Review on the flow pattern of molten steel in the submerged entry nozzle and the mold of continuous casting slabs
-
摘要: 通过系统分析连铸水口及结晶器内钢液流态的研究现状,深入探讨了不同工况条件下流态的转变规律、共性特征、影响因素及其对铸坯质量的影响,并着重分析了结晶器流动的非对称性。认为:①水口内存在气泡流、膜状流、环状流和段塞流等多种流态,流态受液体流量、气体流量和中间包液位影响。其中,气泡流相对稳定,有利于连铸生产。②当板坯结晶器处于对称的双辊流状态,且液面流速控制在0.26~0.43 m/s时,有助于显著提高铸坯质量;同时,较高的拉速、较低的氩气流量以及增大的水口浸入深度有助于形成双辊流。③流动非对称性会引发偏流,通过精准的工艺操作可保障生产顺行并提高铸坯质量。Abstract: Through a systematic analysis of the current researches on flow patterns in the nozzle and mold, this study explores the transformation laws, common characteristics, influencing factors, and their effects on slab quality under various operating conditions, with a particular focus on the asymmetry of flow in the mold. The conclusions are as follows: multiple flow patterns, including bubbly flow, film flow, annular flow, and slug flow, exist within the nozzle and are influenced by liquid flow rate, gas flow rate, and the level of liquid in the tundish. Bubbly flow is relatively stable and beneficial for continuous casting production. When the slab mold operates in a symmetric double-roll flow pattern and the mold surface flow velocity is controlled between 0.26 and 0.43 m/s, it significantly improves the quality of the cast slabs. Meanwhile, a higher casting speed, a lower argon flow rate, and an increased immersion depth of the nozzle have benefit for the formation of the double-roll flow pattern. Flow asymmetry can lead to bias flow. Thus, precise process control can ensure smooth production and enhance slab quality.
-
Key words:
- slab continuous casting /
- mold /
- submerged entry nozzle /
- flow patterns /
- asymmetric flow
-
0. 引言
在双碳背景下,超低排放、高拉速已成为高效连铸技术面临的重要挑战[1−2],并成为促进我国钢铁行业可持续发展的重要途径。在板坯连铸过程中,结晶器内钢液的流动形态(流态)对连铸坯质量的影响重大[3−4],其中,涉及到的物理现象非常复杂,如氩气泡和夹杂物的运动、液面的瞬态波动、卷渣行为、弯月面过冷以及流股对坯壳的冲刷等。这些现象不仅会直接影响连铸坯的质量,还会影响到连铸的生产效率,尤其是高拉速条件下,会加重上述物理现象对铸坯质量的影响[5−7]。此外,浸入式水口(简称水口)常吹入氩气来防止堵塞[8],因氩气会改变水口内的流态[9],进而显著影响侧孔流股的状态以及结晶器内的流态。因此,水口和结晶器内流态的优化和控制至关重要。
在对水口及结晶器内流态进行深入研究和优化时,需要从多个角度分析,包括流态特征、影响因素对铸坯质量的影响,以及结晶器内流动的非对称性等,以提升铸坯质量及生产效率。然而,近年来大多数研究集中于特定工况下水口及结晶器内的流态特征,而对于不同工况条件下的流态转变及其共性现象,尤其是在吹气条件下的研究相对匮乏。为此,笔者系统分析并总结了水口及结晶器内流态的研究现状,明确了不同工况条件下的流态转变规律、共性现象、影响因素及其对铸坯质量的影响,旨在为连铸工艺优化提供理论依据和参考,以实现无缺陷连铸坯高效生产,并推动连铸工艺向绿色低碳方向进一步发展。
1. 浸入式水口内的流态
1.1 水口内的流态及特征
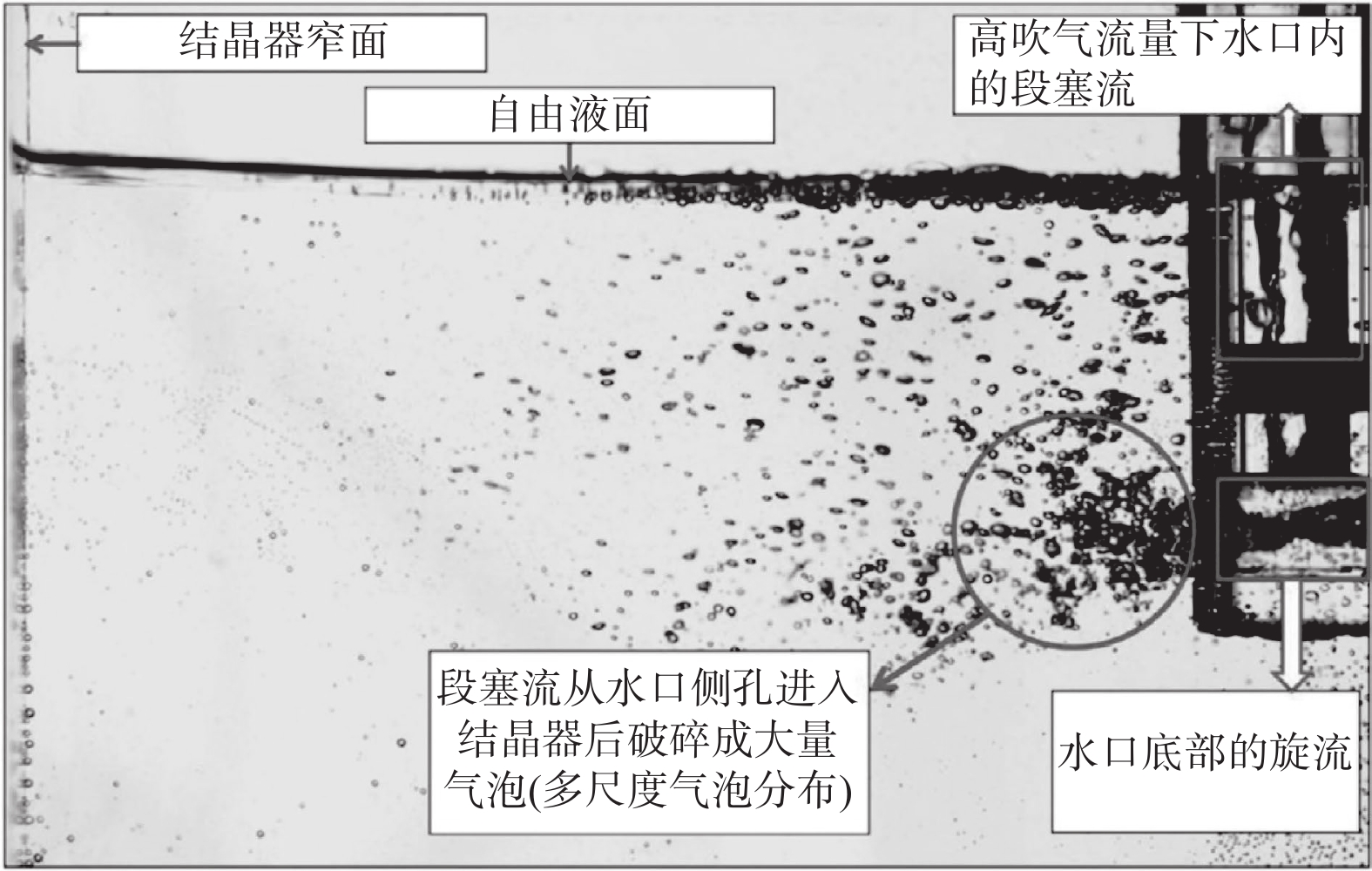
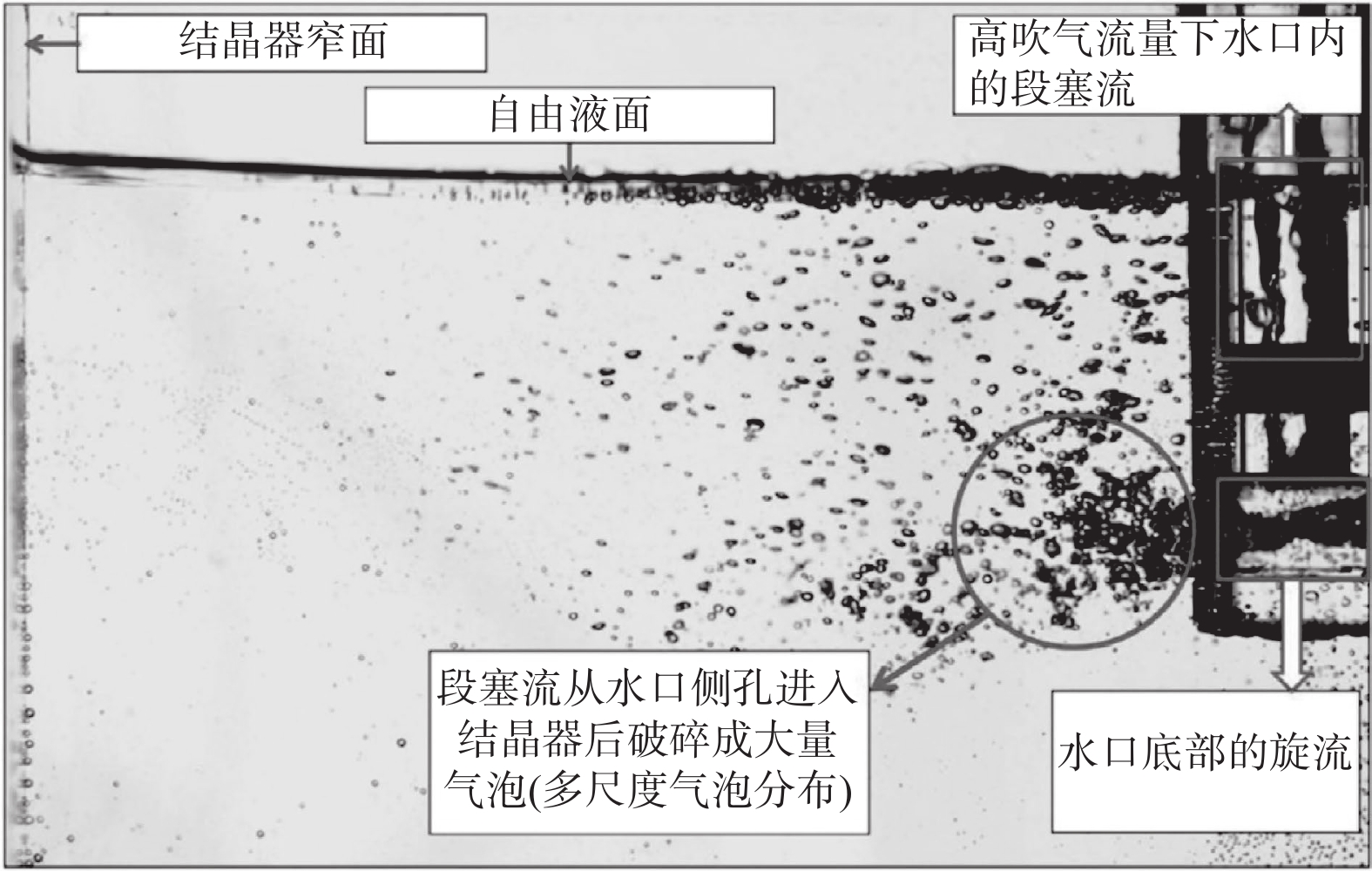
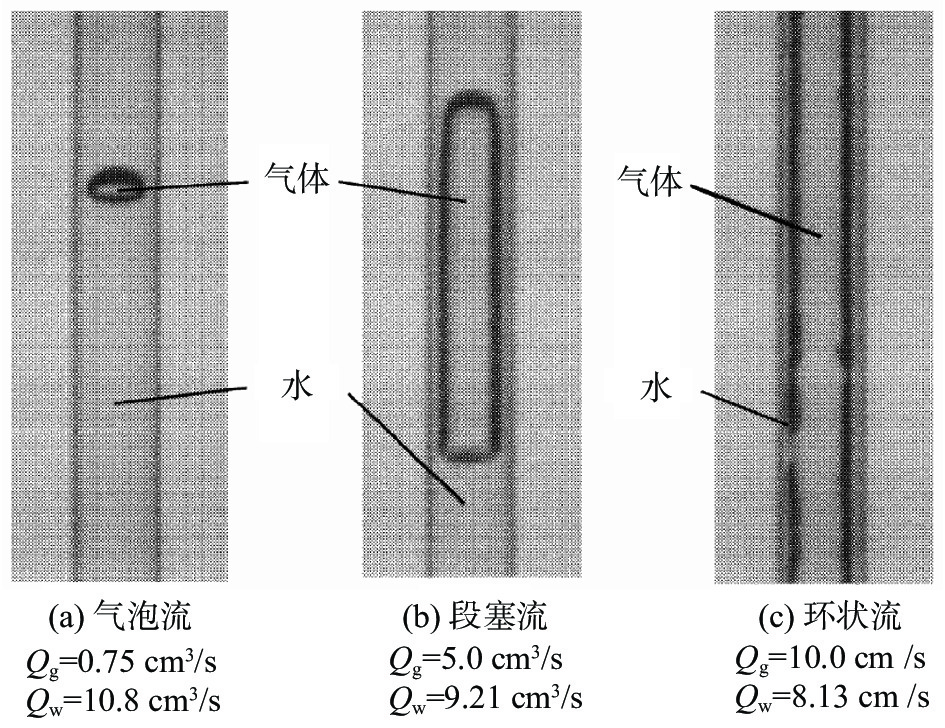
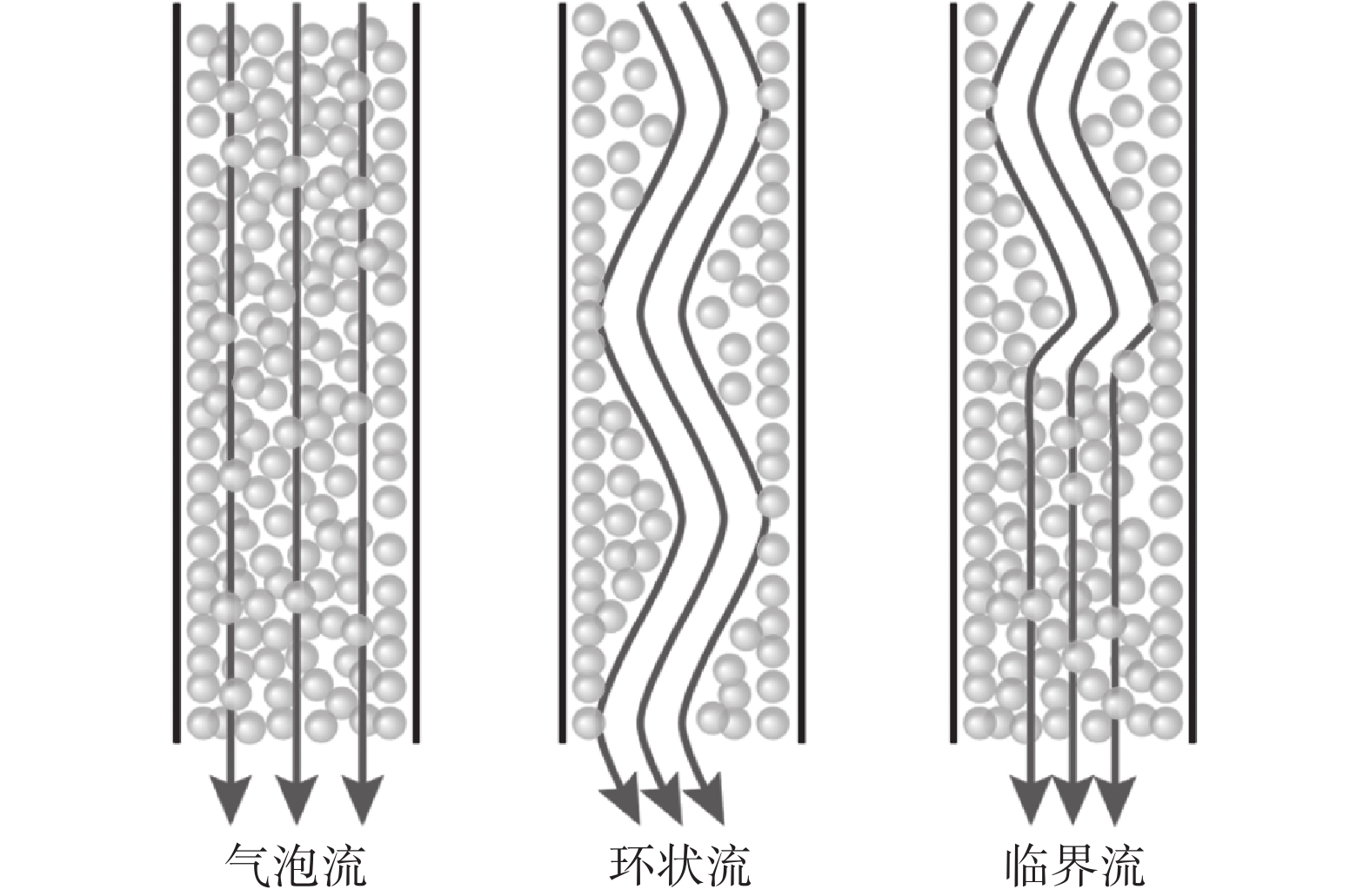
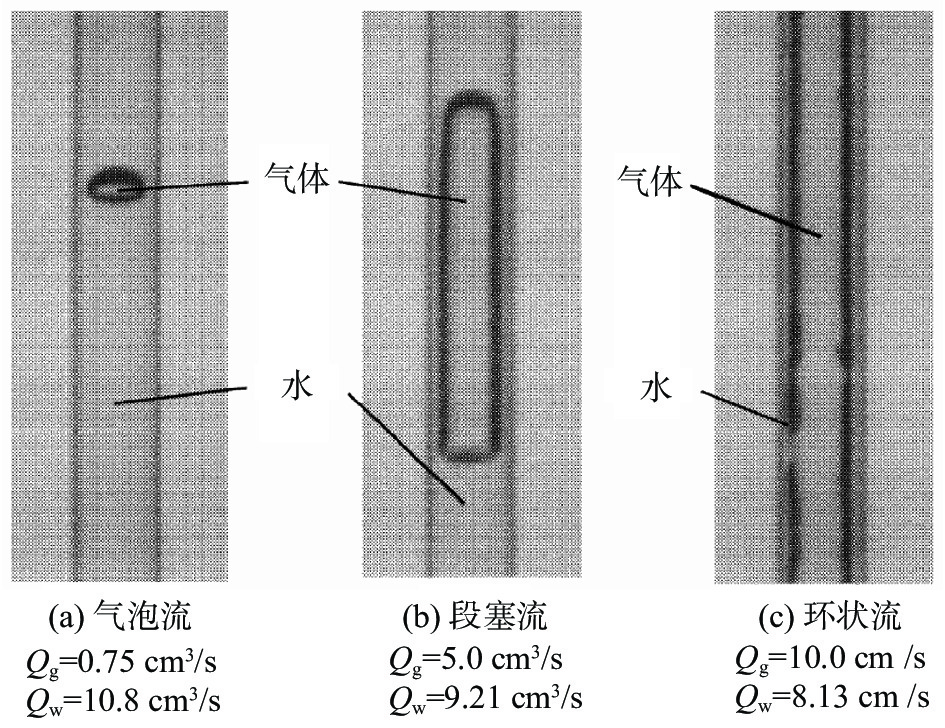
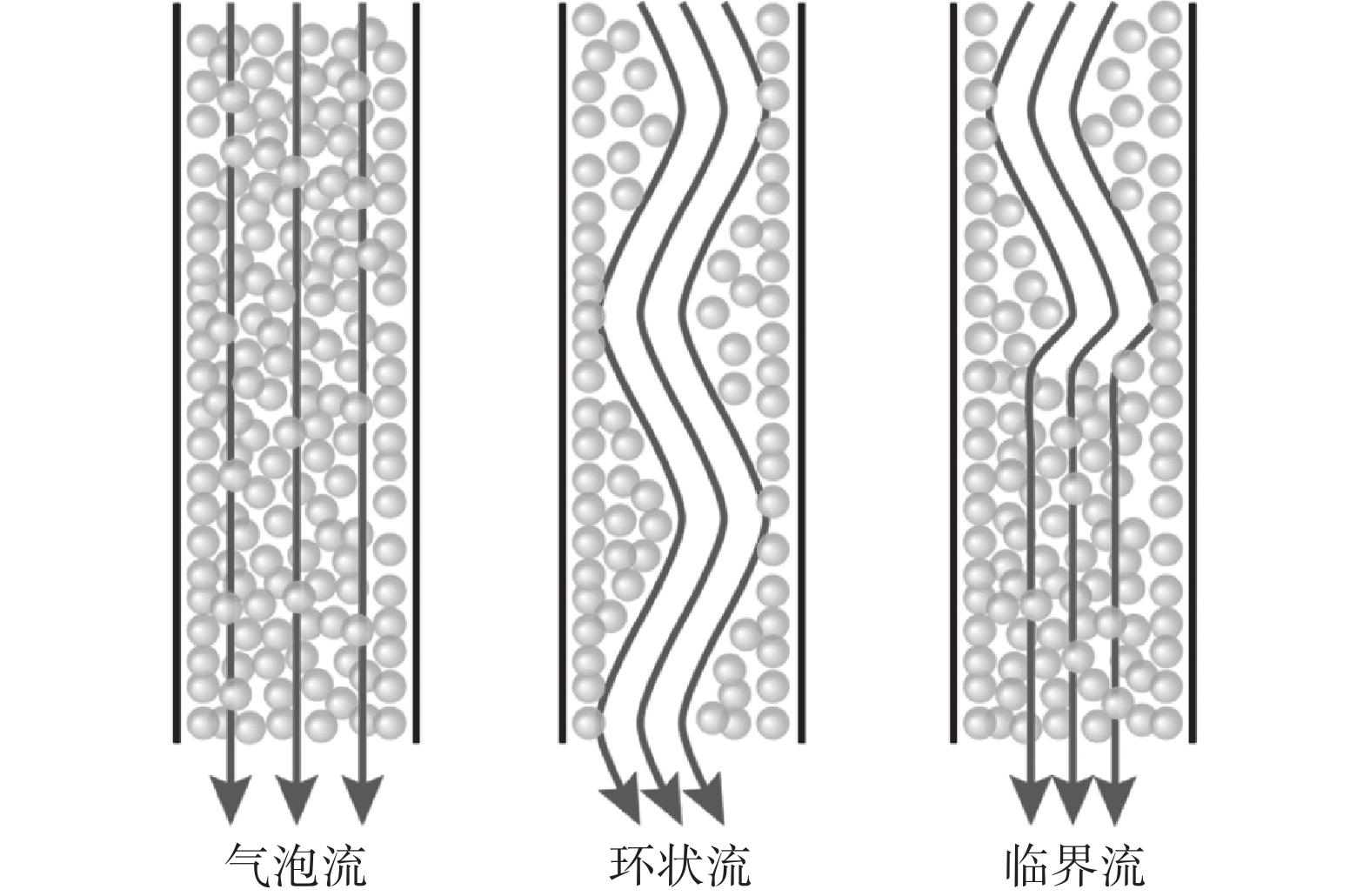
为了减缓或避免水口堵塞,通常会在水口内吹入氩气。然而,气体流量的大小会影响水口内的流态,从而也会进一步影响结晶器内的流动稳定性。因此,确保水口内流态合理非常重要。诸多学者通过物理模拟研究了吹气条件下水口内的流态,发现水口内存在的流态主要有气泡流、膜态流、环状流、段塞流或临界流等[9-13]。Zhang等人[9]通过建立0.6比例的物理模型研究了吹气条件下浸入式水口内钢液的流动行为。结果表明,水口内主要存在三种流态,分别是气泡流、环状流以及临界流,如图1所示。Liu等人[10]通过建立1/4比例的物理模型研究了气体在水口以及结晶器内的行为和分布。结果表明,在气体流量较大的情况下,水口内会出现明显的段塞流。当段塞流从水口侧孔进入结晶器后,会破碎成大量的气泡,如图2所示。因此,这会加剧结晶器内流动的不稳定性。
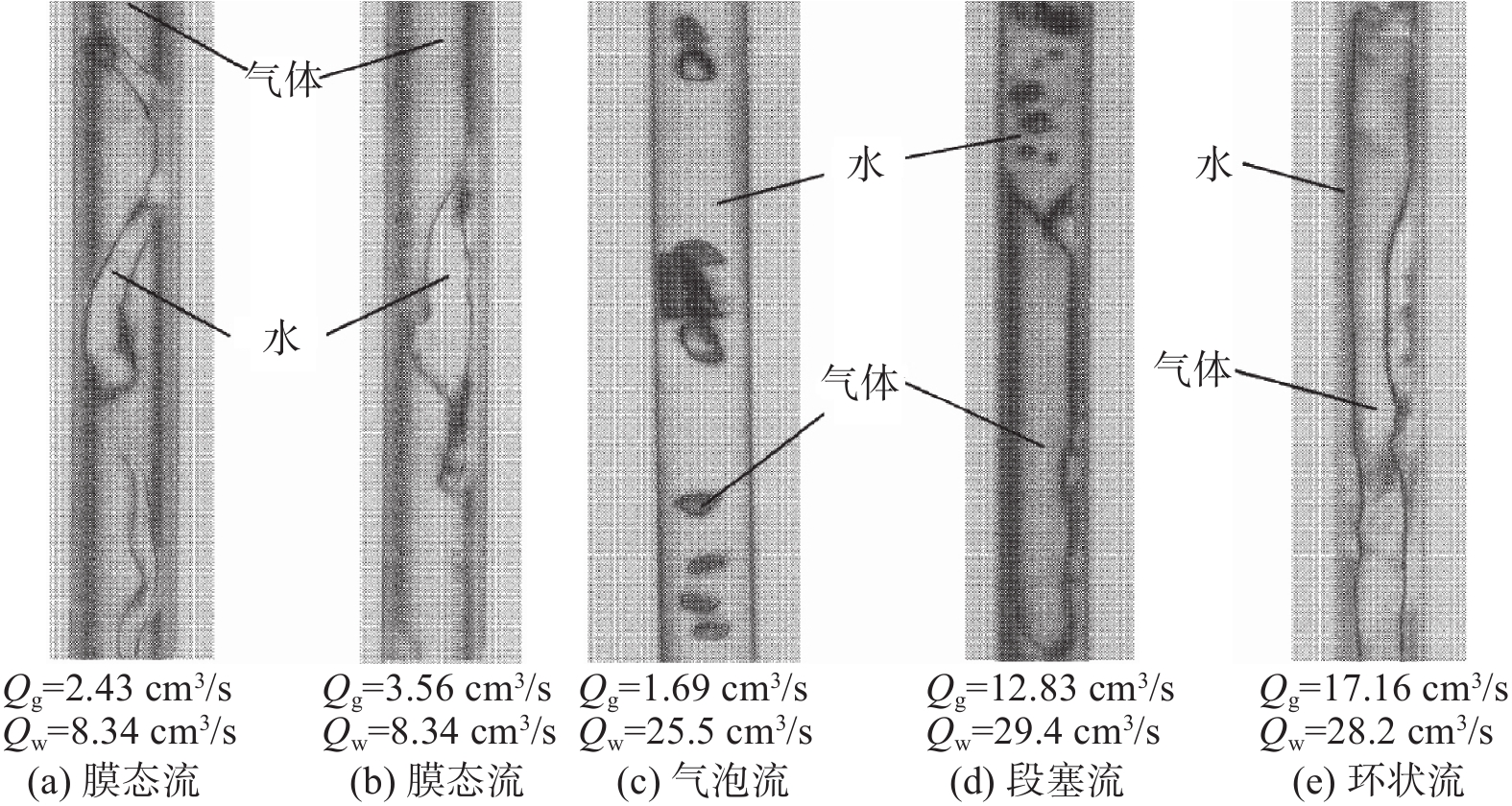
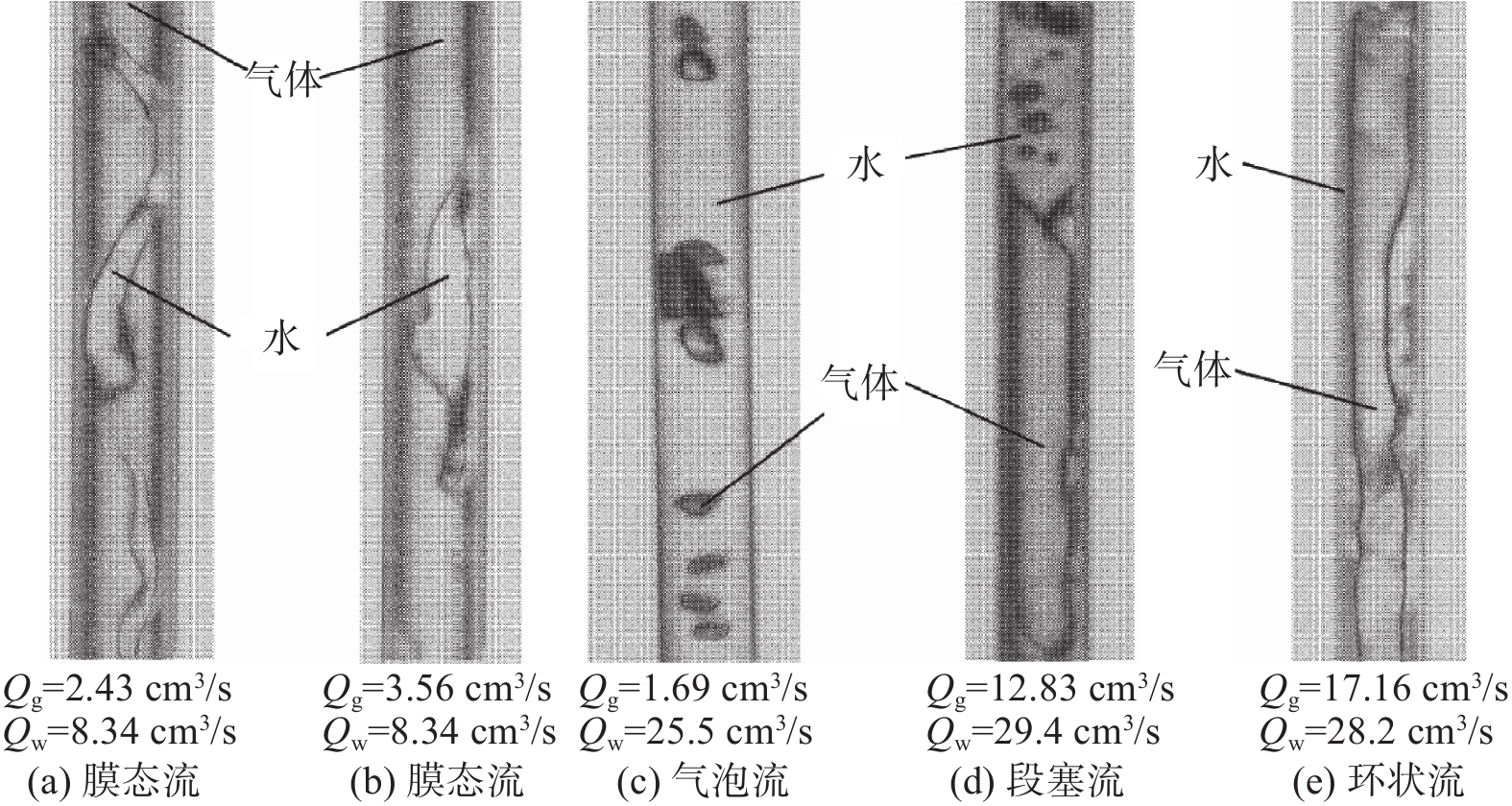
Ishiguro等人[11]通过建立物理模型研究了气体在水口内不同润湿条件下的行为以及流态。结果表明,当润湿条件较好时(润湿角θw=77°),水口内主要存在三种流态,分别为气泡流、段塞流以及环状流,如图3所示;当润湿条件较差时(润湿角θw=104°),水口内主要存在四种流态,分别为膜态流、气泡流、段塞流以及环状流,如图4所示。
Zhang等人[9]系统研究了水口内气泡流、环状流以及临界流的流态特征,结果表明,气泡流中水、气两相充分混合,结晶器内流动均匀,流股对窄侧的冲击较弱;而在环状流中,钢液呈螺旋状进入水口,并沿水口内壁竖直向下流动,同时气、液分离。虽然钢液的能量损失较小,但对结晶器窄侧的冲击较大。水口内的临界流呈现为气泡流和环状流的复合状态,流态不稳定,既可能突然转变为环状流,也可能突然转变为气泡流,影响生产稳定性。
段塞流在湍流作用下会破碎成大量多尺度气泡进入结晶器[10],这也是一种亚稳定流态。膜态流则指气体倾向于贴近水口内壁,液体沿水口内壁向下流动的流态[11]。当液体的润湿性较差时,膜态流更容易形成。因此,在吹气条件下,水口内形成稳定的气泡流更有利于连铸生产。
1.2 水口内流态转变规律
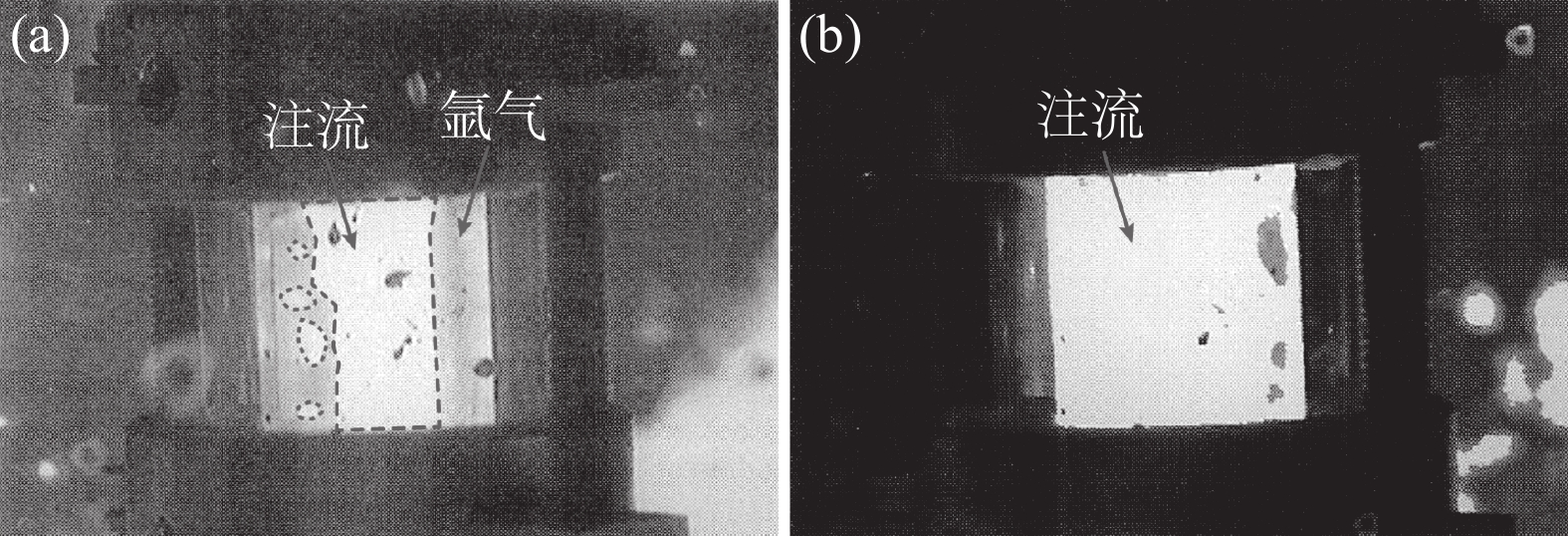
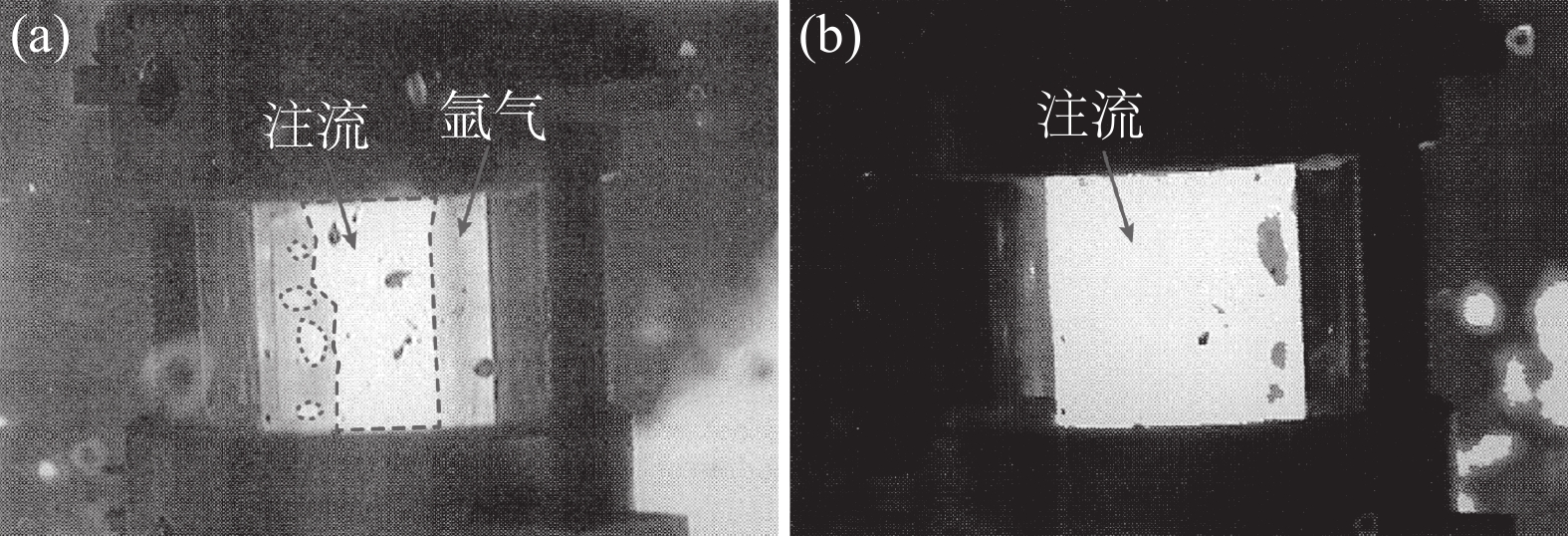
Ishiguro等人[11]的研究结果表明,水口内流态的转变、形成与气/液流量比有关,该比值越大,越倾向形成段塞流或环状流,这与Terauchi等人[12]的研究结果相近。此外,还受到水口的压力与材质的润湿性影响。Zhang等人[9]表明,水口内的流态取决于气/液流量比与水口压力,而水口压力与中间包液位有关。Burty等人[13]通过中试试验证实了上述结果,如图5所示。其中图5(a)为高氩气流量水口内的流态,可见水口内的注流被气体环绕,呈现出典型的环状流;图5(b)为低氩气流量水口内的流态,可见水口内的气泡均匀地分布于注流中,呈现出典型的气泡流。
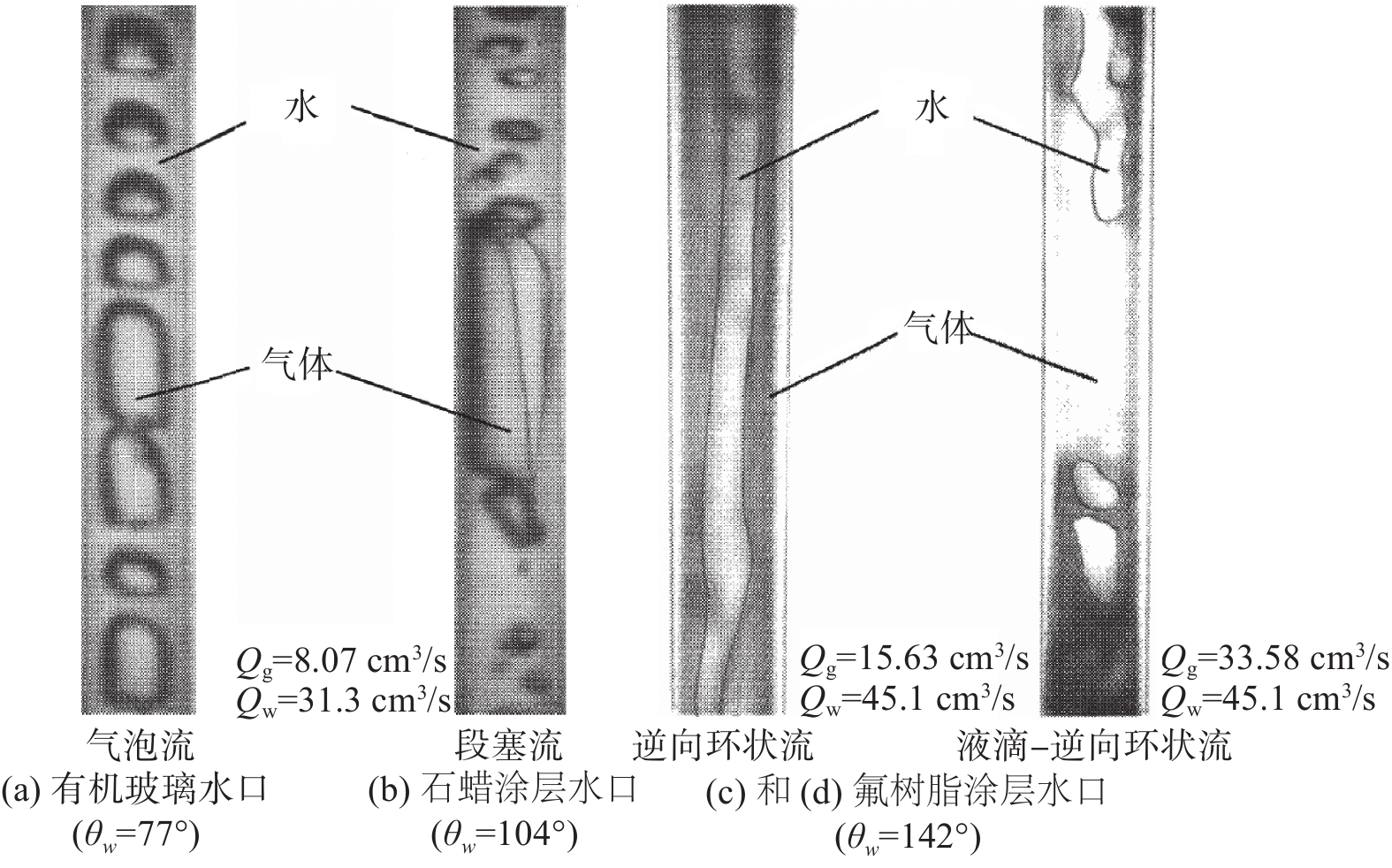
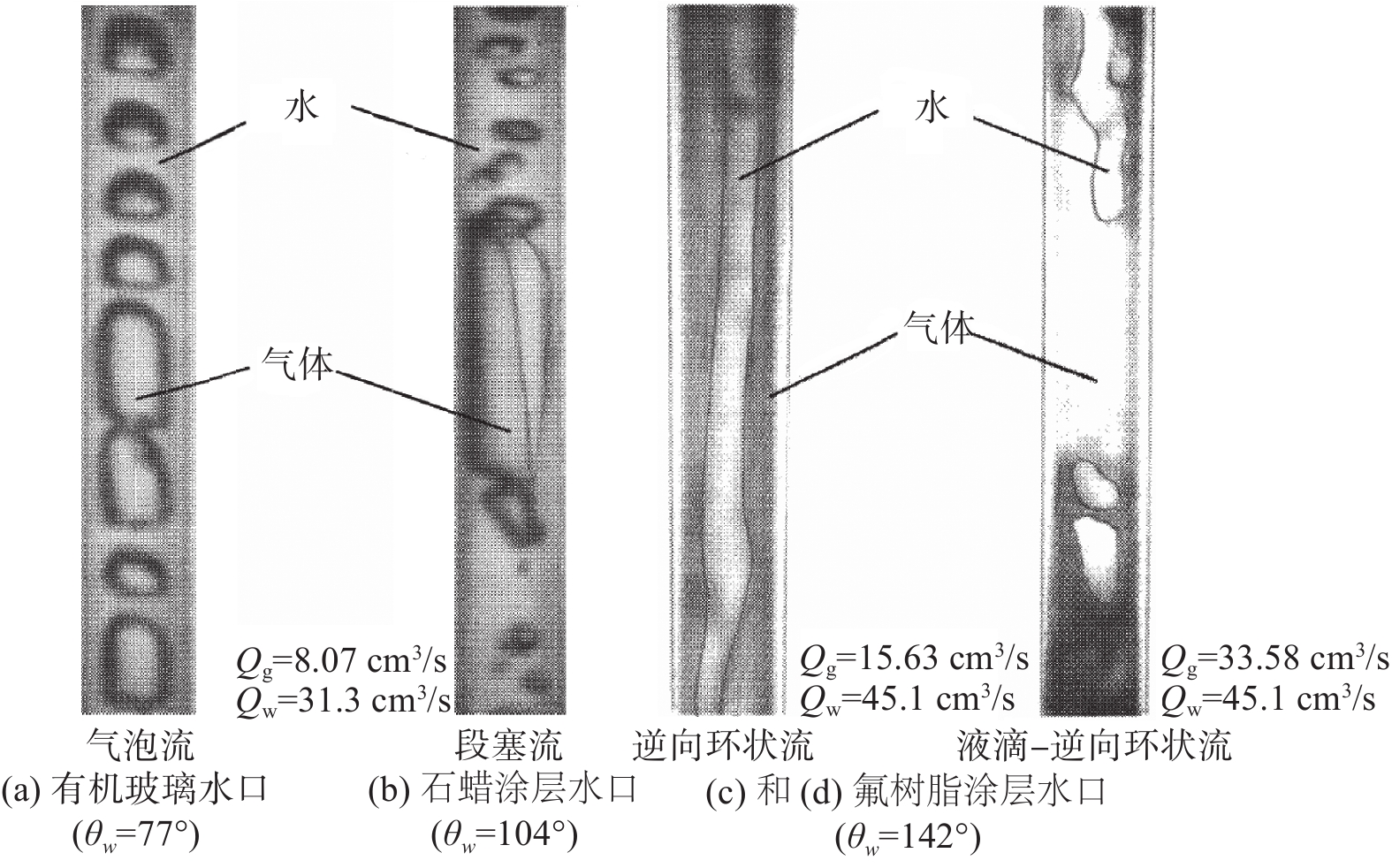
图6(a)~(b)对比了有机玻璃水口(Acrylic pipe)和石蜡涂层水口(Paraffin-coated pipe)在相同气/液流量比条件下的流态。结果表明,有机玻璃水口的润湿性较好,在水口内形成了气泡流,而石蜡涂层水口的润湿性略差,在水口内形成了段塞流,即较好的润湿条件会促进水口内气泡流的形成;图6(c)~(d)对比了不同气/液流量比条件下润湿性较差的氟树脂涂层水口(Fluororesin-coated pipe)内的流态。结果表明,当气/液流量比较小时,气体贴近水口内壁向下流动,因此液体在水口中心附近形成了连续的逆向环状流;然而随着气/液流量比增大,更多的气体涌入水口,不仅贴近内壁流动,而且阻断了液体连续的环状流动,最终使之变为逆向断续的大尺寸液滴-逆向环状流。
因此,在吹气条件下,当水口结构一定时,其流态由液体流量、气体流量以及中间包液位共同决定。当拉速恒定时,存在一个临界气体流量来维持气泡流。如果气体流量超过该临界值,水口内的流态将转变为段塞流或环状流。此外,增大水口侧孔尺寸会减小流动瞬变的阻力[9],使侧孔顶部出现低速区,这些区域易受气泡行为影响,并促进不稳定临界流的形成,进而加剧结晶器内流动的不对称。因此,合理控制吹气量和水口侧孔尺寸对于流态控制至关重要,而临界流态的形成则是大尺寸侧孔水口的典型流动特征。
2. 板坯结晶器内的流态
2.1 结晶器内的流态及特征
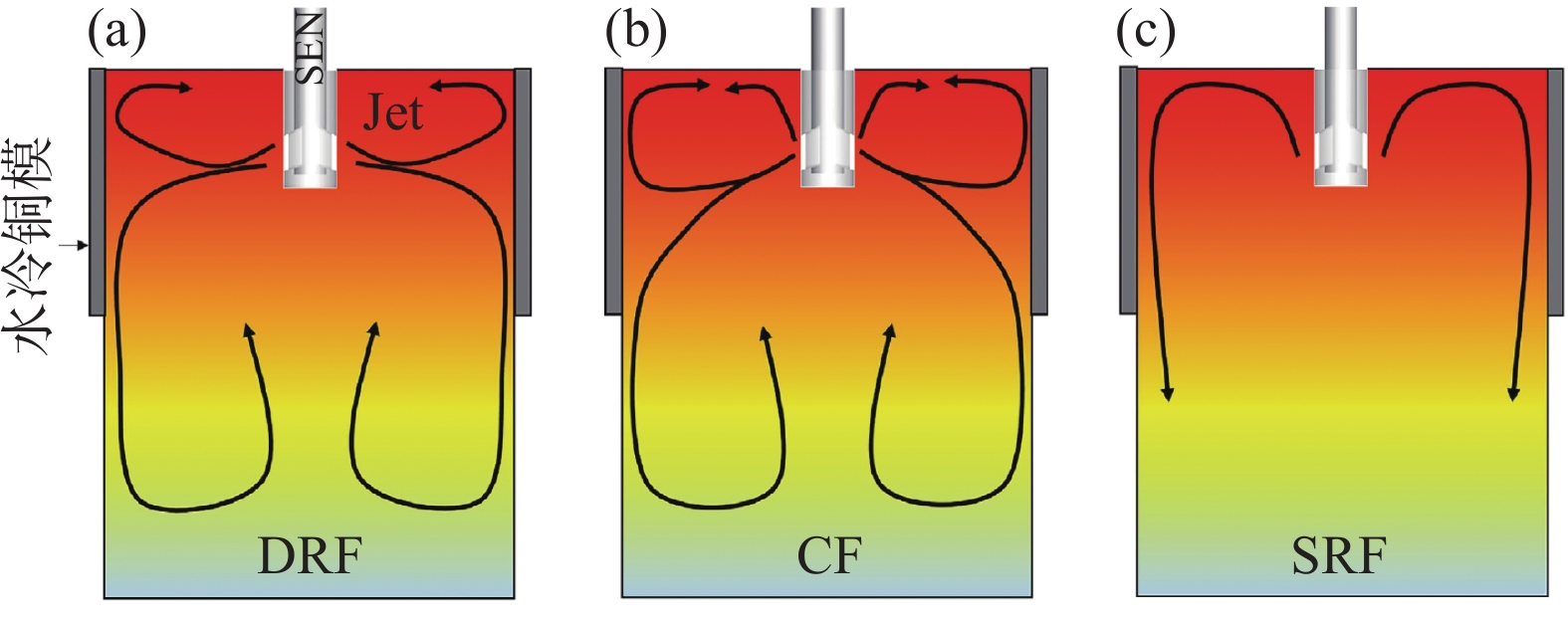
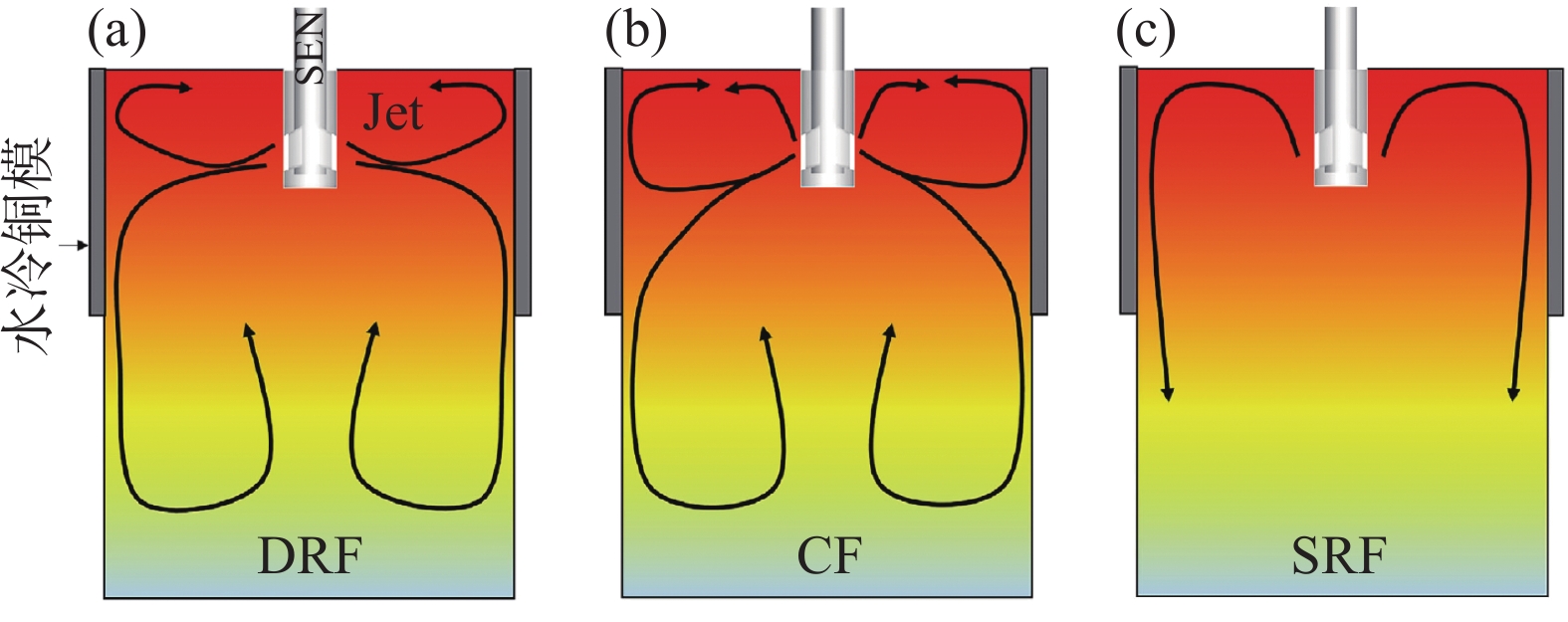
结晶器内的流态对连铸坯以及终端产品的质量有非常重要的影响,并且近年来已被众多学者采用数学物理模拟进行了广泛的研究[9,14−21]。对于板坯结晶器,通常采用双侧孔水口进行浇注。因此,结晶器内流态不是唯一的,目前最广泛讨论的流态有双辊流和单辊流[22−23],如图7(a)(c)所示。双辊流结晶器液面的钢液从窄侧径直流向水口,在结晶器宽度方向两侧均形成上下两个回旋区,而单辊流结晶器液面的钢液则是从水口流向窄侧,没有形成返向水口方向的上回旋区。一般认为,这两种流态是由Andrzejewski等人通过对
2765 mm×220 mm结晶器的物理模型研究而首次提出[21],为板坯结晶器中存在的典型流态。此外,Kohler等人[25]对德国克虏伯·赫斯(Krupp-Hoesch)钢厂的3#板坯连铸机进行了长达97 h的流态监测。结果表明,结晶器内除了典型的单辊流和双辊流之外,还发现存在另外一种流态,称之为弯月面流,如图8所示。这种流态的主要特征是结晶器内宽度方向左右两侧的流场不对称,其中一侧的钢液从窄侧流向水口,而另一侧的钢液却从水口流向窄侧。Liu等人[26]建立了数学物理模型研究了吹氩结晶器内的流态。结果表明,在吹氩条件下,板坯结晶器内存在三种流态,并且流态之间的转变按照氩气流量的大小从小到大排列依次为双辊流、三辊流以及单辊流。Salazar-Campoy等人[27]确认了板坯结晶器内存在三种流态,分别是双辊流、单辊流以及永久不稳定流。Zhang等人[28]通过数值计算以及实测表明,除了单辊流和双辊流之外,结晶器还存在介于二者之间的过渡流。Liu等人[29]以及Huang等人[24]同样提出了一种过渡流态,称之为复杂流,如图7(b) 所示。这是一种吹气条件下的介于双辊流和单辊流之间的过渡流态。通过诸多学者的研究结果可知,单辊流和双辊流是板坯结晶器内存在的典型流态,而第三种流态是不稳定的,具有不确定性 。
2.2 结晶器内流态对连铸坯质量影响
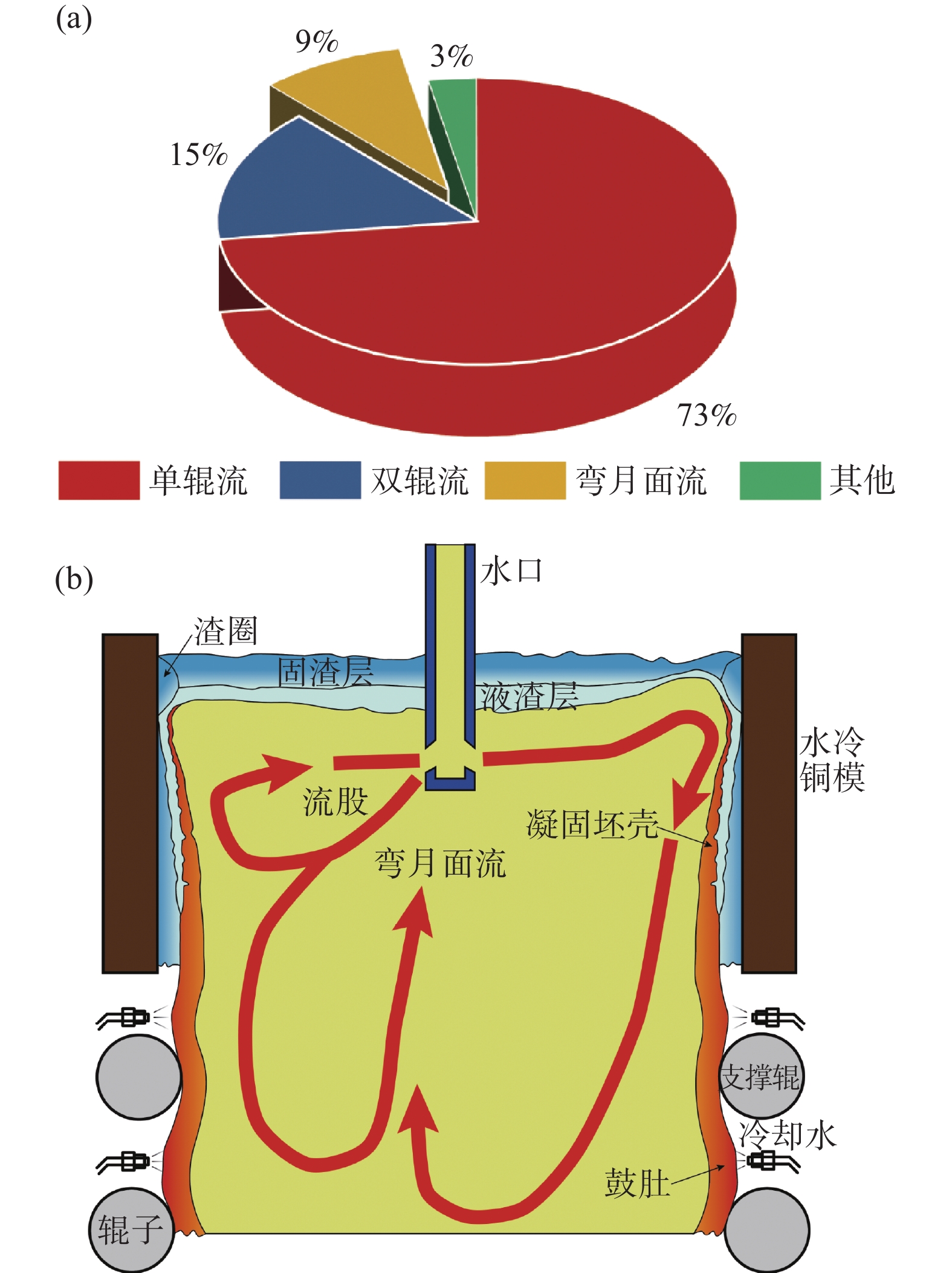
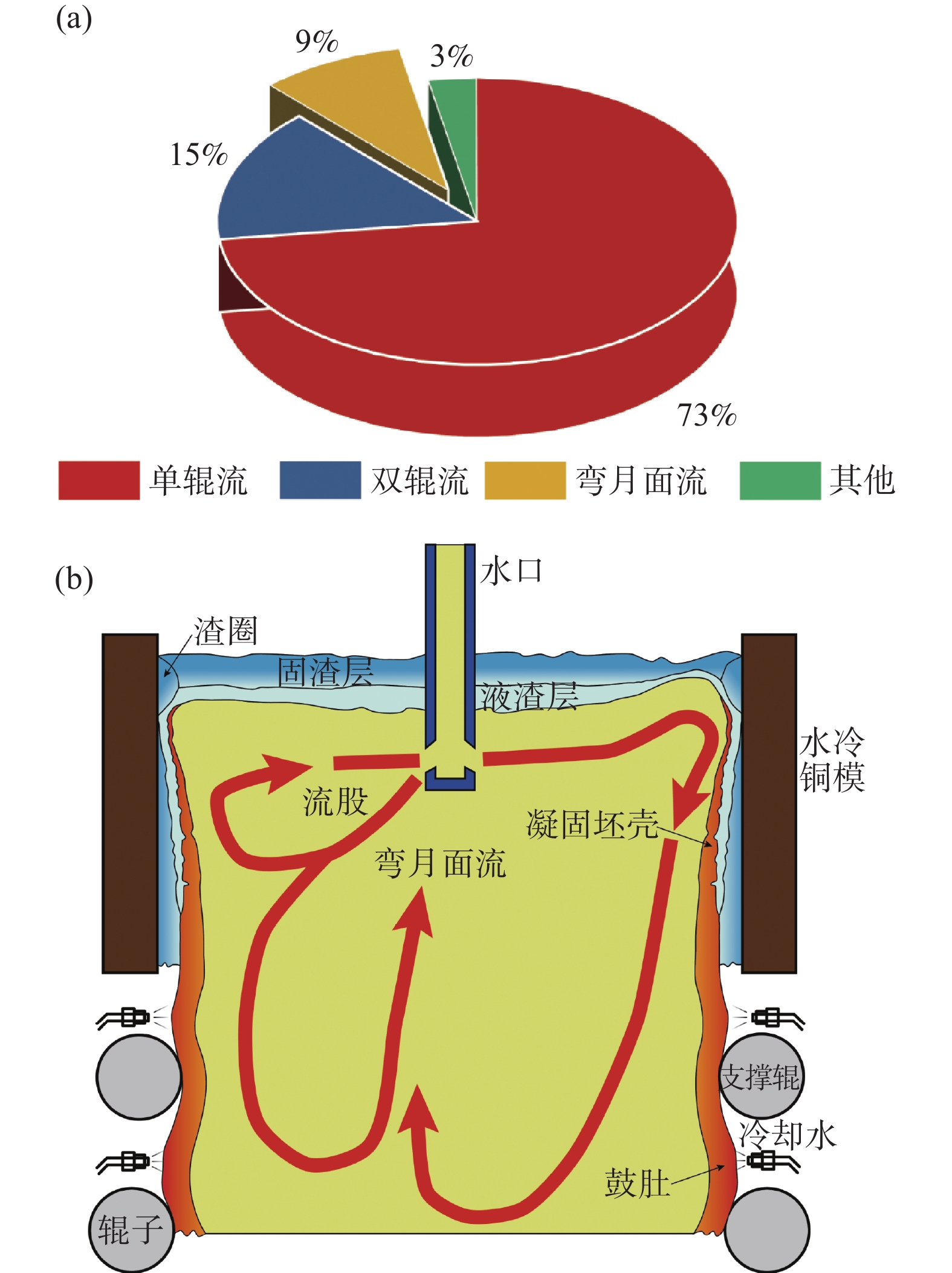
铸坯的质量与结晶器内的流态及其稳定性息息相关[30]。Andrzejewski等人[31]认为,当板坯结晶器处于对称的双辊流状态并且液面具有适宜的流速时,铸坯的缺陷率最低。Hibbeler等人[32]表明,液面流速控制在0.26~0.43 m/s的范围为宜。Li等人[33]认为在双辊流态下结晶器的卷渣率最低。然而,如果液面驻波显著或者流速过大,会导致结晶器窄侧区域的液渣层变薄甚至裸露,增大了二次氧化的风险。因此,双辊流条件下液面的流速控制至关重要。
Dauby等人[4,19]的研究结果表明,单辊流比双辊流容易产生更多的铸坯缺陷,例如条状缺陷(Slivers)和铅芯缺陷(Pencil Pipe)。这是因为单辊流会导致水口出流的钢液向上冲击弯月面,继而流向结晶器窄侧,同时也会将保护渣、气泡以及夹杂物推向结晶器窄侧[34],进而导致水口附近的液渣减少、润滑不足以及气泡、夹杂物在铸坯角部聚集[35]。Chen等人[17]也认为,单辊流条件下水口附近液面的流速较高,会增大卷渣的几率。Liu等人[36]通过数学模拟表明,在吹气条件下,单辊流更容易引起液面剧烈的波动和卷渣。由于单辊流的促成需要较大的氩气流量或较小的水口浸深[34],因此,这也会加剧液态保护渣的乳化以及液面的湍动程度。对于弯月面流,Andrzejewski等人[31]认为这种流态下的结晶器宽度方向两侧具有不同程度的风险特征,其中一侧的涡流会造成卷渣,而另一侧的单回旋流股会造成夹杂物不易上浮去除。周海忱等人[37]表明,复杂流态容易引起结晶器液面卷渣。由此可见,避免结晶器内形成单辊流以及其他不稳定流态有助于改善铸坯质量。
2.3 结晶器内流态的影响因素
氩气流量、拉速、水口浸入深度以及结晶器断面等对结晶器内的流态的形成、转变有重要影响。当这些参数发生变化时,结晶器内的流态可能会在不同流态之间发生转变,加剧了流动的不稳定性。然而,水口结构对结晶器内流态转变的影响较小,不如氩气流量和拉速等参数对流态的影响显著。邓小旋等人[22]表明,拉速和吹气量是影响流态的决定性因素。此外流态也受结晶器断面尺寸的影响,减小断面尺寸有利于促进双辊流的发展。陈威等人[38]通过工业插钉试验研究了吹氩对板坯连铸结晶器内流态的影响。结果表明,结晶器流态随着氩气流量的增大逐渐由双辊流转变为复杂流和单辊流。Zhou等人[39]表明,高拉速、低氩气流量以及增大水口的浸深有利于促成双辊流,反之则为单辊流。Thomas等人[40]的研究结果表明,当氩气的体积分数超过10%时,结晶器上回旋区液面的流向直接发生逆转;增大氩气流量或者减小氩气泡尺寸均可以显著影响流态的转变。Salazar-Campoy等人[27]认为,氩气量增大会促进结晶器内的流态从双辊流转变为单辊流,显著地改变了钢液、熔渣以及坯壳之间的相互作用。Zhang等人[9]的研究结果证实了增大氩气流量、减小水口浸深以及降低拉速可以促进结晶器内单辊流的形成。Andrzejewski等人[31]通过对结晶器流态长达500 h的监测,得出拉速、氩气流量以及浇注时间(水口堵塞)对流态的影响非常显著,但浸入深度的影响较小;氩气流量越大,促成的单辊流越稳定。Deng等人[3]通过建立1:1物理模型研究了工艺参数对结晶器内流态的影响。结果表明,板坯结晶器内的流态由拉宽比指数(CMI)和气体流量共同决定;增大CMI、减小气体流量以及增大水口浸入深度有利于促进凸底、小倾角水口条件下结晶器内双辊流的形成,其中CMI的定义如式(1)所示。
$$ \mathrm{CMI}=\frac{V_{\mathrm{C}}}{W\mathrm{_M}}\times10^4 $$ (1) 其中,VC为拉速(m·min−1),WM为结晶器宽度(mm)。因此,保证工艺参数处在合理的范围来获得结晶器稳定的双辊流是连铸生产顺行的重要保障。
3. 板坯结晶器内流动的非对称性
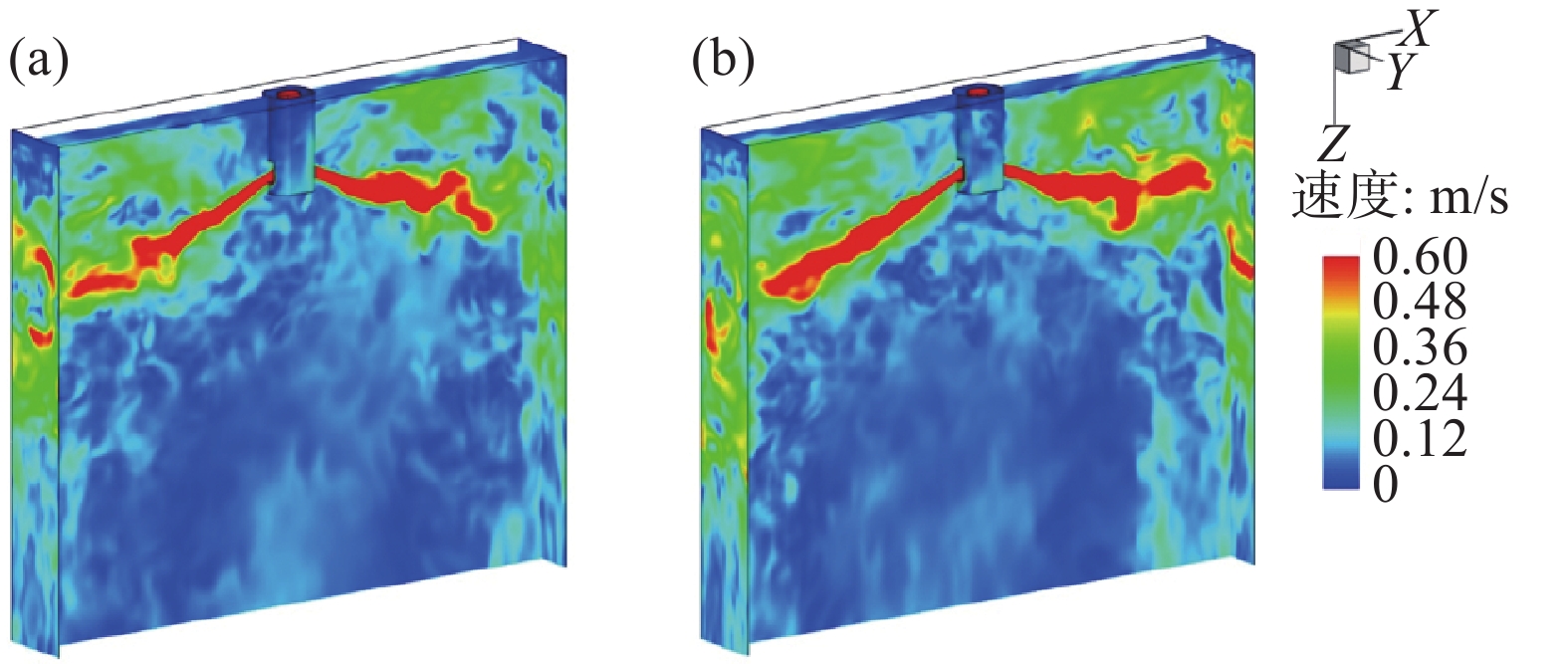
结晶器内的流动是非对称的[41−44],水口左右两侧的流股存在周期性的振荡与摆动[45−46],如图9所示。李宝宽等人[47−48]表明,即便浸入式水口精确对中,板坯结晶器内的流场也不会完全对称,而是一直处在瞬变和随机的状态,并会形成涡流。Ren等人[49]也得到了上述相近的结论,但又表明板坯结晶器内的流动在时均上具有对称性。Liu等人[41]表明,结晶器内流动的非对称状态并不是静止不变的,而是会在一段时间之后转变为前一状态的镜像,并且流股的振荡会加剧这种流动的非对称性。Birat等人[50]表明结晶器内水口的出流是振荡的,并会破坏弯月面的传输行为。Lee等人[51]发现,结晶器内的流动虽然是不对称的,但却具有一定的周期性。Yuan等人[52]表明,板坯结晶器内流动的不对称分为短时不对称和长时不对称;短时不对称是指水口侧孔以及流股的流动,而长时不对称是指液面和下回旋区的流动,同时又指出这种长时不对称的成因是湍流的本质特性。
对于结晶器流动的非对称性的成因,目前尚未形成统一的解释,其根本原因还需进一步的明确。Torres-Alonso等人[53]表明,结晶器内流动的不对称主要是流股的持续振荡所致。Honeyands等人[45]采用水模型研究了薄板坯结晶器内的流股的振荡机理,证实了结晶器内流股的振荡是由水口侧孔出流与再回旋流股相互作用以及产生的压力差平衡/不平衡而形成的;振荡频率可以采用斯特劳哈尔相似准则(Strouhal similarity criterion)进行理论计算,是拉速、水口结构以及浸入深度的函数。Gupta等人[54−56]通过物理模拟试验表明,结晶器内的钢液具有瞬态的振荡及非对称特性,这是因为水口的出流存在着旋转性,如果旋转的流股与结晶器宽面相遇,则容易引起非对称的流动;结晶器下半区的流态取决于下回旋区尺寸的大小,如果下回旋区的流动均能到达结晶器底部,则流态总体上对称;然而结晶器底部区域的流动实际上是非对称的,并且总是集中在结晶器的某一侧,并且会频繁地从一侧转向另一侧。Torres-Alonso等人[57−58]采用数学物理模拟方法研究了薄板坯结晶器内的流动。结果表明,薄板坯结晶器的流动是非对称的,并且伴随着液面的不稳定以及涡流;流动的非对称性与由流股和上回旋区流体相互作用产生的高雷诺应力引起的大尺度动态畸变时间有关,为结晶器内两侧流股和回旋流体的压力差的动态平衡/不平衡所致。
此外,水口的堵塞[59]、水口或塞棒不对中[60]、吹入氩气、中间包内不对称的流动[61]以及采用滑动水口控流[62−64]等还会造成结晶器内的偏流,并会随着时间而发生不断的变化[65−66]。Wang等人[67]表明,偏流会造成卷渣以及不均匀传热。Li等人[66]表明,水口偏离结晶器中心会导致偏流,改变了回旋区的大小和强度,进而形成涡流。偏流会增大结晶器液面涡旋的深度和频率,因此可以通过减小或者杜绝偏流来预防涡旋的生成[68]。Herbertson等人[69]表明,水口不对中、堵塞以及被侵蚀等会产生偏流,进而会造成坯壳的不均匀生长、涡流以及卷渣,还会加剧液面的波动。Lawson等人[70]表明,偏流会增大结晶器在线调宽漏钢的风险。Wang等人[67]表明,偏流不仅会造成卷渣以及不均匀传热,还会加剧水口的堵塞,是影响液位变化的重要原因。尽管结晶器内的非对称流动是不可避免的,然而可以通过精准的工艺操作来减小或者杜绝偏流以保障连铸生产顺行和提高连铸坯质量。此外,还可以采用先进的控制措施来减小偏流,例如电磁技术[71−72]。
4. 结论
1)在吹气条件下,水口内流态随气体流量变化可能呈现气泡流、膜状流、环状流、段塞流或临界流等类型。其中,气泡流较为稳定,有利于连铸顺行;而环状流、段塞流和临界流则较不稳定。水口润湿性越好、气/液流量比越小,越容易形成气泡流;大尺寸侧孔水口则易促进不稳定的临界流形成。
2)当板坯结晶器处于对称的双辊流状态,且液面流速控制在0.26~0.43 m/s时,有助于显著提高铸坯质量。氩气流量和拉速是影响板坯结晶器内流态转变的关键因素。较高的拉速、较低的氩气流量以及增大的水口浸入深度有利于形成双辊流,而相反的条件则倾向于形成单辊流。
3)结晶器内的流动是非对称的,与流股的持续振荡有关,然而在时均上具有对称性。流动非对称性的加剧会引发偏流,进而造成卷渣、涡流以及不均匀传热等不利现象。因此,可以通过精准的工艺操作来减小或者杜绝偏流,以保障连铸生产顺行和提高连铸坯质量。
-
-
[1] Gan Yong, Peng Suping, Mao Jingwen, et al. High-quality development strategy for the supply chain of critical minerals and its material industry in China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022,24(3):1-9. (干勇, 彭苏萍, 毛景文, 等. 我国关键矿产及其材料产业供应链高质量发展战略研究[J]. 中国工程科学, 2022,24(3):1-9. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.001Gan Yong, Peng Suping, Mao Jingwen, et al. High-quality development strategy for the supply chain of critical minerals and its material industry in China[J]. Strategic Study of CAE, 2022, 24(3): 1-9. doi: 10.15302/J-SSCAE-2022.03.001 [2] Zhu Miaoyong. A study of transport phenomena and key technologies for high-speed continuous casting of steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021,56(7):1-12. (朱苗勇. 高拉速连铸过程传输行为特征及关键技术探析[J]. 钢铁, 2021,56(7):1-12.Zhu Miaoyong. A study of transport phenomena and key technologies for high-speed continuous casting of steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 2021, 56(7): 1-12. [3] Deng X, Ji C, Cui Y, et al. Flow pattern control in continuous slab casting moulds: physical modelling and plant trials[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2017,44(6):461-471. [4] Dauby P H. Continuous casting: make better steel and more of it[J]. Revue De Métallurgie, 2012,109(2):113-136. [5] Pütz O, Rödl S. Investigations of unsteady and asymmetric flow phenomena in continuous casting moulds by advanced simulation techniques[J]. Steel Research International, 2003,74(2):104-113. doi: 10.1002/srin.200300168 [6] Wang Y, Zhang L. Transient fluid flow phenomena during continuous casting: Part II—Cast speed change, temperature fluctuation, and steel grade mixing[J]. ISIJ international, 2010,50(12):1783-1791. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.50.1783 [7] Yuan Peng, Wang Xinhua, Jiang Min, et al. Inclusions in low carbon aluminum killed steel slabs at high casting speed[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016,38(3):342-350. (苑鹏, 王新华, 姜敏, 等. 高拉速连铸低碳铝镇静钢铸坯中夹杂物[J]. 工程科学学报, 2016,38(3):342-350.Yuan Peng, Wang Xinhua, Jiang Min, et al. Inclusions in low carbon aluminum killed steel slabs at high casting speed[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016, 38(3): 342-350. [8] Chen Wei, Zhang Lifeng, Ren Qiang, et al. Large eddy simulation on four-phase flow and slag entrainment in the slab continuous casting mold[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2022,53(3): 1446-1461. [9] Zhang Lifeng, Yang Subo, Cai Kaike, et al. Investigation of fluid flow and steel cleanliness in the continuous casting strand[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2007,38(1):63-83. doi: 10.1007/s11663-006-9007-0 [10] Liu Z Q, Qi F S, Li B K, et al. Modeling of bubble behaviors and size distribution in a slab continuous casting mold[J]. International Journal of Multiphase Flow, 2016,79:190-201. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2015.07.009 [11] Ishiguro K, Iguchi M. Model experiment on the behavior of argon gas in immersion nozzle[J]. ISIJ International, 2003,43(5):663-670. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.43.663 [12] Terauchi Y, Iguchi M, Kosaka H, et al. Wettability effect on the flow pattern of air-water two-phase flows in a vertical circular pipe[J]. Tetsu-to-Hagane, 1999,85(9):645-651. doi: 10.2355/tetsutohagane1955.85.9_645 [13] Burty M, Larrecq M, Pusse C, et al. Experimental and theoretical analysis of gas and metal flows in submerged entry nozzles in continuous casting[J]. Revue de Metallurgie-CIT, 1996,93(10):1249-1255. doi: 10.1051/metal/199693101249 [14] Ren Lei, Zhang Lifeng, Wang Qiangqiang, et al. Study on fluid flow in a continuous casting slab mold using particle image velocimetry[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016,38(10):1393-1403. (任磊, 张立峰, 王强强, 等. 基于 PIV 技术的板坯连铸结晶器内钢水流动行为研究[J]. 工程科学学报, 2016,38(10):1393-1403.Ren Lei, Zhang Lifeng, Wang Qiangqiang, et al. Study on fluid flow in a continuous casting slab mold using particle image velocimetry[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2016, 38(10): 1393-1403. [15] Liu Rui, Thomas B G, Sengupta J, et al. Measurements of molten steel surface velocity and effect of stopper-rod movement on transient multiphase fluid flow in continuous casting[J]. ISIJ International, 2014,54(10):2314-2323. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.54.2314 [16] Zhu Xiaowei, Li Dewei, Wu Chunlei, et al. Influence of large-scale vortex movement in lower recirculation zone on instable flow field in the mold[J]. ISIJ International, 2018,58(9):1687-1694. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2018-160 [17] Chen Wei, Ren Ying, Zhang Lifeng, et al. Numerical simulation of steel and argon gas two-phase flow in continuous casting using LES+ VOF+ DPM model[J]. JOM, 2019,71(3):1158-1168. doi: 10.1007/s11837-018-3255-8 [18] Liu Zhongqiu, Li Baokuan, Jiang Maofa, et al. Modeling of transient two-phase flow in a continuous casting mold using Euler-Euler large eddy simulation scheme[J]. ISIJ International, 2013,53(3):484-492. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.53.484 [19] Dauby P H, Assar M B, Lawson G D. PIV and MFC measurements in a continuous caster mould. New tools to penetratethe caster black box[J]. Revue de Métallurgie, 2001,98(4):353-366. [20] Salazar-Campoy M M, Morales R D, Najera-Bastida A, et al. A physical model to study the effects of nozzle design on dense two-phase flows in a slab mold casting ultra-low carbon steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2017,48(2):1376-1389. doi: 10.1007/s11663-017-0918-8 [21] Andrzejewski P, Köhler K U, Pluschkell W. Model investigations on the fluid flow in continuous casting moulds of wide dimensions[J]. Steel Research, 1992,63(6):242-246. doi: 10.1002/srin.199200508 [22] Deng Xiaoxuan, Ji Chenxi, Cui Yang, et al. Flow pattern in continuous casting slab mold with argon blowing[J]. Iron & Steel, 2016,51(10):23-30. (邓小旋, 季晨曦, 崔阳, 等. 吹氩板坯连铸结晶器内钢水流态[J]. 钢铁, 2016,51(10):23-30.Deng Xiaoxuan, Ji Chenxi, Cui Yang, et al. Flow pattern in continuous casting slab mold with argon blowing[J]. Iron & Steel, 2016, 51(10): 23-30. [23] Asad A, Kratzsch C, Schwarze R. Numerical investigation of the free surface in a model mold[J]. Steel Research International, 2016,87(2):181-190. doi: 10.1002/srin.201400600 [24] Huang Caide, Zhou Haichen, Zhang Lifeng, et al et al. Effect of casting parameters on the flow pattern in a steel continuous casting slab mold: numerical simulation and industrial trials[J]. Steel Research International, 2022,93(2):2100350. doi: 10.1002/srin.202100350 [25] Kohler K U, Andrzejewski P, Julius E, et al. Steel flow velocity measurement and flow pattern monitoring in the mould[C]//78th Steelmaking Conference Proceedings. Warrendale: Iron and Steel Society, 1995: 445-449. [26] Liu Zhongqiu, Qi Fengsheng, Li Baokuan, et al. Vortex flow pattern in a slab continuous casting mold with argon gas injection[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, International, 2014,21(12):1081-1089. doi: 10.1016/S1006-706X(14)60187-4 [27] Salazar-Campoy M M, Morales R D, Nájera-Bastida A, et al. A physical model to study the effects of nozzle design on dispersed two-phase flows in a slab mold casting ultra-low-carbon steels[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2018,49(2):812-830. doi: 10.1007/s11663-018-1181-3 [28] Zhang Tao, Yang Jian, Jiang Peng. Measurement of molten steel velocity near the surface and modeling for transient fluid flow in the continuous casting mold[J]. Metals, 2019,9(1):36. doi: 10.3390/met9010036 [29] Liu Fenggang, Zhou Haichen, Zhang Lifeng, et al. Dependency of flow pattern in the mold on the distribution of inclusions along the thickness of continuous casting slabs[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2021,52(4):2536-2550. doi: 10.1007/s11663-021-02201-x [30] Assar M B, Dauby P H, Lawson G D. Opening the black box: PIV and MFC measurements in a continuous caster mold[C]//83rd Steelmaking Conference Proceedings. Warrendale: Iron and Steel Society, 2000: 397-411. [31] Andrzejewski P, Gotthelf D, Julius E, et al. Mould flow monitoring at no. 3 slab caster, Krupp Hoesch Stahl AG[C]//80th Steelmaking Conference proceedings. Warrendale: Iron and Steel Society, 1997: 153-157. [32] Hibbeler L C, Thomas B G. Mold slag entrainment mechanisms in continuous casting molds[J]. Iron and Steel Technology, 2013,10(10):121-136. [33] Li Xianglong, Li Baokuan, Liu Zhongqiu, et al. Evaluation of slag entrapment in continuous casting mold based on the LES-VOF-DPM coupled model[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2021,52(5):3246-3264. doi: 10.1007/s11663-021-02253-z [34] Kunstreich S, Dauby P H. Effect of liquid steel flow pattern on slab quality and the need for dynamic electromagnetic control in the mould[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 2005,32(1):80-86. [35] Burty M, De Santis M, Gesell M. Behaviour of argon gas bubbles in the continuous casting machine[J]. Metallurgical Research & Technology, 2002,99(1):49-53. [36] Liu Yibo, Yang Jian, Huang Fuxiang, et al. Comparison of the flow field in a slab continuous casting mold between the thicknesses of 180 mm and 250 mm by high temperature quantitative measurement and numerical simulation[J]. Metals, 2021,11(12):1886. doi: 10.3390/met11121886 [37] Zhou Haichen, Luo Yanzhao, Li Haibo, et al. Online prediction of surface velocity, vortex position and fluid flow pattern in mold[J]. Continuous Casting, 2023(5):80-86. (周海忱, 罗衍昭, 李海波, 等. 结晶器表面流速、涡心位置和流场流态在线预测[J]. 连铸, 2023(5):80-86.Zhou Haichen, Luo Yanzhao, Li Haibo, et al. Online prediction of surface velocity, vortex position and fluid flow pattern in mold[J]. Continuous Casting, 2023(5): 80-86. [38] Chen Wei, Zhou Haichen, Wang Shengdong, et al. Nail board industrial experiment on effect of argon flow rate on mold flow field[J]. Iron & Steel, 2019,54(8):102-106. (陈威, 周海忱, 王胜东, 等. 吹氩流量对结晶器流场影响的插钉工业试验[J]. 钢铁, 2019,54(8):102-106.Chen Wei, Zhou Haichen, Wang Shengdong, et al. Nail board industrial experiment on effect of argon flow rate on mold flow field[J]. Iron & Steel, 2019, 54(8): 102-106. [39] Zhou Haichen, Zhang Lifeng, Chen Wei, et al. Determination of transient flow pattern in steel continuous casting molds using nail board measurement and onsite top flux observation[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2021,52(2):1106-1117. doi: 10.1007/s11663-021-02083-z [40] Thomas B G, Huang X, Sussman R C. Simulation of argon gas flow effects in a continuous slab caster[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1994,25(4):527-547. doi: 10.1007/BF02650074 [41] Liu Zhongqiu, Li Baokuan, Jiang Maofa. Transient asymmetric flow and bubble transport inside a slab continuous-casting mold[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2014,45(2):675-697. doi: 10.1007/s11663-013-9972-z [42] Robertson T, Moore P, Hawkins R J. Computational flow model as aid to solution of fluid flow problems in the steel industry[J]. Ironmaking & Steelmaking, 1986,13(4):195-203. [43] Tripathi A, Ajmani S K, Chandra S. Numerical investigation of bias flow in a slab caster mould[J]. Canadian Metallurgical Quarterly, 2021,60(3):203-214. doi: 10.1080/00084433.2021.1997278 [44] Liu Zhongqiu, Li Baokuan, Zhang Li, et al. Analysis of transient transport and entrapment of particle in continuous casting mold[J]. ISIJ International, 2014,54(10):2324-2333. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.54.2324 [45] Honeyands T, Herbertson J. Flow dynamics in thin slab caster moulds[J]. Steel Research International, 1995,66(7):287-293. doi: 10.1002/srin.199501126 [46] Yasunaka H, Taniguchi K, Kokita M, et al. Surface quality of stainless steel type 304 cast by twin-roll type strip caster[J]. ISIJ International, 1995,35(6):784-789. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.35.784 [47] Li B K, Tsukihashi F. Vortexing flow patterns in a water model of slab continuous casting mold[J]. ISIJ International, 2005,45(1):30-36. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.45.30 [48] Li Baokuan, Liu Zhongqiu, Qi Fengsheng, et al. Large eddy simulation for unsteady turbulent flow in thin slab continuous casting mold[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012,48(1):23-32. (李宝宽, 刘中秋, 齐凤升, 等. 薄板坯连铸结晶器非稳态湍流大涡模拟研究[J]. 金属学报, 2012,48(1):23-32. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2011.00464Li Baokuan, Liu Zhongqiu, Qi Fengsheng, et al. Large eddy simulation for unsteady turbulent flow in thin slab continuous casting mold[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2012, 48(1): 23-32. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1037.2011.00464 [49] Ren Lei, Ren Ying, Zhang Lifeng, et al. Investigation on fluid flow inside a continuous slab casting mold using particle image velocimetry[J]. Steel Research International, 2019,90(11):1900209. doi: 10.1002/srin.201900209 [50] Birat, J P, Larrecq M, Lamant J Y, et al. The continuous casting mold: a basic tool for surface quality and strand productivity[C]//74th Steelmaking Conference Proceedings. Warrendale: Iron and Steel Society, 1991: 39-50. [51] Lee J, Kim Y, Yi K. Analysis of the origin of periodic oscillatory flow in the continuous casting mold[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2015,21(2):295-302. doi: 10.1007/s12540-015-4223-2 [52] Yuan Q, Thomas B G, Vanka S P. Study of transient flow and particle transport in continuous steel caster molds: Part I. Fluid flow[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2004,35(4):685-702. doi: 10.1007/s11663-004-0009-5 [53] Torres-Alonso E, Morales R D, Palafox-Ramos J, et al. Oscillating jet flows in a thin slab mold and their influence on meniscus stability[J]. Steel Research International, 2008,79(7):553-563. doi: 10.1002/srin.200806166 [54] Gupta D, Lahiri A K. A water model study of the flow asymmetry inside a continuous slab casting mold[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 1996,27(5):757-764. [55] Gupta D, Chakraborty S. Asymmetry and oscillation of the fluid flow pattern in a continuous casting mould: a water model study[J]. ISIJ International, 1997,37(7):654-658. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.37.654 [56] Gupta D, Subramaniam S, Lahiri A K. Study of fluid flow and residence-time distribution in a continuous slab casting mould[J]. Steel Research, 1991,62(11):496-500. doi: 10.1002/srin.199100438 [57] Torres-Alonso E, Morales R D, Demedices LG, et al. Flow dynamics in thin slab molds driven by sustainable oscillating jets from the feeding SEN[J]. ISIJ International, 2007,47(5):679-688. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.47.679 [58] Torres-Alonso E, Morales R D, García-Hernández S, et al. Cyclic turbulent instabilities in a thin slab mold. Part I: physical model[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2010,41(3):583-597. doi: 10.1007/s11663-010-9361-9 [59] Bai H, Thomas B G. Effects of clogging, argon injection, and continuous casting conditions on flow and air aspiration in submerged entry nozzles[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 2001,32(4):707-722. [60] Lee G G, Shin H J, Thomas B G, et al. Asymmetric multi-phase fluid flow and particle entrapment in a continuous casting mold[C]//Proceedings of AISTech 2008 Steelmaking Conference. Pittsburgh: The Association for Iron and Steel Technology, 2008: 63-73. [61] Zhang Lifeng, Wang Yufeng, Zuo Xiangjun. Flow transport and inclusion motion in steel continuous-casting mold under submerged entry nozzle clogging condition[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2008,39(4):534-550. doi: 10.1007/s11663-008-9154-6 [62] Bai H, Thomas B G. Turbulent flow of liquid steel and argon bubbles in slide-gate tundish nozzles: Part II. Effect of operation conditions and nozzle design[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2001,32(2):269-284. doi: 10.1007/s11663-001-0050-6 [63] Honeyands T, Lucas J, Chambers J, et al. Preliminary modelling of steel delivery to thin slab caster moulds[C]//75th Steelmaking Conference Proceedings. Warrendale: Iron and Steel Society, 1992: 451-459. [64] Najjar F M, Thomas B G, Hershey D E. Numerical study of steady turbulent flow through bifurcated nozzles in continuous casting[J]. Metallurgical & Materials Transactions B, 1995,26(4):749-765. [65] Scoones D J, Nijman S. Measurement of steel velocities in the mould[J]. Revue de Métallurgie, 2003,100(6):633-635. [66] Li B, Okane T, Umeda T. Modeling of biased flow phenomena associated with the effects of static magnetic-field application and argon gas injection in slab continuous casting of steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2001,32(6):1053-1066. doi: 10.1007/s11663-001-0094-7 [67] Wang Y H. A study of the effect of casting conditions on fluid flow in the mold using water modelling[C]//73rd Steelmaking Conference Proceedings. Warrendale: Iron and Steel Society, 1990: 473-480. [68] He Qinglin. Observations of vortex formation in the mould of a continuous slab caster[J]. ISIJ International, 1993,33(2):343-345. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.33.343 [69] Herbertson J, He Q L, Flint P J, et al. Modeling of metal delivery to continuous casting moulds[C]//74th Steelmaking Conference Proceedings. Warrendale: Iron and Steel Society, 1991: 171-185. [70] Lawson G D, Sander S C, Emling W H, et al. Prevention of shell thinning breakouts associated with widening width changes[C]//77th Steelmaking Conference Proceedings. Warrendale: Iron and Steel Society, 1994: 329-336. [71] Han S W, Cho H J, Jin S Y, et al. Effects of simultaneous static and traveling magnetic fields on the molten steel flow in a continuous casting mold[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2018,49:2757-2769. doi: 10.1007/s11663-018-1356-y [72] Schurmann D, Glavinić I, Willers B, et al. Impact of the electromagnetic brake position on the flow structure in a slab continuous casting mold: An experimental parameter study[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2020,51(1):61-78. doi: 10.1007/s11663-019-01721-x -






 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载: