Study on the behavior of unburnt pulverized coal and reduction productions of TiO2 in high-titanium blast furnace slag
-
摘要: 采用旋转柱体法对配加未燃煤粉的高钛型高炉渣的黏度进行了测量,结合试验样品的宏观形貌和不同部位微观结构的表征,对未燃煤粉及其还原产物在高钛型高炉渣中的行为进行了分析。结果表明,未燃煤粉不可避免地会与渣中TiO2反应,残余的未燃煤粉及其还原产物,如Ti(C,N)或TiCxOy等高熔点物相不均匀分布于渣中。随着初始未燃煤粉含量从0增加至5.51%,渣中TiC和TiN含量之和从0.456%升高至2.515%,反应生成的高熔点物质向下沉降聚集,残余的未燃煤粉则向上运动,与上部炉渣中的TiO2继续反应生成高熔点物质或形成泡沫渣,并导致炉渣黏度显著升高,波动显著加剧,炉渣中部则几乎没有残余未燃煤粉和高熔点还原产物。Abstract: In this study, the viscosity of high-titanium blast furnace slags uniformly mixed with unburnt pulverized coal (UPC) was measured by using the method of rotating cylinder firstly. Then the distribution and behavior of the residual UPC and the reduction products were analyzed according to the macro morphology of these samples and their microscopic morphology of different parts. It was found that TiO2 would inevitably be reduced by UPC, the high melting point reduction products such as Ti(C,N), TiCxOy and unburnt UPC distributed nonuniformly in the slag. As the initial UPC content increased from 0% to 5.51%, the total content of TiC and TiN increased from 0.456% to 2.515%. The high melting point reduction products deposited downwards and aggregated, while the unburnt UPC floated upwards and continued to react with TiO2 to form foam slag, resulting in a significant increase in both viscosity and its fluctuation. However, there were negligible residual unburnt UPC and high melting point reduction products in the middle of the slag.
-
0. 引言
随着高炉冶炼技术的发展,喷吹煤粉与富氧鼓风技术逐渐从最初部分代替焦炭逐渐发展为一项独立的强化冶炼技术。但研究[1-3]表明,煤粉从进入喷枪至离开风口回旋区一共只有10~30 ms,在喷吹过程中并不能完全燃烧。例如,宝钢高炉喷煤比为175 kg/t和210~230 kg/t时,其燃烧率分别只有84.9%和70.5%~72.0%[1]。朱子宗等[4]的研究结果表明,当攀钢4# 高炉的富氧率为4%、喷煤比为120 kg/t时,煤粉的燃烧率只有70.3%。
在冶炼过程中,未燃煤粉主要以残碳颗粒、微变原煤、气孔原煤和灰渣等形式聚焦于回旋区前端、软熔带根部和内侧[5-7]。虽然未燃煤粉的气化速率比焦炭快[8-11],可以延缓焦炭的破损,但是未燃煤粉仍能以沉积碳或形成高熔点物质恶化炉渣性能[12-13]。特别是对于高钛型高炉渣,未燃煤粉能与其中TiO2反应生成熔点高达
3160 ℃的TiC以及熔点为2927 ℃的TiN及其固溶体Ti(C,N),使高钛型高炉渣性能显著恶化[14-18]。关于未燃煤粉对炉渣性能的影响,以前的研究主要集中于对配加一定比例煤粉后炉渣的黏度和熔化性温度的测量[19-20],几乎未涉及对未燃煤粉及其与TiO2的还原产物在渣中行为的研究。为此,笔者在实验室开展了配加未燃煤粉炉渣黏度-温度曲线的测量。然后,对渣中残余未燃煤粉及其与TiO2的还原产物在渣中的含量和分布进行了微观分析,由此确定未燃煤粉及其还原产物在炉渣中的行为,为加深未燃煤粉对高钛型高炉渣影响的理解和寻找相应的预防措施提供理论参考。
1. 试验原料及方法
1.1 试验原料
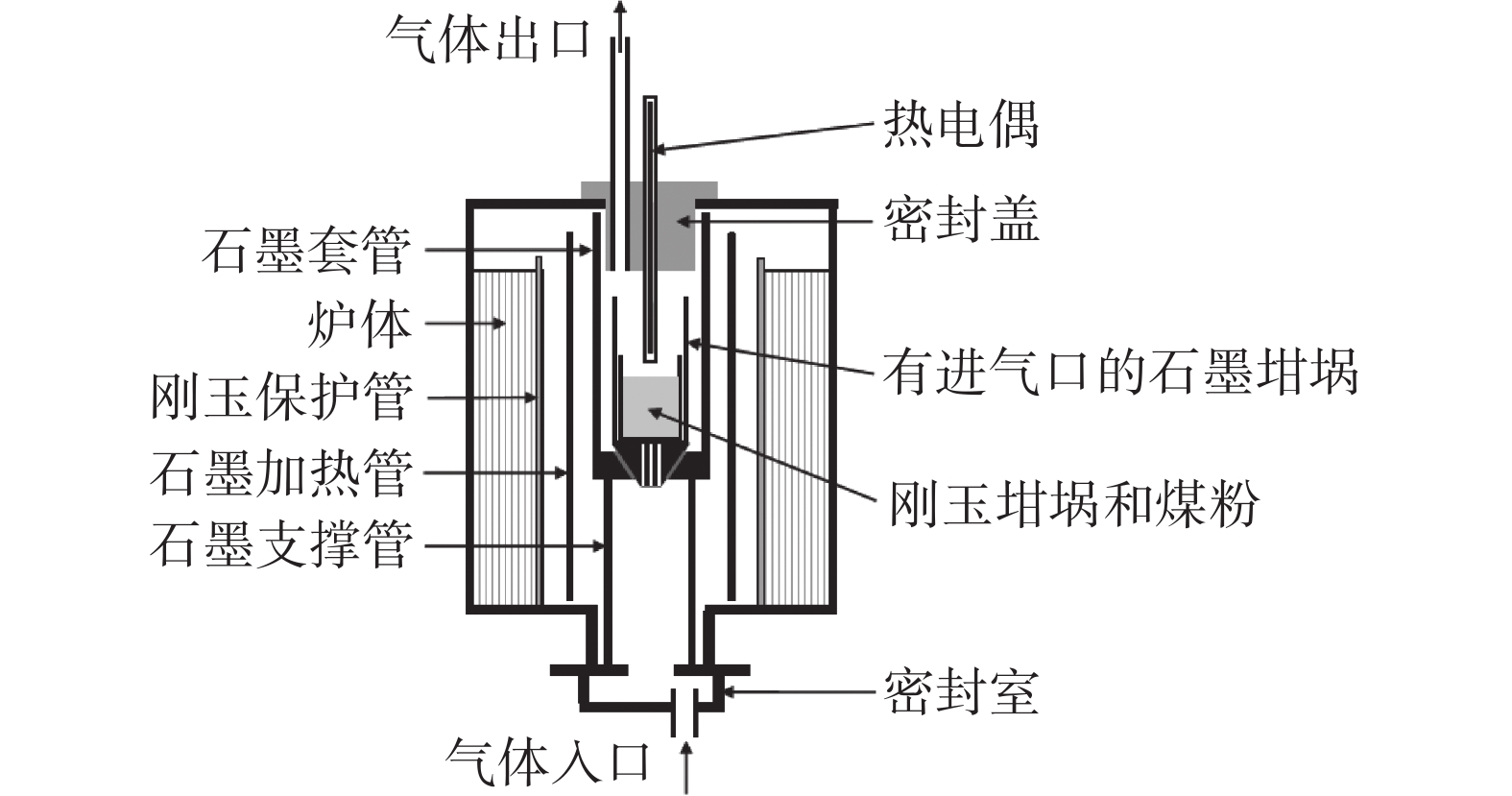
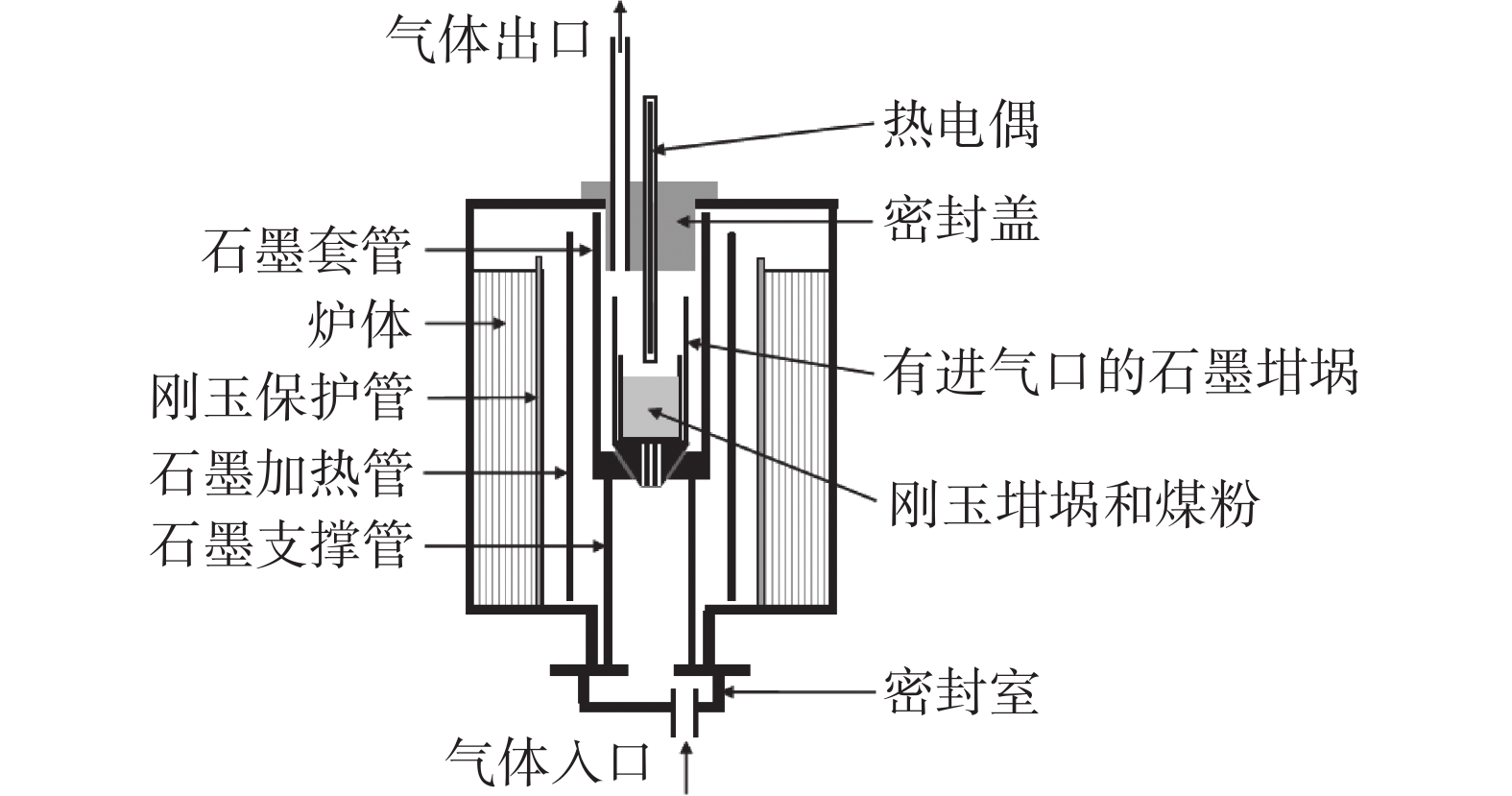
取现场喷吹煤粉100 g置于刚玉坩埚内。将盛放好煤粉的坩埚放入试验竖炉内,在30% CO+70% N2、15 L/min的条件下以10 ℃/min的升温速率从室温升温至
1350 ℃,恒温30 min后降温至100 ℃,以获得未燃煤粉。制备未燃煤粉的竖炉示意见图1,喷吹煤粉和未燃煤粉的化学成分见表1。与喷吹煤粉相比,未燃煤粉的固定碳含量从80.60%升高至88.70%,而挥发份含量则从9.78%降低至0.17%。表 1 喷吹煤粉和未燃烧煤粉的化学成分Table 1. Chemical compositions of PCI and UPC% 名称 Cad Vdaf Ad St 灰分分析 CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 Fe2O3 TiO2 K2O Na2O 喷吹煤粉 80.60 9.78 11.74 0.78 1.88 49.51 0.44 38.13 3.90 1.18 0.722 1.32 未燃煤粉 88.70 0.17 11.97 0.48 2.10 50.54 0.54 37.65 3.36 1.38 0.66 1.13 取生产现场高炉渣破碎后研磨至粒度小于0.05 mm作为基准渣,化学成分见表2。可见基准渣样中TiC和TiN含量之和为0.456%,根据已有的研究结果[18, 21],这样的炉渣在未凝固前的黏度值仍然很低。根据生产实际,在渣铁比为600 kg/t、喷煤比为140 kg/t的条件下,制定了不同煤粉燃烧率时的未燃煤粉配加方案,如表3所示。将基准渣样与未燃煤粉混合均匀,进行炉渣黏度-温度曲线测量。
表 2 基准高炉渣化学成分Table 2. Chemical composition of on-site blast furnace slag% CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 MnO FeO TiO2 Ti2O3 TiO TiC TiN 26.46 25.52 8.40 13.70 0.63 1.03 21.20 0.897 0.504 0.100 0.356 1.2 试验方法
采用旋转柱体法在RTW-10型熔体物性测定仪上测量炉渣的黏度-温度曲线,测量方法在以前的文献[21]中已有报道。将170 g炉渣置于内衬金属钼片的石墨坩埚内,在高纯Ar气(2 L/min)保护下从常温升温至
1480 ℃并恒温180 min后,采用金属钼测头测量温度降低过程中(2 ℃/min)炉渣的黏度。表 3 炉渣未燃煤粉配加方案Table 3. Adding scheme of UPC to slag编号 燃烧率/% 炉渣质量/g 未燃煤粉质量/g 未燃煤粉含量/% M0 100 170.00 0 0 M1 90 168.04 1.96 1.15 M2 80 166.12 3.88 2.28 M3 70 164.25 5.75 3.38 M4 60 162.42 7.58 4.46 M5 50 160.63 9.37 5.51 测量结束后,将残余的未燃煤粉从炉渣中清理干净,收集整理后分析其化学成分和微观形貌的变化。将炉渣沿纵向从中部剖成两半,一部分用于化学成分分析,一部分采用扫描电镜和光学显微镜进行物相确认和显微结构表征。根据试验样品的化学成分、残余未燃煤粉和炉渣不同部位的宏观和微观形貌以及物相分布,得到未燃煤粉及其与TiO2的还原产物在炉渣中的分布和行为。
采用X射线荧光光谱法分析试验原料和样品的化学成分,采用扫描电镜(美国,俄勒冈,希尔斯伯勒,FEI)确定炉渣不同部位还原产物的物相,采用光学显微镜(德国,耶拿,ZEISS Axio Imager M2m)表征煤粉和炉渣不同部位的微观形貌。
2. 试验结果及讨论
2.1 未燃煤粉的变化
测量结束后,将样品从坩埚中取出,在样品顶部和粘附在钼测头上的炉渣中可见少量未消耗完的残余未燃煤粉。在Xiang等[12]对TiO2含量为0.59%的炉渣黏度的研究中也有类似现象,但并没有报道未消耗的未燃煤粉的数量和C含量。
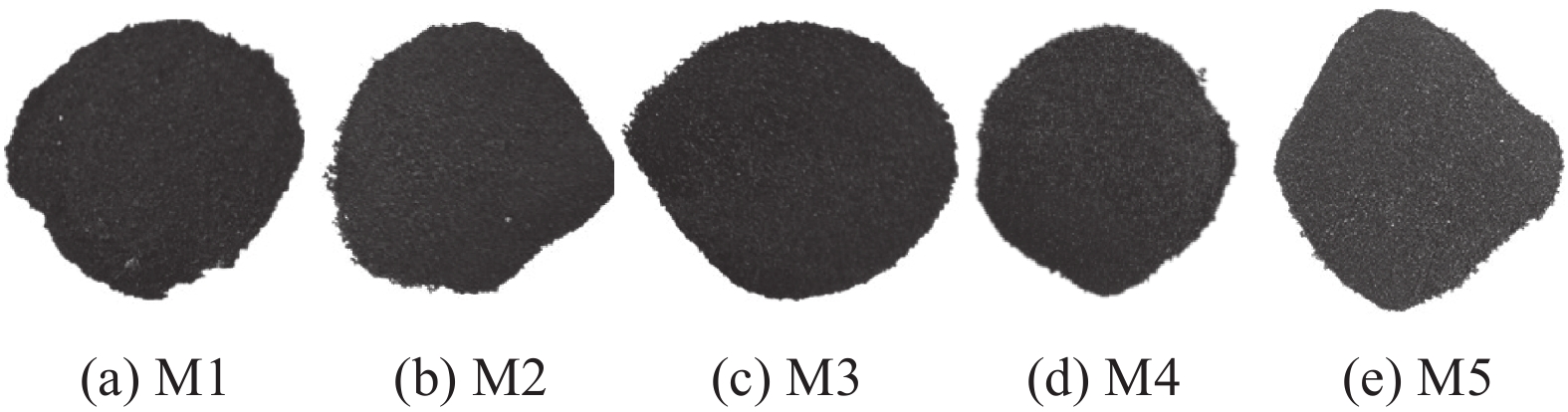
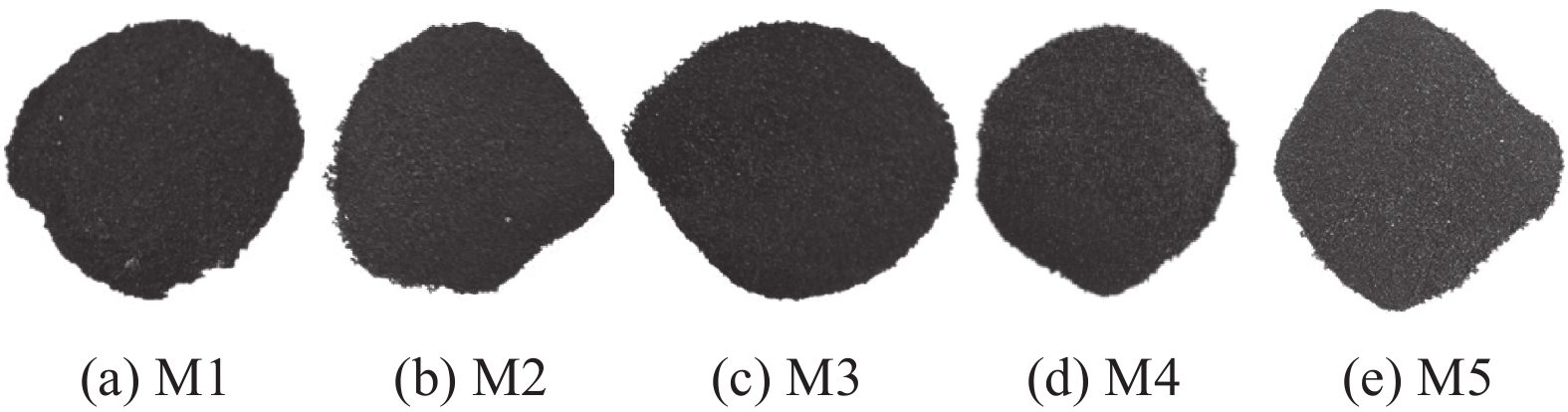
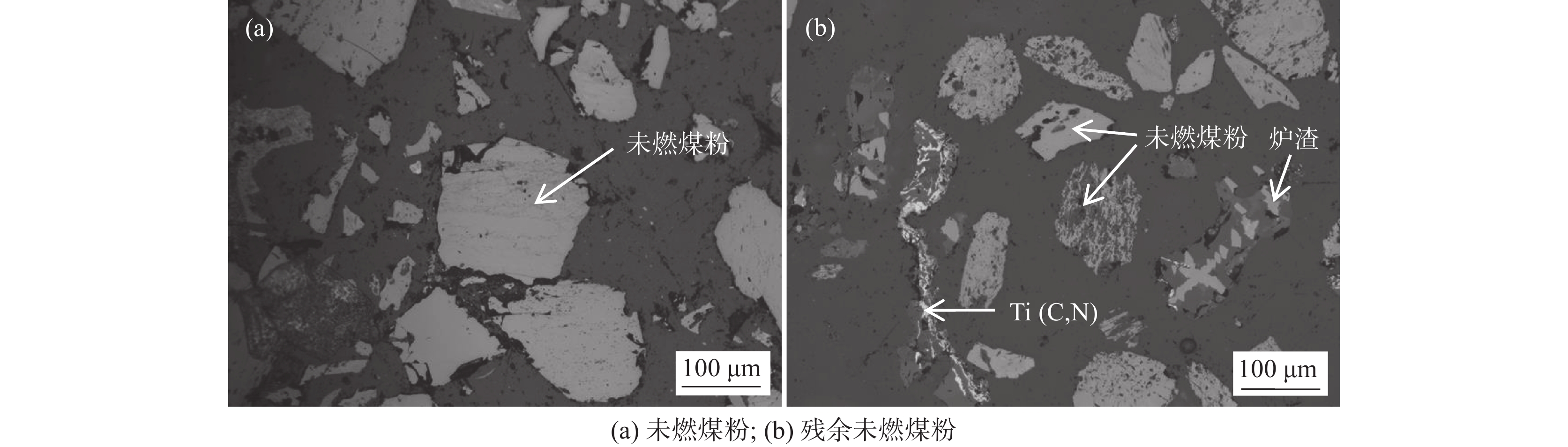
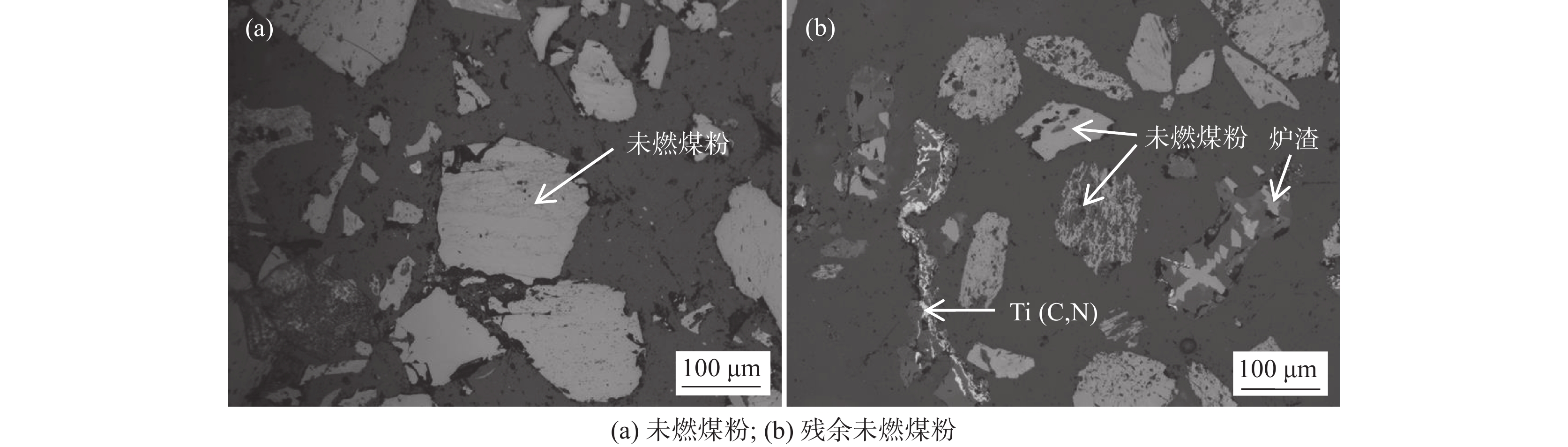
不同样品的残余未燃煤粉的照片见图2,质量和C含量见表4。可见,随着未燃煤粉配比升高,残余未燃煤粉从深棕色逐渐变为暗灰色,粒度逐渐变粗,质量和C含量逐渐升高。图3为未燃煤粉和M4试验残余未燃煤粉样品的光学显微照片,其它试验残余未燃煤粉的微观形貌与M4试验样品类似。由图3可见,残余未燃煤粉中混合有少量炉渣和碳氮化钛,且煤粉颗粒的孔洞数量增加、孔径增大。这表明残余未燃煤粉经过一定程度的消耗,因此C含量降低。
表 4 残余未燃煤粉的质量和C含量Table 4. The mass and C contents of unconsumed UPC编号 质量/g C/% M1 0.87 84.40 M2 2.77 84.80 M3 4.00 85.80 M4 6.82 86.00 M5 7.50 86.90 2.2 未燃煤粉对黏度的影响
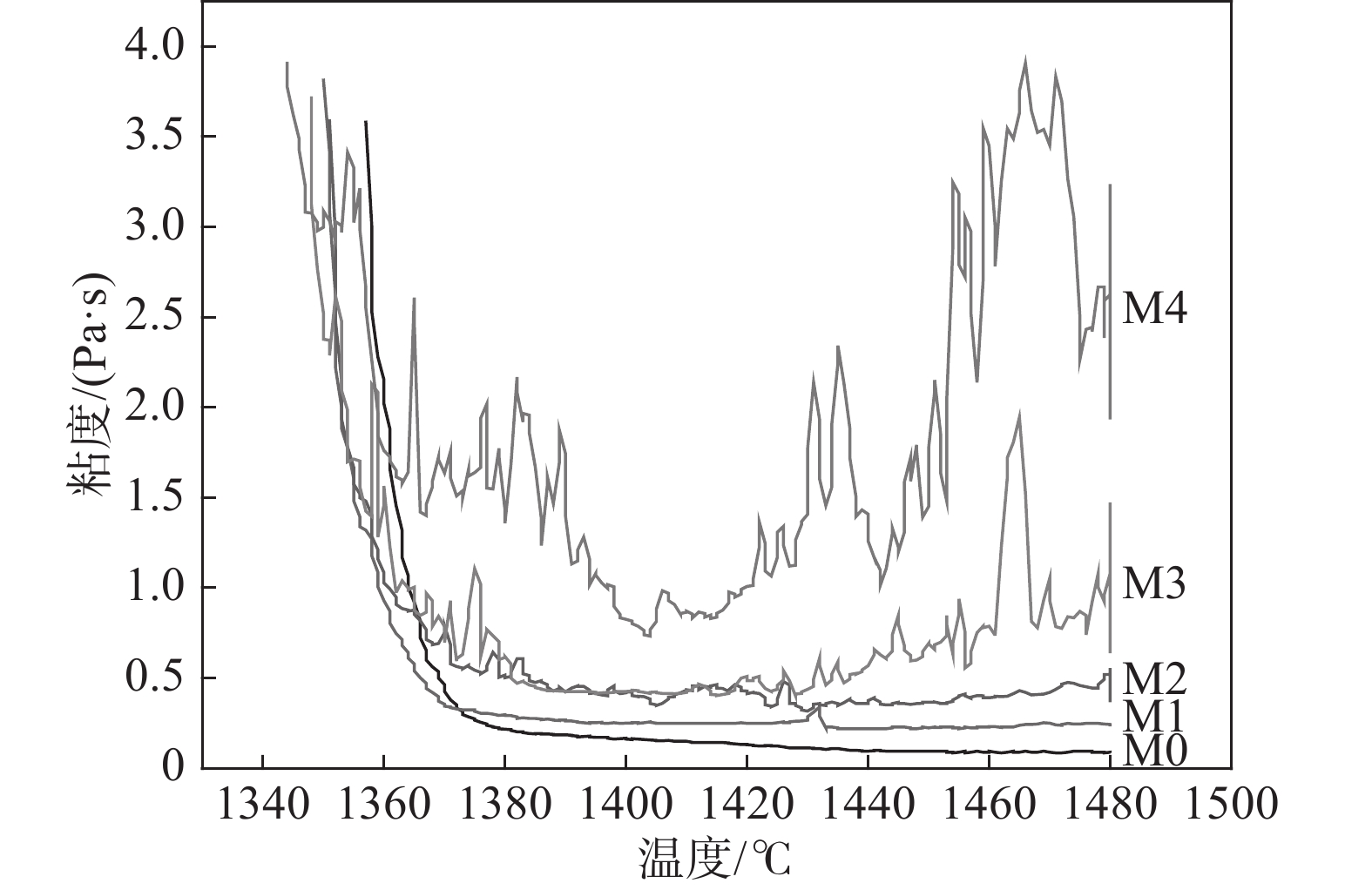
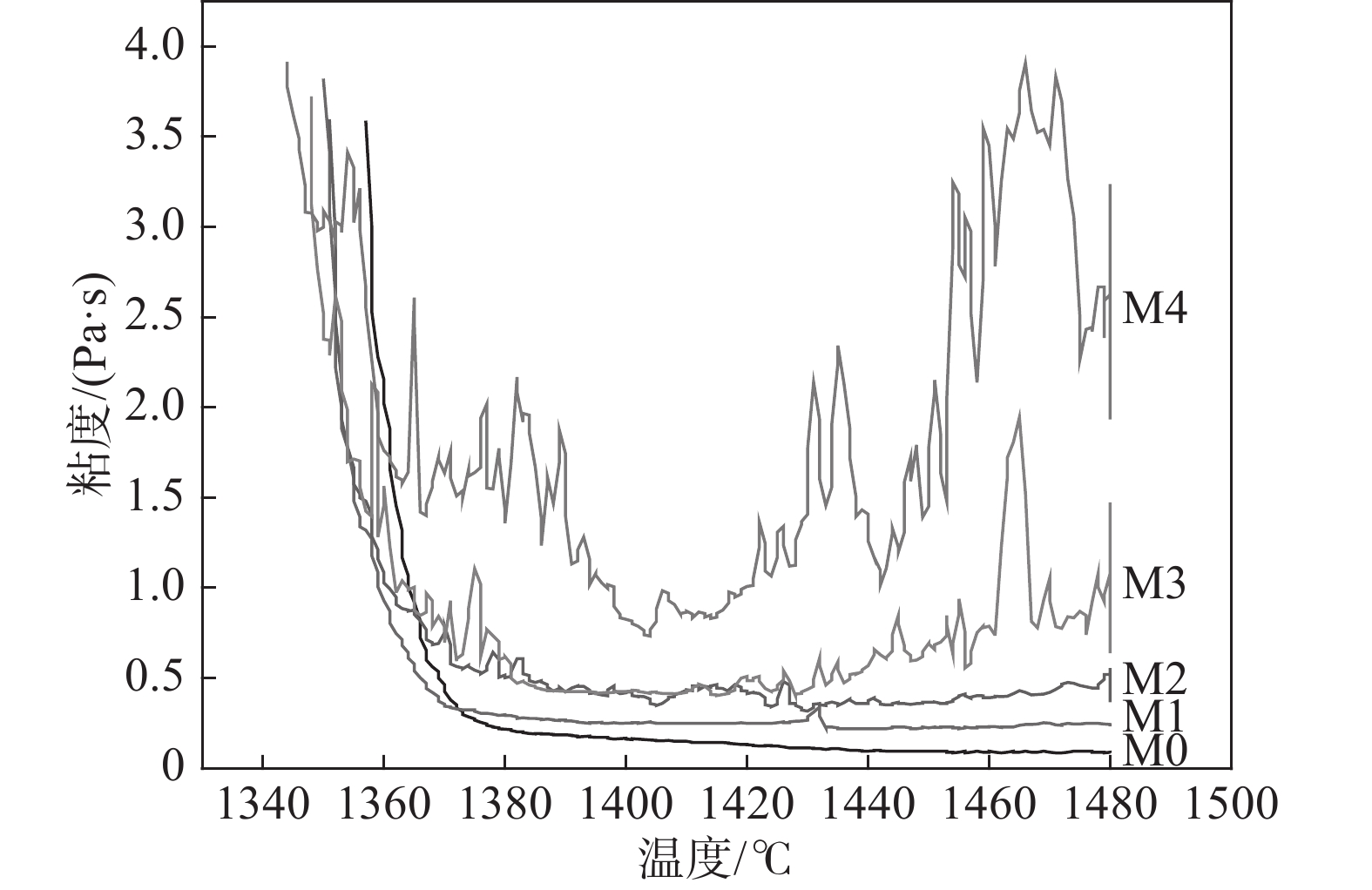
配加未燃煤粉后炉渣的黏度-温度曲线测量结果见图4。由图4可见,当温度较高时,随着渣中初始未燃煤粉增加,在相同温度下炉渣的黏度显著升高、波动明显加剧。样品M0和M1的黏度低于0.25 Pa·s,随温度降低缓慢升高。而样品M2、M3和M4的黏度显著升高,M3和M4的黏度值随温度降低剧烈波动。M4在
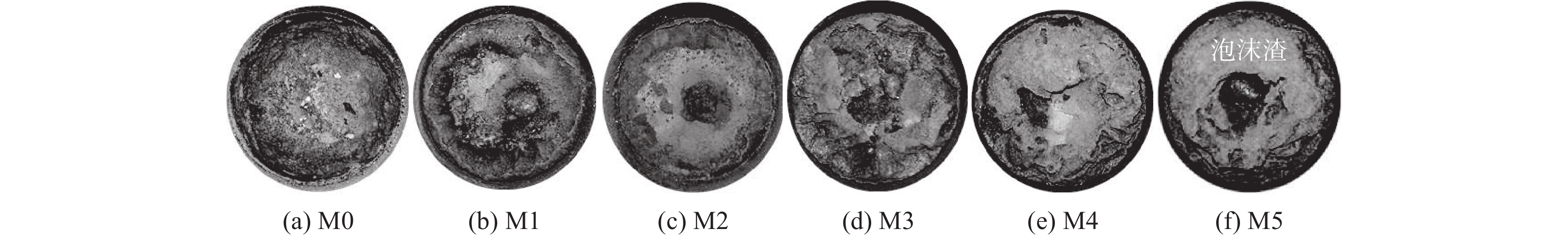
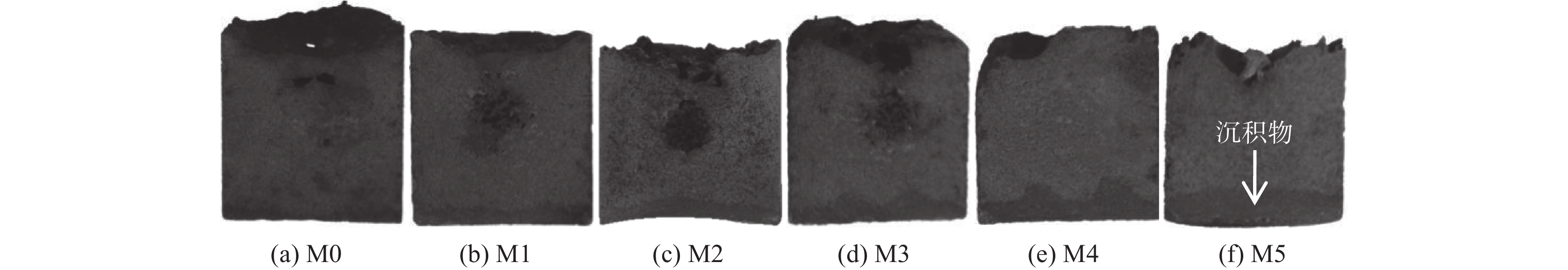
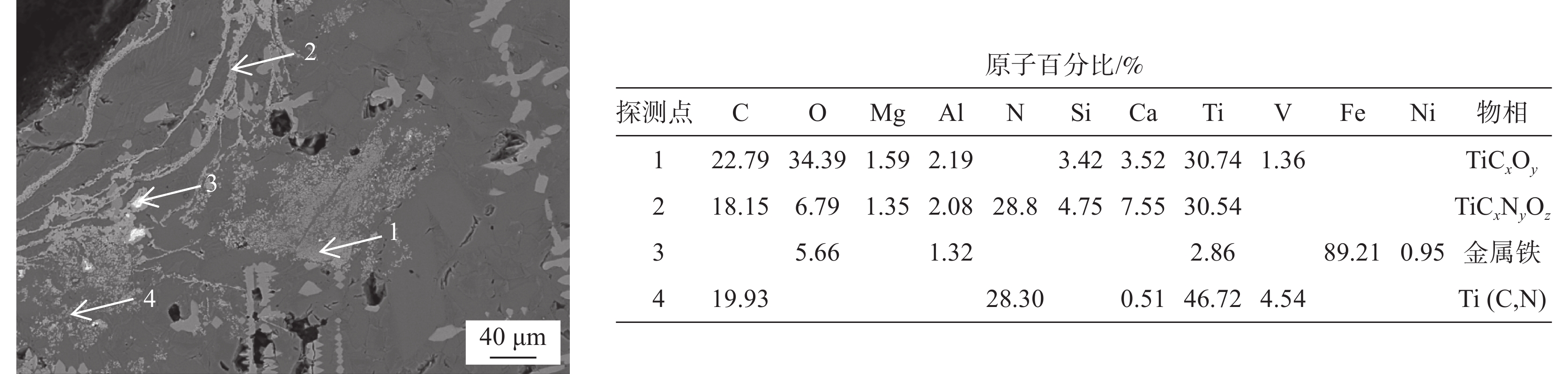
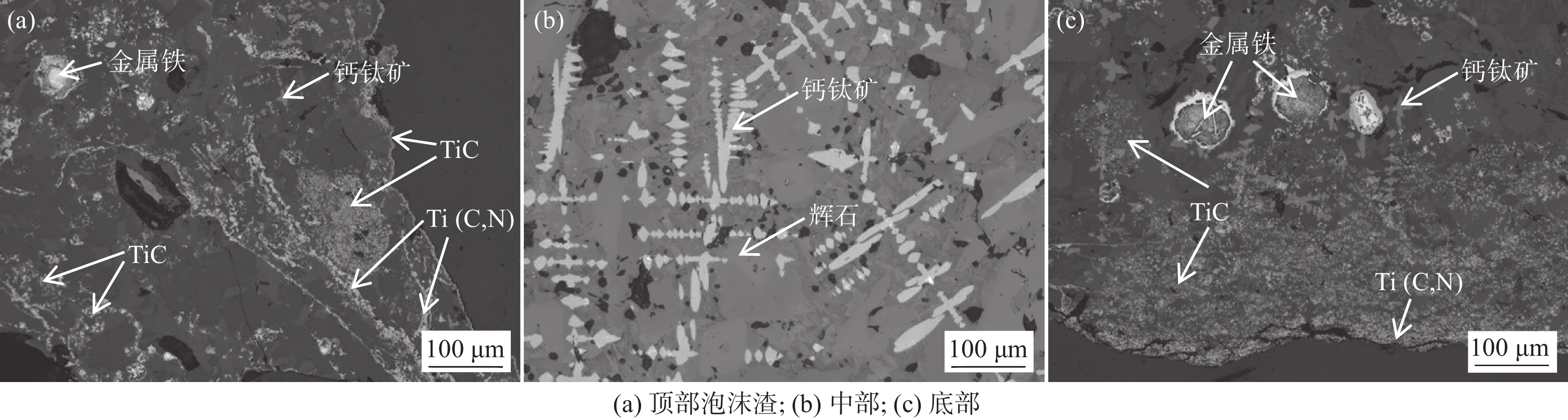
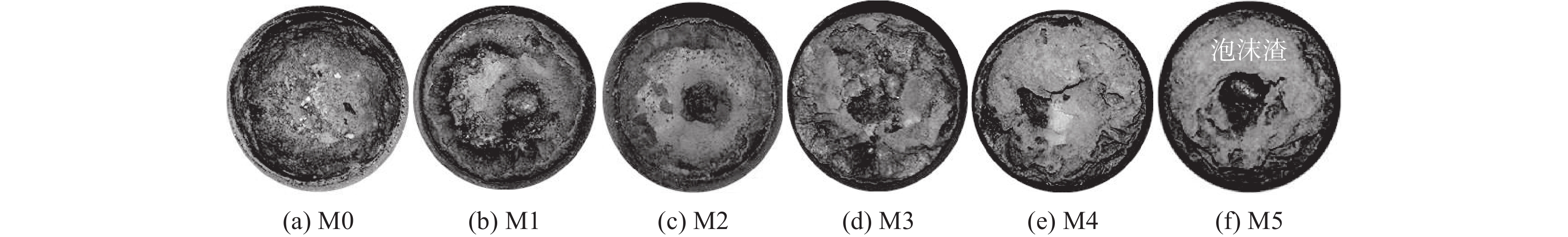
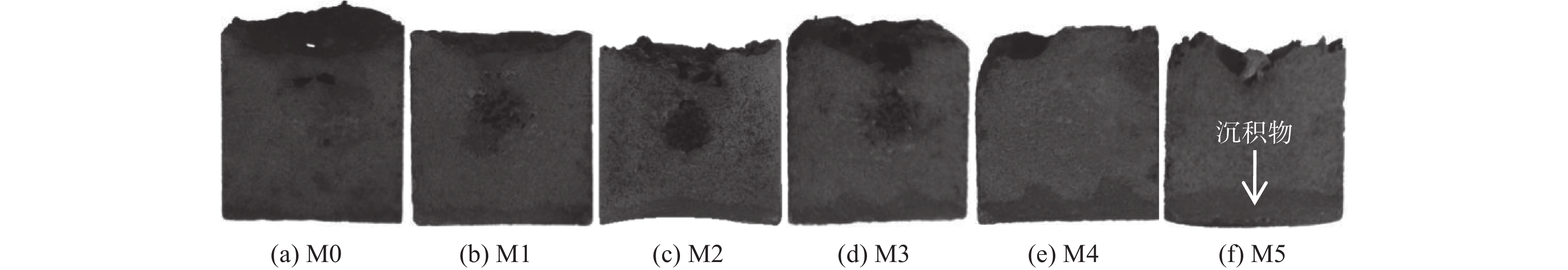
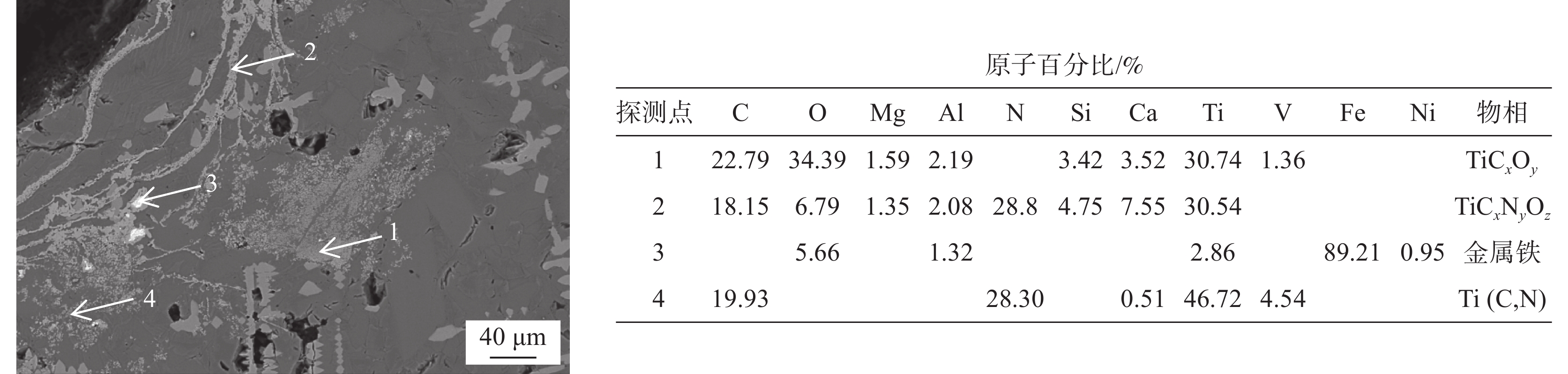
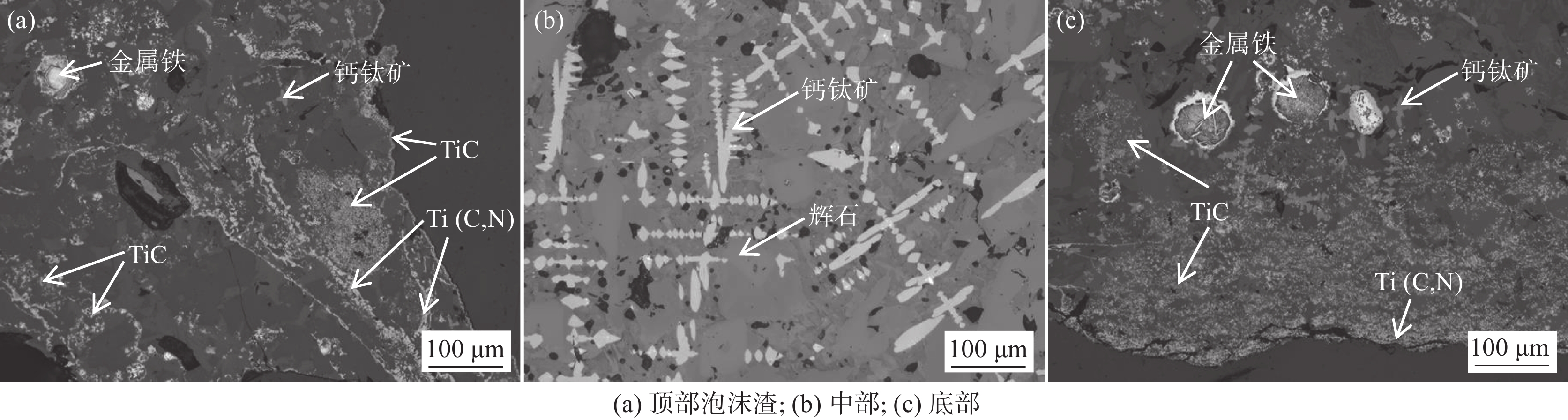
1460 ~1475 ℃的黏度大于3.5 Pa·s,在1400 ~1420 ℃的黏度却低于1.0 Pa·s。样品M5的黏度超出试验设备测量范围,未得到测量结果。炉渣黏度-温度的测量结果表明,未燃煤粉对高钛型高炉渣的黏度影响显著,随着渣中初始未燃煤粉增加,炉渣的黏度以及波动程度均显著增大。图5为测量结束后样品的俯视照片,图6为将泡沫渣去除后的样品沿纵向从中心剖开的照片。可见,随着初始未燃煤粉增加,在样品顶部逐渐可见明显的泡沫渣。在样品底部可见黑色的沉积物,初始未燃煤粉越多,沉积物越厚。以样品M4为例,其底部以及沉积物的扫描电镜照片和微区能谱分析结果见图7。可见,沉积物富含如Ti(C,N)、碳氮氧化钛等TiO2的还原产物。图8(a)为样品M4顶部泡沫渣的光学显微照片。在泡沫渣中可以观察到大量灰色的TiC和金黄色的Ti(C,N),有的团聚在一起,有的以链状形式分布于渣中。图8(b)为样品M4中部的光学显微照片。可见,M4中部的主要物相为钙钛矿和辉石,几乎观察不到TiC或Ti(C,N)。图8(c)为样品M4底部的光学显微照片,可以观察到大量TiC和Ti(C,N)聚集于炉渣底部,金属铁的聚集程度有所增加。
以上结果表明,在高温下未燃煤粉与渣中TiO2发生了反应,反应产物主要是TiC、Ti(C,N)和TiCxNyOz,主要分布于样品的底部或聚集于顶部的泡沫渣中,样品中部几乎没有这些还原产物。在黏度-温度曲线的测量过程中,钼测头没有直接接触到底部的沉积物,沉积物对测量的黏度值的影响很小。样品中部的还原产物少,也不会使炉渣黏度显著升高。在测量过程中,有部分未燃煤粉悬浮于样品顶部并持续与渣中TiO2反应生成高熔点的物质和气泡,从而形成泡沫渣[22]。泡沫渣将钼测杆包围并阻碍测杆的旋转,导致测量的黏度显著升高且剧烈波动。渣中初始未燃煤粉越多,顶部的残余未燃煤粉、生成的高熔点物质和泡沫越多,它们对测杆的阻碍越严重,所测得的黏度越大,黏度的波动越剧烈。
2.3 TiO2的还原
黏度-温度曲线测量结束后,不同样品的低价钛化合物含量见表5,表5中TiO2含量为将不同价态的Ti化合物按TiO2换算后的总和。进行化学成分分析时,Ti2O3和TiO为TiO2的中间还原产物,TiC和TiN为最终还原产物。由表5可见,随着渣中初始未燃煤粉增加,渣中TiC和TiN含量之和从0.456%增加至2.515%,Ti2O3和TiO的含量先升高后降低,这种变化规律与Xie等[23]的研究结果一致。
表 5 不同样品的低价钛化合物含量Table 5. Mass fractions of different titanium compounds of slags after viscosity measurements% 编号 TiO2 Ti2O3 TiO TiC TiN M0 21.20 0.897 0.504 0.100 0.356 M1 21.43 2.570 0.955 0.905 0.681 M2 21.64 2.570 1.050 1.110 0.727 M3 21.55 2.270 1.250 1.360 0.681 M4 21.19 0.247 1.910 1.730 0.526 M5 21.24 0.648 1.880 2.190 0.325 TiC和TiN的生成可按式(1)和式(2)表示。
$$ \begin{split} &{\mathrm{TiO}}_{2}+3{\mathrm{C}}={\mathrm{TiC}}+2{\mathrm{CO}} \\ &\Delta G^{\theta}=527\;400-336.56T \end{split} $$ (1) $$ \begin{split} &{\mathrm{TiO}}_{2}+2{\mathrm{C}}+1/2{\mathrm{N}}_{2}={\mathrm{TiN}}+2{\mathrm{CO}} \\ &\Delta G^{\theta}=375\;900-255.86T \end{split}$$ (2) 在标准状态下,TiC和TiN的开始生成温度分别为
1294 ℃和1196 ℃。根据高炉解剖的结果[24],在软熔带顶部就有TiC和TiN生成。本试验的温度最高达到1480 ℃,远高于TiC和TiN的生成温度,因此TiO2不可避免地会与未燃煤粉反应生成Ti2O3、TiO、TiC和TiN。初始未燃煤粉是影响TiO2还原以及TiC和TiN含量的关键因素。以RO表示TiO2的失氧率,RTCN表示Ti(C,N)的生成率,RC表示未燃煤粉的碳消耗率,如式(3) ~ (5)所示。
$$ R_{{\mathrm{O}}}={\mathrm{O}}_{{\mathrm{loss}}}/{\mathrm{O}}_{{\mathrm{TiO}}_2}\times 100\% $$ (3) $$ R_{{\mathrm{TCN}}}={\mathrm{Ti}}_{{\mathrm{TiCN}}}/{\mathrm{Ti}}_{{\mathrm{TiO}}_2}\times 100\% $$ (4) $$ R_C=\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{coms}}/\mathrm{C}_{\mathrm{UPC}}\times100\% $$ (5) 其中,Oloss为TiO2分别还原为Ti2O3、TiO、TiC和TiN时失去的O的质量;${\mathrm{O}}_{{\mathrm{TiO}}_2} $为将Ti2O3、TiO、TiC和TiN换算为TiO2时失去的O的质量;TiTiCN为以TiC和TiN存在的Ti的总质量;${\mathrm{T}}_{{\mathrm{TiO}}_2} $为渣中Ti的总质量;Ccoms为还原TiO2时消耗的C的质量;CUPC为TiO2未被还原时渣中未燃煤粉中C的质量。
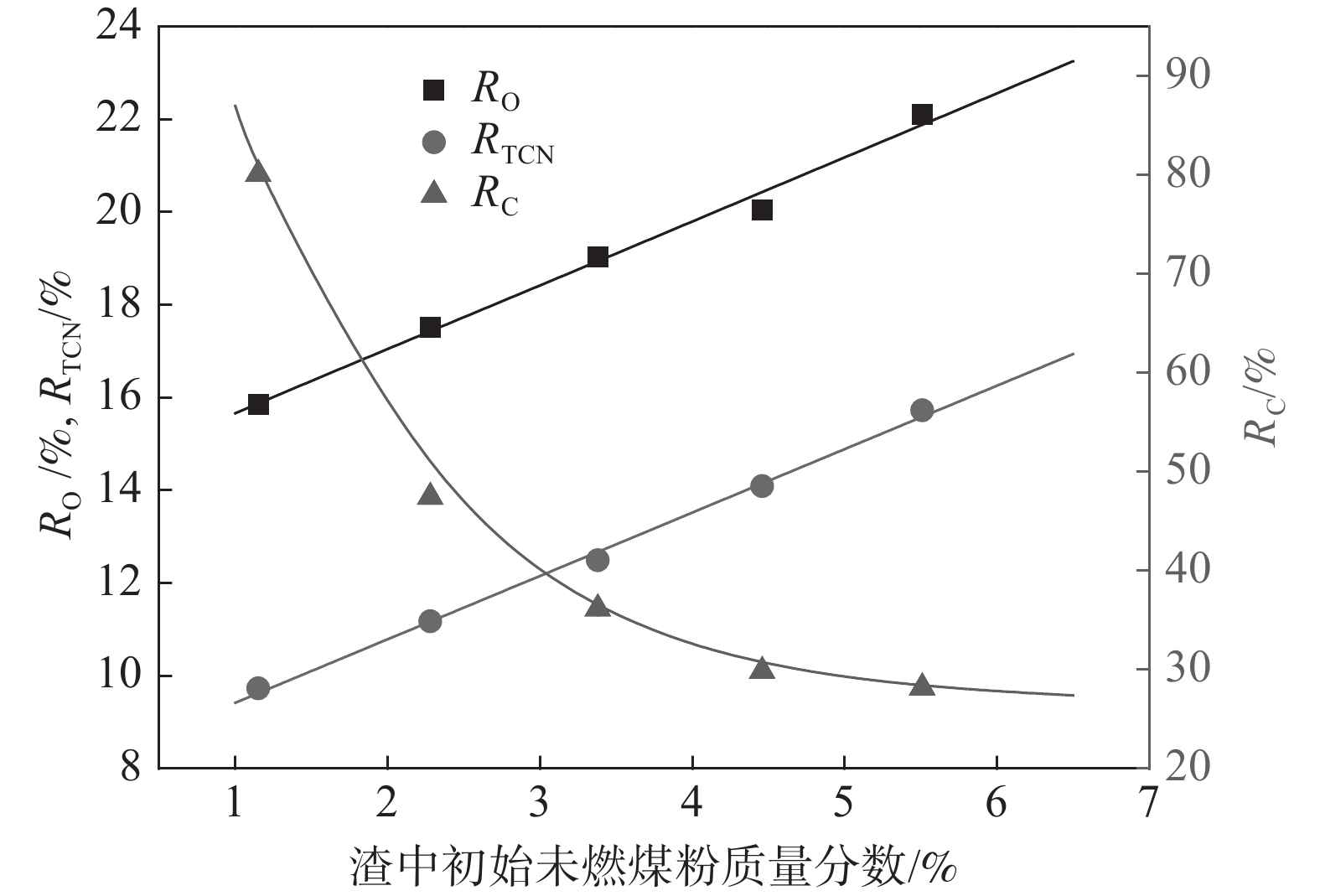
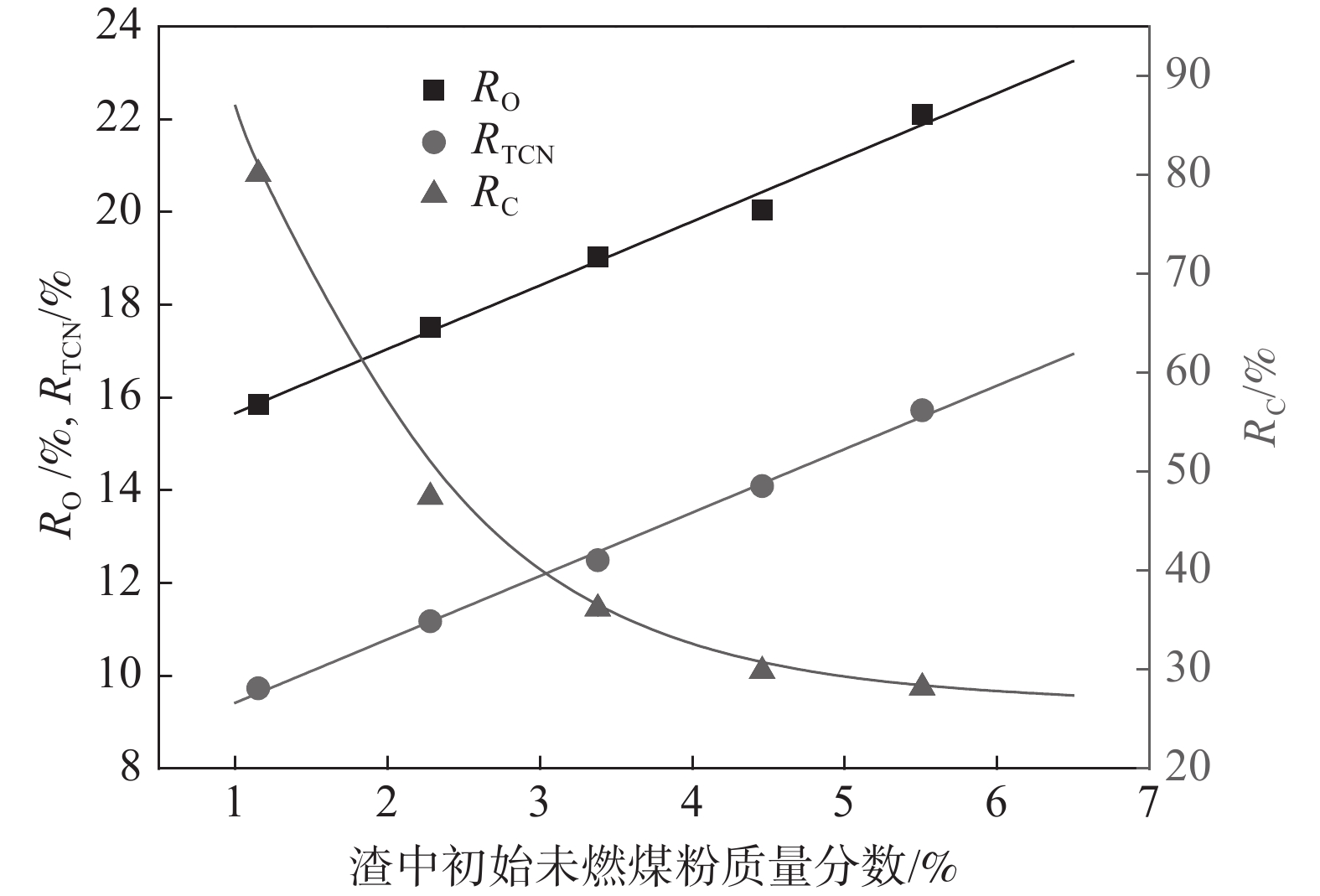
根据炉渣和未燃煤粉的化学成分,可计算得到RO、RC和RTCN,如表6所示。以初始未燃煤粉含量为自变量,RO、RC和RTCN随初始未燃煤粉含量变化的拟合结果见表7和图9。可见,随着初始未燃煤粉增加,RO和RTCN几乎呈线性增大,而RC则呈指数函数形式逐渐减小。这种差异表明未燃煤粉中C的消耗速率和渣中TiO2的还原速率远低于渣中初始未燃煤粉的增加速率。由此可知,未燃煤粉在渣中可以向上运动,其中一些来不及与渣中TiO2反应就到达了炉渣顶部。如果初始未燃煤粉的含量很低,绝大多数的未燃煤粉会被炉渣捕获而被消耗掉。随着初始未燃煤粉含量增大,TiO2与未燃煤粉的接触机会增加,促进了还原反应的发生,使消耗的未燃煤粉和还原产物增加,因此RO和RTCN增大。另一方面,未燃煤粉消耗的增加幅度小于初始未燃煤粉含量的增加幅度,相应地,残余的未燃煤粉迅速增加,因此Ccoms与CUPC的比值显著减小,RC呈指数函数形式减小。
表 6 RO、RC和RTCN的计算结果Table 6. The calculation results of RO, RC and RTCN编号 Oloss/g ${\mathrm{O}}_{{\mathrm{TiO}}_2} $/g RO/% Ccoms/g CUPC/g RC/% TiTiCN/g ${\mathrm{Ti}}_{{\mathrm{TiO}}_2} $/g RTCN/% M1 2.28 14.40 15.85 1.392 1.74 80.08 2.10 21.61 9.73 M2 2.52 14.38 17.51 1.633 3.44 47.44 2.41 21.57 11.17 M3 2.70 14.16 19.04 1.845 5.10 36.17 2.65 21.24 12.49 M4 2.76 13.77 20.05 2.008 6.72 29.86 2.91 20.65 14.09 M5 3.02 13.65 22.10 2.342 8.31 28.18 3.22 20.47 15.72 表 7 RO、RC和RTCN的拟合结果Table 7. The calculation results of RO, RC and RTCNequation a b c Adj. R2 RO y = a + bx 14.28 1.38 0.988 RTCN y = a + bx 8.05 1.37 0.996 RC y = aexp(-x/b) + c 136.27 1.23 26.70 0.999 炉渣黏度降低可能是RC呈指数函数减小的主要原因。炉渣黏度与温度的关系通常可表示为Weymann–Frenkel’s方程[25],如式(6)所示。
$$ \eta=\mathrm{\mathit{A}\mathit{T}exp}(E_{\eta}/\mathrm{\mathit{R}}T) $$ (6) 其中,A为比例常数;Eη为粘流表观自由能;R为气体常数;T为绝对温度。
随着黏度降低,与TiO2反应的未燃煤粉中的C以及RO和RTCN随着初始未燃煤粉含量线性增加。当炉渣变为液态以后,黏度随着温度升高以指数函数形式减小,炉渣对未燃煤粉向上浮动的阻力也以指数函数形式减小,促使未与渣中TiO2反应的未燃煤粉中的C以指数函数形式增加,因此RC以指数形式减小。
2.4 未燃煤粉及其还原产物在渣中的分布和行为
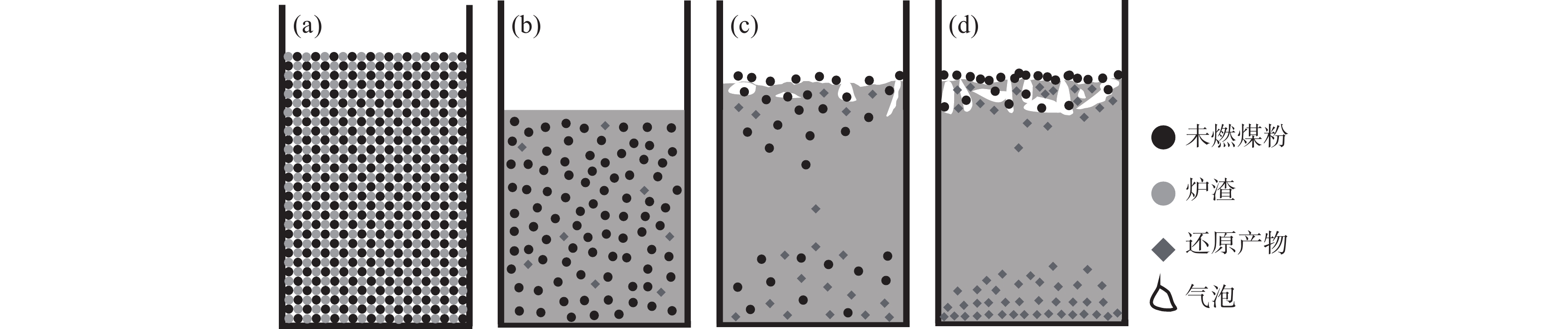
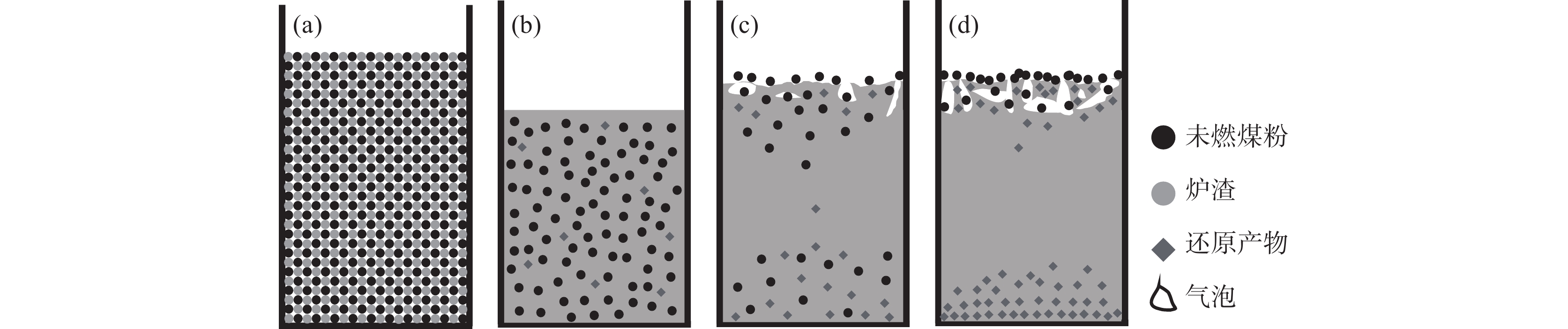
根据试验结束后对残余未燃煤粉的收集和分析,由图5、图6所示的炉渣宏观照片以及图8所示的不同部位的光学显微照片可知,试验前混合均匀的炉渣和未燃煤粉在试验结束后,残余的未燃煤粉向上运动并继续参与还原反应,已生成的高熔点物质则向下沉降聚集,由此可推测得到未燃煤粉及其还原产物在炉渣中的分布和行为,如图10所示。可见,在试验开始时,炉渣与煤粉混合均匀(图10(a))。随着温度升高,炉渣逐渐熔化变为液态。在此过程中,随着TiO2被未燃煤粉还原,还原产物逐渐增加(图10(b))。温度进一步升高,未被还原的炉渣黏度减小,对未燃煤粉上升和还原产物沉降的阻力减小。因此,残余的未燃煤粉逐渐向上浮动并聚集在炉渣顶部,还原产物则逐渐向下沉降并聚集在炉渣底部(图10(c)),在炉渣中部则没有未燃煤粉残留以及少量的还原产物(图10(d))。这样,残余的未燃煤粉和还原产物并没有均匀分布于渣中。大多数的还原产物沉降聚集于底部,部分分布于顶部的泡沫渣中,极少数分布中部。而残余的未燃煤粉聚集于顶部或泡沫渣中。
还原产物比液态炉渣的的密度大,如TiC的密度为4.92~4.938 g/cm3、TiN的密度为5.43 g/cm3 [14],而液态炉渣的密度约2.8~3.2 g/cm3 [26],因此,还原产物会向下沉降并逐渐聚集于渣样底部。未燃煤粉的密度只有1.25~1.8 g/cm3 [27],远低于液态炉渣的密度,当未燃煤粉的重力和液态炉渣对它的阻力之和小于煤粉颗粒受到的向上的浮力时,残余的未燃煤粉就会从液态炉渣内部向上运动,最终在顶部与渣中TiO2反应形成泡沫渣。
因此,配加未燃煤粉的炉渣最终将变为底部聚集高熔点还原产物、顶部形成泡沫渣和残余未燃煤粉、中间为正常炉渣的混合物。由此可以推断,在实际生产过程中,进入炉缸的未燃煤粉不可避免地会与渣中TiO2反应,高熔点的还原产物如TiC、TiN和Ti(C,N)等将沉积于渣铁界面或焦炭表面。随着未燃煤粉增加,沉积的还原产物增加,严重时可能导致炉缸堆积。而残余的未燃煤粉随煤气流向上运动,部分随煤气流从炉顶逸出炉外,部分被滴落的炉渣捕获,进一步反应生成高熔点物质或泡沫渣,这可能导致滴落带焦炭柱透气透液性的恶化。而在此过程中形成的高熔点还原产物最终仍将进入炉缸中。
3. 结论
1)未燃煤粉对高钛型高炉渣的黏度有显著影响,随着渣中初始未燃煤粉增加,在相同温度下炉渣的黏度显著升高,黏度波动明显加剧。
2)未燃煤粉不可避免地会与渣中TiO2反应生成如TiC、TiN、TiCxNyOz或Ti(C,N)等高熔点物质。高熔点物质向下沉降聚集,残余的未燃煤粉则向上运动与上部炉渣中的TiO2继续反应生成高熔点物质或形成泡沫渣,并导致炉渣黏度显著升高。
-
表 1 喷吹煤粉和未燃烧煤粉的化学成分
Table 1. Chemical compositions of PCI and UPC
% 名称 Cad Vdaf Ad St 灰分分析 CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 Fe2O3 TiO2 K2O Na2O 喷吹煤粉 80.60 9.78 11.74 0.78 1.88 49.51 0.44 38.13 3.90 1.18 0.722 1.32 未燃煤粉 88.70 0.17 11.97 0.48 2.10 50.54 0.54 37.65 3.36 1.38 0.66 1.13 表 2 基准高炉渣化学成分
Table 2. Chemical composition of on-site blast furnace slag
% CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 MnO FeO TiO2 Ti2O3 TiO TiC TiN 26.46 25.52 8.40 13.70 0.63 1.03 21.20 0.897 0.504 0.100 0.356 表 3 炉渣未燃煤粉配加方案
Table 3. Adding scheme of UPC to slag
编号 燃烧率/% 炉渣质量/g 未燃煤粉质量/g 未燃煤粉含量/% M0 100 170.00 0 0 M1 90 168.04 1.96 1.15 M2 80 166.12 3.88 2.28 M3 70 164.25 5.75 3.38 M4 60 162.42 7.58 4.46 M5 50 160.63 9.37 5.51 表 4 残余未燃煤粉的质量和C含量
Table 4. The mass and C contents of unconsumed UPC
编号 质量/g C/% M1 0.87 84.40 M2 2.77 84.80 M3 4.00 85.80 M4 6.82 86.00 M5 7.50 86.90 表 5 不同样品的低价钛化合物含量
Table 5. Mass fractions of different titanium compounds of slags after viscosity measurements
% 编号 TiO2 Ti2O3 TiO TiC TiN M0 21.20 0.897 0.504 0.100 0.356 M1 21.43 2.570 0.955 0.905 0.681 M2 21.64 2.570 1.050 1.110 0.727 M3 21.55 2.270 1.250 1.360 0.681 M4 21.19 0.247 1.910 1.730 0.526 M5 21.24 0.648 1.880 2.190 0.325 表 6 RO、RC和RTCN的计算结果
Table 6. The calculation results of RO, RC and RTCN
编号 Oloss/g ${\mathrm{O}}_{{\mathrm{TiO}}_2} $/g RO/% Ccoms/g CUPC/g RC/% TiTiCN/g ${\mathrm{Ti}}_{{\mathrm{TiO}}_2} $/g RTCN/% M1 2.28 14.40 15.85 1.392 1.74 80.08 2.10 21.61 9.73 M2 2.52 14.38 17.51 1.633 3.44 47.44 2.41 21.57 11.17 M3 2.70 14.16 19.04 1.845 5.10 36.17 2.65 21.24 12.49 M4 2.76 13.77 20.05 2.008 6.72 29.86 2.91 20.65 14.09 M5 3.02 13.65 22.10 2.342 8.31 28.18 3.22 20.47 15.72 表 7 RO、RC和RTCN的拟合结果
Table 7. The calculation results of RO, RC and RTCN
equation a b c Adj. R2 RO y = a + bx 14.28 1.38 0.988 RTCN y = a + bx 8.05 1.37 0.996 RC y = aexp(-x/b) + c 136.27 1.23 26.70 0.999 -
[1] Xu Wanren, Wu Ken, Zhu Renliang, et al. Influence of increasing PCI rate on characteristics of tuyere coke in blast furnace[J]. Iron and Steel, 2005,40(2):11-14. (徐万仁, 吴铿, 朱仁良, 等. 提高喷煤量对高炉风口焦性状的影响[J]. 钢铁, 2005,40(2):11-14.Xu Wanren, Wu Ken, Zhu Renliang, et al. Influence of increasing PCI rate on characteristics of tuyere coke in blast furnace[J]. Iron and Steel, 2005, 40(2): 11-14. [2] Yuji Iwanag. Investigation on behavior of unburnt pulverized coal in blast furnace[J]. ISIJ International, 1991,31(5):494-499. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.31.494 [3] Tang Qinhua, He Dahua, Ma Shuhan. Combustion of pulverized coal injected with oxygen enriched blast and its influence on blast furnace operation[J]. Iron and Steel, 1989,24(1):5-9, 21. (汤清华, 何大华, 马树涵. 高炉富氧喷煤的煤粉燃烧及其对高炉冶炼的影响[J]. 钢铁, 1989,24(1):5-9, 21.Tang Qinhua, He Dahua, Ma Shuhan. Combustion of pulverized coal injected with oxygen enriched blast and its influence on blast furnace operation[J]. Iron and Steel, 1989, 24(1): 5-9, 21. [4] Zhu Zizong, Zhang Binghuai, Xu Chushao. Limit of injected coal rate under oxygen-rich high PCI rate at Pangang 4# BF[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1998,19(4):1-5. (朱子宗, 张丙怀, 徐楚韶. 攀钢4#高炉富氧大喷煤条件下喷煤极限研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1998,19(4):1-5. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1998.04.001Zhu Zizong, Zhang Binghuai, Xu Chushao. Limit of injected coal rate under oxygen-rich high PCI rate at Pangang 4# BF[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1998, 19(4): 1-5. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1998.04.001 [5] Liu Xin, Chen Xingqiu. Experimental investigation on behavior of UPC (unburnt pulverized coal) in blast furnace[J]. Journal of Northeast University (Natural Science), 2000,21(2):177-180. (刘新, 陈星秋. 未燃煤粉在高炉内的分布特性的实验研究[J]. 东北大学学报, 2000,21(2):177-180.Liu Xin, Chen Xingqiu. Experimental investigation on behavior of UPC (unburnt pulverized coal) in blast furnace[J]. Journal of Northeast University (Natural Science), 2000, 21(2): 177-180. [6] Wang Zhumin, Lü Qin, Wang Lei. Analysis of UPC in BF coal injection process[J]. Journal of Northeast University (Natural Science), 2010,31(2):389-393. (王竹民, 吕庆, 王磊. 高炉喷煤过程中未燃煤粉分析[J]. 东北大学学报(自然科学版), 2010,31(2):389-393.Wang Zhumin, Lü Qin, Wang Lei. Analysis of UPC in BF coal injection process[J]. Journal of Northeast University (Natural Science), 2010, 31(2): 389-393. [7] Zhen Tao, Wu Ken, Xu Wanren, et al. Ratio between unconsumed pulverized coal and coke in BF dust[J]. Iron and Steel, 2006,41(3):20-24. (郑涛, 吴铿, 徐万仁, 等. 高炉炉尘中未消耗煤粉和焦炭比例的研究[J]. 钢铁, 2006,41(3):20-24.Zhen Tao, Wu Ken, Xu Wanren, et al. Ratio between unconsumed pulverized coal and coke in BF dust[J]. Iron and Steel, 2006, 41(3): 20-24. [8] Li Yanjiang, Zhang Jianliang, Wang Guangwei, et al. Assessment on the effect of unburned pulverized coal on the properties of coke in blast furnace[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2020,47(3):228-237. doi: 10.1080/03019233.2019.1709699 [9] Yuji Iwanag. Gasification rate analysis of unburnt pulverized coal in blast furnace[J]. ISIJ International, 1991,31(5):500-504. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.31.500 [10] Chai Yifan, Luo Guoping, An Shengli, et al. Influence of unburned pulverized coal on gasification reaction of coke in blast furnace[J]. High Temp. Mater. Proc, 2019,38:733-738. doi: 10.1515/htmp-2019-0016 [11] Xiang D W, Shen F M, Jiang X, et al. Protective mechanism of unburned pulverized coal to coke in blast furnace[J]. J. Min. Metall. Sect. B-Metal, 2019, 55 (3): 371-380. [12] Xiang Dongwen, Shen Fengman, Jiang Xin, et al. Effect of unburned pulverized coal on the melting characteristics and fluidity of blast furnace slag[J]. Crystals, 2021(11):579. [13] Gao Peng, Wei Jun, Li Huajun, et al. An experimental study of effect of unburned pulverized coal on properties of coke and slag[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Technology (Natural Science), 2018,35(1):1-4. (高鹏, 魏军, 李华军, 等. 未燃煤粉对焦炭和炉渣性能影响的实验研究[J]. 安徽工业大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,35(1):1-4.Gao Peng, Wei Jun, Li Huajun, et al. An experimental study of effect of unburned pulverized coal on properties of coke and slag[J]. Journal of Anhui University of Technology (Natural Science), 2018, 35(1): 1-4. [14] Jams F Shackelford, Yong Hwan Han, Sukyoung Kim, et al. CRC materials science and engineering handbook[M]. 4th ed. London New York, Boca Raton, CRC Press, 2016: 344-400. [15] Morizane Y, Ozturk B, Fruehan R J. Thermodynamics of TiOx in blast furnace–type slags[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1999,30B:29-43. [16] Liu Y X, Zhang J L, Zhang G H, et al. Influence of Ti(C0.3N0.7) on viscosity of blast furnace slags[J]. Ironmaking and Steelmaking, 2017,44(8):609-618. doi: 10.1080/03019233.2016.1223907 [17] Jiang Tao, Liao Demin, Zhou Mi, et al. Rheological behavior and constitutive equations of heterogeneous titanium-bearing molten slag[J]. International Journal of Minerals, Metallurgy and Materials, 2015,22(8):804-810. doi: 10.1007/s12613-015-1137-4 [18] Bai Chengguang, Pei Henian, Zhao Shijin, et al. An investigation of the relationship between the particle size of titanium carbonitride and the viscosity of blast furnace slag bearing high titania[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1995,16(3):6-9. (白晨光, 裴鹤年, 赵诗金, 等. 碳氮化钛粒度与熔渣粘度关系的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1995,16(3):6-9. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1995.03.002Bai Chengguang, Pei Henian, Zhao Shijin, et al. An investigation of the relationship between the particle size of titanium carbonitride and the viscosity of blast furnace slag bearing high titania[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1995, 16(3): 6-9. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.1995.03.002 [19] J]. Iron and Steel, 2004, 39(9): 14-16. (刁日升, 胡宾生, 攀钢高炉未燃煤粉对炉渣流动性的影响[]J]. 钢铁, 2004, 39(9): 14-16.Diao Risheng, Hu Binsheng. Influence of unburned PCI on the blast furnace slag viscosity in Panzhihua Steel Co [20] Zhu Zizong, Zhang Binhuai, Qiu Guibao. Effect of UPC on the properties of high titanium-bearing slag of blast furnace slag[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 1999,11(4):1-4. (朱子宗, 张丙怀, 邱贵宝. 未燃煤粉对高钛型高炉渣性能的影响[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 1999,11(4):1-4.Zhu Zizong, Zhang Binhuai, Qiu Guibao. Effect of UPC on the properties of high titanium-bearing slag of blast furnace slag[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research, 1999, 11(4): 1-4. [21] Xie Hong’en, Qin Xinguo, Zheng Kui, et al. Analysis of effect factors of smelting temperature of high-taitaium-tpye blast furnace slag[J]. China Metallurgy, 2017,27(9):13-19. (谢洪恩, 秦兴国, 郑魁, 等. 高钛型高炉渣熔化性温度影响因素分析[J]. 中国冶金, 2017,27(9):13-19. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20170058Xie Hong’en, Qin Xinguo, Zheng Kui, et al. Analysis of effect factors of smelting temperature of high-taitaium-tpye blast furnace slag[J]. China Metallurgy, 2017, 27(9): 13-19. doi: 10.13228/j.boyuan.issn1006-9356.20170058 [22] Du Hegui, Guo Xingmin. Study on the formation of foamed slag in blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1986,7(6):12-17. (杜鹤桂, 郭兴敏. 高炉泡沫渣成因的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1986,7(6):12-17.Du Hegui, Guo Xingmin. Study on the formation of foamed slag in blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1986, 7(6): 12-17. [23] Xie Dongsheng, Mao Yuwen, Guo Zhaoxin. Viscosity-changing rule of titanium-containing blast furnace slags under reducing conditions[M]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1985, 6(6): 16-26. (谢冬生, 毛裕文, 郭昭信, 等. 高炉钛渣高温还原变粘规律[M]. 钢铁钒钛, 1985, 6(6): 16-26.Xie Dongsheng, Mao Yuwen, Guo Zhaoxin. Viscosity-changing rule of titanium-containing blast furnace slags under reducing conditions[M]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1985, 6(6): 16-26. [24] Zhan Xing. Anatomical study on smelting vanadium titano-magnetite by small blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1984, 5(2): 3-14. (詹星. 小高炉冶炼钒钛铁磁铁矿解剖研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 1984, 5(2): 3-14.Zhan Xing. Anatomical study on smelting vanadium titano-magnetite by small blast furnace[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 1984, 5(2): 3-14. [25] Urbain G. Viscosity estimation of slags[J]. Steel Res., 1987,58:111-116. doi: 10.1002/srin.198701513 [26] Huang Xihu. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2018: 315. (黄希祜. 钢铁冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2018: 315.Huang Xihu. Principles of iron and steel metallurgy[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2018: 315. [27] China Research Institute, Beijing Institute of Coal Chemistry. A laboratory manual of coal[M]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Press, 1981: 550. (煤炭科学研究院, 北京煤化学研究所. 煤炭化验手册[M]. 北京: 煤炭工业出版社, 1981: 550.China Research Institute, Beijing Institute of Coal Chemistry. A laboratory manual of coal[M]. Beijing: China Coal Industry Press, 1981: 550. -






 下载:
下载:









 下载:
下载: