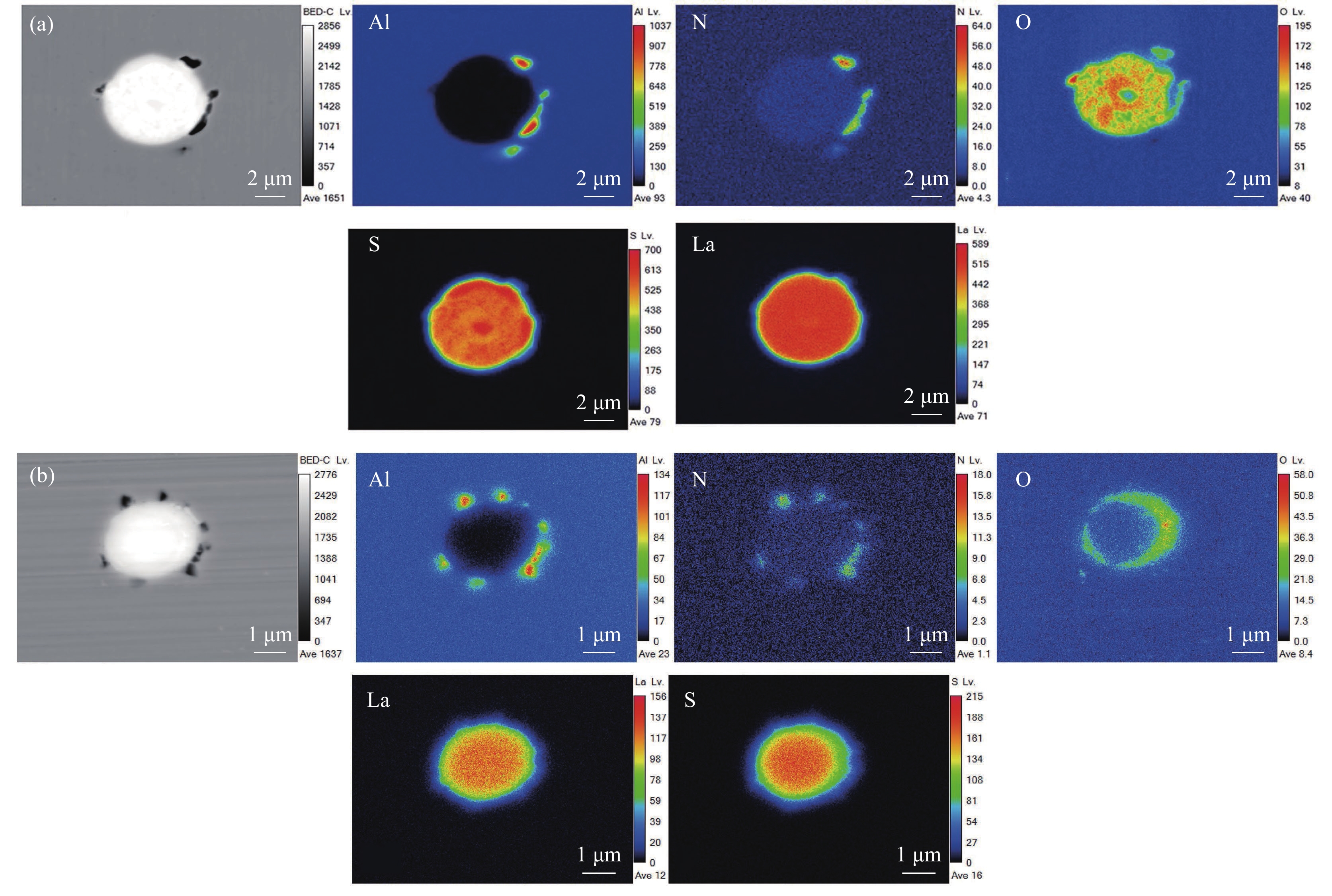
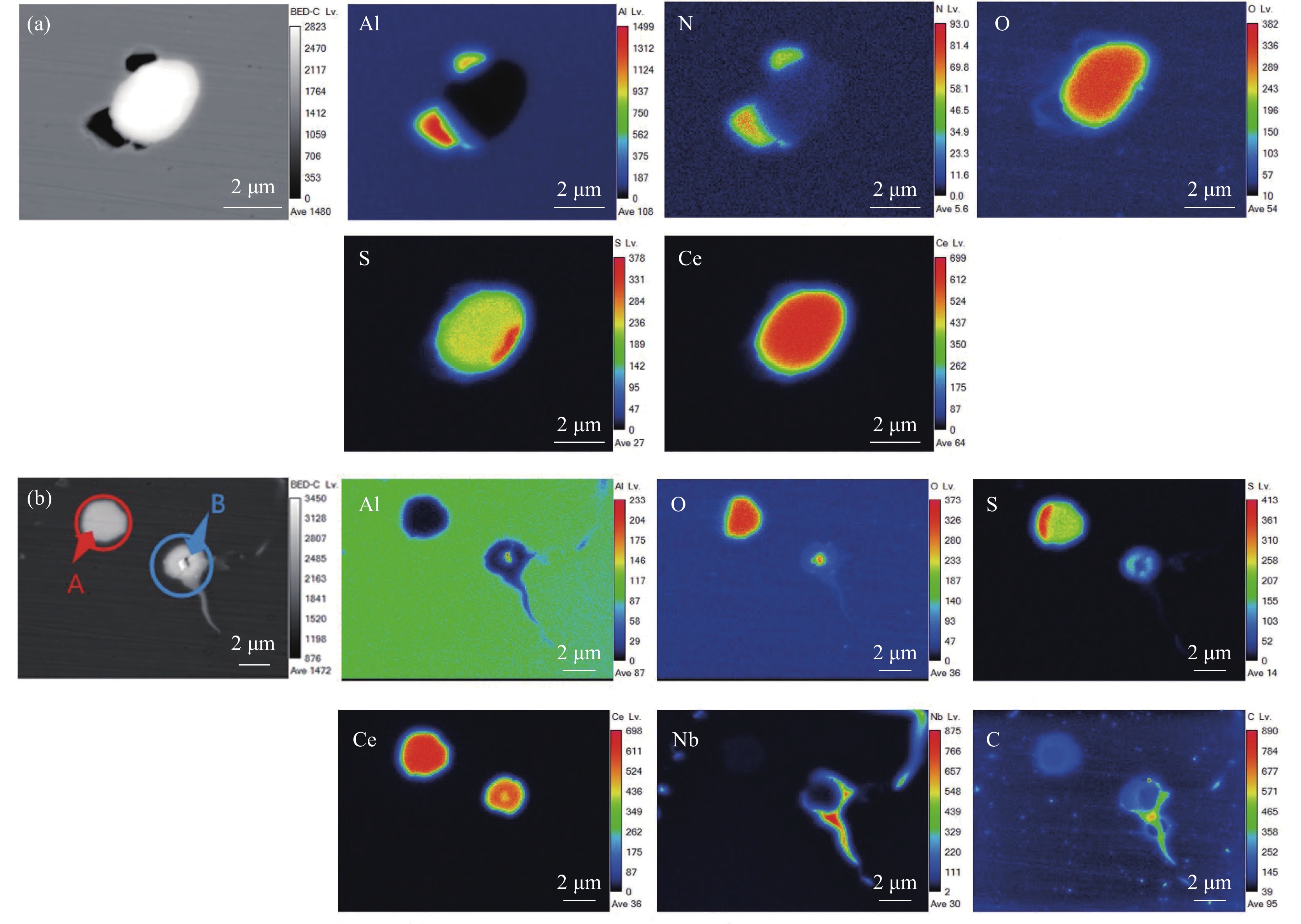
图2为加入稀土Ce的2#试验钢,可以看出其夹杂物主要包括三类。如图2(a)所示,第一类为Ce-O-S,并在边缘区域有不规则的AlN伴生;第二类为Ce-O-S相,如图2(b)中A区所示,组成近圆形的稀土夹杂物,未见其他元素参与其中;第三类夹杂物如图2(b)中B区所示,此类夹杂物由Ce-Al-O和少量的Ce-S化合物组成,并且Ce-Al-O在整个复合夹杂物的芯部位置,同时依附于Ce-S相表面形成乳白色Nb-C相,并向外延伸。与1#试验钢第一类和第二类夹杂比较可以看出,加入稀土后,钢中的AlN逐渐被稀土硫氧化物与AlN的复合夹杂所取代。
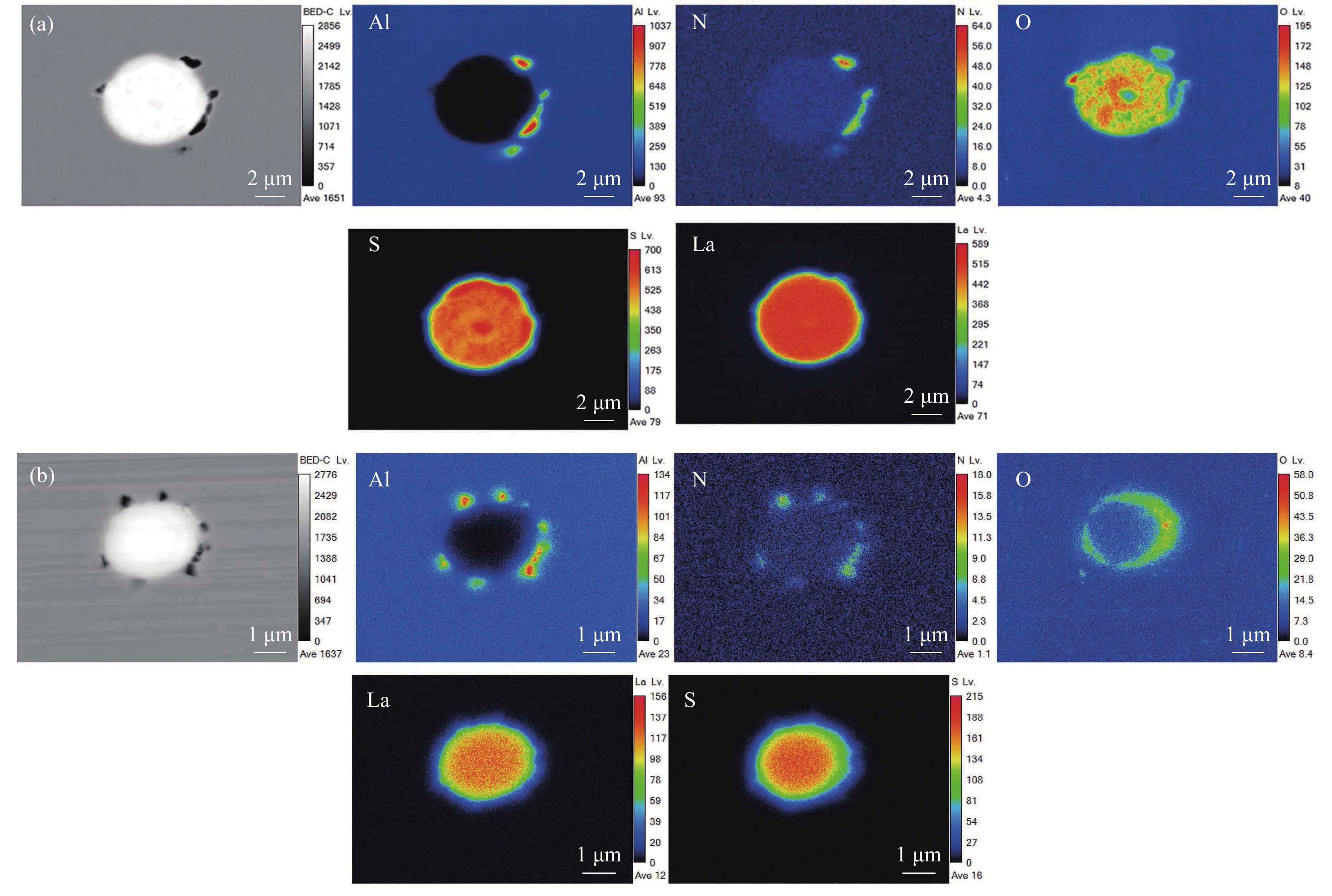
加入稀土La的3#试验钢中的夹杂物主要分为两类,如图3所示。第一类主体为La-O-S相,并有少量的Al2O3-AlN复合夹杂在表面伴生;第二类夹杂与2#试验钢中的第一类夹杂类似,由稀土氧硫化物为主体,在其附近富集Al-N相组成。两者区别在于稀土化物的组成,2#试验钢中O和S混合分布,而3#中的O-S分布有明显的界限。图3(b)的亮白色物质显示出其芯部及外部包裹区域由La-O-S组成,中间部分由La-S相组成,存在着明显的分层现象,并且在富氧周围有少量的Al元素富集。这可能是稀土元素改性了AlN,且由于稀土元素的富集导致La-Al-O再一次改性成为La-O-S。
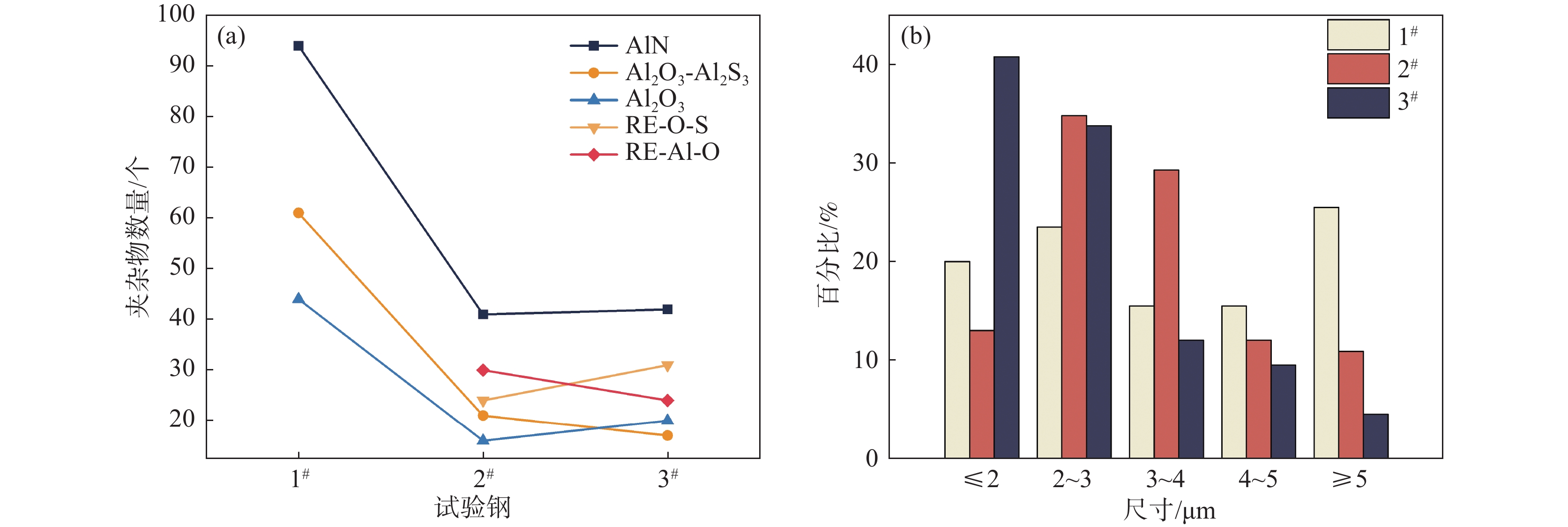
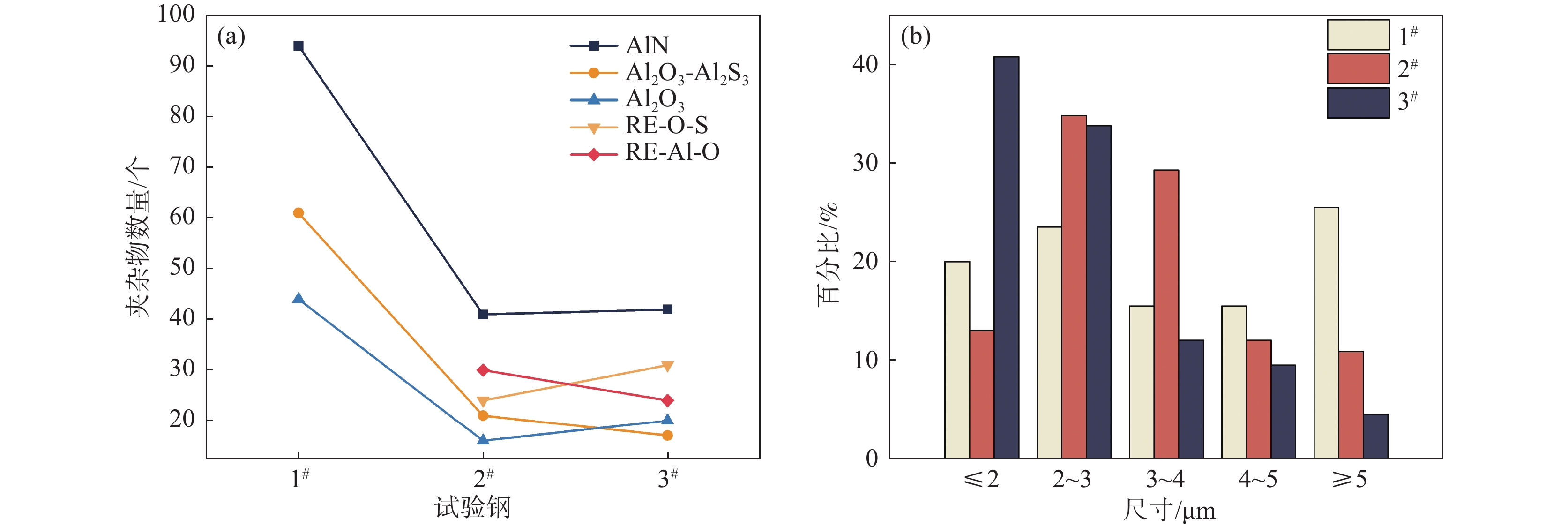
利用OTS全自动非金属夹杂物分析系统对3个试验钢中的夹杂物尺寸、数量和成分进行分析,每个试样统计面积为500 μm2,在检测到夹杂物后,将该夹杂物的长度方向的测量值记录为其尺寸。图4为OTS分布,主要存在AlN、Al2O3-Sulfide、Al2O3,其中AlN的数量最多,其次是Al2O3-Sulfide和Al2O3;与1#试验钢相比,2#、3#试验钢中AlN、Al2O3和Al2O3-Sulfide的数量明显减少,同时新增了含稀土的RE-O-S和RE-Al-O夹杂物,并且新增的稀土夹杂物与不含稀土的非金属夹杂物总体数量比较接近;尺寸统计结果表明,1#试验钢中夹杂物的平均尺寸为3.87 μm,其中大于5 μm的夹杂物占比达到25.5 %,这些尺寸的夹杂物在冲击载荷下萌生裂纹,并向外延展,导致韧性下降[14]。2#试验钢中夹杂物尺寸主要集中在2~4 μm范围内,其平均尺寸为3.22 μm,相较于1#减少了16.5 %。3#试验钢中的夹杂物的尺寸主要集中在1~3 μm,其平均尺寸为2.93 μm,相较于1#中夹杂物的尺寸减少了24%,较2#减少了9%。
通过上述分析可以看出,添加稀土后,钢中出现含稀土的夹杂物,使钢中原本不规则的非金属夹杂物变质为近球形的稀土夹杂物,此外夹杂物的尺寸和数量有明显的下降趋势,从而改善了钢的塑韧性。
3. 讨论
为了探索稀土加入后夹杂物的形成机理,利用化学等温方程计算了钢中夹杂物生成的吉布斯自由能[20]。
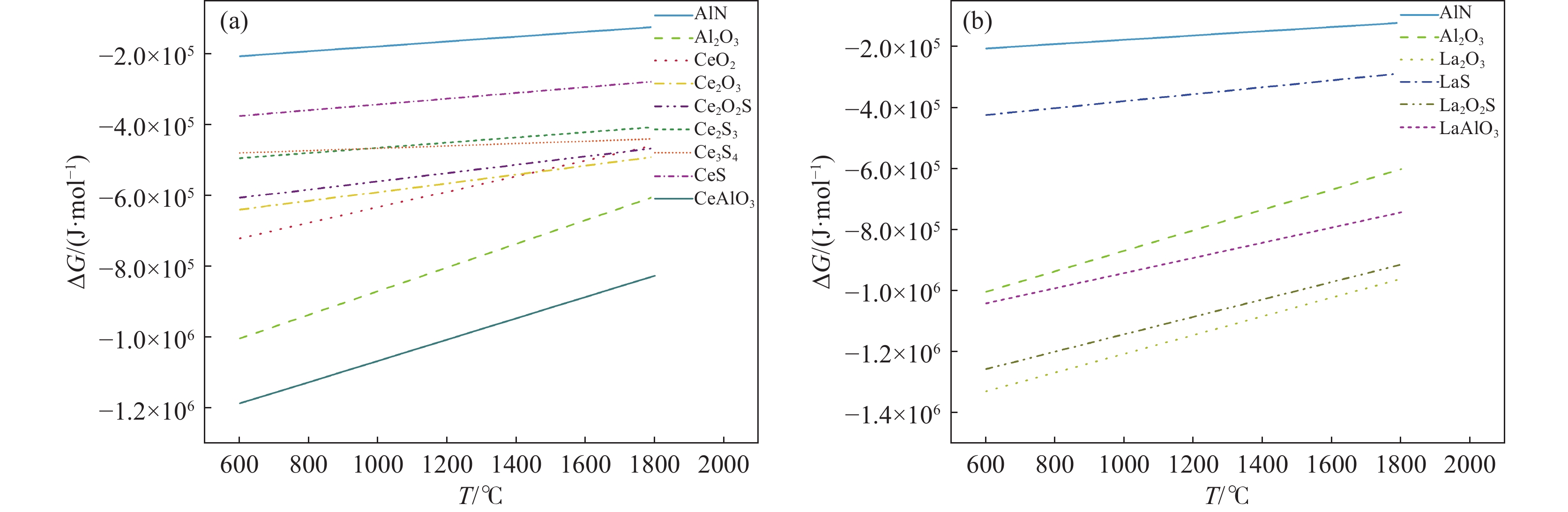
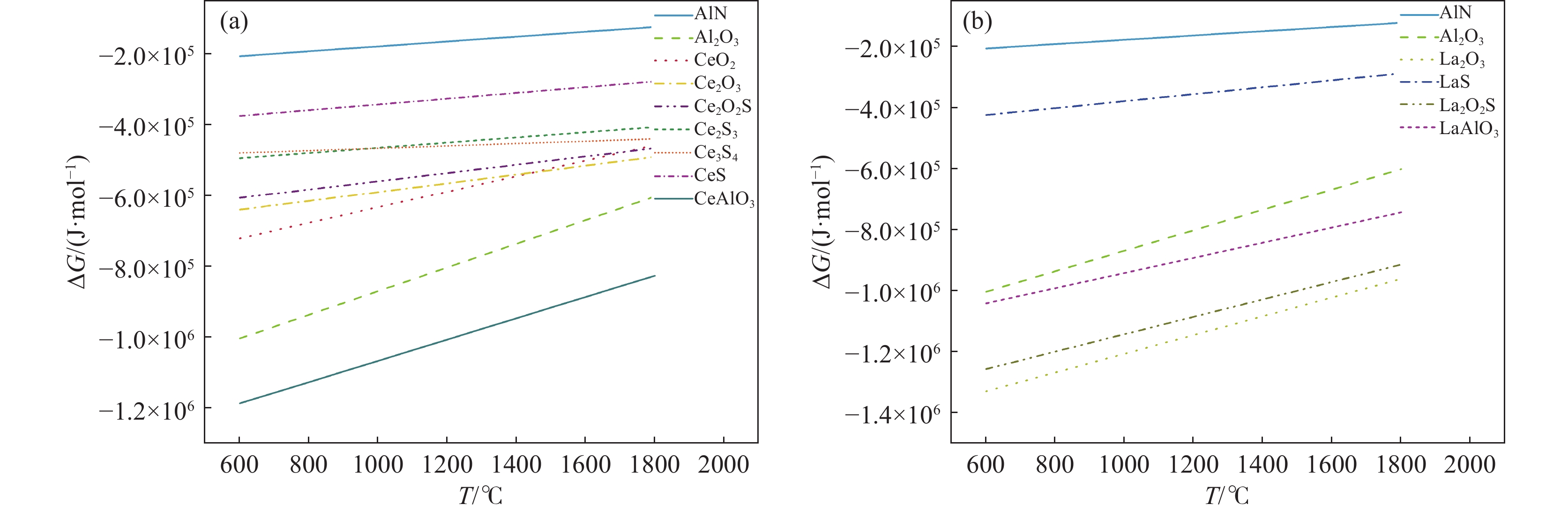
$$ {a}_{\mathrm{i}}={f}_{i}w\left(i\right) $$ (1) $$ \mathrm{l}\mathrm{g}{f}_{i}=\sum {e}_{i}^{j}w\left(j\right) $$ (2) $$ \Delta G=\Delta\mathrm{\mathit{G}}^{{\theta}}+\mathrm{\mathit{R}}T\mathrm{l}\mathrm{n}K $$ (3) 式中:$ {e}_{i}^{j} $为钢液组元j对i的组员相互作用系数,其数值见表2[21],根据表3钢液中化合物的生成的标准吉布斯自由能,绘制出各氧化物和硫化物的生成物吉布斯自由能随温度变化情况,如图5所示。从图5可以看出,在炼钢温度
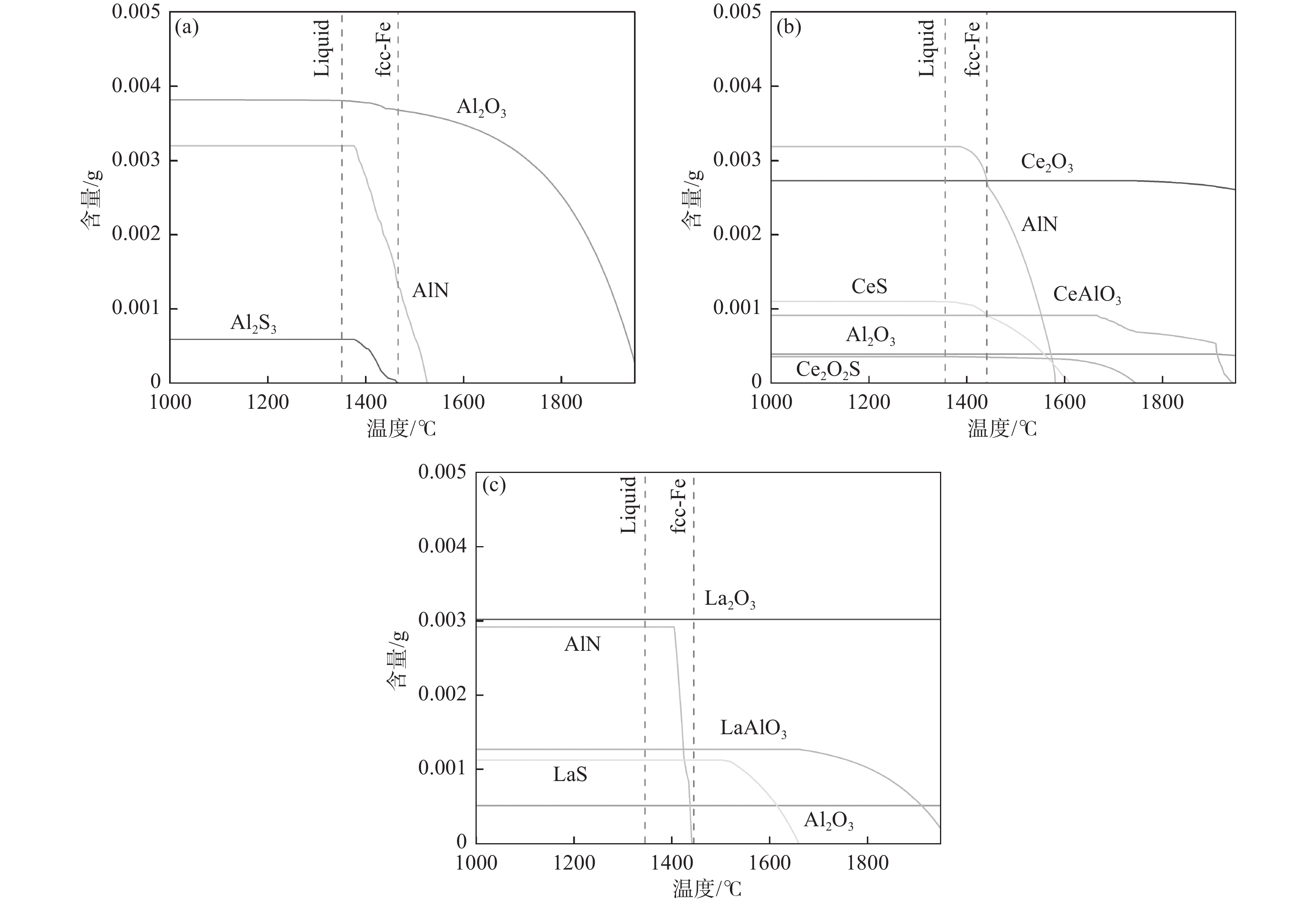
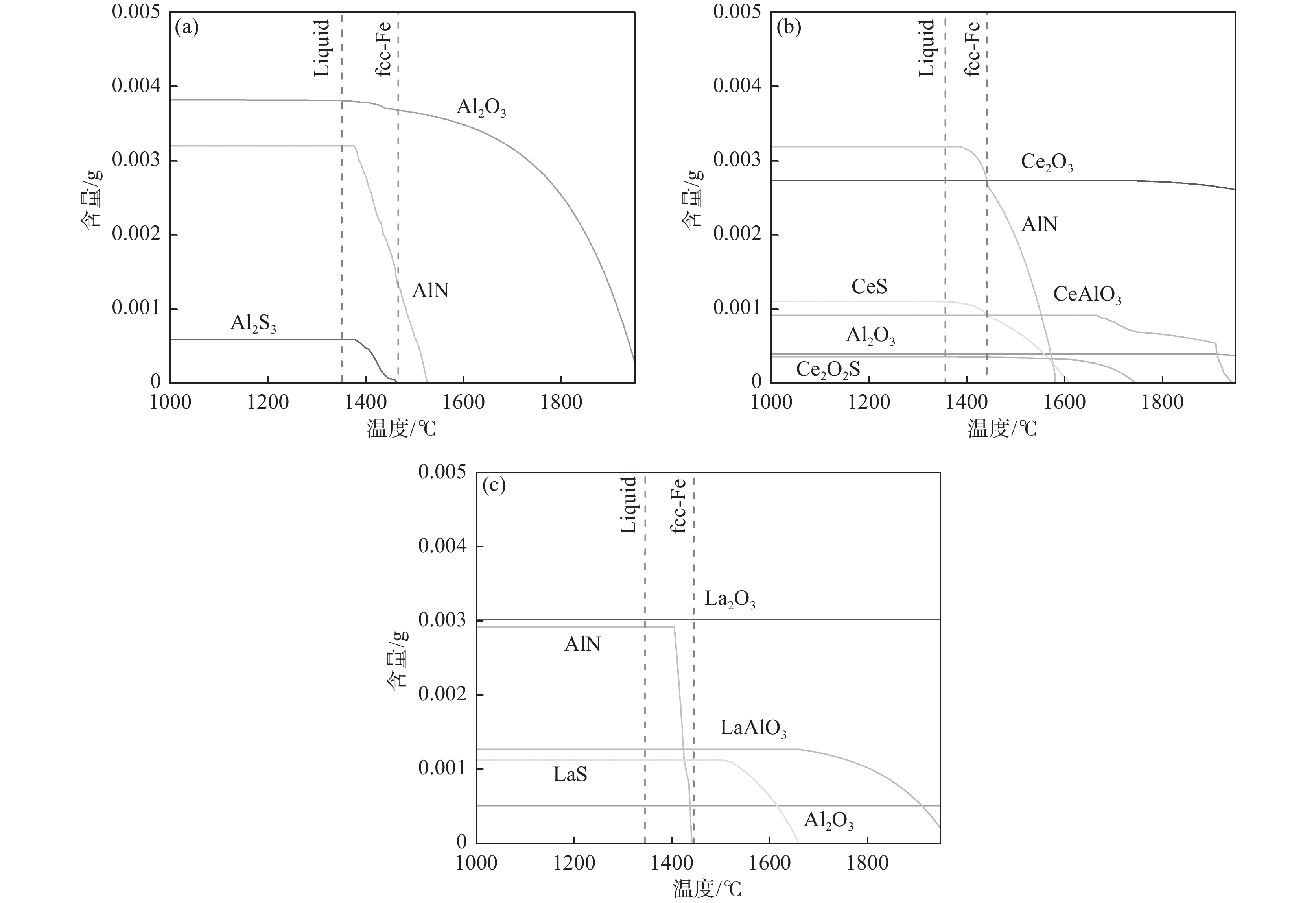
1650 ℃时,对于稀土La和Ce在钢液中生成物的热力学稳定顺序是不同的,在添加稀土Ce的钢液中能够优先生成CeAlO3,导致钢液中[O]含量减低,从而使独立存在的Al2O3形成概率降低。相比于Ce而言,添加稀土La后在钢液中优先形成稀土氧化物和稀土硫氧化物,从而降低钢中的[O]、[S]含量,减少钢中的非金属夹杂物的形成。宿成等人[20]的研究表明,稀土与[O]、[S]结合形成的稀土夹杂物与钢基体的硬度和热膨胀系数较为接近,使比表面积能降低,与钢基体组织结合力增强,稀土夹杂物与基体连续结合性增强,有利于改善钢的力学性能。值得注意的是,尽管通过钢液中化合物生成的吉布斯自由能能够初步判断钢液中化合物的形成趋势,但是稀土元素与[O]、[S]结合形成的氧、硫化物不仅受到平衡浓度的影响,还受到钢液中合金元素的浓度控制,因此,应在考虑凝固过程中成分和温度不断变化的条件下,进一步探索夹杂物的形成机理。表 21600 ℃时钢中各元素活度的相互作用系数Table 2. Interaction coefficients of the elements activities in steel at1600 ℃元素 作用系数 C Al O S N B Ni Ce La O −0.450 −3.900 −0.200 −0.133 −2.600 −2.600 0.006 −0.570 −0.570 S 0.110 0.035 −0.270 −0.028 0.010 0.130 0.000 −0.231 −0.231 Al 0.091 0.045 −6.600 0.030 −0.058 −0.043 −0.043 N 0.130 −0.028 0.050 0.007 0.000 0.094 Ce −0.077 −2.250 −5.030 −39.8 −6.599 La −4.980 根据表1中试验钢实测的元素组分含量,利用FactSage8.1热力学软件中的Equilib模块计算过程,在Cooling Calculation选项中选择Scheil-Guiliver cooling,鉴于软件中稀土硫氧化物热力学数据的缺失,笔者在软件优化库中补充了Ce2O2S热力学数据,在Equilib模块中选择FToxid、FTmisc、FSstel和优化数据库,计算结果如图6所示。从图6(a)可以看出,钢中的非金属夹杂物都是在高温熔融状态下就已经形成,并随着凝固温度的降低而逐渐增加,Al2O3在液相线左右达到最大值并趋于稳定,AlN在
1520 ℃左右开始析出,在1380 ℃左右达到最大值并趋于稳定。Al2S3在fcc-Fe形成后开始析出,由于Al2S3与Al2O3结构比较相似,所以两者易于以形成复合夹杂物的方式出现。进而形成图1(c)所示的第三类复合夹杂物。加入稀土元素Ce后,如图6(b)所示,Al2O3和Ce2O3在熔炼开始就已稳定存在,并且随着温度的降低由CeAlO3率先析出,并按照CeAlO3→Ce2O2S→CeS的顺序依次析出。AlN相较于未加入稀土元素的1#的析出温度有少许提高,但析出的最大值并没有太大的改变。加入稀土元素La之后,如图6(c)所示,与2#相似,在高温熔融状态下Al2O3与La2O3就已经稳定存在,且LaAlO3与LaS的析出顺序与添加稀土元素Ce的析出顺序相似。AlN的析出温度进一步降低,在fcc-Fe之后开始析出并在1400 ℃达到稳定。此外,综合图6可以看出稀土的添加对AlN夹杂物的析出应没有明显影响,对Al2O3的影响较大,且在加入稀土元素后使本就析出较少的Al2S3夹杂物析出更加微量,在热力学模拟中几乎看不见其存在的含量。不含稀土的马氏体时效钢中,主要包含AlN、Al2O3等夹杂物。AlN和Al2O3的热膨胀系数分别为4.5×10−6 ℃−1和18.1×10−6 ℃−1,与基体的热膨胀系数12.5×10−6 ℃−1相差较大,致使夹杂物与基体之间的结合性较差[24]。同时,试验也发现,不含稀土的马氏体时效钢中夹杂物形状呈长条或其他不规则形状,这会导致在变形过程中引起应力集中作用,导致微裂纹的萌生及成长,从而降低钢材的韧性。
Table 3. Standardized Gibbs free energies of inclusions in steel liquids化学方程式 ∆Gθ / (J·mol−1) [Al] + [N] = AlN(s) − 245900 + 107. 59T2[Al] + 3[O] = Al2O3(s) − 1203623 + 386.7T[Ce]+2[O]=CeO2(s) −852720 +249. 96T2[Ce]+3[O]= 2Ce2O3(s) − 714380 +179. 74T2[Ce]+2[O]+[S]=Ce2O2S(s) − 675700 +165. 5T2[Ce]+3[S]= Ce2S3(s) − 536420 +163. 86T3[Ce]+4[S]= Ce3S4(s) − 497670 +146. 3T[Ce]+[S]=CeS(s) − 422100 +120. 38T[Ce]+3[O]+[Al]=CeAlO3(s) − 1366460 +364. 3T2[La] + 3[O] = La2O3(s) − 1511520 + 379.2T2[La] + 2[O] + [S] = La2O2S(s) − 1425820 + 351.0T[La] + [S] = LaS(s) − 490000 + 171.0T[Al] +[La] + 3[O] = LaAlO3(s) − 1188616 + 310.6T加入稀土后,稀土优先与[O]、[Al]反应形成REAlO3,并在凝固过程中与[O]、[S]反应形成近球形的RE-O-S,所形成的RE2O2S的热膨胀系数为11.5×10−6 ℃−1,与基体的热膨胀系数相近,从而使夹杂物与基体之间的连续结合性增强[20,25]。此外,球形的稀土夹杂物附近在变形过程中减轻了应力的集中,从而明显减弱了裂纹的萌生。同时,由于形成Ce2S3和La2S3对钢液中[S]的消耗,使2#和3#试验钢中未能形成Al2S3。值得注意的是,稀土的加入不仅改性了夹杂物,也显著减少了夹杂物数量,这也为改善试验钢力学性能作出了贡献。
4. 结论
通过制备Fe-Ni-Al马氏体时效钢,利用试验和热力学计算方法研究稀土对马氏体时效钢夹杂物的影响。SEM-EDS、EPMA和OTS分析结果表明:
1)马氏体时效钢中加入稀土元素后,形成了含稀土的RE-O-S和RE-Al-O,抑制了Al2 S3的形成,对AlN夹杂物的形成没有明显影响,夹杂物经稀土改性后形状由条状和不规则的几何形状转变为接近球状。同时,添加稀土使试验钢中夹杂物数量和平均尺寸由1#的3.87 μm分别降低至2#的3.22 μm、3#的2.93 μm。
2)基于试验结果,借助FactSage热力学软件,增加Ce2O2S热力学数据后进行计算,结果表明,添加稀土元素后,钢液中可能形成的夹杂物热力学稳定性大致为REAlO3→Al2O3→稀土硫化物→AlN。在高温熔融态下钢液中RE2O3和Al2O3就已稳定存在,并且随着冷却温度的降低,钢中的夹杂物按REAlO3→RE2O2S→RES的顺序逐渐析出,稀土La和Ce的夹杂物演化路径基本相同。
-
表 1 试验钢化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of experimental steels
% 样本 C Ni Al Mo Nb B O N S La Ce Fe 1 # 0.039 19.157 2.342 3.886 0.657 0.017 0.0018 0.011 0.0033 Bal 2 # 0.049 19.735 2.338 3.133 0.646 0.016 0.0011 0.012 0.0021 0.019 Bal 3 # 0.046 19.109 2.641 3.262 0.675 0.018 0.0010 0.010 0.0020 0.018 Bal 表 2
1600 ℃时钢中各元素活度的相互作用系数Table 2. Interaction coefficients of the elements activities in steel at
1600 ℃元素 作用系数 C Al O S N B Ni Ce La O −0.450 −3.900 −0.200 −0.133 −2.600 −2.600 0.006 −0.570 −0.570 S 0.110 0.035 −0.270 −0.028 0.010 0.130 0.000 −0.231 −0.231 Al 0.091 0.045 −6.600 0.030 −0.058 −0.043 −0.043 N 0.130 −0.028 0.050 0.007 0.000 0.094 Ce −0.077 −2.250 −5.030 −39.8 −6.599 La −4.980 Table 3. Standardized Gibbs free energies of inclusions in steel liquids
化学方程式 ∆Gθ / (J·mol−1) [Al] + [N] = AlN(s) − 245900 + 107. 59T2[Al] + 3[O] = Al2O3(s) − 1203623 + 386.7T[Ce]+2[O]=CeO2(s) −852720 +249. 96T2[Ce]+3[O]= 2Ce2O3(s) − 714380 +179. 74T2[Ce]+2[O]+[S]=Ce2O2S(s) − 675700 +165. 5T2[Ce]+3[S]= Ce2S3(s) − 536420 +163. 86T3[Ce]+4[S]= Ce3S4(s) − 497670 +146. 3T[Ce]+[S]=CeS(s) − 422100 +120. 38T[Ce]+3[O]+[Al]=CeAlO3(s) − 1366460 +364. 3T2[La] + 3[O] = La2O3(s) − 1511520 + 379.2T2[La] + 2[O] + [S] = La2O2S(s) − 1425820 + 351.0T[La] + [S] = LaS(s) − 490000 + 171.0T[Al] +[La] + 3[O] = LaAlO3(s) − 1188616 + 310.6T -
[1] Gao Xueyun, Wang Haiyan, Li Jie, et al. Cerium-alloyed ultra-high strength maraging steel with good ductility: Experiments, first-principles calculations and phase-field simulations[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2022,846:143306. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2022.143306 [2] Feng Jiawei, Niu Mengchao, Wang Wei, et al. Relationship between mechanical behavior and microstructure for an ultra-high strengthmaraging steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2019,33(9):641. (冯家伟, 牛梦超, 王威, 等. 超高强度马氏体时效钢的力学行为与微观组织演化的关系[J]. 材料研究学报, 2019,33(9):641. doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2018.707Feng Jiawei, Niu Mengchao, Wang Wei, et al. Relationship between mechanical behavior and microstructure for an ultra-high strengthmaraging steel[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2019, 33(9): 641. doi: 10.11901/1005.3093.2018.707 [3] Pereloma E V, Shekhter A, Miller M K, et al. Ageing behaviour of an Fe–20Ni–1.8 Mn–1.6 Ti–0.59 Al (wt%) maraging alloy: clustering, precipitation and hardening[J]. Acta Materialia, 2004,52(19):5589. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2004.08.018 [4] Sha W, Malinov S. Titanium alloys: modelling of microstructure, properties and applications[M]. Elsevier, 2009. [5] Shin J H, Jeong J S, Lee J W. Microstructural evolution and the variation of tensile behavior after aging heat treatment of precipitation hardened martensitic steel[J]. Materials Characterization, 2015,99:230. doi: 10.1016/j.matchar.2014.11.024 [6] Pereloma E V, Stohr R A, Miller M K, et al. Observation of precipitation evolution in Fe-Ni-Mn-Ti-Al maraging steel by atom probe tomography[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2009,40:3069. doi: 10.1007/s11661-009-9993-z [7] Taillard R, Pineau A, Thomas B J. The precipitation of the intermetallic compound NiAl in Fe-19wt. % Cr alloys[J]. Materials Science and Engineering, 1982,54(2):209. doi: 10.1016/0025-5416(82)90115-X [8] Erlach S D, Leitner H, Bischof M, et al. Comparison of NiAl precipitation in a medium carbon secondary hardening steel and C-free PH13-8 maraging steel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2006,429(1-2):96. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2006.05.071 [9] Kürnsteiner P, Wilms M B, Weisheit A, et al. Massive nanoprecipitation in an Fe-19Ni-xAl maraging steel triggered by the intrinsic heat treatment during laser metal deposition[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017,129:52. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2017.02.069 [10] Watanabe K, Goto H, Itagaki M. Flow injection analysis of phosphorus in steel using filter tube preconcentration[J]. ISIJ International, 2003,43(11):1767. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.43.1767 [11] Wang X, Wu Z, Li B, et al. Inclusions modification by rare earth in steel and the resulting properties: A review[J]. Journal of Rare Earths, 2023,42(3):431-445. [12] Chen L, Ma X, Wang L. Effect of rare earth element yttrium addition on microstructures and properties of a 21Cr–11Ni austenitic heat-resistant stainless steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2011,32(4):2206. [13] Li Linlong, Yang Liqi, Xue Weihai, et al. Sliding friction and wear between rare earth modified GCR15 steel against cage materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2023,37(6):408. (李林龙, 杨丽琪, 薛伟海, 等. 稀土改性GCr15钢与保持架材料间的滑动摩擦磨损[J]. 材料研究学报, 2023,37(6):408.Li Linlong, Yang Liqi, Xue Weihai, et al. Sliding friction and wear between rare earth modified GCR15 steel against cage materials[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research, 2023, 37(6): 408. [14] Liu Chengjun, Jiang Maofa, Li Chunlong, et al. Mechanism and effect of rare earth on the impacting toughness of heavy rail steel[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2006(1):135. (刘承军, 姜茂发, 李春龙, 等. 稀土对重轨钢冲击韧度的影响作用机制[J]. 过程工程学报, 2006(1):135. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2006.01.031Liu Chengjun, Jiang Maofa, Li Chunlong, et al. Mechanism and effect of rare earth on the impacting toughness of heavy rail steel[J]. The Chinese Journal of Process Engineering, 2006(1): 135. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1009-606X.2006.01.031 [15] Zhang Xiaofeng, Tang Jianping, Han Chunpeng, et al. Analysis on the role of rare earth in steel and the present situation of industrial production[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2021,42(4):117. (张晓峰, 唐建平, 韩春鹏, 等. 稀土在钢中作用及工业化生产现状浅析[J]. 稀土, 2021,42(4):117.Zhang Xiaofeng, Tang Jianping, Han Chunpeng, et al. Analysis on the role of rare earth in steel and the present situation of industrial production[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2021, 42(4): 117. [16] Wang Y, Li C R, Wang L Z, et al. Effect of yttrium treatment on alumina inclusions in high carbon steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research International, 2022,29(4):1. [17] Chu R S, Mu S K, Liu J, et al. The influence of high heat input and inclusions control for rare earth on welding in low alloy high strength steel[J]. IOP Conference Materials Science and Engineering Series, 2017, 242(1): 012065. [18] Liu H L, Liu C J, Jiang M F, et al. Effect of rare earths on impact toughness of a low-carbon steel[J]. Materials & Design, 2012,33:306. [19] Gao Jianbing, Chang Pengfei, Zhang Binbin, et al. Effect of Ce on inclusion modification in a new type super duplex stainless steel 2707HD[J]. Iron and Steel, 2018,53(9):37. (高建兵, 常朋飞, 张彬彬, 等. 铈对新型超级双相不锈钢2707HD夹杂物变性的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2018,53(9):37.Gao Jianbing, Chang Pengfei, Zhang Binbin, et al. Effect of Ce on inclusion modification in a new type super duplex stainless steel 2707HD[J]. Iron and Steel, 2018, 53(9): 37. [20] Su Cheng, Feng Guanghong, Zhi Jianguo, et al. Effect of rare earth on low temperature impact toughness of NM400 wear-resistant steel plate[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel, 2021,33(12):1289. (宿成, 冯光宏, 智建国, 等. 稀土对耐磨板NM400低温冲击韧性的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2021,33(12):1289.Su Cheng, Feng Guanghong, Zhi Jianguo, et al. Effect of rare earth on low temperature impact toughness of NM400 wear-resistant steel plate[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel, 2021, 33(12): 1289. [21] Lü Yong, Peng Jun, Cai Changkun, et al. Rare earth Ce on thermodynamics of titanium containing inclusions in steel and its experimental research[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(3):93. (吕勇, 彭军, 蔡长焜, 等. 稀土铈对钢中含钛夹杂物析出行为的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(3):93. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.03.017Lü Yong, Peng Jun, Cai Changkun, et al. Rare earth Ce on thermodynamics of titanium containing inclusions in steel and its experimental research[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019, 40(3): 93. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.03.017 [22] Li Wenchao. Thermodynamic of rare earth inclusions generation in steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 1986(3):7. (李文超. 钢中稀土夹杂物生成的热力学规律[J]. 钢铁, 1986(3):7.Li Wenchao. Thermodynamic of rare earth inclusions generation in steel[J]. Iron and Steel, 1986(3): 7. [23] Wang H P, Yu P, Jiang S L, et al. Evolution of inclusions in steelmaking process of rare earth steels containing arsenic with alumina crucibles[J]. Metals, 2020,10(2):275. doi: 10.3390/met10020275 [24] Liu X, Yang J C. Effect of Ce on inclusions and impact property of 2Cr13 stainless steel[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 2010,17(12):59. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(10)60198-7 [25] Champi A, Marques F C. Thermal expansion coefficient, mechanical and structural properties of hydrogenated carbon nitrides[J]. Diamond and Related Materials, 2012,25:124. doi: 10.1016/j.diamond.2012.02.021 -





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载: