Study on the effects of oxygen enrichment modes on the tuyere raceway states of blast furnace
-
摘要: 依据国内某企业冶炼钒钛磁铁矿高炉的实际尺寸建立了三维物理模型,利用数值模拟的方法对比研究了不同富氧方式下煤粉在风口回旋区内的流动、燃烧行为。结果表明,减风富氧与定风富氧方式工况下,风口气流速度变化随富氧率变化的整体趋势一致,但变化幅度差距显著,即富氧率增加1%,风口截面速度分别增加4.25 m/s(定风)和0.41 m/s(减风)。两种富氧方式下,回旋区内的温度、还原气体含量及煤粉燃尽率与富氧率的变化趋势一样,即富氧率增加,温度增加,高温区域扩大,还原气体含量增加,煤粉的燃尽率上升。其中,减风富氧时由于热风流量减小,带入高炉的N2量减少,煤气中CO和H2的含量变化较大,对高炉减少氮化碳和碳化钛生成、改善铁矿还原效果具有较好的帮助,建议高炉提高富氧率采用减风富氧模式。经计算,富氧率每增加1%,回旋区平均温度增加34.22 K(定风)和32.88 K(减风);减风富氧条件下,富氧率每增加1%,热风带入高炉的N2量减少10 m3/min,煤气中的CO质量浓度上升8.61%。Abstract: In this paper, based on the actual dimension of the vanadium titanomagnetite blast furnace of a domestic enterprise, a three-dimensional physical model is established. The numerical simulation method is used to compare and study the flow and combustion behavior of pulverized coal in the tuyere gyration area under different oxygen enrichment methods. The results show that the overall trend of the tuyere velocity change with the oxygen enrichment rates is consistent with that of the constant air enrichment mode, but the difference in the change amplitude is significant. That is, when the oxygen enrichment rate is increased by 1%, the cross-sectional velocity of the tuyere is increased by 4.25 m/s (fixed air) and 0.41 m/s (reduced air), respectively. Under the two oxygen enrichment modes, the temperature, reducing gas content and burnout rate of the pulverized coal in the gyratory area have the same trend with the oxygen enrichment rates. As temperature increases, the high temperature area expands with the increase in the reducing gas content, and the burnout rate of pulverized coal increases. Among them, the amount of N2 brought into the blast furnace decreases due to the decrease in hot air flow rate, and the content of CO and H2 in the coal gas changes greatly, preventing the formation of carbon nitrides and titanium carbides, and improving the reduction effect of iron ore in the blast furnace. It is calculated that the average temperature of the gyratory zone is increased by 34.22 K (fixed air) and 32.88 K (reduced air) for every 1% increase in the oxygen enrichment rate. Under the condition of reduced air and oxygen enrichment, the N2 content brought into the blast furnace is reduced by 10 m3/min and the CO concentration in the gas is increased by 8.61%.
-
Key words:
- blast furnace /
- oxygen-enriching mode /
- raceway status /
- CFD numerical simulation
-
0. 引言
随着社会的高速发展,钢铁需求量日益增加,钢铁行业在中国国民经济中发挥着不可替代的作用[1]。基于高炉的长流程炼铁工艺是钢铁行业最耗能的工艺之一。为了降低炼铁成本,炼铁工作者在高炉风口喷入更低成本的煤粉来替代焦炭,并为此做出了巨大的努力[2−3],提煤降焦就是炼铁工作者长期以来追求的目标[4−8]。然而,随着煤比的增加,高炉炼铁的污染排放加剧,合理优化高炉生产过程,降低钢铁行业碳排放迫在眉睫。高炉生产采用富氧鼓风与煤粉喷吹相结合,既能强化冶炼,又可以大幅度节约焦炭[9],带来了巨大的经济效益和环保效益,因而得到国内外钢铁企业的充分重视。截至目前,高炉富氧喷煤仍是现代高炉重要的节能减排和低碳绿色技术,是现代高炉炼铁必须坚持发展的重点技术。
高炉富氧喷煤技术始于20世纪初,并随着风口喷吹燃料和工业制氧技术的成熟迅速发展。1979年二次石油危机的爆发使得全世界范围进入高炉喷煤技术应用的高峰期[10]。20世纪90年代以来,为了进一步提高高炉喷煤能力,世界上许多国家,如瑞典、韩国、荷兰等先后对高富氧大喷煤技术进行了研究开发和推广应用。韩国浦项光阳4号高炉,富氧率10.47%,风温
1250 ℃,入炉风量7000 m3/min,达到焦比290 kg/t,煤比200 kg/t,燃料比490 kg/t,利用系数2.5 t/(m3·d),日产铁量13750 t的效果;韩国现代唐津1号高炉,富氧率5.6%,入炉风量7250 m3/min,产生了焦比310 kg/t,煤比180 kg/t的效果[11];荷兰艾莫伊登7号4450 m3高炉的富氧率为10%,入炉风量6400 m3/min,在此工况条件下高炉的焦比为280 kg/t,煤比为230 kg/t,利用系数为2.25 t/(m3·d),日产铁量为10000 t。德国迪林根公司萨尔厂2356 m3高炉,采用30根同轴氧枪喷吹煤粉,喷煤比达到200 kg/t[12]。此外,前苏联是世界各国中高炉用氧最普遍、持续时间最长,也是高炉富氧率最高的国家,富氧率基本维持在10%~20%[10]。总体来看,国外高炉富氧喷煤的整体水平较高。同期我国也开始进行了高富氧大喷煤操作的探索,但由于我国计量、监测、自动控制水平与国外尚有差距,该技术在20世纪末才有较大的发展。80年代末期,鞍钢2#高炉进行富氧大喷吹冶炼试验,最高含氧量达到28.6%,最大喷煤量为170 kg/t ,高炉利用系数从2.28 t/ (m3·d)提高到2.40 t/ (m3·d),引起炼铁界的普遍重视[13]。武钢8号高炉的富氧率可以维持在6%~7%,鼓风湿度10~18 g/m3,燃料比达到了495.89 kg/t,平均日产铁量10000 t,高炉处于较高的冶炼水平[14]。沙钢5800 m3大型高炉的富氧率为9.6%,风温水平1230 ℃,入炉风量7510 m3/min,在该操作条件下,高炉的焦比为341 kg/t,煤比升高至161 kg/t[15]。宝钢4号高炉的富氧率最高达到5.5%,鼓风动能大于15000 kg·m/s,煤比164.7 kg/t,实现日产铁量11533 t,煤气利用率为50.23%的高水平冶炼效果[16]。富氧率的变化会对煤粉的燃烧特性以及高炉下部的温度、气体成分产生较大的影响。但是,由于高炉高温、高压的特性,通过现场直接测量获得数据十分困难,计算机技术的快速发展为解决这一难题提供了一种方便快捷的方法。Computational fluid dynamics (CFD)计算流体动力学,是一种可针对流体流动、传热传质以及化学反应等过程进行计算的方法[17−18]。众多学者利用CFD方法研究了富氧率变化对高炉内状态的影响。Shen等人[19]基于传统高炉尺寸构建高炉风口区域完整模型,研究了鼓风温度、含氧量以及喷煤载气种类对煤粉燃烧的影响,结果表明鼓风含氧量对煤粉燃尽率的影响较其它二者更显著。当氧气浓度从21%增加到25%时,煤粉的燃尽率增加了5%。Zhou等人[20]研究了不同富氧条件下的煤粉的燃烧特性。结果表明,富氧显著提高了氧气的利用率和煤粉燃烧率。O2浓度为24%时煤粉燃尽率为86.29%,相较于基本工况增加了13.13%。Jovanovic等人[21]以不同氧含量下煤粉的着火位置为研究对象,采用试验和数值模拟相互验证的方法,得出了高氧势下煤粉由均匀着火向非均匀着火转变的结论,在此基础上提出了煤粉顺次燃烧的修正模型,该模型的模拟结果与试验结果高度吻合。Nie等人[22]开发了多流体过程模型来模拟富氧率变化对炉内现象的影响,详细分析了氧含量从21%增加至100%时,炉内流动和热化学行为,研究结果显示,富氧量的增加会使得软熔带位置下移,同时发现虽然通过反应产生的热损失增加,但炉顶气体的热损失依旧减少。
前人研究主要基于特定富氧方式下富氧率变化对高炉内状态的影响,而以不同的富氧方式进行富氧操作会如何影响风口回旋区内的温度、煤气成分,进而如何影响高炉的生产过程尚不明确。因此,笔者结合国内某钢厂高炉的实际生产条件,建立了高炉高富氧的风口回旋区三维物理模型,并利用该模型系统地研究了不同富氧方式下富氧率变化对煤粉的燃烧行为、风口和回旋区内的速度场、温度场、气体成分分布的影响,为钢铁厂选择富氧方式和富氧率提供理论支撑。
1. 仿真模型及几何模型描述
笔者基于Ansys-Fluent软件,建立国内某钢厂高炉下部风口区域三维模型,研究不同富氧方式下富氧率变化对煤粉在高炉风口、回旋区内由于气固流动、燃烧行为而引起的煤粉燃尽率、速度场、温度场、气体成分变化情况。建立的下部风口3D模型主要包括直吹管、风口、煤枪、回旋区和焦炭床层。
1.1 基本公式
用欧拉-拉格朗日法求解模型的解,对连续相(气相)在欧拉框架下求解3D Reynolds-averaged Navier−Stokes方程,并用$k - \varepsilon $湍流公式来描述流体区域的湍流流动状态[23]。在公式中,${C_\mu }$,${C_{1\varepsilon }}$,${C_{2\varepsilon }}$,${\sigma _k}$,${\sigma _s}$是常数,分别取0.09,1.44,1.92,1.0,1.3。对于煤粉颗粒的运动,用拉格朗日法来求解,在求解过程中其被视为离散相。且假设粒子为球形,粒子的轨迹受牛顿第二定律影响,考虑粒子在运动过程中受到的阻力作用。煤粉的温度变化受三个物理过程的影响:对流传热、潜热传递、辐射传热[24]。
煤粉燃烧过程由多步交互过程组成:预热阶段、挥发分析出阶段、气体燃烧阶段、残炭的氧化/气化阶段。
在挥发分析出阶段,煤粉经过脱挥发分过程释放出挥发分和残炭,由于煤粉在低温区和高温区脱挥发分速率差别较大,不能采用单步反应模型描述热解焦整个脱挥发分过程。因此,这一过程采用双反应竞争模型进行求解[25],该模型认为煤粉的热解由两个不同速率的反应构成:
$$ {{\mathrm{Pulverized}} - {\mathrm{Coal}}}\xrightarrow{{{k_1}}}{\alpha _1}{\text{V}}{{\text{M}}_1} + (1 - {\alpha _1}){C_1} $$ (1) $$ {{\mathrm{Pulverized}} - {\mathrm{Coal}}}\xrightarrow{{{k_2}}}{\alpha _2}{\text{V}}{{\text{M}}_2} + (1 - {\alpha _2}){C_2} $$ (2) 上述两个反应的化学反应速率常数k统一用阿伦尼乌斯公式计算:
$$ k = A\exp ( - E/T) $$ (3) 挥发分脱出速率可表示为:
$$ \dfrac{\mathrm{d}_w(\text{VM})}{\mathrm{d}t}=(\alpha_1k_1+\alpha_2k_2)C_0 $$ (4) 式中,${k_1}$,${k_2}$分别为低温区和高温区的脱挥发分速率值,m2/s2;${C_0}$为煤粉去除灰分后的质量分数,%;VM为体积模型;两个反应的指前因子和活化能分别为A1=
430000 s−1,A2=1.46×1013 s−1,E1=149000 J/mol,E2=251000 J/mol[26]。${\alpha _1}$取干燥无灰基中挥发分的质量分数,${\alpha _2} = 1.25\alpha _1^2 + 0.92{\alpha _1}$。气体(包括挥发分、CO和H2)的燃烧采用有限速率/涡流耗散模型来模拟计算。总的反应速率为Arrhenius模型中的反应速率$ R_{\mathrm{g,Arr}} $和涡流耗散模型中的反应物的反应速率${R_{{\mathrm{g,EBU,R}}}}$和生成物的反应速率$R_{{\mathrm{g,EBU,R}}}^{'}$的最小值。
$$ {R_{\mathrm{g}}} = \min ({R_{{\mathrm{g,Arr}}}},{R_{{\mathrm{g,EBU,R}}}},R_{{\mathrm{g,EBU,R}}}^{'}) $$ (5) $$ R_{{\mathrm{g, A r r}}}=\left(v_p-v_R\right) M_w\left(k_{r, f} \displaystyle\Pi_R C_R^{\alpha P}-k_{r, b} \displaystyle\Pi_P C_P^{\alpha P}\right) $$ (6) $$ R_{{\mathrm{g, E B U, R}}}=v_R M_w A \rho \frac{\varepsilon}{k} {\min}_{R}\left(\frac{Y_R}{v_R M_w, R}\right) $$ (7) 粒子的表面发生了3种非均相反应(即残碳的氧化和气化),这3种反应用多表面反应模型来模拟和计算。该模型考虑了气体的扩散速率和反应速率,扩散速率可以用以下公式计算得到:
$$ {D_{0,r}} = {C_{j,r}}\frac{{{{[({T_p} + {T_g})/2]}^{0.75}}}}{{{d_p}}} $$ (8) 1.2 几何模型和操作条件
笔者基于国内某钢厂
1750 m3高炉的实际数据进行模拟研究,将模型简化处理,模拟中用到的三维物理模型主要包括直吹管、风口、煤枪、回旋区和焦炭床层。煤粉和载流气体(N2)由煤枪喷入高炉内,富氧热风由直吹管进入。煤枪的直径为20 mm,喷枪中心线与风口中心线夹角为12°。风口直径为120 mm,风口长度为450 mm,风口倾斜角度为6°。通过计算回旋区的深度为1.66 m,与钢铁厂提供的数据相接近。表1中列举了高炉的实际操作条件。表 1 高炉的实际操作条件Table 1. Actual operating conditions of blast furnaces风口数/个 高炉有效容积/m3 风量/(m3·min−1) 风压/kPa 氧气浓度/% 煤比/(kg·t−1) 热风温度/℃ 载气成分 24 1750 4000 360 24(基准工况) 95 1220 氮气 1.3 模型验证
在本文的工作中,由于煤枪与直吹管、风口与回旋区之间存在非正交结构,为了保证网格的质量,网格结构为非结构性网格,回旋区计算域使用比其他区域更细的网格。仿真前进行了网格独立性试验。采用四种不同的网格分辨率(网格数量为
503849 、594677 、702693 和801253 )进行网格独立性分析。在基本工况模拟条件下,四种网格分辨率下的直吹管-风口-回旋区平均温度分别为2230.11 、2229.72 、2230.96 ℃ 和2232.12 ℃。结果几乎是一致的,小的差异可能是由于在网格节点的位置的差距。因此,为了平衡数值精度和效率,笔者选择594677 个网格单元进行后续工作。2. 结果与讨论
本文研究中提到的定风富氧指热风流量一定,富氧率增加后总风量增加的富氧方式;减风富氧指总风量一定,富氧率增加后热风流量减小的富氧方式。为明确不同富氧方式对高炉下部状态的影响,对比研究了减风富氧和定风富氧,富氧率分别为3%、5%、7%、9%、11%时炉内的流场、温度场、浓度场以及煤粉的燃烧特性变化情况。
2.1 基本工况下的炉内现象
结合表1的实际工况参数,选取热风中富氧率为3%,单煤枪插入进行煤粉喷吹,喷枪出口在风口中心线上作为标准工况,对煤粉在高炉内的燃烧过程进行数值模拟,目的在于研究标准工况下高炉喷吹煤粉过程气-固两相的流动、气相温度、炉内气体分布和煤粉燃烧过程特征。
2.1.1 气-固两相流场分布
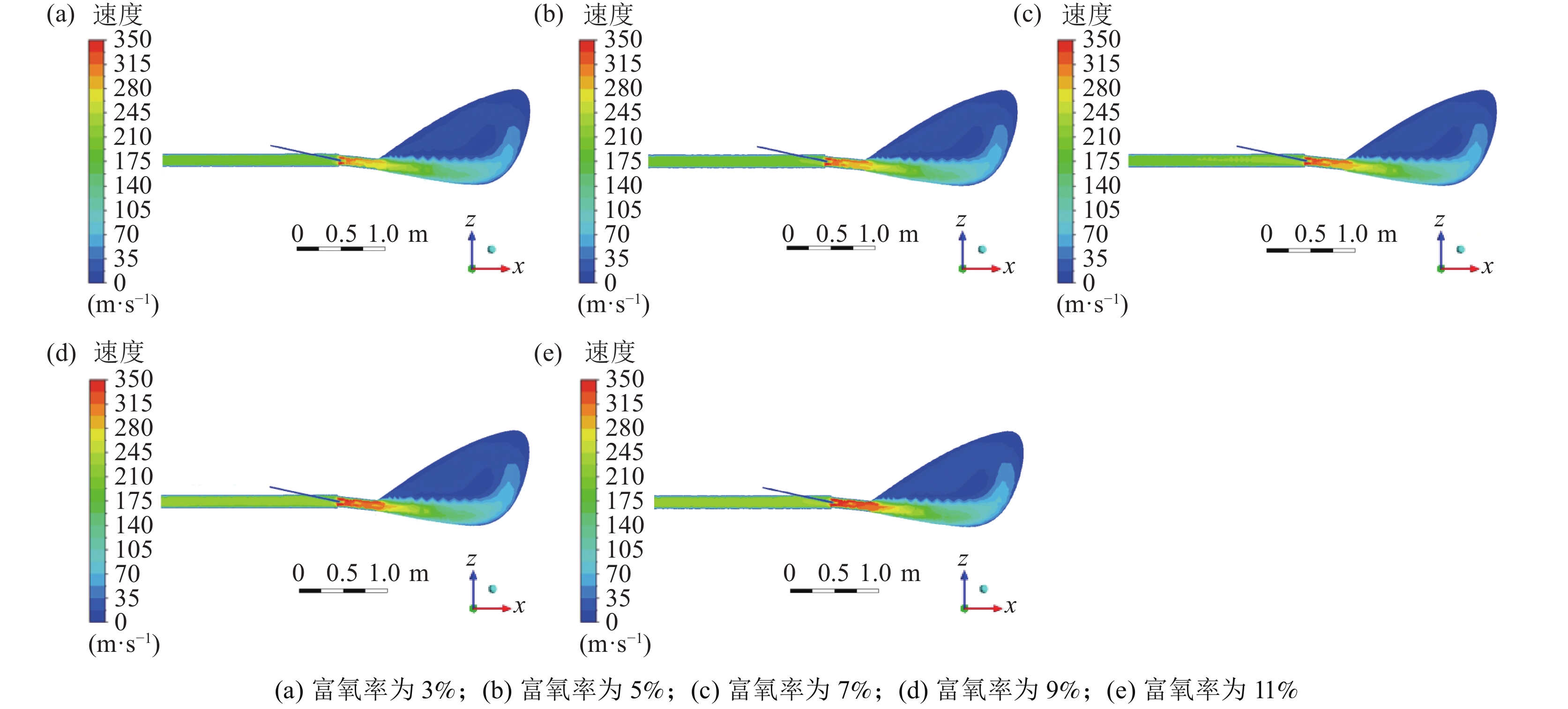
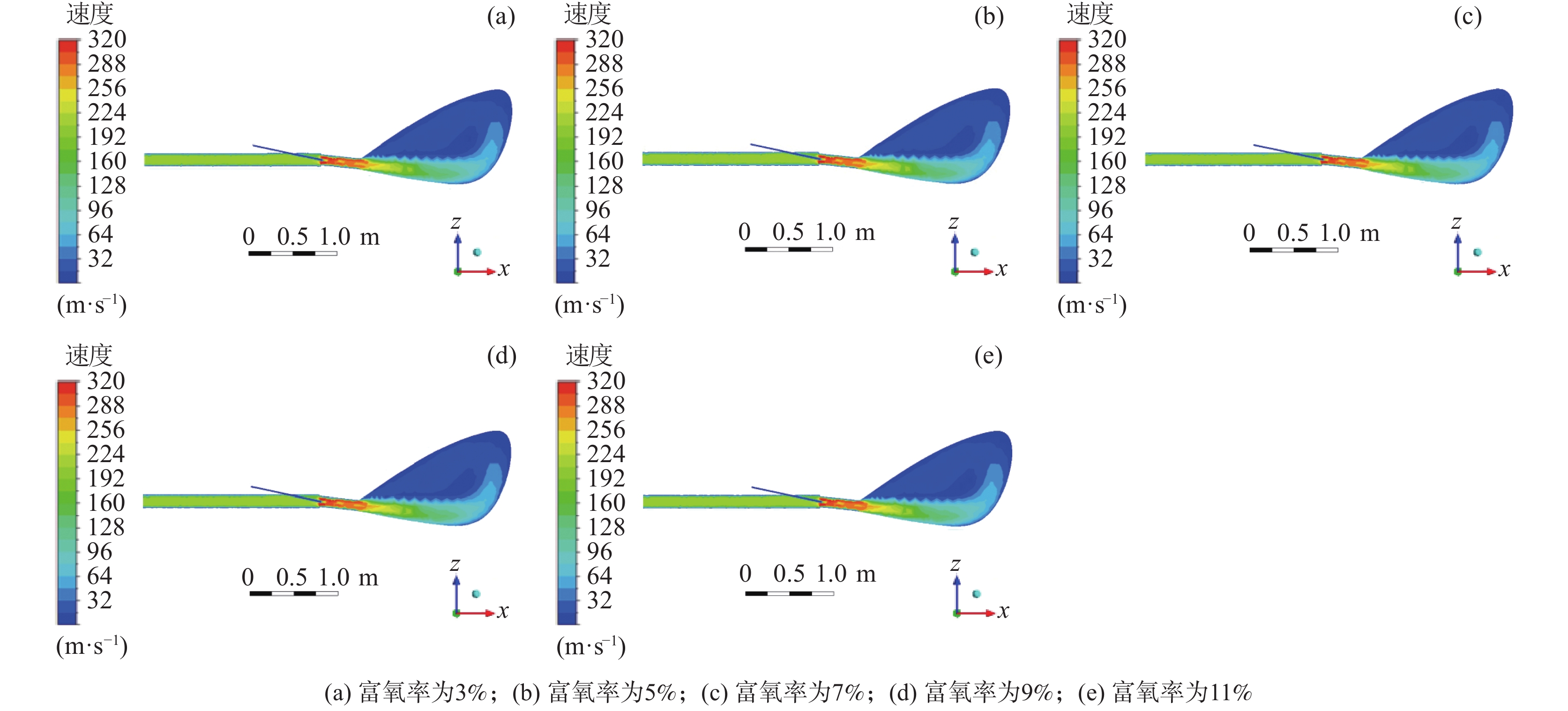
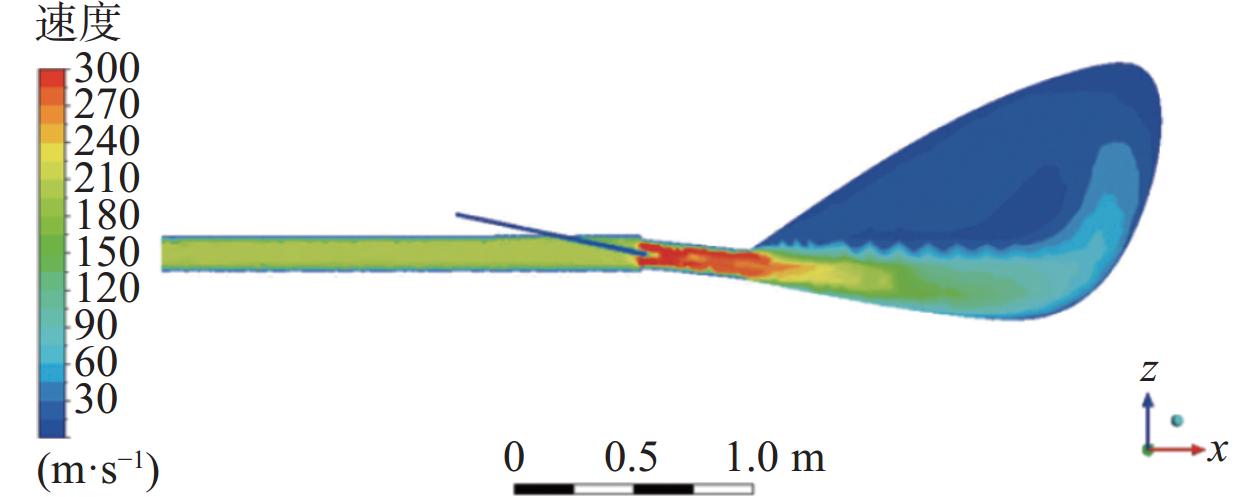
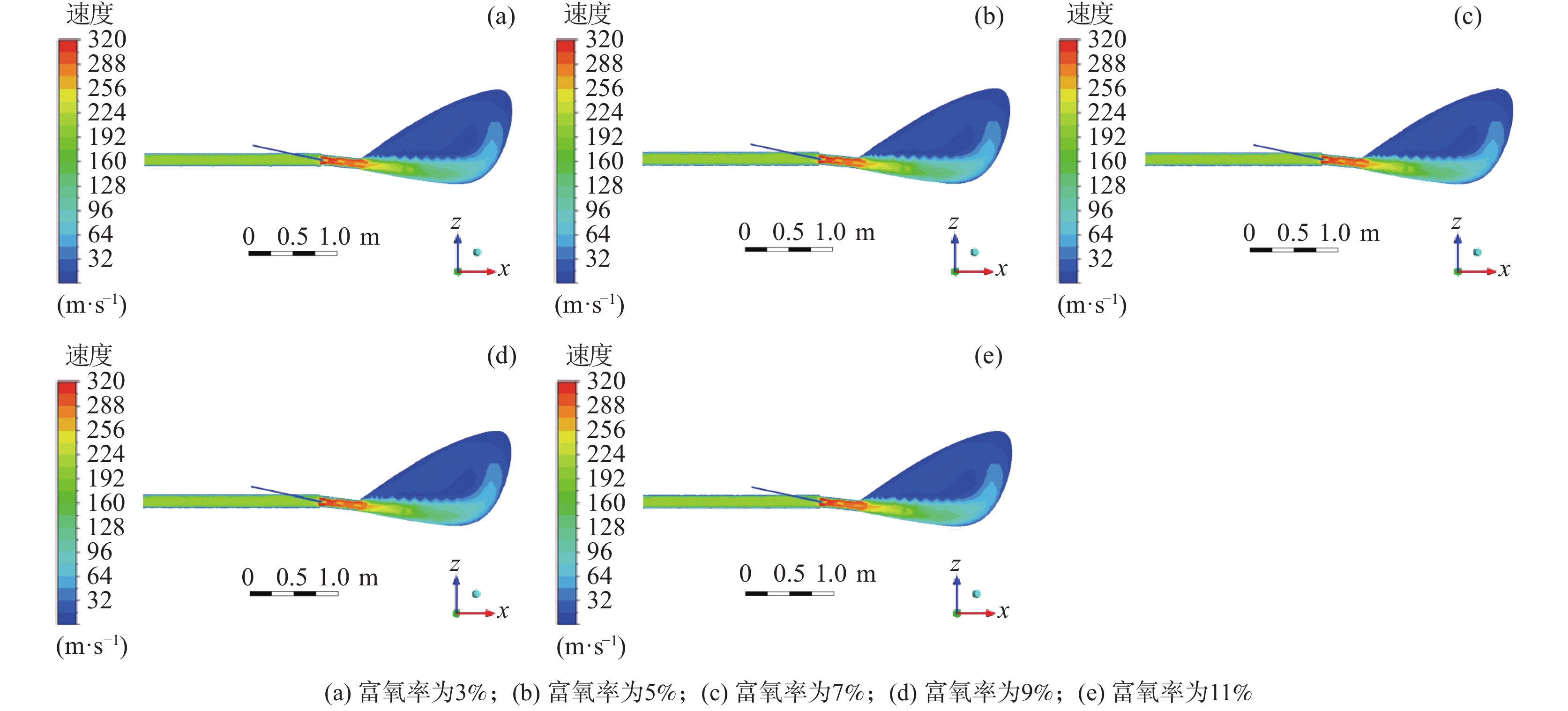
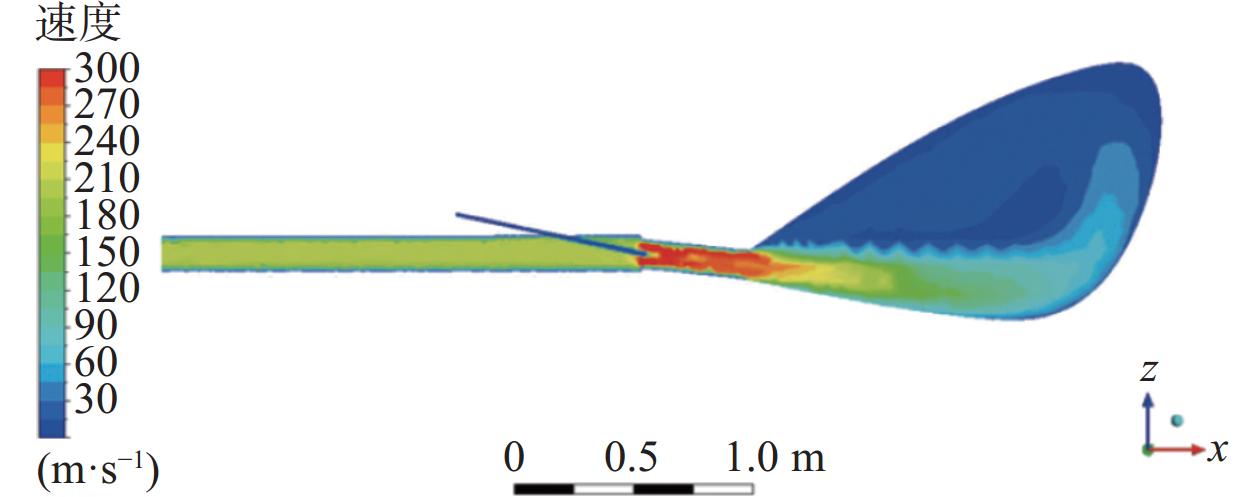
图1为物理模型的中心截面的气相速度云图。当富氧的高温热风自直吹管进入高炉炉内时,由于受到喷煤枪喷煤的影响,鼓风受到挤压,气体速度在该区域略有增加,之后由于风口直径减小,速度升高并达到最大值[27]。经计算,通过风口的气体速度约为280 m/s。鼓风进入回旋区后,受空间突然增大的影响,致使鼓风速度逐渐降低,并沿风口方向继续向回旋区内部运动。气体在风口和回旋区内的流动主要可分为两部分:高速射流和大规模再循环。
2.1.2 温度场分布
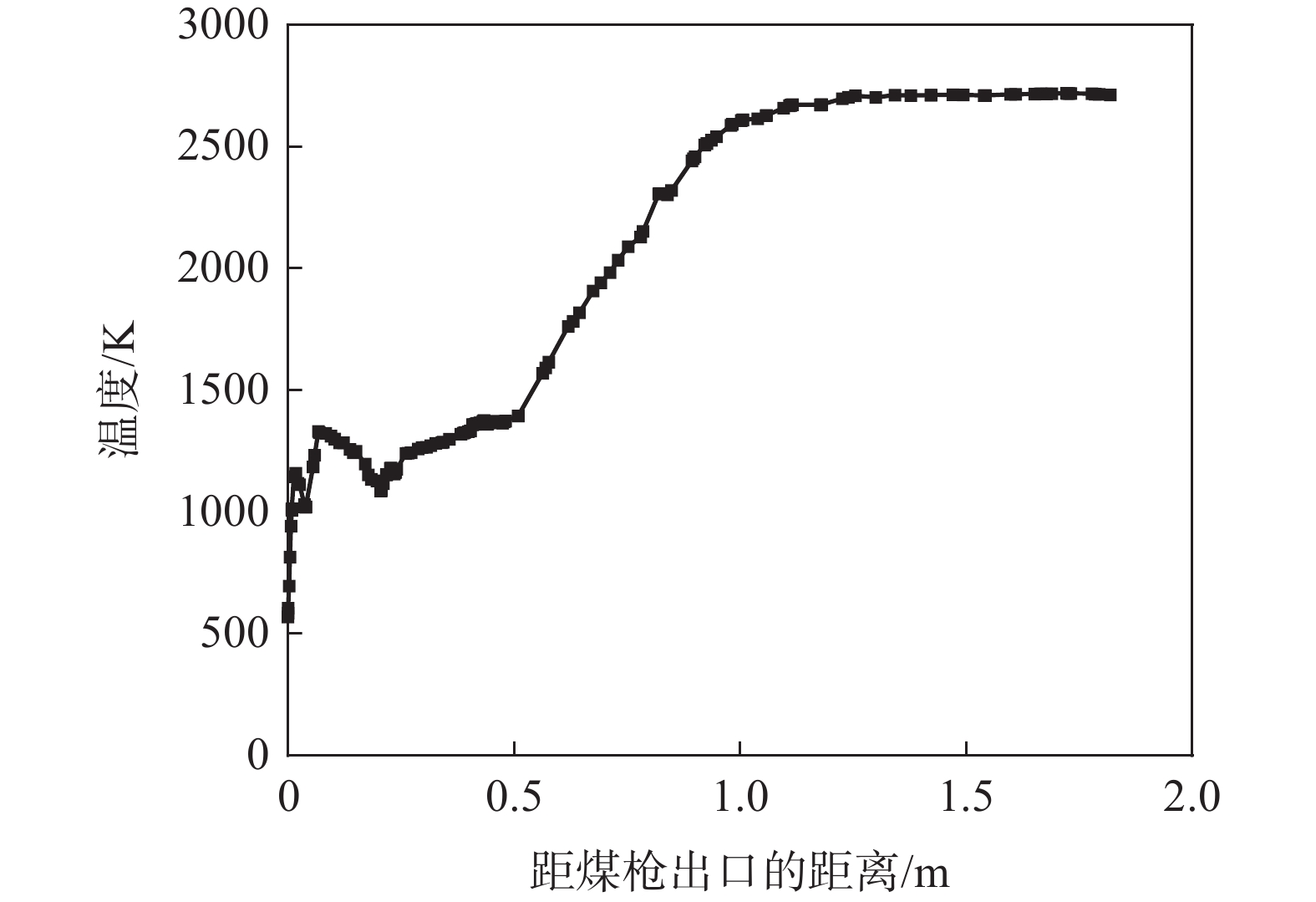
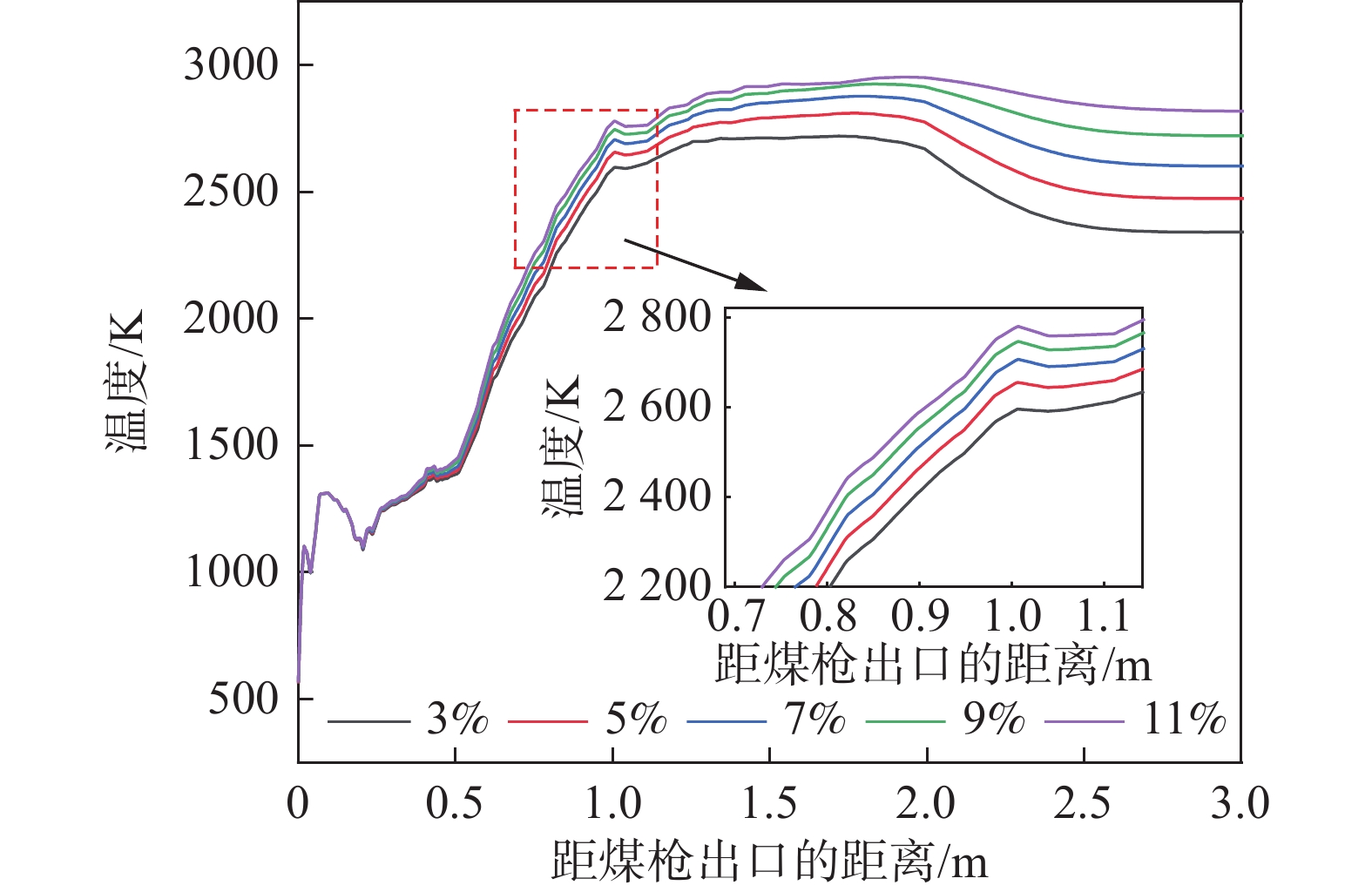
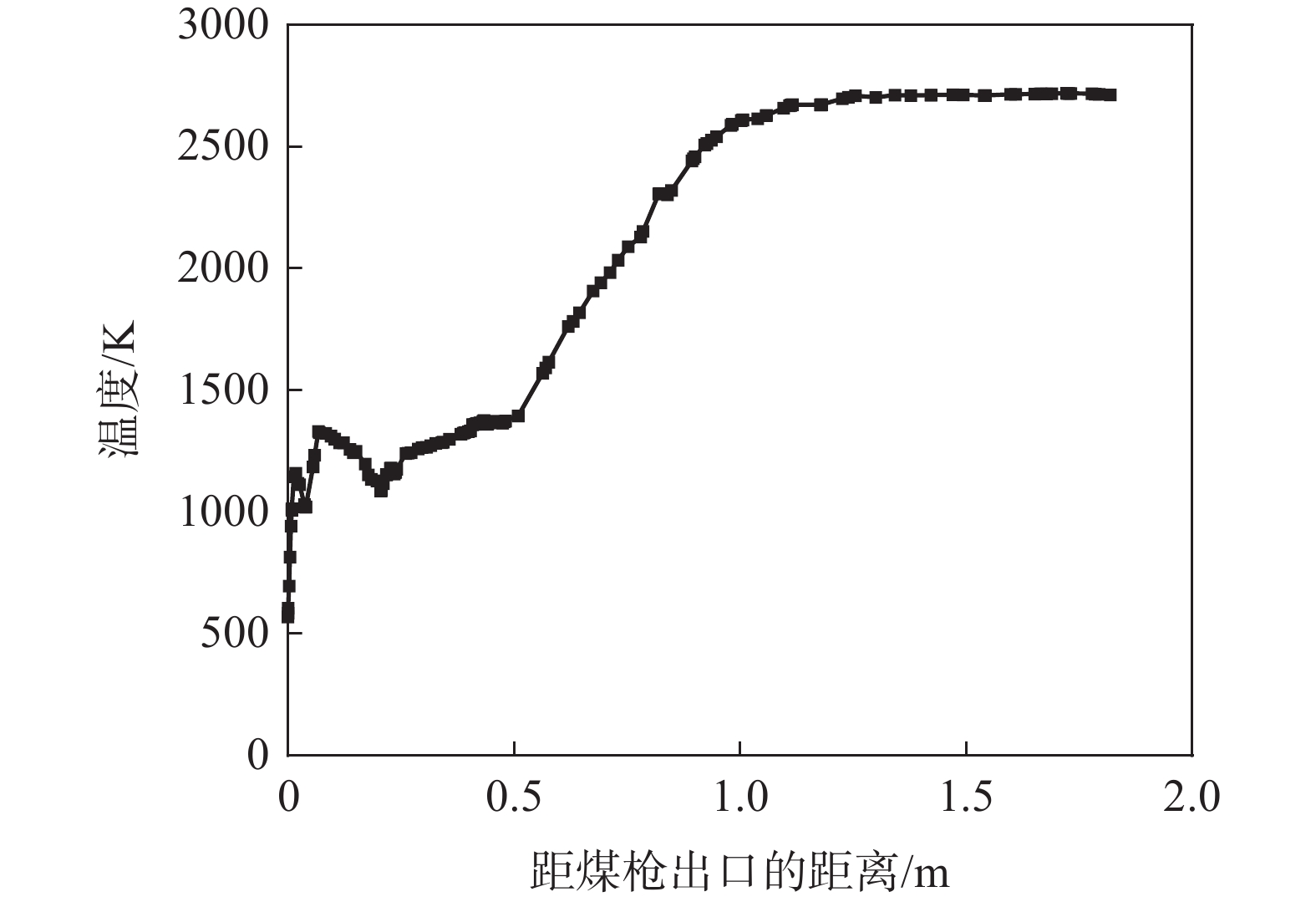
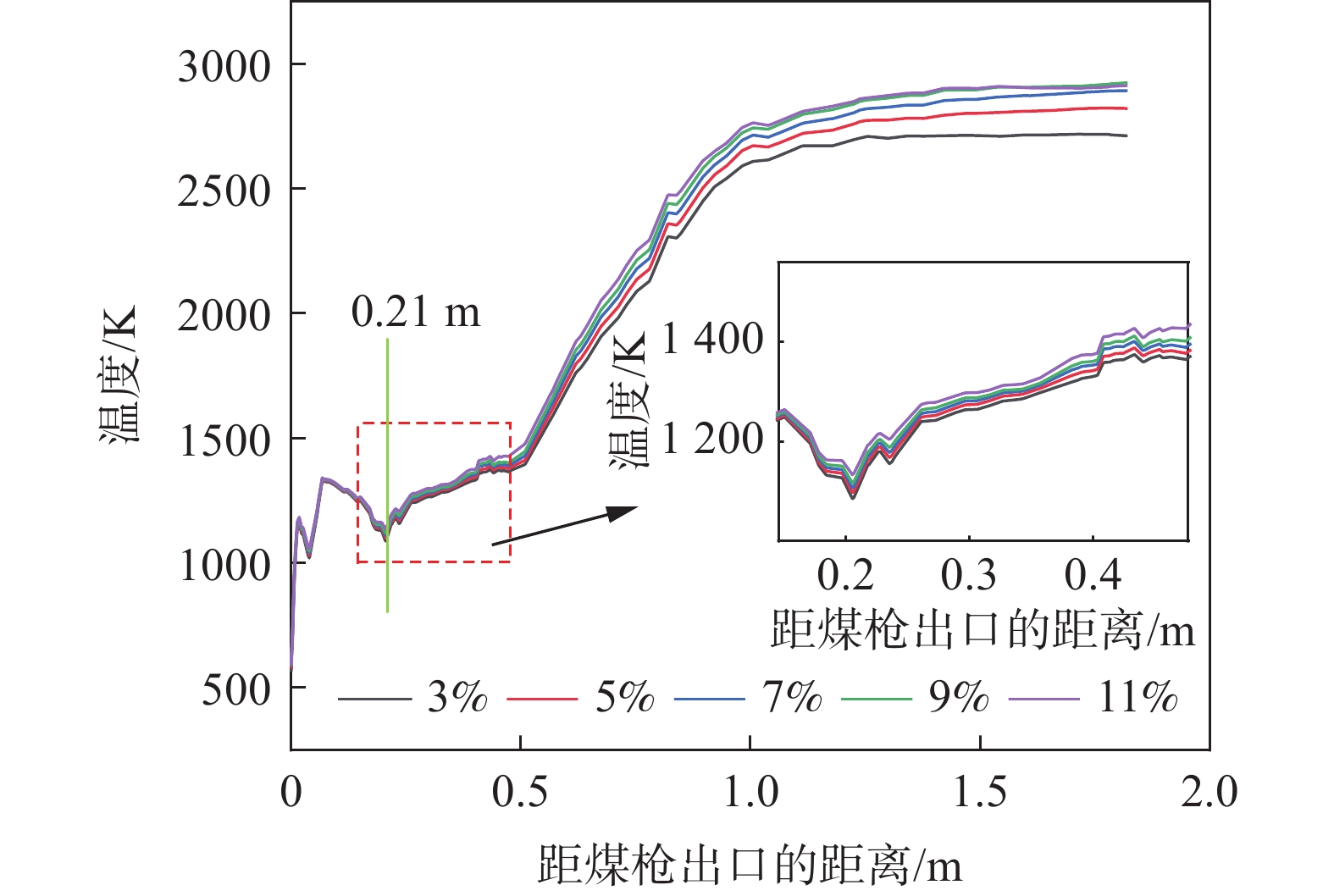
在高炉喷吹煤粉过程中,煤粉从喷枪中出来后与周围高温气体不断进行热量交换,经过一系列物理化学过程释放热量,进而提高了回旋区的温度。图2为沿风口中心线方向气体温度变化曲线。煤粉在高炉内的反应大致可以分为4个部分,分别为煤粉的预热、挥发分析出、挥发分和部分残碳燃烧以及残碳的氧化和气化。
煤粉、载气与高温热风在风口内混合,由于煤粉与载气的温度都远低于鼓风温度,煤粉被周围的热风预热,并且煤粉的脱挥发分过程需要吸收一部分热量,从而造成了煤粉离开煤枪出口后在风口内的某一区域温度较低[28]。此外,在图2可以看出,在煤粉射流的周围,煤粉更易被鼓风加热分解且与鼓风中的氧气接触更加充分,因此煤粉在此区域燃烧剧烈。随着热量不断向煤粉流股中心传递,中心处煤粉燃烧,获得的最高温度可达
2400 K以上。但在高炉内部不同位置温度相差比较大。高温区主要集中于沿回旋区中下游区域,而在回旋区上游以及风口前端的温度则相对较低。分析原因如下:在风口前端及回旋区上游区域煤粉预热、析出挥发分会吸收热量,气体的温度较低;在进入回旋区后,速度下降,挥发分和残碳燃烧,因而出现了高温区域,此区域即为燃烧带。从图2还可发现,回旋区内的温度在空间上分布并不均匀,与气体的速度场分布相符。
可以看出,气体温度的变化具体表现为:在距煤枪出口距离为0~0.07 m阶段气体的温度逐渐升高。之后热解生成的挥发分和残碳等物质与周围热风中的氧气剧烈反应,生成CO2等气体并释放出大量热,燃烧放热产生高温场,如图2中0.21~1.11 m阶段。挥发分燃烧之后煤粉中的残碳继续与氧气反应,由于此阶段氧气含量有限,煤粉不能充分燃烧,因此温度上升一段距离后趋于平稳。
2.1.3 成分分布
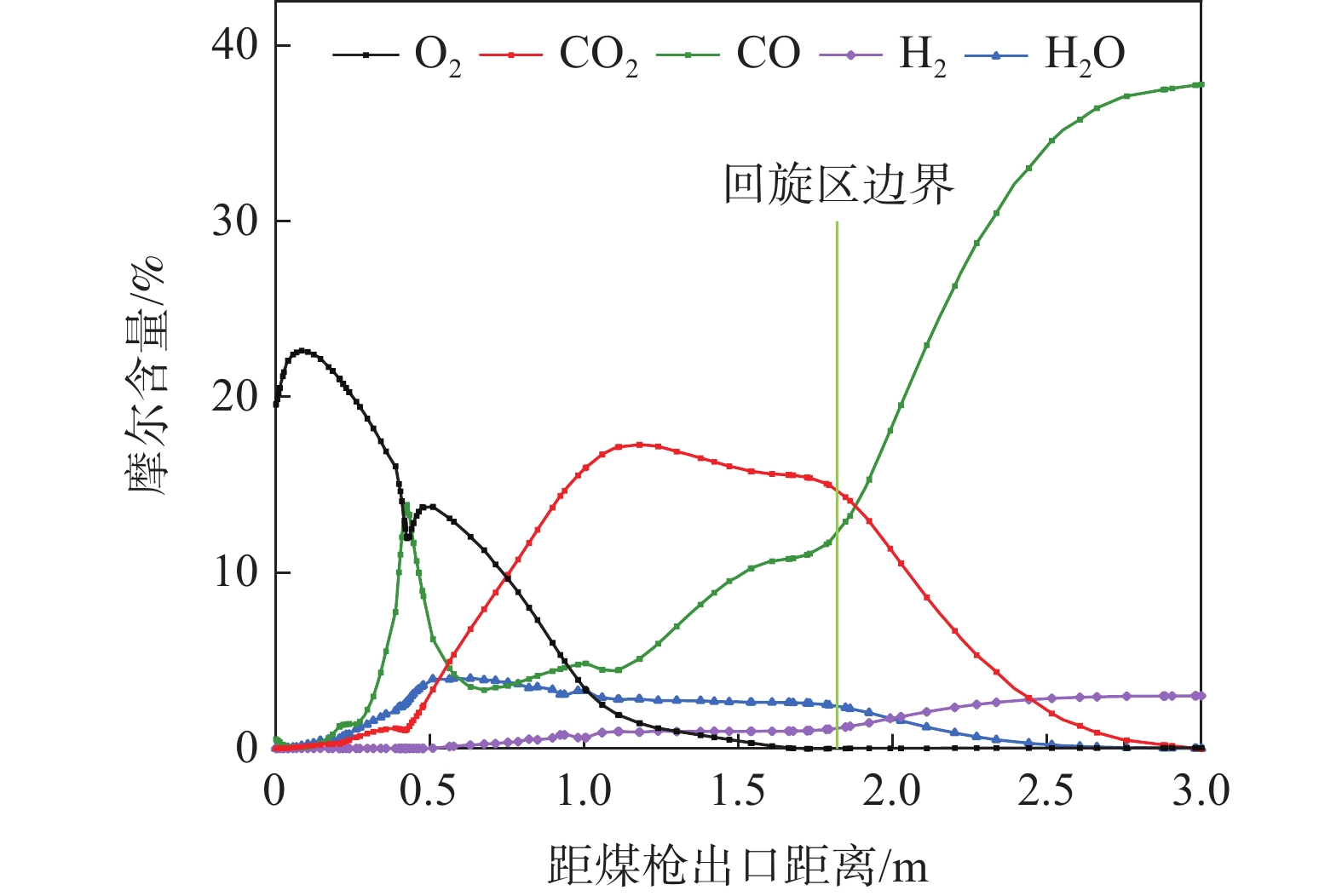
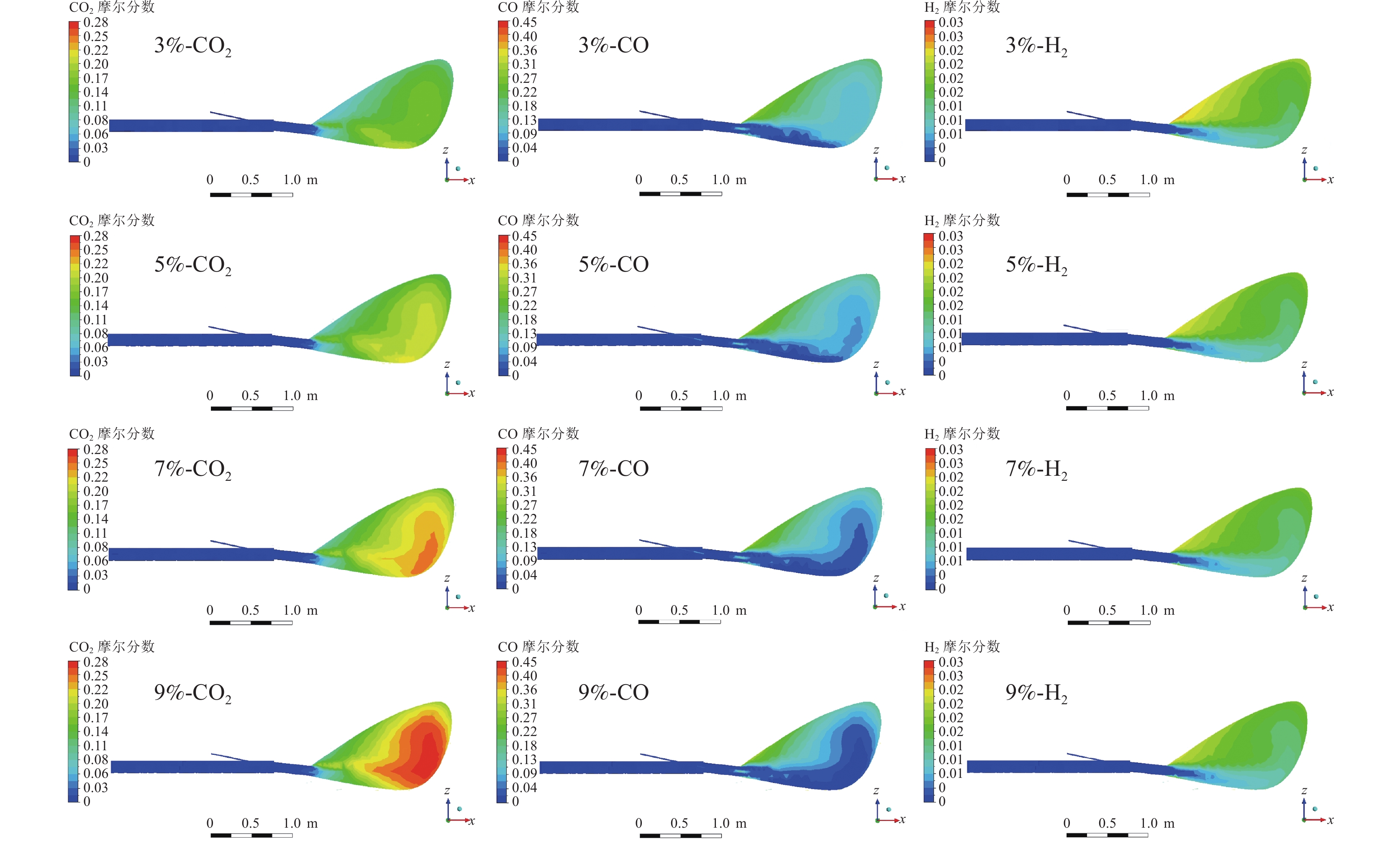
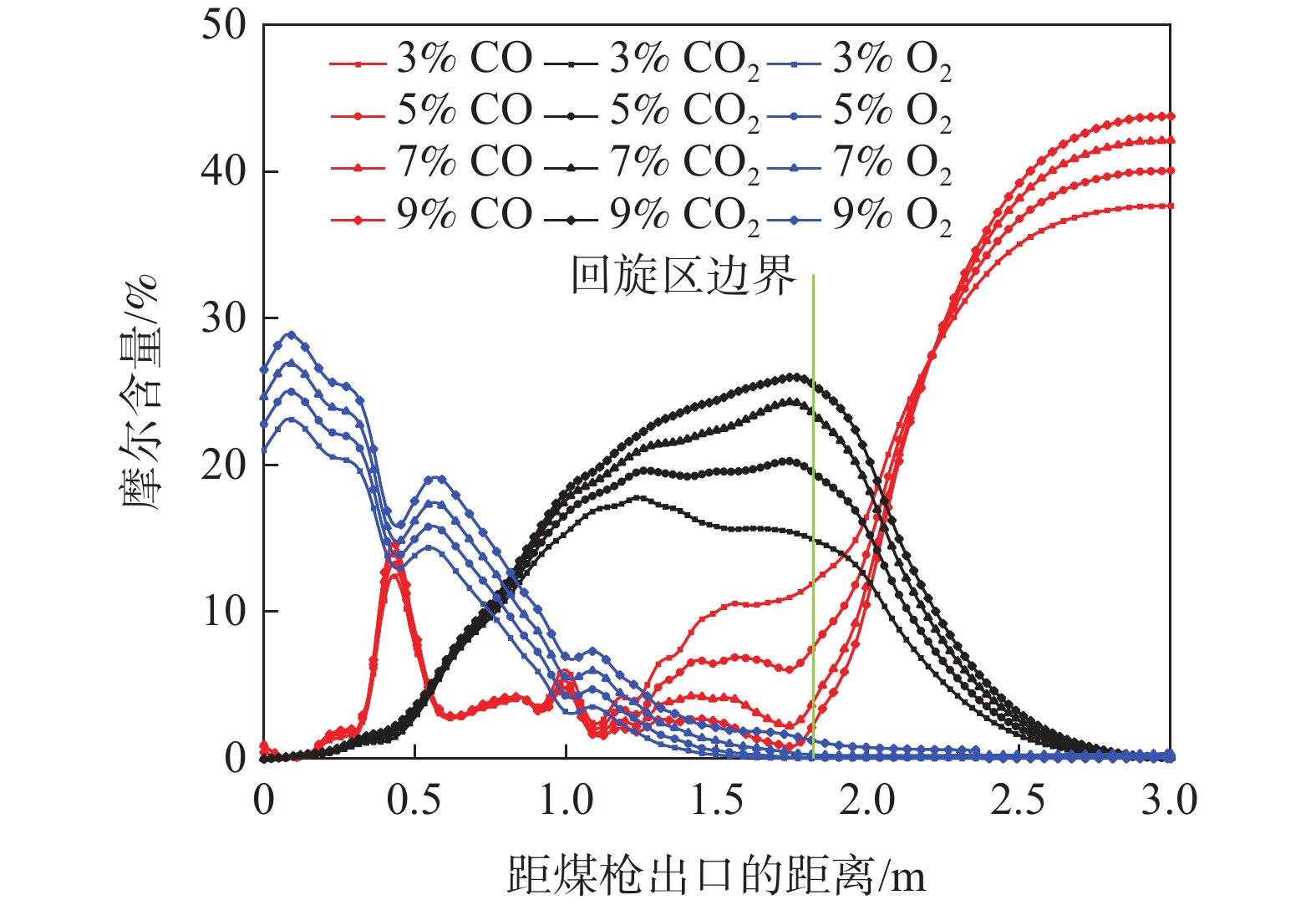
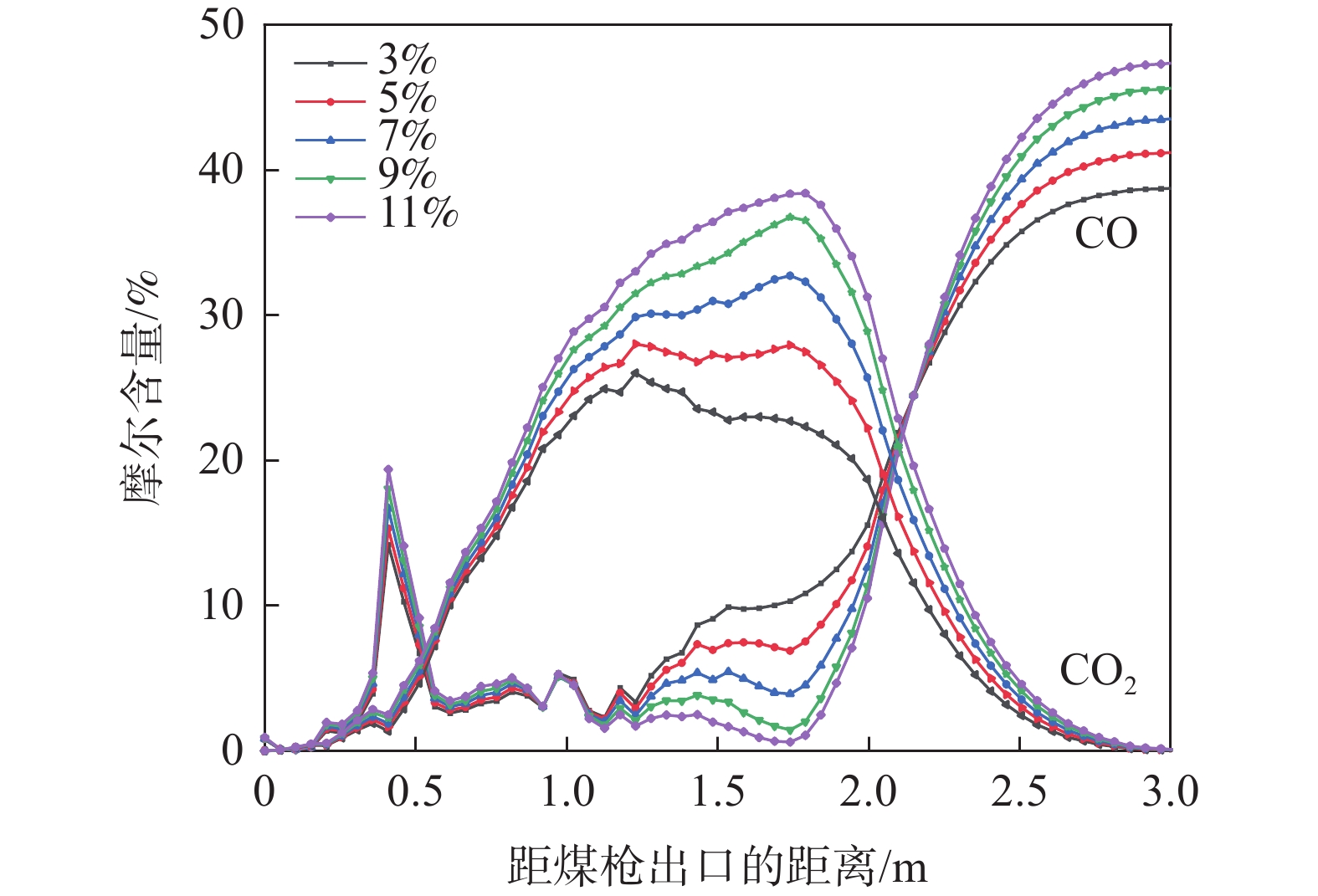
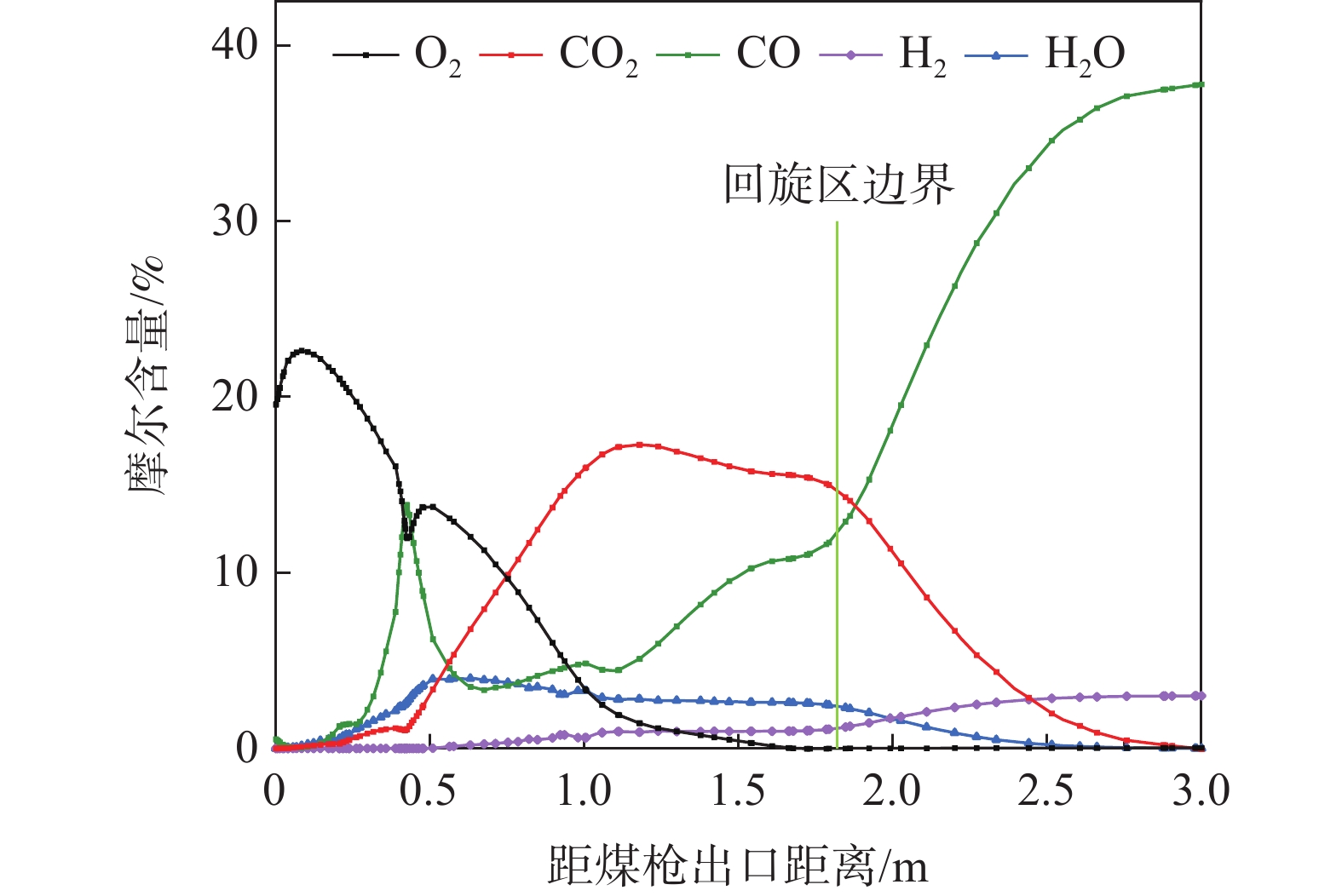
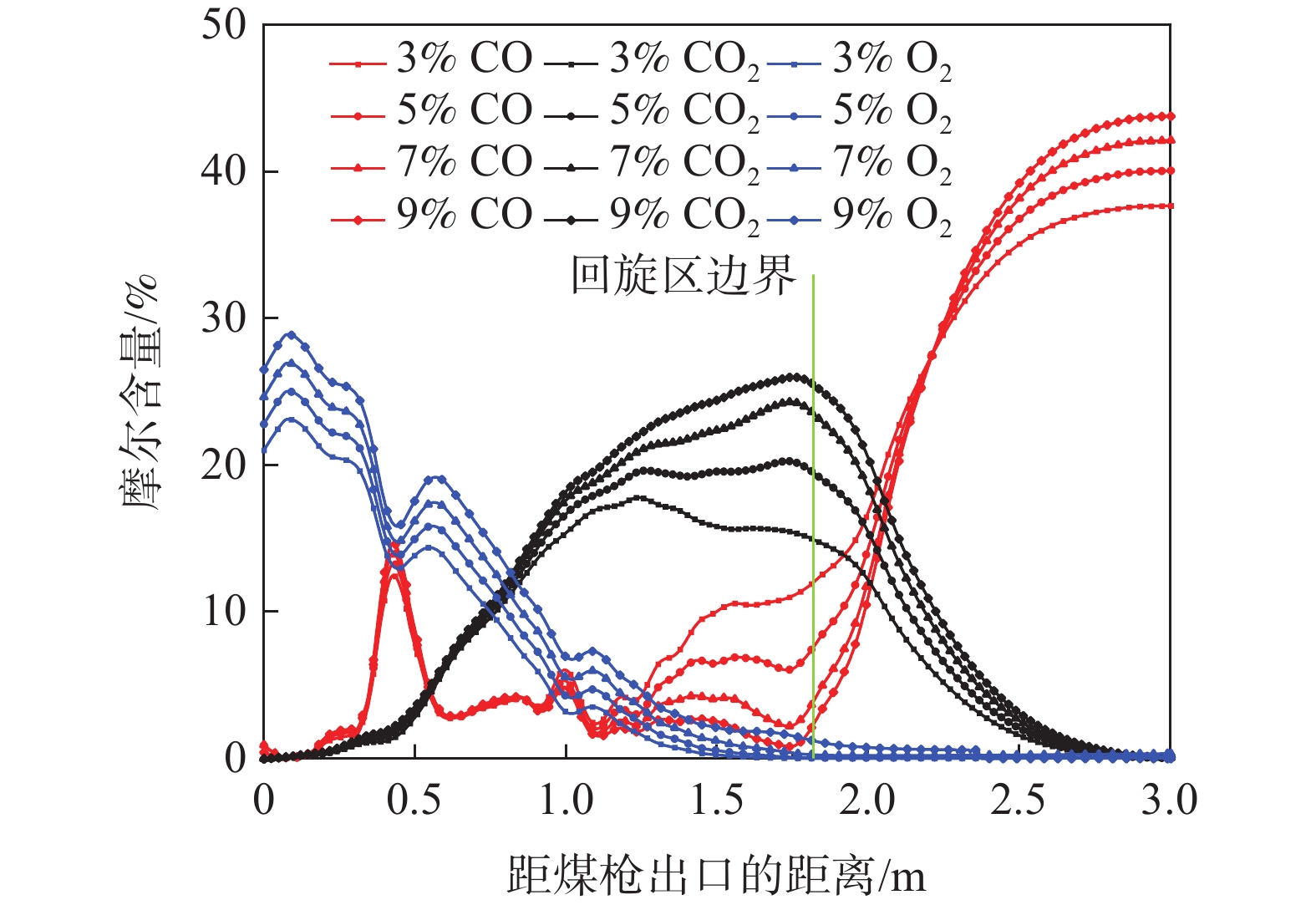
煤粉从出喷煤枪后与高温热风相混合,当煤粉温度上升到一定数值时,煤粉中挥发分开始快速析出,析出的挥发分和残碳与热风中的氧气发生反应。在风口内及回旋区上游O2含量较为充足,析出的挥发分和残碳与热风中的氧气发生反应,主要生成二氧化碳,这导致了氧气在回旋区内就已经被消耗完毕,并且随着距离增大,越来越多的煤粉被加热燃烧,使O2消耗量增加,CO2和H2O的生成量增加,CO和H2组分在风口前缘的生成量非常少。主要是由于喷煤过程煤粉燃烧初期热风中O2浓度较高,煤粉能够完全反应,燃烧产物主要是CO2和H2O,在回旋区内会发生气化反应,因而会生成少量CO和H2。
根据图3,由于风口前端O2相对充足,煤粉燃烧较为充分,CO2和H2O的摩尔含量分别在距煤枪出口处约1.12、0.51 m处达到最大值,为17.62%和4.14%。在距枪尖1.52 m处,氧气消耗殆尽,CO和H2含量不断增加;煤气流通过回旋区边缘深入焦炭床层后CO和H2含量达到峰值,分别为37.66%和3.04%。
2.1.4 燃尽率分布
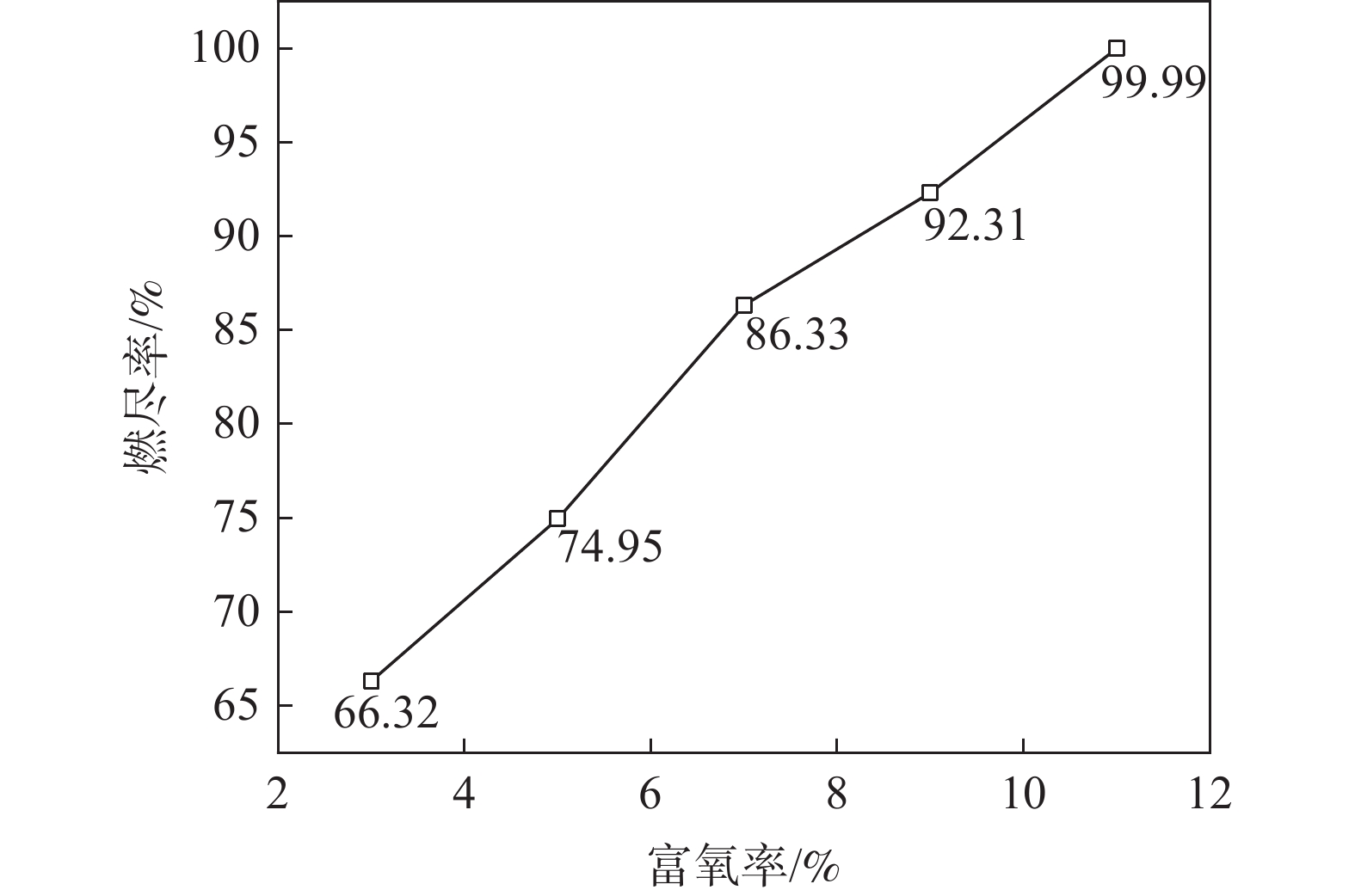
为了进一步了解煤粉的燃烧特性,研究了热风中氧气浓度为24%时煤粉燃尽率的变化。煤粉的燃烧过程主要分为以下几个阶段:挥发分析出、气体燃烧、残炭的氧化和气化、焦炭的氧化和气化。通过计算发现,在回旋区出口处煤粉的燃尽率为66.32%。
2.2 定风富氧条件下富氧率变化对回旋区状态的影响
定风富氧条件下,富氧率变化时通过计算得到的总风量如表2所示。在热风温度为
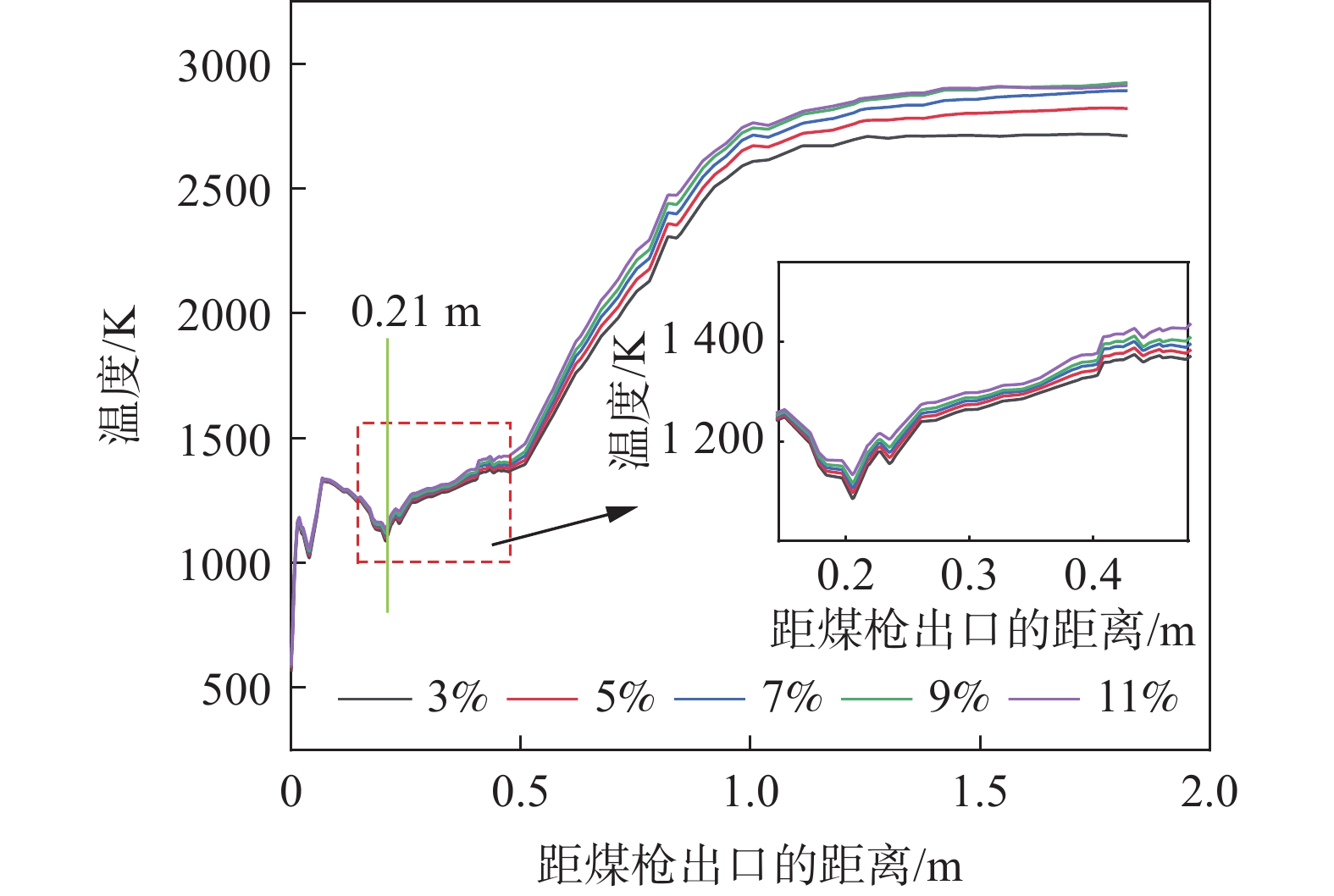
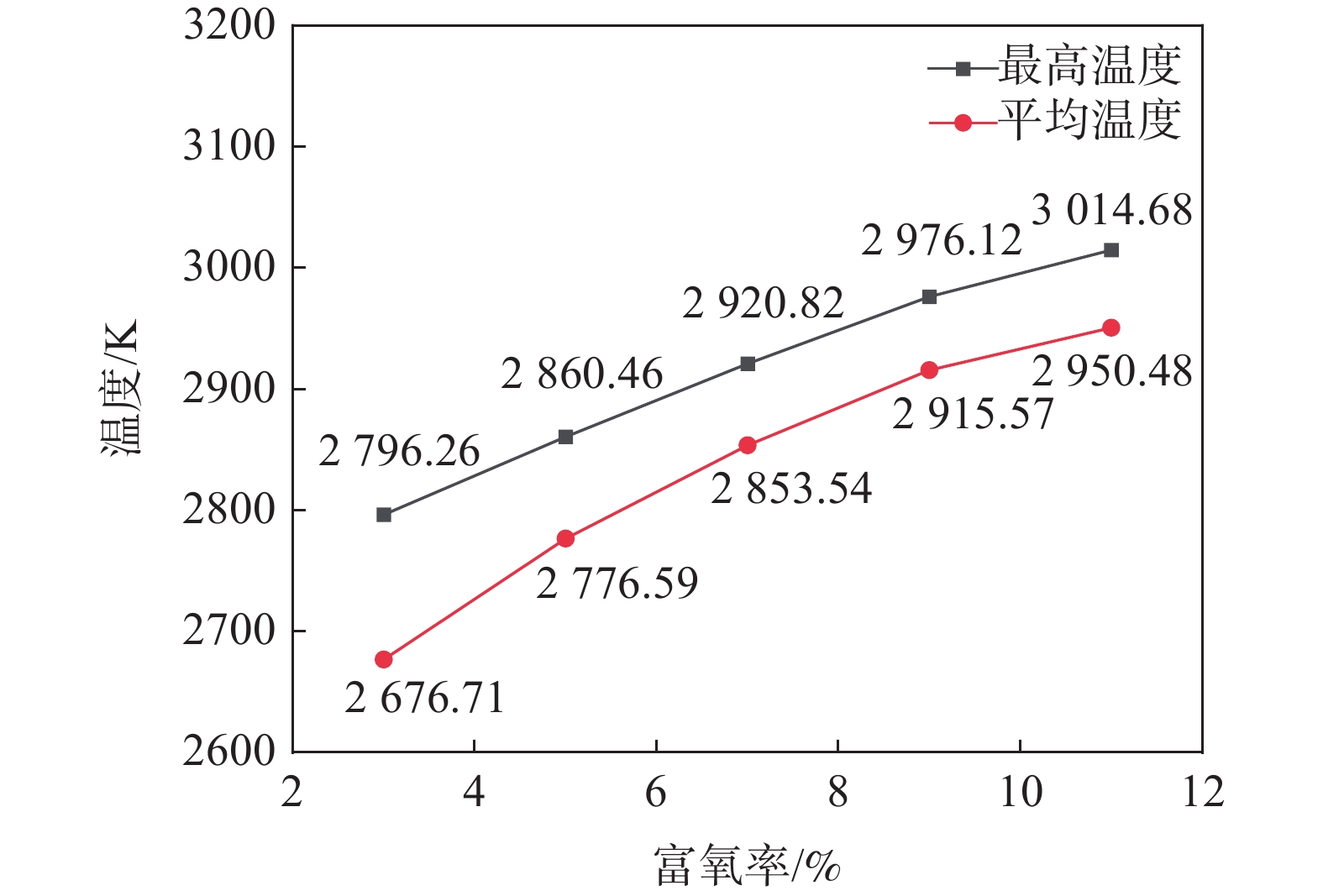
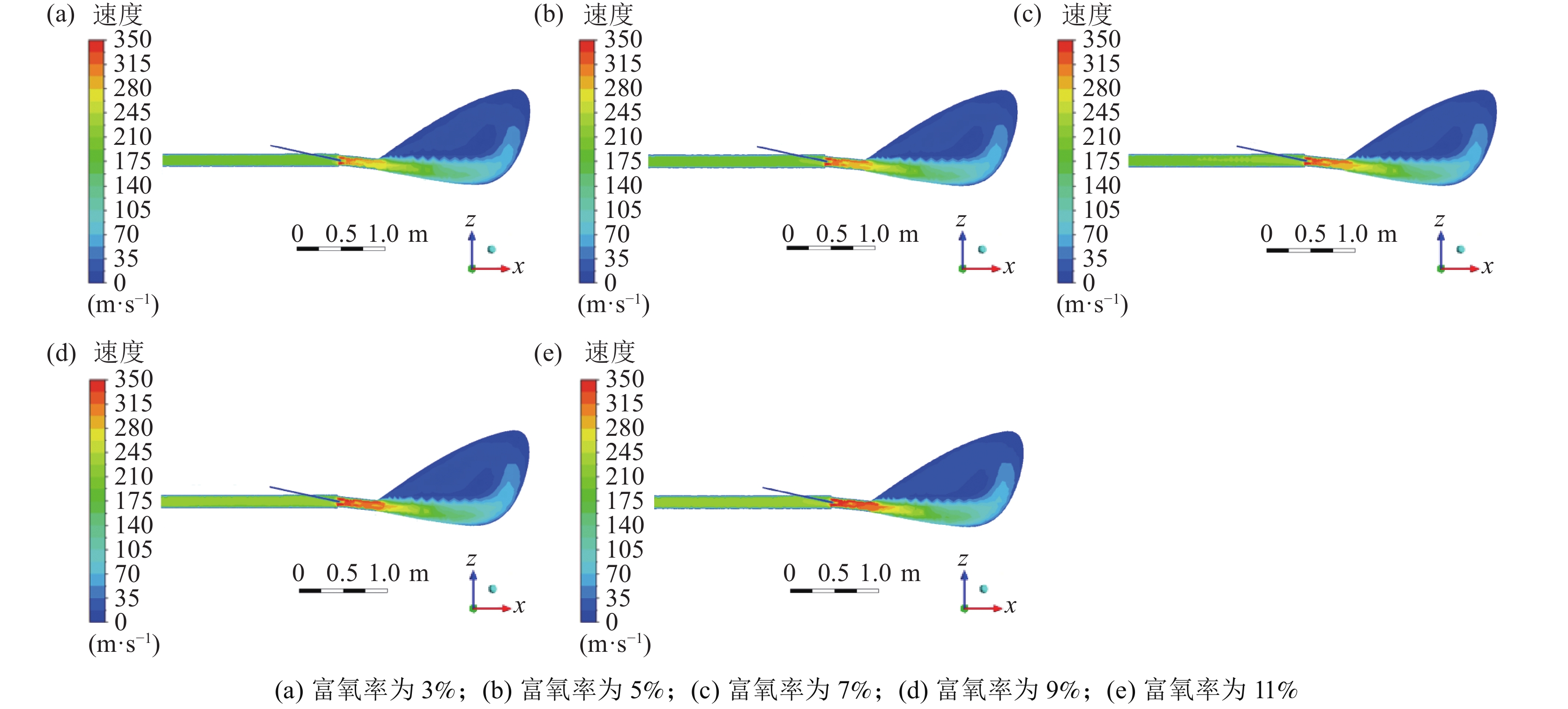
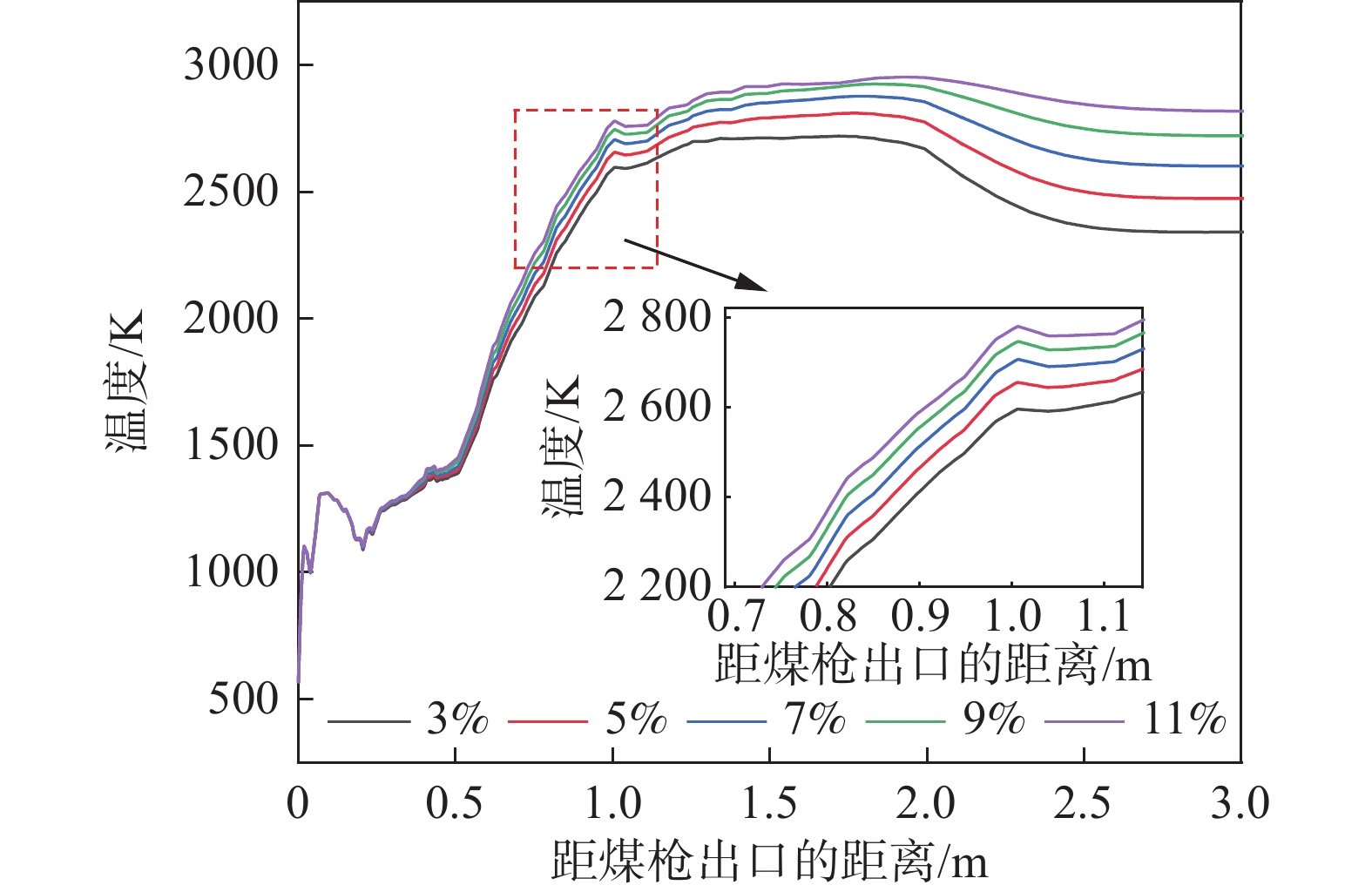
1220 ℃,煤比为95 kg/t不变的情况下改变富氧率,研究定风富氧时富氧率变化对煤粉燃烧过程的影响,富氧率分别为3%、5%、7%、9%和11%,首先得到了高炉风口、回旋区内气体速度的变化情况。图4是不同富氧率下风口处速度变化。富氧率增加时,直吹管内的热风速度增加,通过风口时气体的速度增加,当富氧率为3%、5%、7%、9%、11%时,风口处的速度分别能够达到278.63、287.53、296.64、306.11、316.84 m/s。这是由于富氧率增加后促进了挥发分在风口内的燃烧,煤气量增加,因此通过风口处的速度略有增加。从图4也可以看出,在回旋区出口处气体的速度变化较小,且在同一位置处速度的大小与富氧率呈正相关关系。表 2 定风富氧条件下富氧率变化时的风量Table 2. The air volumes with changes of the oxygen enrichment rates of the fixed air序号 定风富氧率/% 总风量(工况条件)/(m3·min−1) 热风流量(工况条件)/(m3·min−1) 直吹管入口速度/(m·s−1) 煤枪入口速度/(m·s−1) 1 3 4157.89 4000 195.77 12.50 2 5 4270.27 4000 201.07 12.50 3 7 4388.89 4000 206.65 12.50 4 9 4514.29 4000 212.56 12.50 5 11 4647.06 4000 218.81 12.50 图5为沿风口中心线气相温度变化曲线。观察可知,富氧率增加后,回旋区内的温度增加[29],在距煤枪出口距离大于0.21 m以后,沿煤粉流股中心线上的同一位置处温度增加。煤粉进行完脱挥发分过程后,富氧率高时,挥发分接触到的氧气相对较高,有利于挥发分的燃烧,燃烧产生的温度较高,较高的温度有利于后续残碳的燃烧。因此,可以发现富氧率升高后,风口、回旋区内的温度增加。
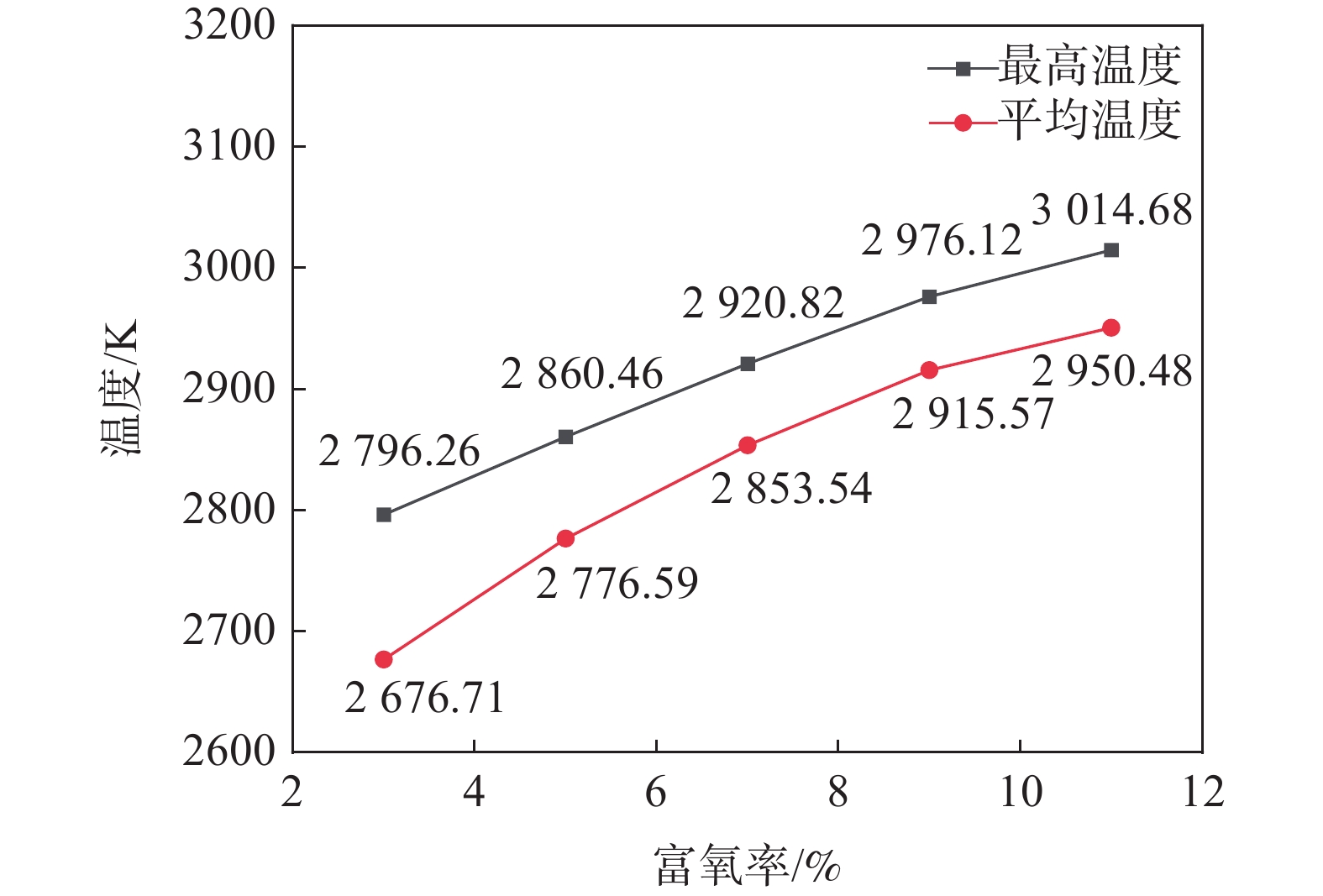
图6为定风富氧时不同富氧率下回旋区内的最高温度和平均温度。富氧率为3%、5%、7%、9%、11%时,煤粉流股中心线上的最高温度分别为
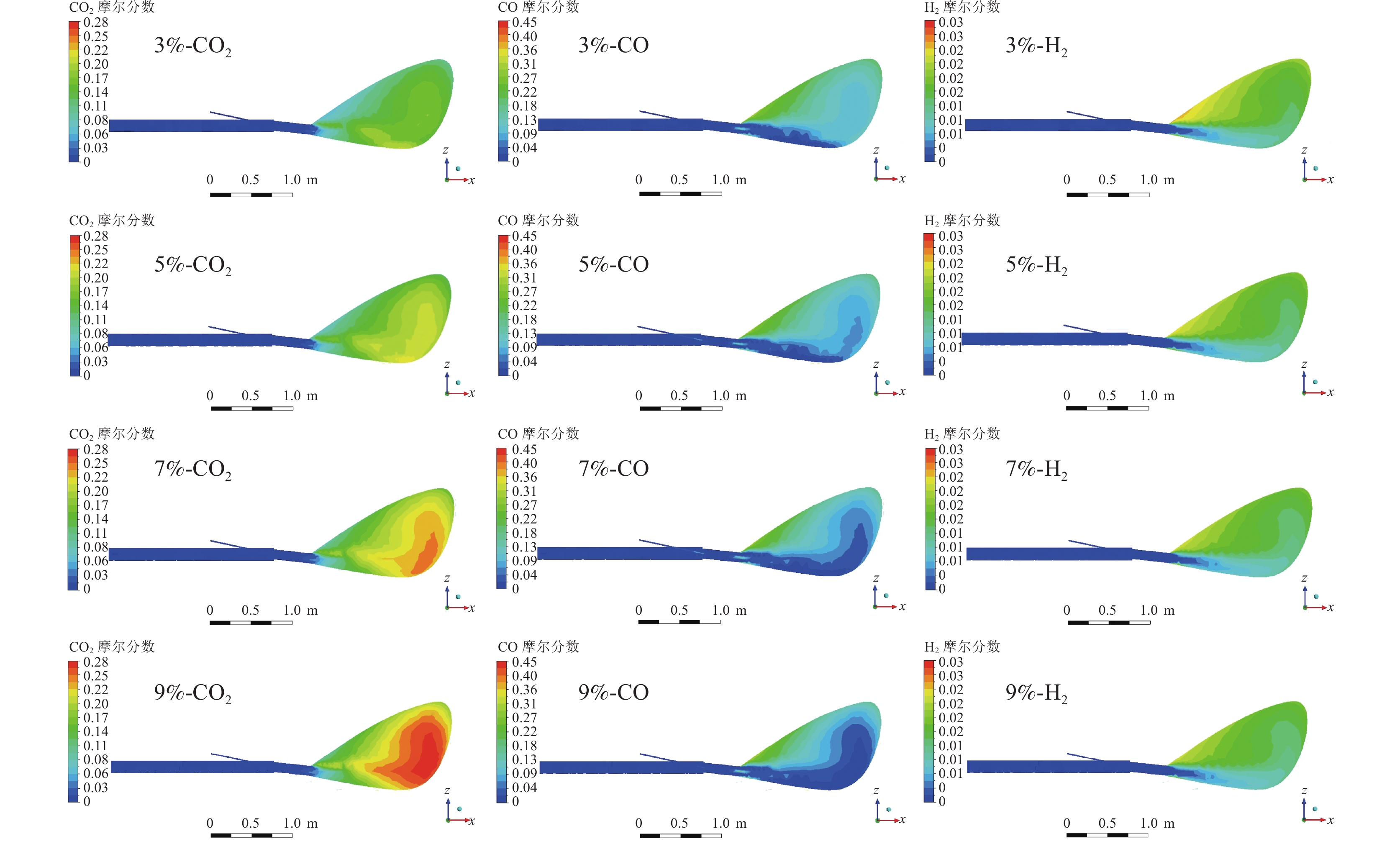
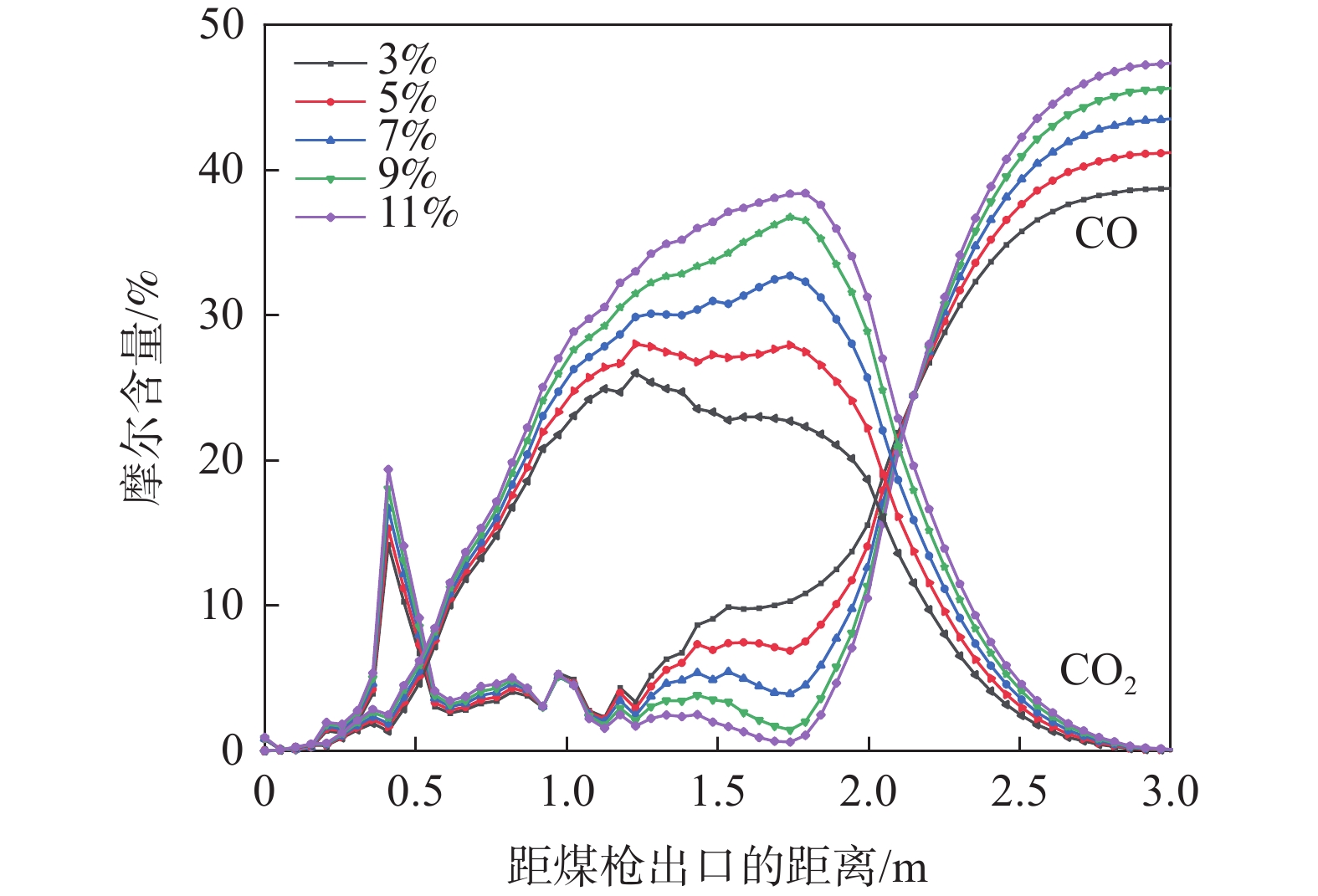
2796.26 、2860.46 、2920.82 、2976.12 、3014.68 K,富氧率增加1%时,最高温度增加了27.30 K左右。而对于回旋区的平均温度而言,富氧率每增加1%,回旋区燃烧的平均温度升高了约40 K;定风富氧条件下,随着富氧率的增加,沿煤粉流股方向上的最高温度和回旋区内平均温度均升高,不过增加的速度均减小。图7为定风富氧时不同富氧率条件下风口、回旋区CO2、CO和H2的分布,图8中曲线为不同富氧率时各气相组分的摩尔含量。从图8可以看出,富氧率增加后,沿煤粉流股中心线上的氧浓度升高,但氧气的消耗速度增加,富氧率增加后促进了煤粉的燃烧。
当富氧率逐渐提高时,在回旋区上游沿风口中心线上的CO2含量逐渐升高,富氧率的增加有利于煤粉燃烧。随着富氧率的不断增加,沿煤粉流股中心线上CO的含量和回旋区内的CO含量减少,这是由于富氧增加以后鼓风带入的氧气含量上升,同时由于高炉较低的煤比,风口区域充足的氧气促使煤粉发生了更多的完全燃烧,生成CO2。图8表明富氧率由3%增加到9%时,回旋区出口处CO2的摩尔含量从13.90%增长到25.20%。随着煤气流经过回旋区继续深入焦炭床层,发生CO2与焦炭的碳素熔损反应,CO的含量急剧上升,CO2含量迅速降低至零,CO的最终含量随着富氧率的增加而增加。
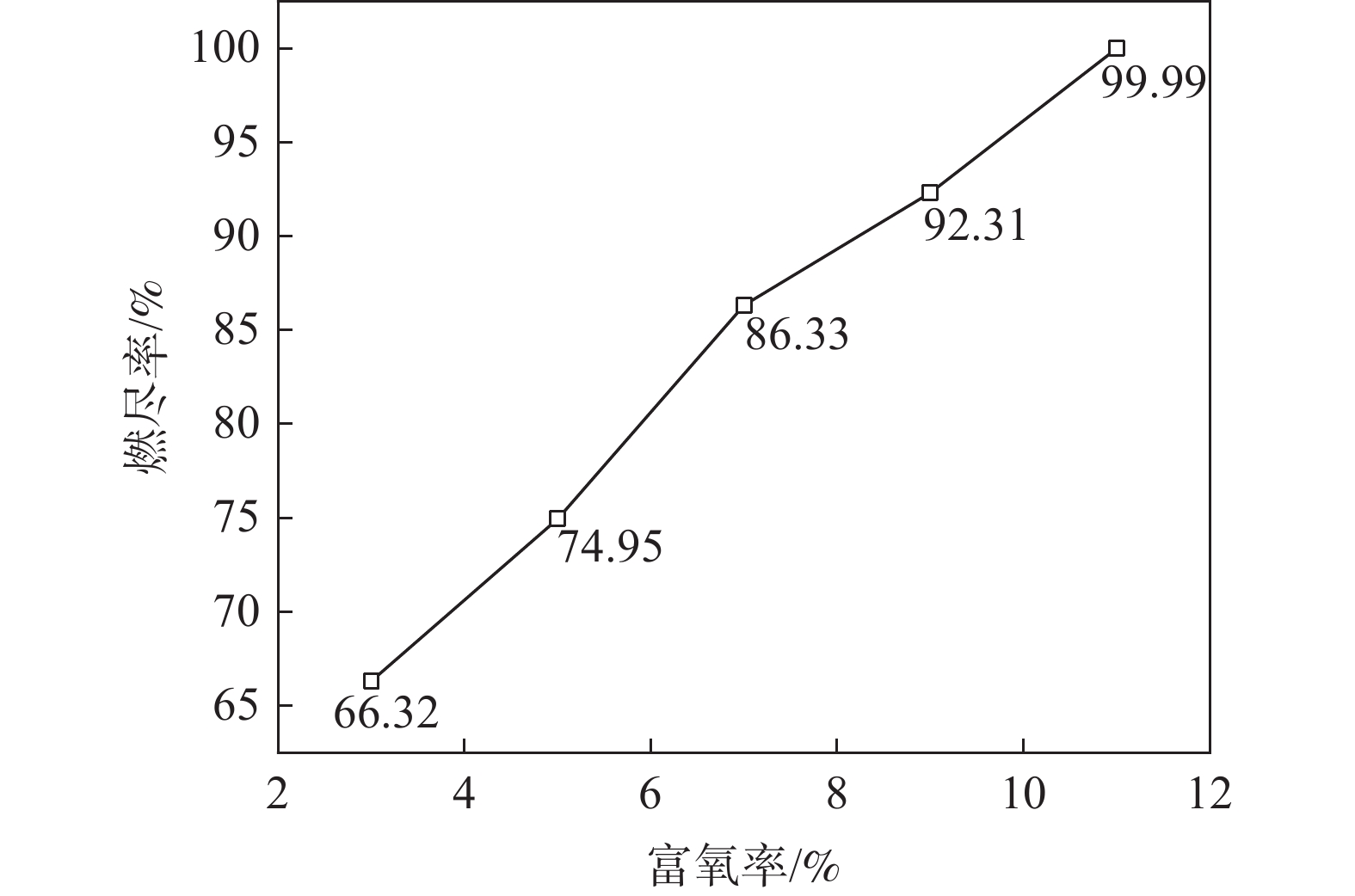
富氧率由3%增加到11%时的回旋区出口处煤粉燃尽率如图9所示。从图9可知,富氧率从3%增加到11%时,燃尽率分别为66.32%、74.95%、86.33%、92.31%和99.99%,燃尽率从66.32%提高到99.99%,提高了33.67个百分点。
2.3 减风富氧条件下富氧率变化对回旋区状态的影响
减风富氧条件下,富氧率变化时通过计算得到的总风量如表3所示。在风温为
1220 ℃,煤比为95 kg/t,保持风量为4000 m3/min,富氧率分别为3%、5%、7%、9%、11%的情况下进行计算,对比分析减风富氧时富氧率变化对回旋区内状态的影响。表 3 减风富氧富氧率变化时的风量条件Table 3. Air volumes with changes of the oxygen enrichment rate of the reduced air序号 减风富氧率/% 总风量(工况条件)/(m3·min−1) 热风流量(工况条件)/(m3·min−1) 直吹管入口速度/(m·s−1) 煤枪入口速度/(m·s−1) 1 3 4157.89 4000 195.77 12.50 2 5 4157.89 3895 195.77 12.50 3 7 4157.89 3789 195.77 12.50 4 9 4157.89 3684 195.77 12.50 5 11 4157.89 3579 195.77 12.50 如图10所示,减风富氧条件下,总风量保持不变,直吹管内的热风速度保持不变,富氧率增加时,气体在通过风口时的速度略有增加,当富氧率为3%、5%、7%、9%、11%时,风口处的速度分别能够达到278.63、279.47、280.27、281.34、282.27 m/s。
为了解减风富氧时富氧率变化对高炉下部风口状态的影响,研究了富氧率变化时高炉回旋区内温度的变化情况,图11为沿煤粉流股上温度的变化。表4为计算的不同富氧率情况下沿煤粉流股上的最高温度和回旋区内的温度变化。
表 4 沿煤粉流股上最高温度和回旋区内平均温度Table 4. Maximum temperatures along the distance from lance tip and average temperature in the raceway减风富氧率/% 沿煤粉流股中心线最高温度/K 回旋区平均温度/K 3 2859.87 2676.71 5 2912.92 2767.03 7 2976.11 2838.74 9 3027.91 2895.40 11 3071.75 2939.71 从模拟计算结果可以看出,减风富氧条件下富氧率对高炉下部的温度影响与定风富氧时是一致的,随着富氧率的逐渐增加,沿煤粉流股中心线上的温度和回旋区内的温度均增加。减风富氧时,富氧率增加1%,沿煤粉流股上的最高温度和回旋区内的平均温度分别增加了23 K和29 K,变化幅度低于定风富氧。这主要是随着富氧率的升高,定风富氧率增加时热风流量增加,带入高炉的热量增加,因此,富氧率升高后在回旋区内的温度变化高于减风富氧时的温度变化。
之后,我们探究了富氧率变化对于煤气成分的影响情况,如图12所示。减风富氧条件下,随着富氧率的升高,CO2和H2的含量增加,较高的O2、H2O含量促进了CO2和H2的生成。富氧率为3%、5%、7%、9%和11%时,在回旋区出口处CO2的摩尔含量分别为15.02%,18.72%,22.42%,25.76%和27.57%。与定风富氧相比,富氧率变化时,减风富氧对气体成分含量的影响更大。随着富氧率的增加,减风富氧时,热风带入的N2较少,O2比例上升,充足的氧气致使煤粉更多地发生完全燃烧,产生CO2,后续随着O2被不断地消耗,CO的成分开始上升,CO2开始下降。同时,在回旋区边界及焦炭床层发生碳素熔损反应,使得CO浓度进一步提高。经计算,减风富氧条件下,该高炉富氧率每增加1%,热风带入的N2量减少10 m3/min,煤气中的CO摩尔含量上升8.61%。
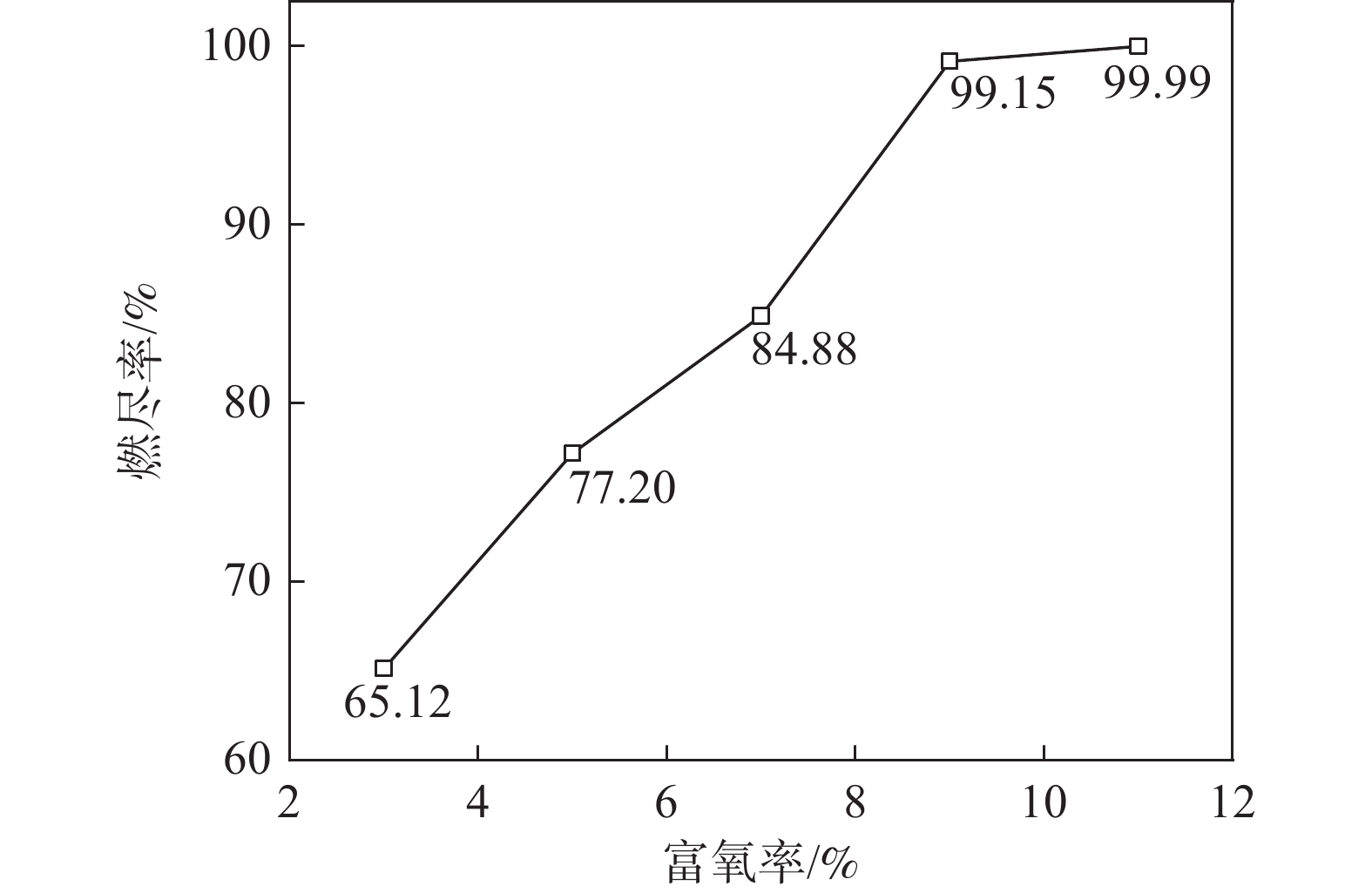
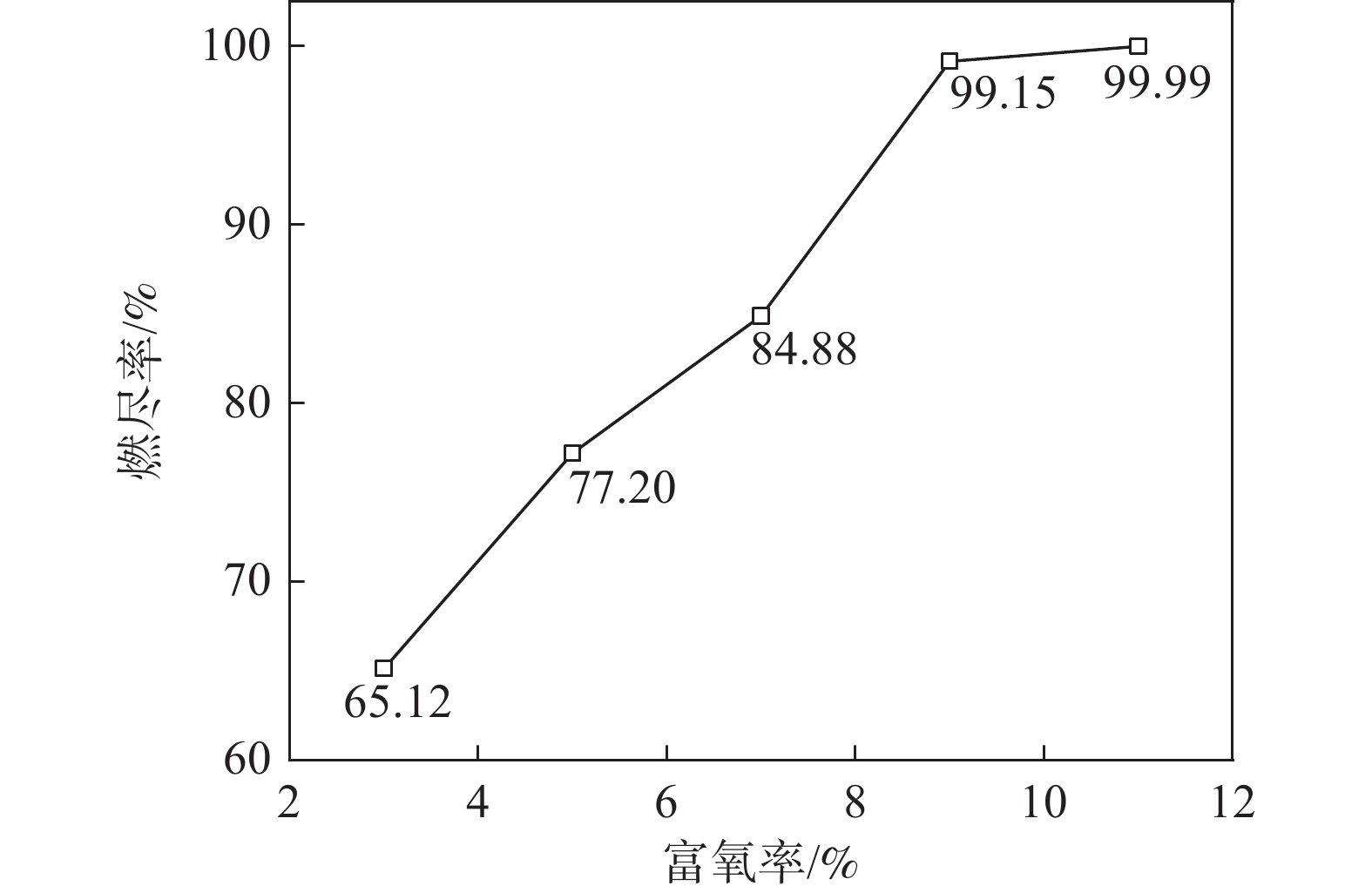
富氧率变化后会对煤粉的燃烧情况产生影响,煤粉燃尽率的结果见图13。富氧率的提高能够促进煤粉的燃烧,提高富氧率可以提高煤粉的燃尽率[30]。从图13可知,富氧率由3%增加到7%再增加至11%时,回旋区边界的煤粉燃尽率分别为65.12%,84.88%和99.99%,富氧率每提高1%,煤粉的燃尽率增加4.36%。煤粉的燃尽率随着富氧率的增加而增加,但是其增加幅度逐渐减缓[31]。
3. 结论
通过建立3D模型,运用数值模拟的方法研究了在定风富氧和减风富氧条件下富氧率变化时高炉的风口和回旋区内流场、温度场、浓度场、煤粉燃烧效果的变化情况。研究的主要结果如下:
1)通过计算表明,两种不同富氧方式(减风富氧、定风富氧)下,回旋区内的温度、还原气体含量及煤粉在出口处的燃尽率变化趋势一样,沿煤粉流股中心线上的温度和回旋区内的温度均增加,高温区域扩大;富氧后还原气体含量增加、煤粉的燃尽率上升,但上升趋势均逐渐放缓。
2)定风富氧后,随着氧浓度增加,风口处的气流速度增加显著;而在减风富氧条件下进行富氧时,气流速度虽然增加,但是变化幅度较小。富氧率增加1%,风口截面速度分别增加4.25 m/s(定风)和0.41 m/s(减风)。
3)在这两种富氧方式中,定风富氧对回旋区内的温度影响较大,减风富氧对回旋区内的温度影响较小。富氧率每增加1%,回旋区平均温度增加34.22 K(定风)和32.88 K(减风)。
4)对于还原性气体而言,定风富氧时H2的含量变化不大;减风富氧时,热风带入的N2量降低,煤气量相对较少,煤气中的CO和H2的含量均变化较大,富氧率增加1%,热风带入的N2量减少10 m3/min,煤气中的CO质量浓度上升8.61%。
5)两种不同的富氧方式中,由于高炉煤比(95 kg/t)较小,煤粉进入风口回旋区后,与充足的氧气接触,造成更多的煤粉发生完全燃烧,生成了CO2,沿着煤粉流股中心线上的CO浓度表现为先下降后上升。
6)减风富氧对高炉回旋区的影响较小,且有助于降低煤气中N2、提高煤气中的H2和CO浓度,对高炉减少氮化碳和碳化钛生成、改善铁矿还原效果具有较好的帮助,建议高炉提高富氧率采用减风富氧模式。
-
表 1 高炉的实际操作条件
Table 1. Actual operating conditions of blast furnaces
风口数/个 高炉有效容积/m3 风量/(m3·min−1) 风压/kPa 氧气浓度/% 煤比/(kg·t−1) 热风温度/℃ 载气成分 24 1750 4000 360 24(基准工况) 95 1220 氮气 表 2 定风富氧条件下富氧率变化时的风量
Table 2. The air volumes with changes of the oxygen enrichment rates of the fixed air
序号 定风富氧率/% 总风量(工况条件)/(m3·min−1) 热风流量(工况条件)/(m3·min−1) 直吹管入口速度/(m·s−1) 煤枪入口速度/(m·s−1) 1 3 4157.89 4000 195.77 12.50 2 5 4270.27 4000 201.07 12.50 3 7 4388.89 4000 206.65 12.50 4 9 4514.29 4000 212.56 12.50 5 11 4647.06 4000 218.81 12.50 表 3 减风富氧富氧率变化时的风量条件
Table 3. Air volumes with changes of the oxygen enrichment rate of the reduced air
序号 减风富氧率/% 总风量(工况条件)/(m3·min−1) 热风流量(工况条件)/(m3·min−1) 直吹管入口速度/(m·s−1) 煤枪入口速度/(m·s−1) 1 3 4157.89 4000 195.77 12.50 2 5 4157.89 3895 195.77 12.50 3 7 4157.89 3789 195.77 12.50 4 9 4157.89 3684 195.77 12.50 5 11 4157.89 3579 195.77 12.50 表 4 沿煤粉流股上最高温度和回旋区内平均温度
Table 4. Maximum temperatures along the distance from lance tip and average temperature in the raceway
减风富氧率/% 沿煤粉流股中心线最高温度/K 回旋区平均温度/K 3 2859.87 2676.71 5 2912.92 2767.03 7 2976.11 2838.74 9 3027.91 2895.40 11 3071.75 2939.71 -
[1] Zhang Cuiliu, Wang Guangwei, Ning Xiaojun, et al. Numerical simulation of combustion behaviors of hydrochar derived from low-rank coal in the raceway of blast furnace[J]. Fuel, 2020,278:118267. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2020.118267 [2] Babich A, Yaroshevskii S, Formoso A, et al. Co-injection of noncoking coal and natural gas in blast furnace[J]. ISIJ International, 1999,39(3):229-238. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.39.229 [3] Peter Richard Austin, Hiroshi Nogami, Jun-ichiro Yagi. A mathematical model of four phase motion and heat transfer in the blast furnace[J]. ISIJ International, 1997,37(5):458-467. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.37.458 [4] Dong X F, Yu A B, Chew S J, et al. Modeling of blast furnace with layered cohesive zone[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 2010,41(2):330-349. doi: 10.1007/s11663-009-9327-y [5] Kuang S B, Li Z Y, Yan D L, et al. Numerical study of hot charge operation in ironmaking blast furnace[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2014, 63: 45-56. [6] Hannu Helle, Mikko Helle, Henrik Saxén. Nonlinear optimization of steel production using traditional and novel blast furnace operation strategies[J]. Chemical Engineering Science, 2011,66(24):6470-6481. doi: 10.1016/j.ces.2011.09.006 [7] Zhang Wei, Zhang Juhua, Xue Zhengliang, et al. Unsteady analyses of the top gas recycling oxygen blast furnace[J]. ISIJ International, 2016,56(8):1358-1367. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2016-090 [8] Kushnir D, Hansen T, Vogl V, et al. Adopting hydrogen direct reduction for the Swedish steel industry: A technological innovation system (TIS) study[J]. J Clean Prod, 2020,242:13. [9] Zhang Fuming, Cao Chaozhen, Meng Xianglong, et al. Technological status and tendency of modern blast furnace[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2013,813:192-195. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.813.192 [10] Duan Guojian, Zhao Zhilong. Discussion of blast furnace oxygen enriched coal injection[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 2017(6):8-12. (段国建, 赵志龙. 高炉富氧喷煤技术探讨[J]. 河北冶金, 2017(6):8-12.Duan Guojian, Zhao Zhilong. Discussion of blast furnace oxygen enriched coal injection[J]. Hebei Metallurgy, 2017(6): 8-12. [11] Zhang Fuming. Technological progress for contemporary ultra large sized blast furnoace[C]// 2012 National Conference on Ironmaking Production Technology and Annual Conference on Ironmaking. Wuxi: Chinese Society for Metals, 2012. (张福明. 当代巨型高炉技术进步[C]//2012年全国炼铁生产技术会议暨炼铁学术年会. 无锡: 中国金属学会, 2012.Zhang Fuming. Technological progress for contemporary ultra large sized blast furnoace[C]// 2012 National Conference on Ironmaking Production Technology and Annual Conference on Ironmaking. Wuxi: Chinese Society for Metals, 2012. [12] Liu Yingshu, Yang Tianjun, Cang Daqiang, et al. The progress of research and development in BF oxygen-coal injection[J]. Ironmaking, 1996(4):9-12. (刘应书, 杨天钧, 苍大强, 等. 高炉富氧喷煤技术研究开发的进展[J]. 炼铁, 1996(4):9-12.Liu Yingshu, Yang Tianjun, Cang Daqiang, et al. The progress of research and development in BF oxygen-coal injection[J]. Ironmaking, 1996(4): 9-12. [13] Cheng Lanbo, Gao Guangchun, Ma Shuhan. Experiment of BF operation with oxygen rich coal injection at Anshan iron and steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 1988(11):1-10. (成兰伯, 高光春, 马树涵. 鞍钢2号高炉富氧大喷吹冶炼试验[J]. 钢铁, 1988(11):1-10.Cheng Lanbo, Gao Guangchun, Ma Shuhan. Experiment of BF operation with oxygen rich coal injection at Anshan iron and steel[J]. Iron & Steel, 1988(11): 1-10. [14] Zeng Weitao, Zhang Qingxi. Operating system adjustment under production limitation mode in WISCO No. 8 BF[J]. Ironmaking, 2022,41(1):6-9. (曾伟涛, 张庆喜. 武钢8号高炉限产模式下操作制度的调整[J]. 炼铁, 2022,41(1):6-9.Zeng Weitao, Zhang Qingxi. Operating system adjustment under production limitation mode in WISCO No. 8 BF[J]. Ironmaking, 2022, 41(1): 6-9. [15] Xiang Mingwu, Zhou Qiang, Zhang Ling, et al. Technical characteristics of Shagang 5800 m3 blast furnace[J]. Ironmaking, 2010,29(2):1-6. (项明武, 周强, 张灵, 等. 沙钢5800 m3高炉工艺技术特点[J]. 炼铁, 2010,29(2):1-6.Xiang Mingwu, Zhou Qiang, Zhang Ling, et al. Technical characteristics of Shagang 5800 m3 blast furnace[J]. Ironmaking, 2010, 29(2): 1-6. [16] Wang Jun, Xu Hui, Zhang Peifeng, et al. Management for maintaining low consumption production in baosteel’s No. 4 BF[J]. Ironmaking, 2020,39(4):1-7. (王俊, 徐辉, 张培峰, 等. 宝钢4号高炉长期低耗生产管理[J]. 炼铁, 2020,39(4):1-7.Wang Jun, Xu Hui, Zhang Peifeng, et al. Management for maintaining low consumption production in baosteel’s No. 4 BF[J]. Ironmaking, 2020, 39(4): 1-7. [17] Liu Yiran, Shen Yansong. Three-dimensional modelling of charcoal combustion in an industrial scale blast furnace[J]. Fuel, 2019,258:116088. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116088 [18] Hu Z J, Liu Y R, Xu H, et al. Co-combustion of semicoke and coal in an industry ironmaking blast furnace: Lab experiments, model study and plant tests[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2019, 196: 106165. [19] Shen Y S, Maldonado D, Guo B Y, et al. Computational fluid dynamics study of pulverized coal combustion in blast furnace raceway[J]. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2009,48(23):10314-10323. doi: 10.1021/ie900853d [20] Zhou Zhenfeng, Wang Ruihao, Yi Qiujie, et al. Combustion enhancement of pulverized coal with targeted oxygen-enrichment in an ironmaking blast furnace[J]. Processes, 2021,9(3):440. [21] Rastko Jovanovic, Aleksandra Milewska, Bartosz Swiatkowski, et al. Numerical investigation of influence of homogeneous/heterogeneous ignition/combustion mechanisms on ignition point position during pulverized coal combustion in oxygen enriched and recycled flue gases atmosphere[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2011,54(4):921-931. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2010.10.011 [22] Nie Haiqi, Li Zhaoyang, Kuang Shibo, et al. Numerical investigation of oxygen-enriched operations in blast furnace ironmaking[J]. Fuel, 2021,296:120662. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2021.120662 [23] Liu Yiran, Shen Yansong. CFD study of charcoal combustion in a simulated ironmaking blast furnace[J]. Fuel Processing Technology, 2019,191:152-167. doi: 10.1016/j.fuproc.2019.04.004 [24] Shen Y S, Yu A B. Modelling of injecting a ternary coal blend into a model ironmaking blast furnace[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016,90:89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2015.12.009 [25] Liu Yiran, Curtis Jennifer, Shen Yansong. Computational fluid dynamics study of re-blowin operation in an ironmaking blast furnace[J]. Powder Technology, 2020,361:145-159. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2019.09.061 [26] Shivadev K Ubhayakar, David B Stickler, Charles W Von Rosenberg, et al. Rapid devolatilization of pulverized coal in hot combustion gases[J]. Symposium (International) on Combustion, 1977,16(1):427-436. doi: 10.1016/S0082-0784(77)80342-1 [27] Du Shanwen, Yeh Chengpeng, Chen Weihsin, et al. Burning characteristics of pulverized coal within blast furnace raceway at various injection operations and ways of oxygen enrichment[J]. Fuel, 2015,143:98-106. doi: 10.1016/j.fuel.2014.11.038 [28] Liao Junhai, Yu Aibing, Shen Yansong. Modelling the injection of upgraded brown coals in an ironmaking blast furnace[J]. Powder Technology, 2016,314:550-556. [29] Kou Mingyin, Zhou Heng, Hong Zhibin, et al. Numerical analysis of effects of different blast parameters on the gas and burden distribution characteristics inside blast furnace[J]. ISIJ International, 2020,60(5):856-864. doi: 10.2355/isijinternational.ISIJINT-2019-389 [30] Xue Qingguo, Dong Zeshang, Wang Jingsong, et al. The introduction and process optimization research of oxygen blast furnace ironmaking technology [M]//Liu Xingbo, Liu Zhengdong, Brinkman Kyle, et al. Energy Materials 2017. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 31-39. [31] Zhou Zhenfeng, Xue Qingguo, Li Changle, et al. Coal flow and combustion characteristics under oxygen enrichment way of oxygen-coal double lance[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering, 2017,123:1096-1105. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.05.177 -





 下载:
下载:













 下载:
下载: