Microstructure and friction and wear properties of titanium modified layer of preset TiCuZnSn by FSP
-
摘要: 为了获得表面综合性能良好的生物医用钛金属,在TA2纯钛表面预置等物质的量的Ti、Cu、Zn、Sn金属粉末,采用搅拌摩擦加工技术对纯钛进行表面改性。通过扫描电镜、能谱仪、电子背散射衍射对钛表面改性层微观组织进行观察和分析,利用纳米压痕、摩擦磨损试验测试改性层机械性能。结果表明:搅拌摩擦加工技术可获得内部无缺陷、与TA2纯钛基体结合良好的表面改性TiCuZnSn合金层,改性层最大深度约2.5 mm;合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn提高了改性层的杨氏模量和硬度,特别是对改性层硬度的提升效果更显著;TiCuZnSn改性层对TA2钛摩擦系数的影响不显著,但改性层的平均磨损率会大幅降低,与TA2钛相比,TiCuZnSn表面改性层平均磨损率降低约28.95%。
-
关键词:
- 钛 /
- 表面改性 /
- TiCuZnSn合金层 /
- 搅拌摩擦加工 /
- 摩擦磨损
Abstract: In order to obtain the biomedical titanium metal with good surface comprehensive properties, the equimolar Ti, Cu, Zn and Sn metal powders were preset on the surface of TA2 pure titanium, and the surface of pure titanium was modified by friction stir processing (FSP). The microstructure of the modified layer was observed and analyzed by scanning electron microscopy, energy dispersive spectrometer and electron back scattering diffraction, and the mechanical properties of the modified layer were tested by nano-indentation and friction and wear tests. The results show that the TiCuZnSn modified layer with no internal defects and good combination with titanium matrix could be obtained by FSP, and the maximum depth of the modified layer is about 2.5 mm. Alloying elements Cu, Zn and Sn could improve the Young’s modulus and hardness of the modified layer, especially the hardness of the modified layer. The TiCuZnSn modified layer has no significant effect on the friction coefficient of TA2 titanium, but the average wear rate of the modified layer is significantly reduced. Compared with TA2 titanium, the average wear rate of the surface modified layer is reduced by about 28.95%.-
Key words:
- titanium /
- surface modification /
- TiCuZnSn alloy layer /
- friction stir processing /
- friction and wear
-
0. 引 言
钛及钛合金具有良好的生物相容性、耐蚀性、无毒性、潜在的成骨反应、高比强度、低杨氏模量和易加工性等[1−2],已成为中高端外科植入物用的主要原材料,特别是在硬组织替代方面[3−4]。钛及钛合金种植体表面是所有生物反应最初发生的基底,种植体表面与周围活体组织的反应过程对实际使用起着至关重要的作用。生物医用钛及其合金通常服役在腐蚀性的体液和复杂的应力环境中,这就要求钛及其合金表面既具有良好的生物相容性、抗菌性能等,同时还应有一定的耐磨性和优异的耐腐蚀性能等[5−6]。表面改性是改善生物医用钛及钛合金表面性能的重要途径,采用表面改性工艺在材料表面制备涂层,有利于提高植入钛及钛合金的综合性能,保持植入钛及钛合金在复杂体液环境中长期服役时结构和性能的稳定[7−8]。
搅拌摩擦加工(FSP)是一种可用于生物医用钛及钛合金表面改性的固相加工技术[9−10]。基于FSP技术在钛合金表面预植入SiC、Zn和Ag等金属添加剂,制备一定厚度的表面复合层,可进一步提高钛及钛合金表面的综合性能[11]。在适当浓度下,含铜的表面改性层会表现出抗炎、促血管生成和成骨作用[12]。锌是人体必需的微量元素,参与骨代谢、细胞信号通路、免疫调节等多种生理过程[13]。Zhang等人[14]研究表明,Zn掺杂TiO2涂层具有良好的抗菌活性和耐腐蚀性能。Hsu等人[15]研究表明,Ti - 1Sn合金具有比工业纯钛更高的弯曲强度和弯曲模量,表现出良好的延展性,是牙科修复应用的最佳候选材料。
基于不同金属添加剂对生物医用钛及钛合金表面性能的影响规律,笔者提出在纯钛表面预置等摩尔Ti、Cu、Zn、Sn混合金属粉,利用FSP对纯钛进行表面加工,在其表面制备TiCuZnSn合金层。以期实现生物医用钛及钛合金表面力学性能和生物相关性能的综合提升。在此基础上,笔者采用扫描电镜(SEM)和电子背散射衍射(EBSD)分析了改性层的微观组织,利用纳米压痕测试技术测试了改性层典型微区的杨氏模量和硬度;利用摩擦磨损试验机测试了摩擦磨损性能,揭示了TiCuZnSn改性层的磨损机制。
1. 试验材料与方法
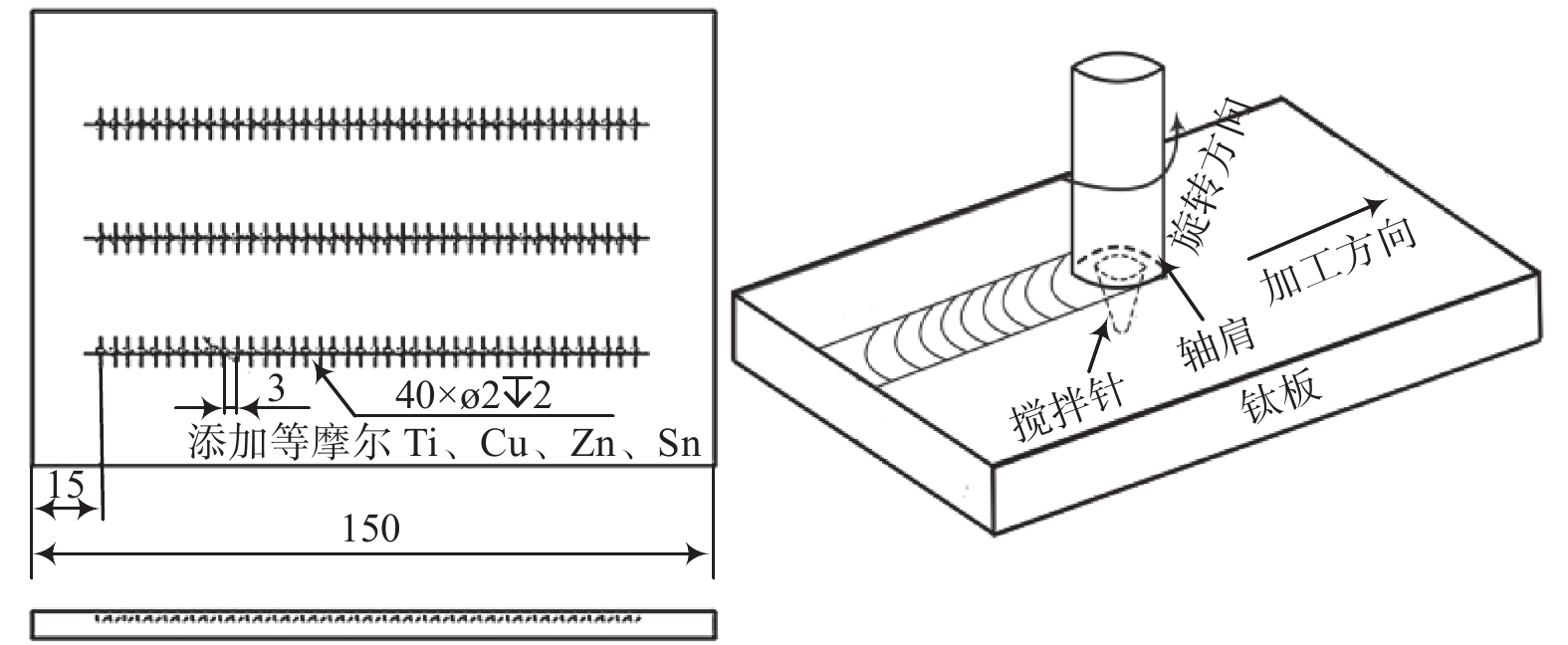
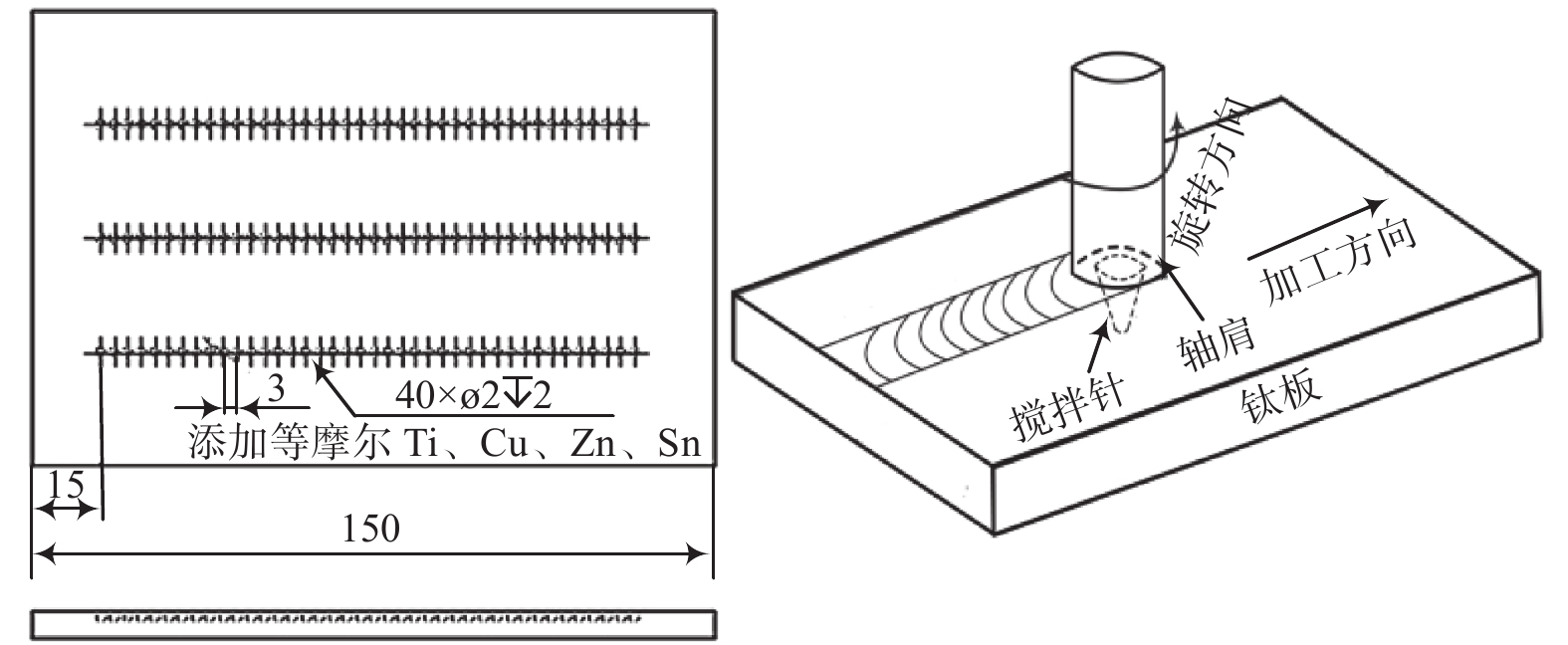
试验基体材料为TA2纯钛板,规格150 mm × 100 mm × 6 mm。钛表面预置等摩尔的Ti、Cu、Zn、Sn金属混合粉末,粉末纯度99.95%,粒径约7 μm。FSP加工过程中用纯度99.99% 的氩气保护钛表面,氩气流量为15 L/min。
图1为钛表面预置TiCuZnSn的搅拌摩擦改性过程示意。预先在钛表面加工直径2 mm,深2 mm的盲孔,盲孔间距3 mm。FSP加工前,采用钢丝刷清理母材表面并用丙酮进行清洗,在盲孔中添加混合金属粉末,并确保压实填满。试验用搅拌头材质为钨铼合金,轴肩直径15 mm,搅拌针呈锥形,上下直径分别是6 mm和4 mm,长度2.7 mm。FSP过程中,沿着盲孔中心线对钛表面进行加工,搅拌头转速225 r/min,沿着加工方向的移动速度为50 mm/min。
2. 试验结果与分析
2.1 表面改性合金层微观组织
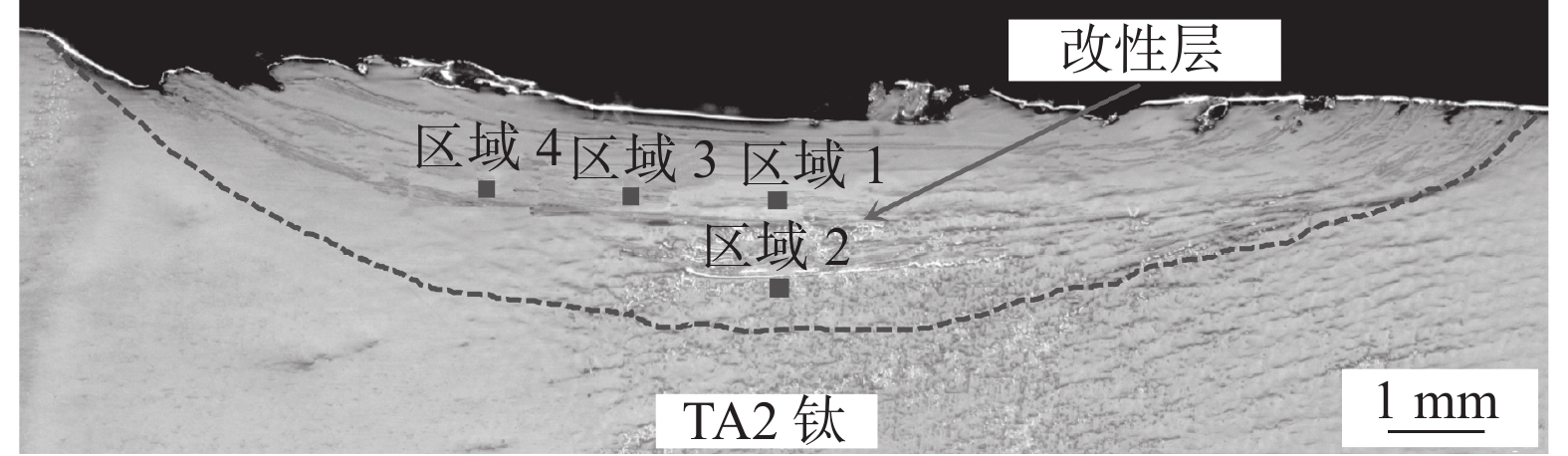
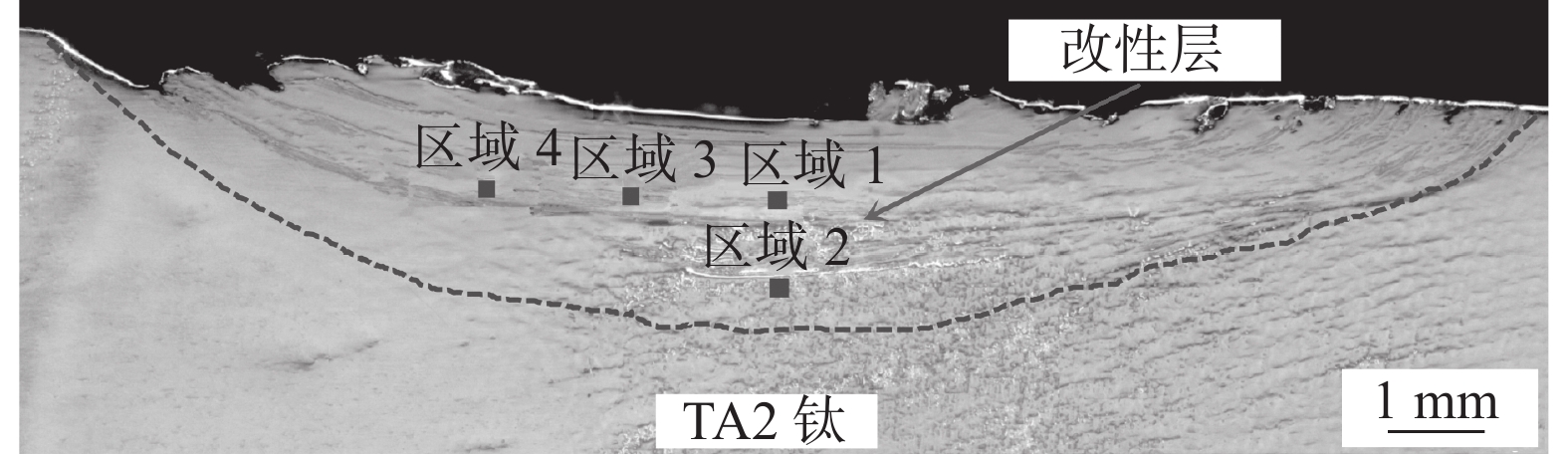
沿着垂直于搅拌摩擦加工的方向,用线切割横向切取钛表面改性层,并按标准制成金相试样,用腐蚀液(1.0 mL HF+2.0 mL HNO3+47 mL H2O)腐蚀试样表面。采用SEM对钛表面改性层横截面进行观察,如图2所示。可以看出TA2钛表面存在一个明显的改性层,其最大深度约2.5 mm;表面改性层内部无缺陷且与钛基体结合良好。该改性层宏观形貌证实,加工过程中该区域组织出现了明显的金属流动迹象,这是由于FSP过程中该区域组织在机械搅拌力和摩擦热的共同作用下金属发生塑性流动造成的[10]。
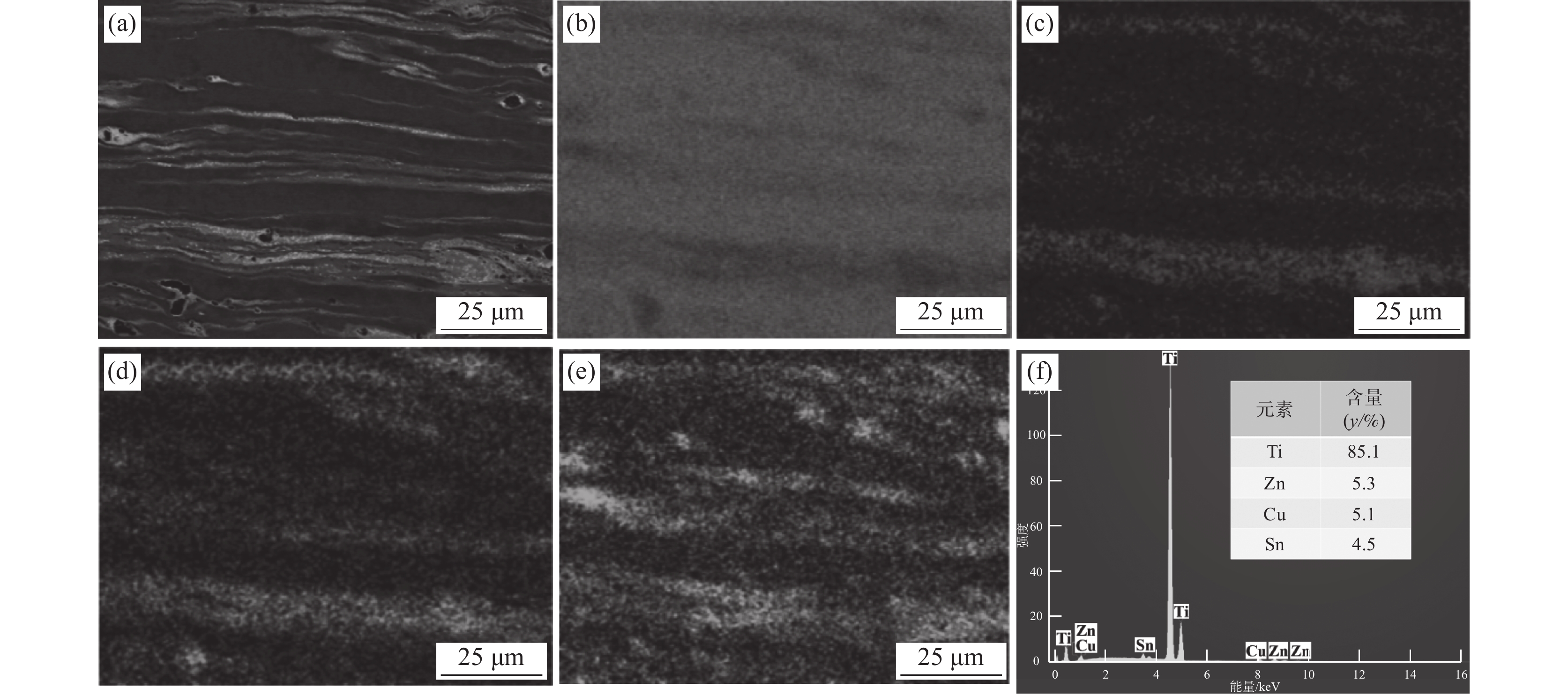
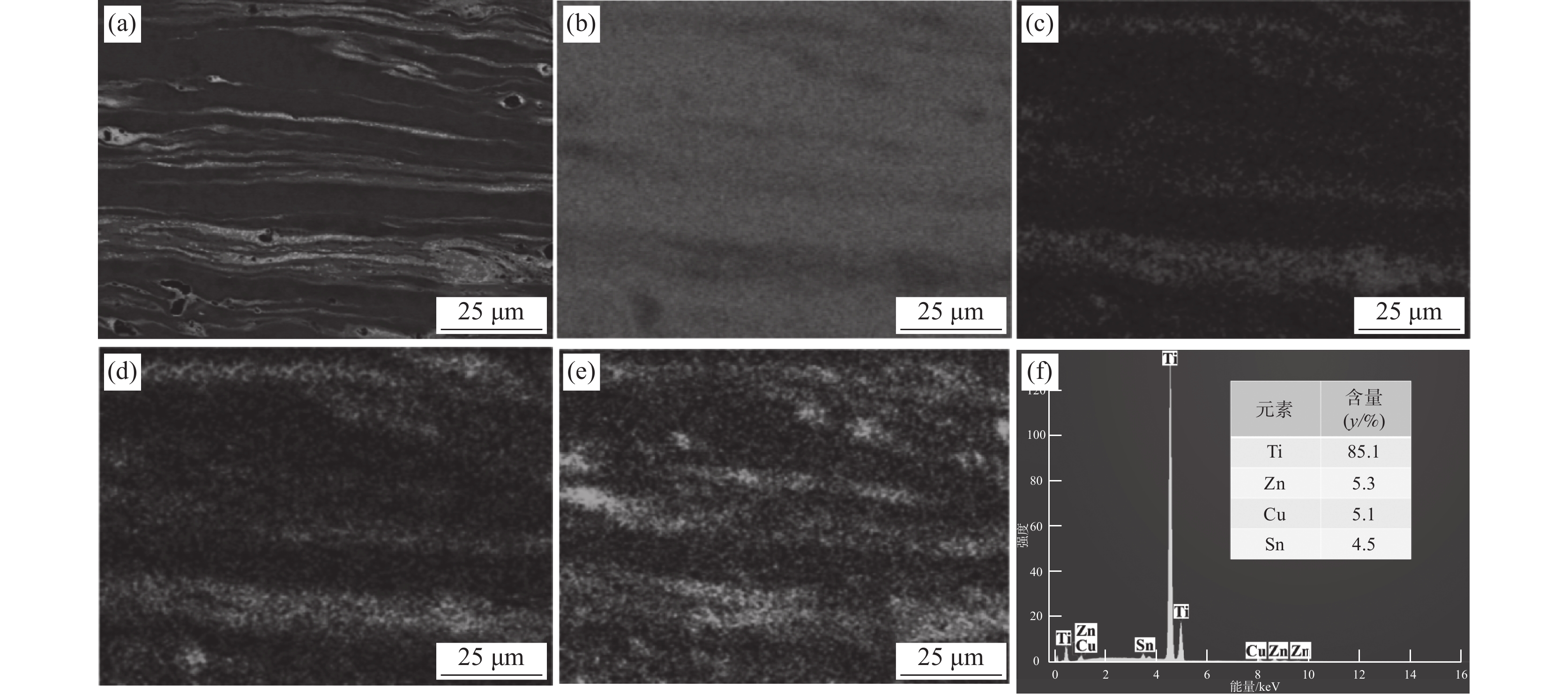
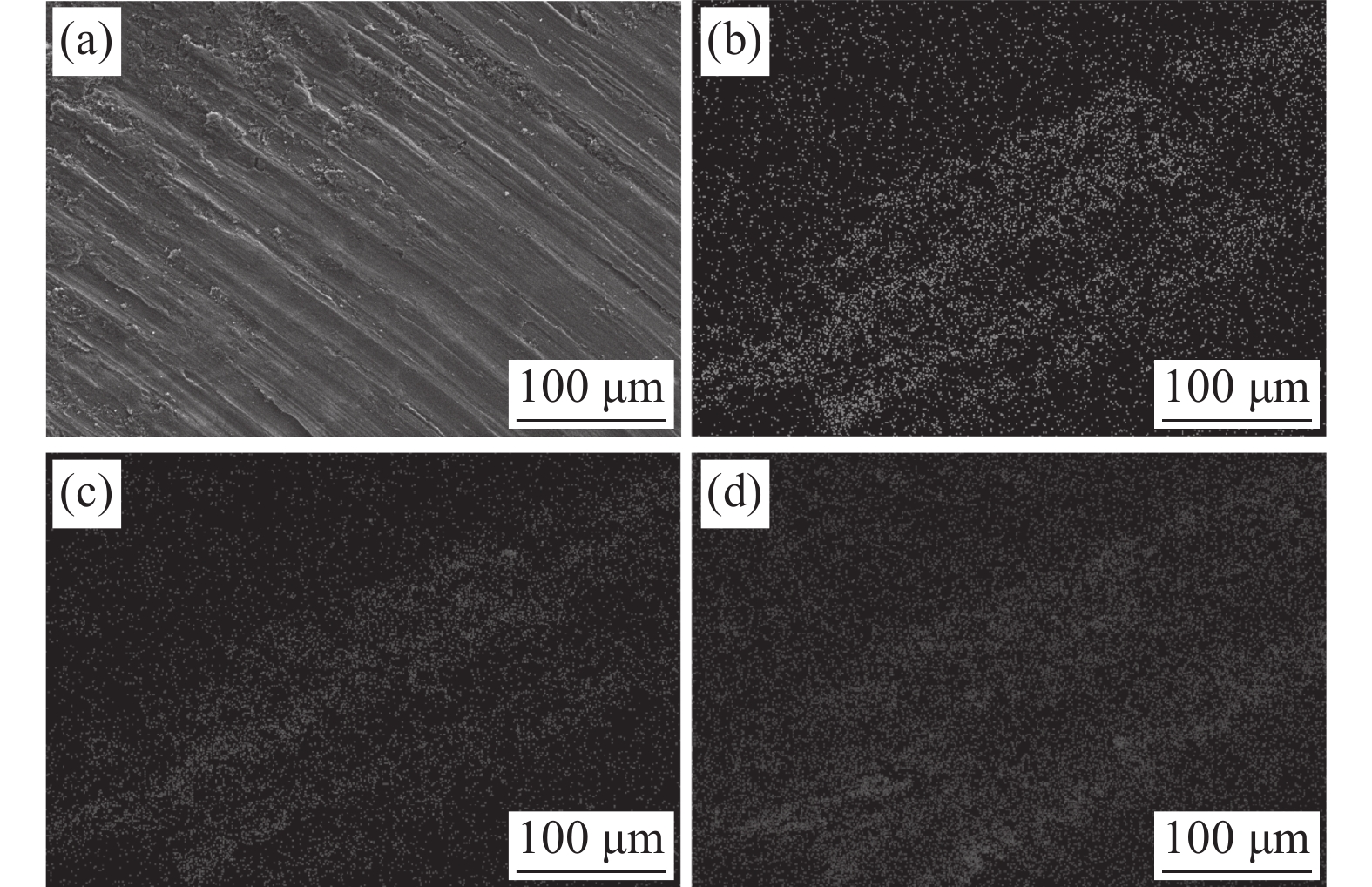
为了进一步分析钛表面改性层组织的化学成分和合金元素分布情况,采用SEM对改性层进行面扫描分析,结果如图3所示。图3(a)所示为改性层组织的背散射电子图像,图中条状分布的白色组织含有大量原子序数较大的合金元素Cu、Zn和Sn;灰色组织合金元素主要为Ti。图3(c)~(e)分别为合金元素Cu、Zn和Sn在表面改性层中的分布图,可以看出,Cu、Zn和Sn以层状结构的形态分布在改性层中,搅拌区塑性流动促使合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn发生扩散是形成该层状结构的主要原因。从图3(f)可知,改性层中合金元素Ti、Cu、Zn、Sn的含量分别为85.1%、5.1%、5.3%和4.5%,预置合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn在改性层中的含量接近。这表明利用搅拌摩擦加工方法在TA2纯钛表面成功制备了TiCuZnSn合金层。
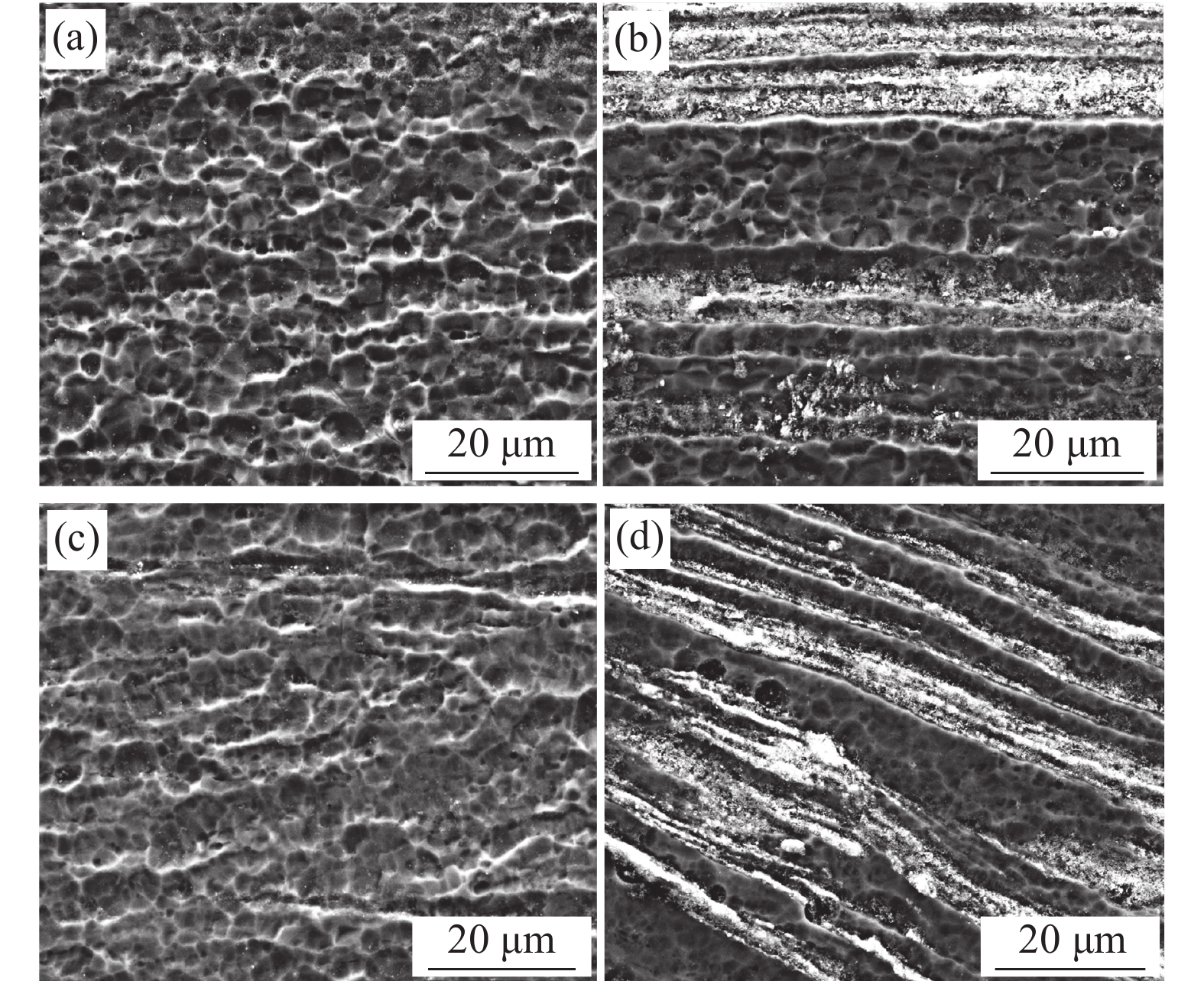
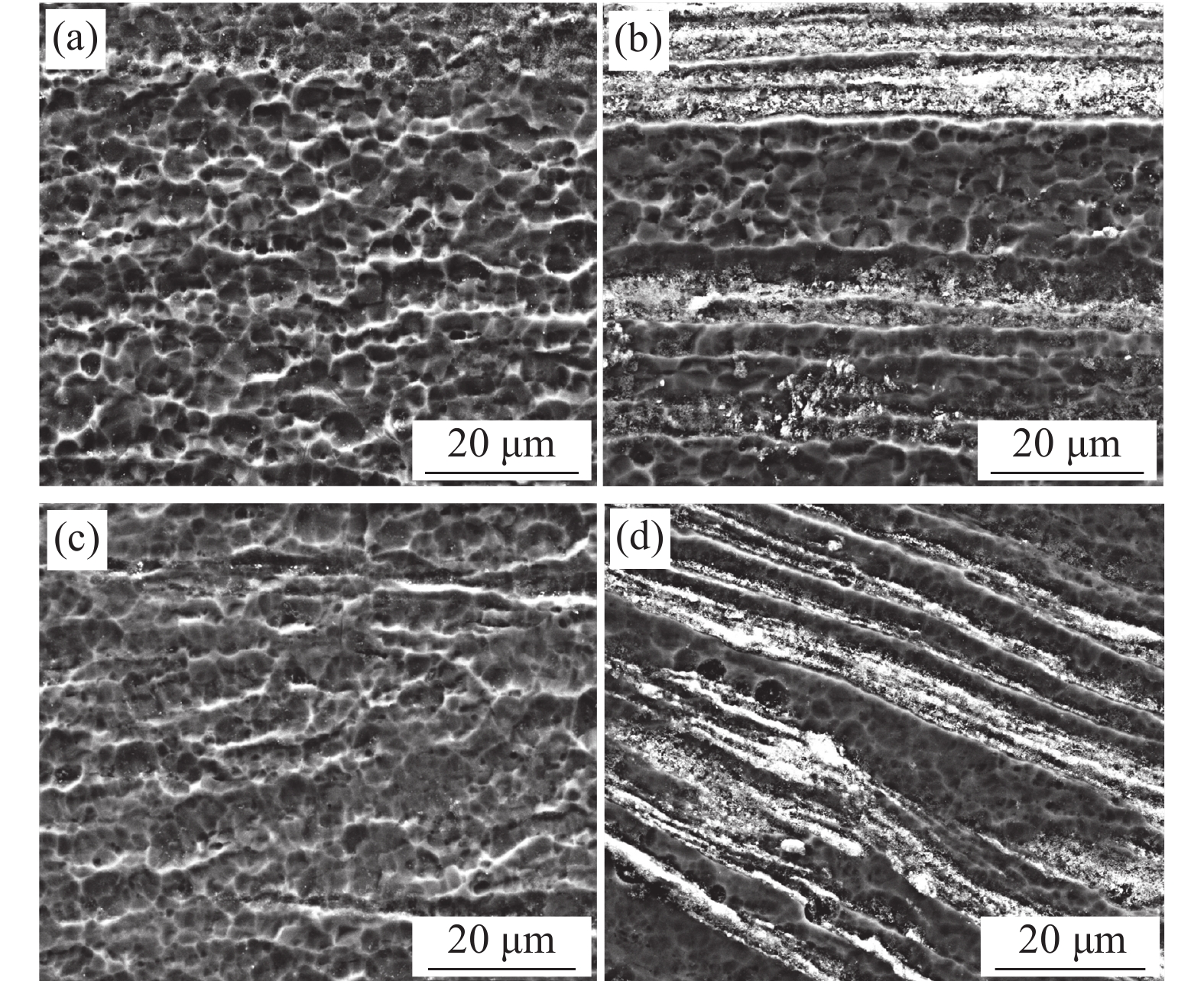
采用SEM分析钛表面TiCuZnSn合金层不同区域的微观组织,测试结果如图4所示。图4(a)~(d)分别为图2中区域1、区域2、区域3和区域4的微观组织。图2中区域1为搅拌区中心位置上部,从图4(a)可以看出,该区域微观组织和合金元素分布均匀,未发现合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn的偏聚。这是由于搅拌针的剧烈搅拌作用使该部分晶粒发生破碎,晶粒呈等轴状[11];此外,搅拌头轴肩产生的摩擦热使该区域温度较高,有利于合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn的充分扩散。图2中区域2为搅拌区中心位置下部,从图4(b)可以看出,该区域局部微区存在呈带状分布的微观组织,该带状组织富含合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn;相较于区域1,作用于区域2的摩擦热少,该区域温度低,金属塑性流动减弱,合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn的扩散不充分,形成了带状分布的微观组织。图2中区域3,由于该区域搅拌针机械搅拌作用减弱,出现了以等轴和条棒状混合分布的组织,如图4(c)所示。但是,搅拌头轴肩和搅拌针的摩擦热使该区域温度较高,有利于合金元素的扩散,因此,区域3微观组织和合金元素分布较均匀,未发现合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn的明显偏聚现象。图2中区域4出现了大量以带状形式分布的微观组织,如图4(d)所示。这是由于FSP过程中搅拌头对该区域组织的机械搅拌作用进一步减弱;另一方面作用于该区域的热输入量降低且散热增加,造成区域4组织温度较低。因此,合金元素的扩散速率显著降低,合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn以带状形态分布在钛基体中[16]。
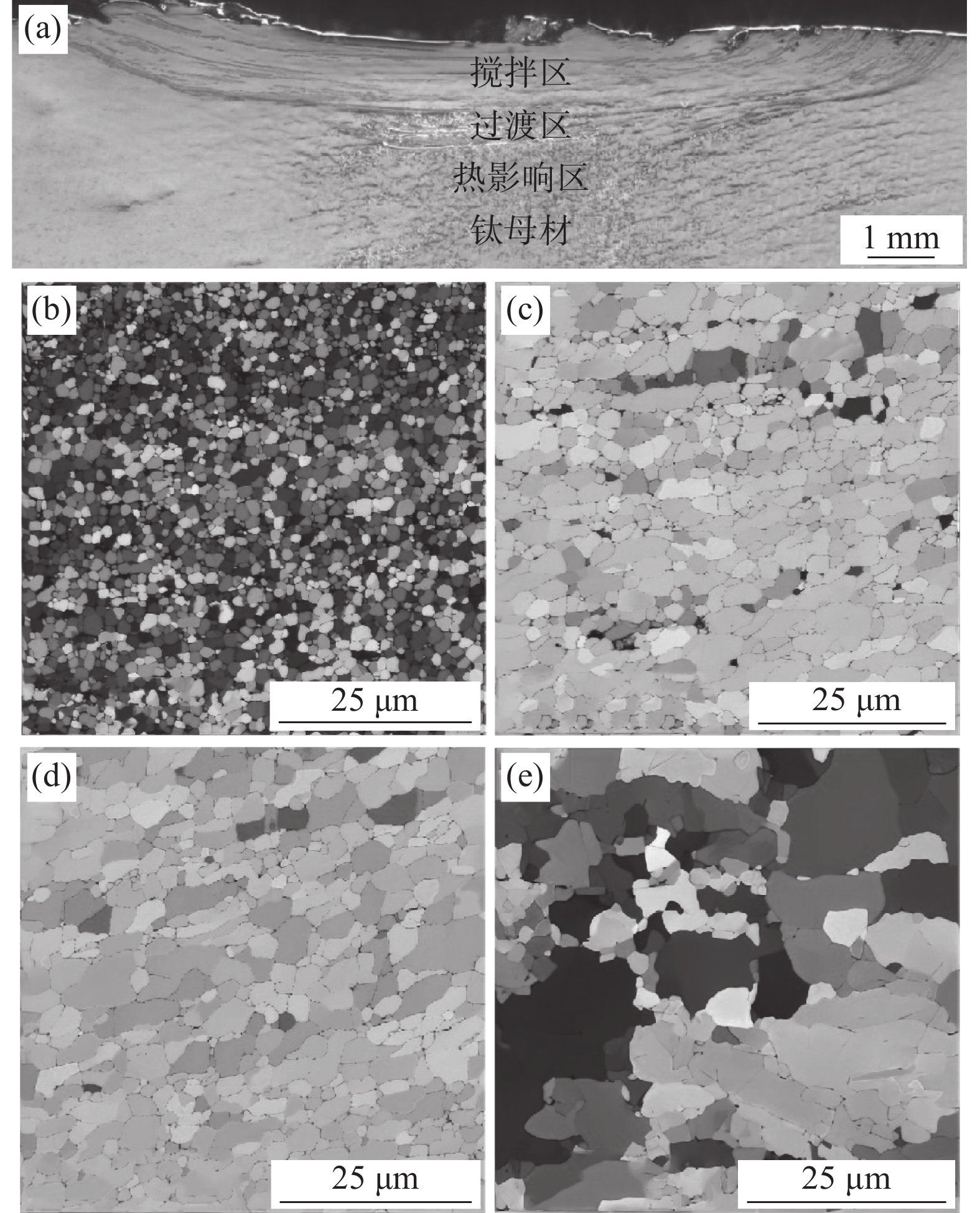
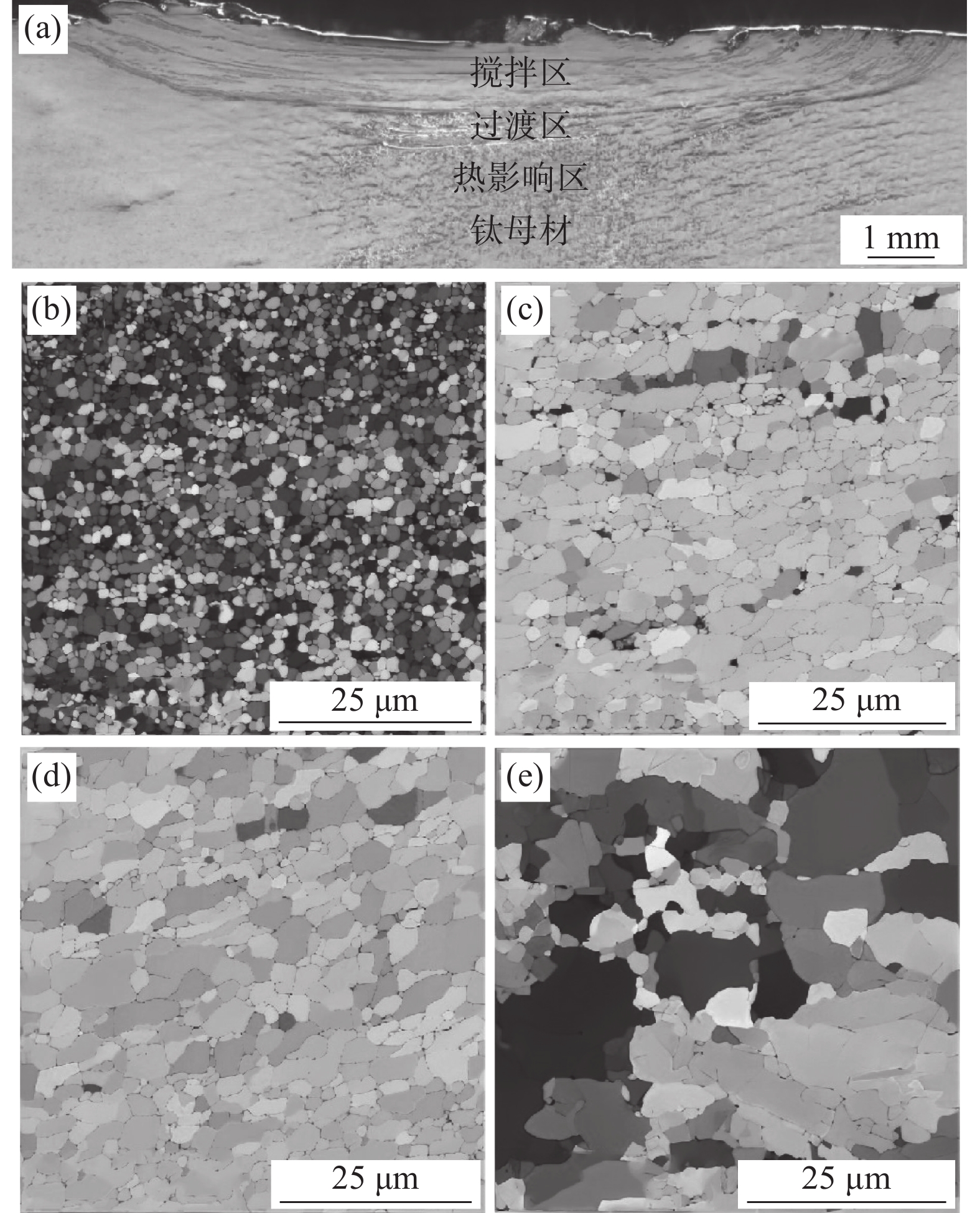
钛表面改性试样从表层至钛基体依次为搅拌区、过渡区、热影响区和钛母材[17],如图5(a)所示。对搅拌摩擦加工试样不同区域的组织进行EBSD分析,图5(b)~(e)分别为搅拌区、过渡区、热影响区和钛母材的欧拉角与晶界图。通过Channel 5软件对不同区域晶粒尺寸进行统计,图5(b) ~ (e)中组织晶粒平均尺寸分别为1.2、7.8、10.8 μm和19.2 μm。图5(b)搅拌区组织在搅拌针剧烈机械搅拌和摩擦热的共同作用下,发生了充分的动态回复 — 再结晶过程,形成了晶粒细小的等轴晶。图5(c)过渡区组织在搅拌头轴肩和搅拌针的机械搅拌和摩擦热作用下发生热塑性流动,晶粒有被拉长的迹象,该区域组织发生了回复 — 再结晶与晶粒长大,与搅拌区晶粒相比,晶粒尺寸明显变大。图5(d)改性层热影响区组织在摩擦热的作用下也发生了回复 — 再结晶。
2.2 表面改性层纳米压痕
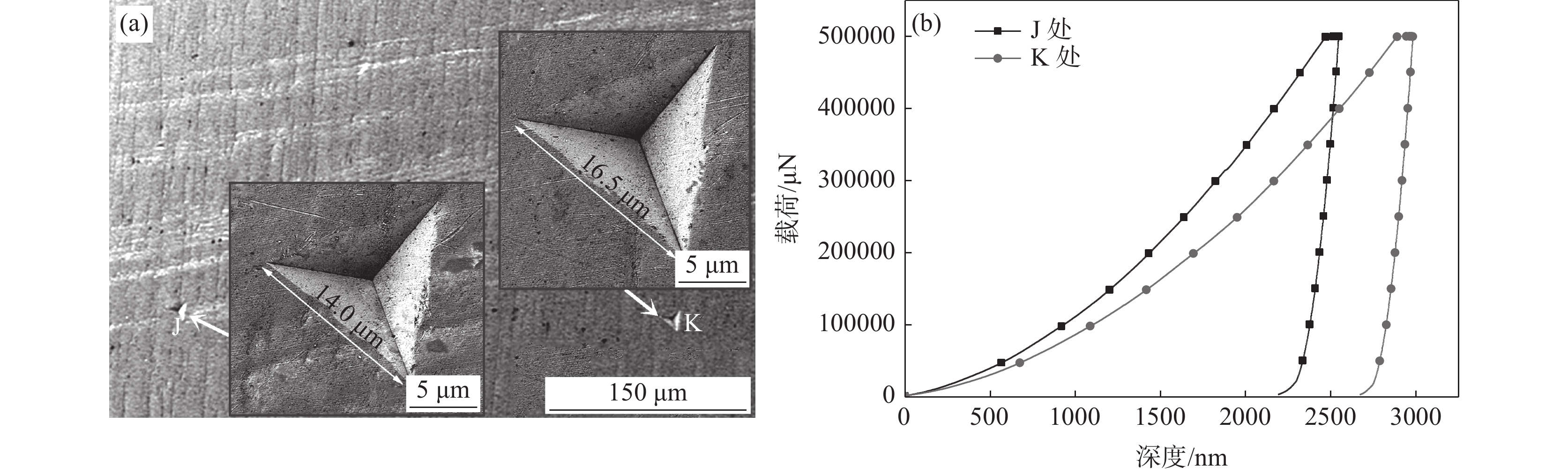
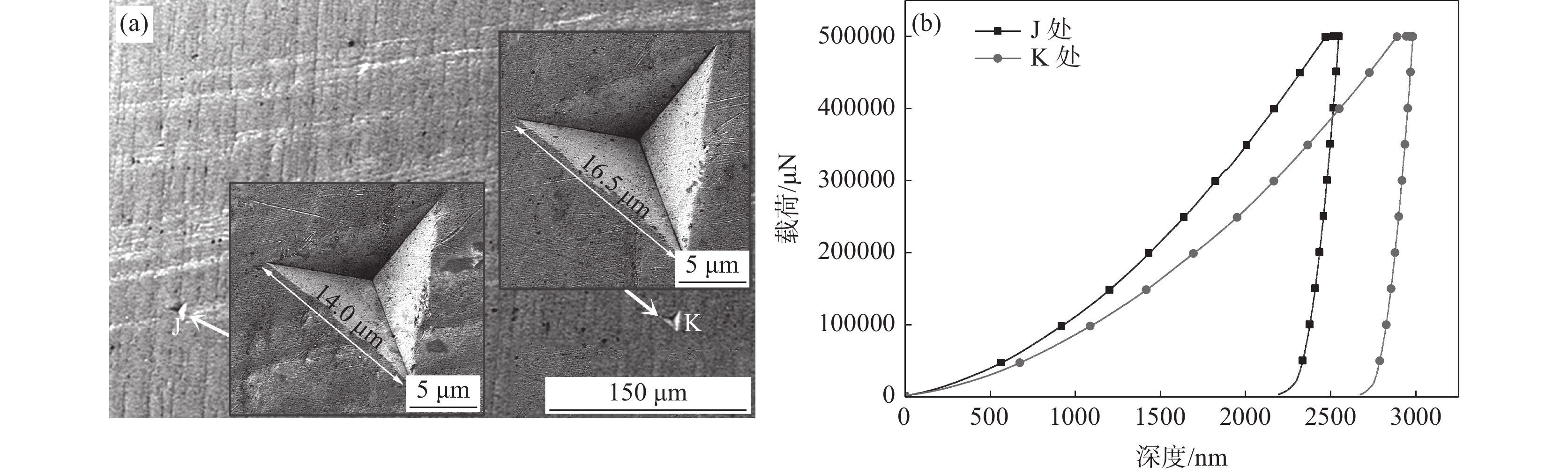
采用纳米压痕试验机测试了钛表面TiCuZnSn合金层典型微区的纳米压痕位移-载荷曲线,并分析了测试试样的微观组织,如图6所示。图6(a)为改性层背散射电子图像,图中白色组织(J处)富含较多合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn,灰色组织(K处)中合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn含量较少,主要为合金元素Ti。图6(b)为J、K两处组织的纳米压痕位移-载荷曲线,依据纳米压痕位移-载荷数据得到了不同微区组织的压痕最大深度、简约杨氏模量和纳米压痕硬度,具体数值见表1。可以发现,改性层中合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn富集区组织的简约杨氏模量和硬度较大,分别为
272.9590 GPa和4.4357 GPa;与改性层其他区域相比,Cu、Zn、Sn富集区组织杨氏模量提高了12.41%,纳米压痕硬度提高了40.04%。由此可以看出,合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn相较于对改性层杨氏模量的提高,对改性层硬度的提升幅度会更加显著。表 1 改性层不同微区纳米压痕测试数值Table 1. Nano-indentation test values of different micro-regions of modified layer位置 压痕最大深度hmax/nm 简约杨氏模量Er/GPa 纳米压痕硬度H/GPa J 2545.7965 272.9590 4.4357 K 2981.7511 242.8243 3.1678 2.3 表面改性层摩擦磨损
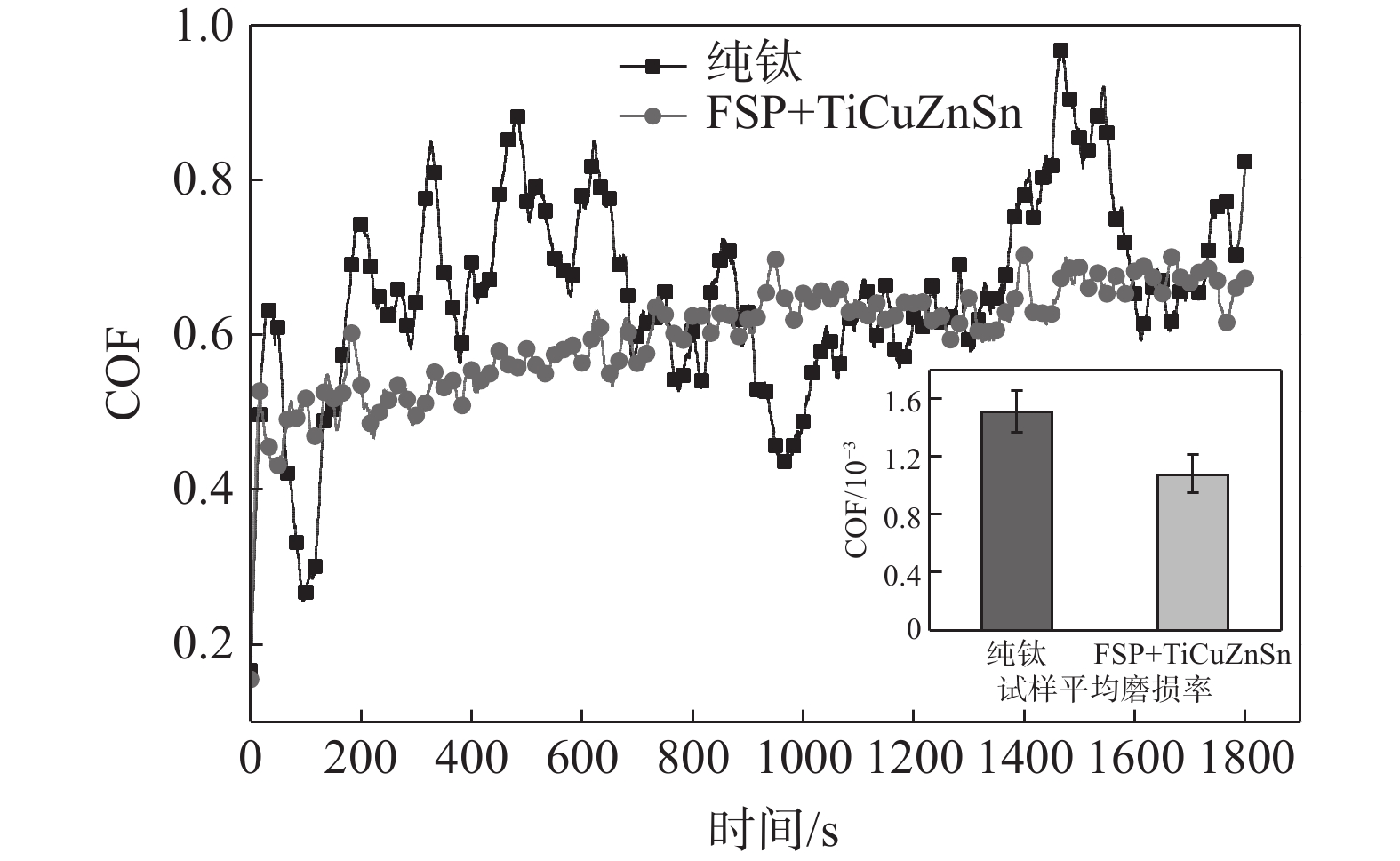
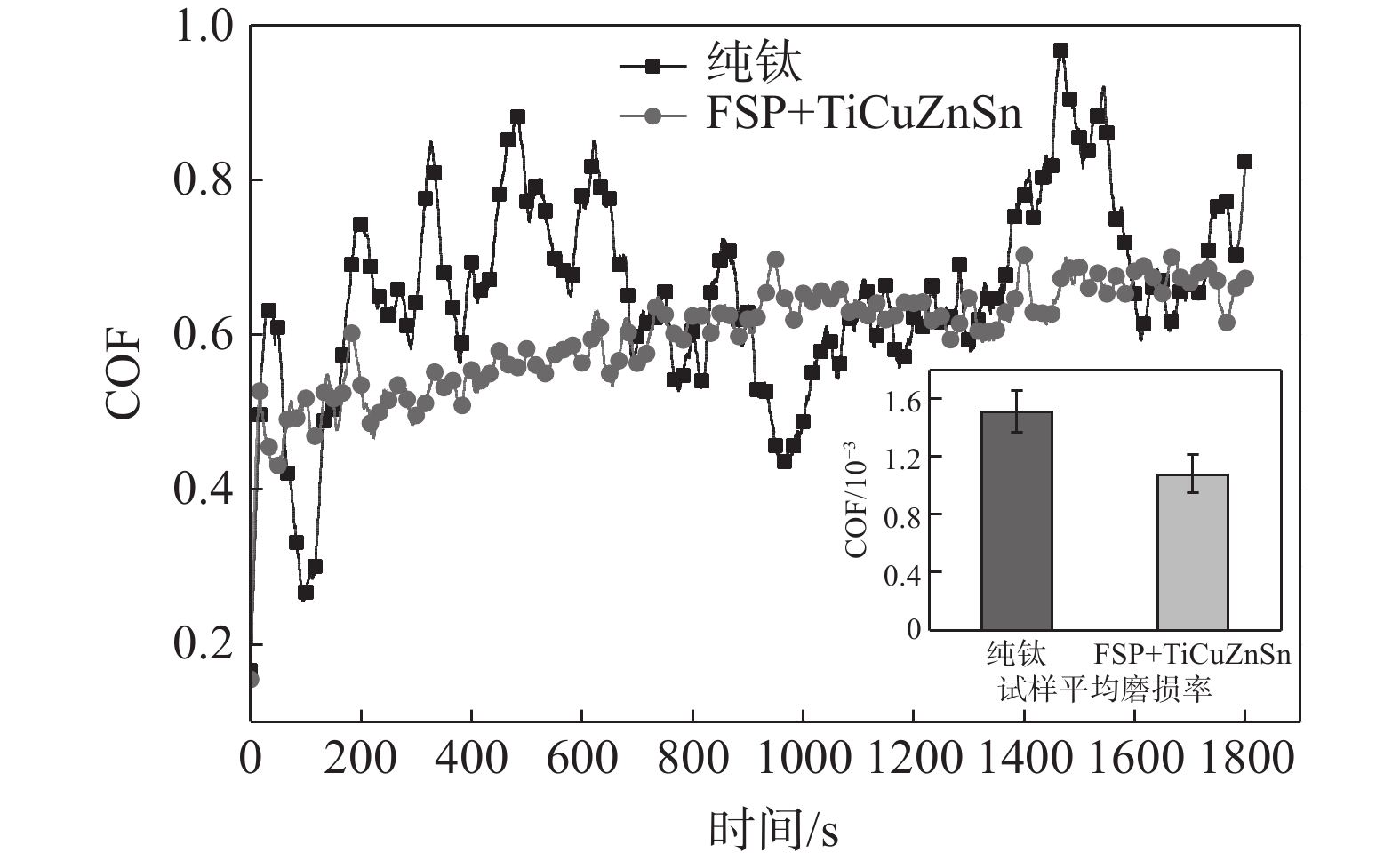
图7所示为纯钛、预置TiCuZnSn钛表面搅拌摩擦改性层的摩擦时间-摩擦因数曲线。摩擦磨损试验采用圆周运动方式,试验载荷330 g、摩擦速率为300 r/min、摩擦时间30 min。可以看出,随着摩擦磨损试验的进行,改性层试样摩擦系数波动减小趋于稳定,纯钛试样摩擦系数波动较大,但两种试样的摩擦系数相差不大。这说明预置TiCuZnSn的钛表面搅拌摩擦改性对钛摩擦系数的影响不显著[18]。依据摩擦磨损试验数据计算得到了两组试样的平均磨损率,纯钛平均磨损率为1.52×10−3,预置TiCuZnSn钛表面搅拌摩擦改性层平均磨损率为1.08×10−3;相较于纯钛试样,TiCuZnSn表面合金层试样平均磨损率降低约28.95%。这是由于FSP使钛表面组织晶粒细化,保持加工硬化状态,其硬度显著提高,降低了磨损率;另一方面,弥散分布在改性层中的合金元素Ti、Cu、Zn与钛基体相互作用,会产生显著的第二相强化作用,进一步提升改性层的摩擦磨损性能。
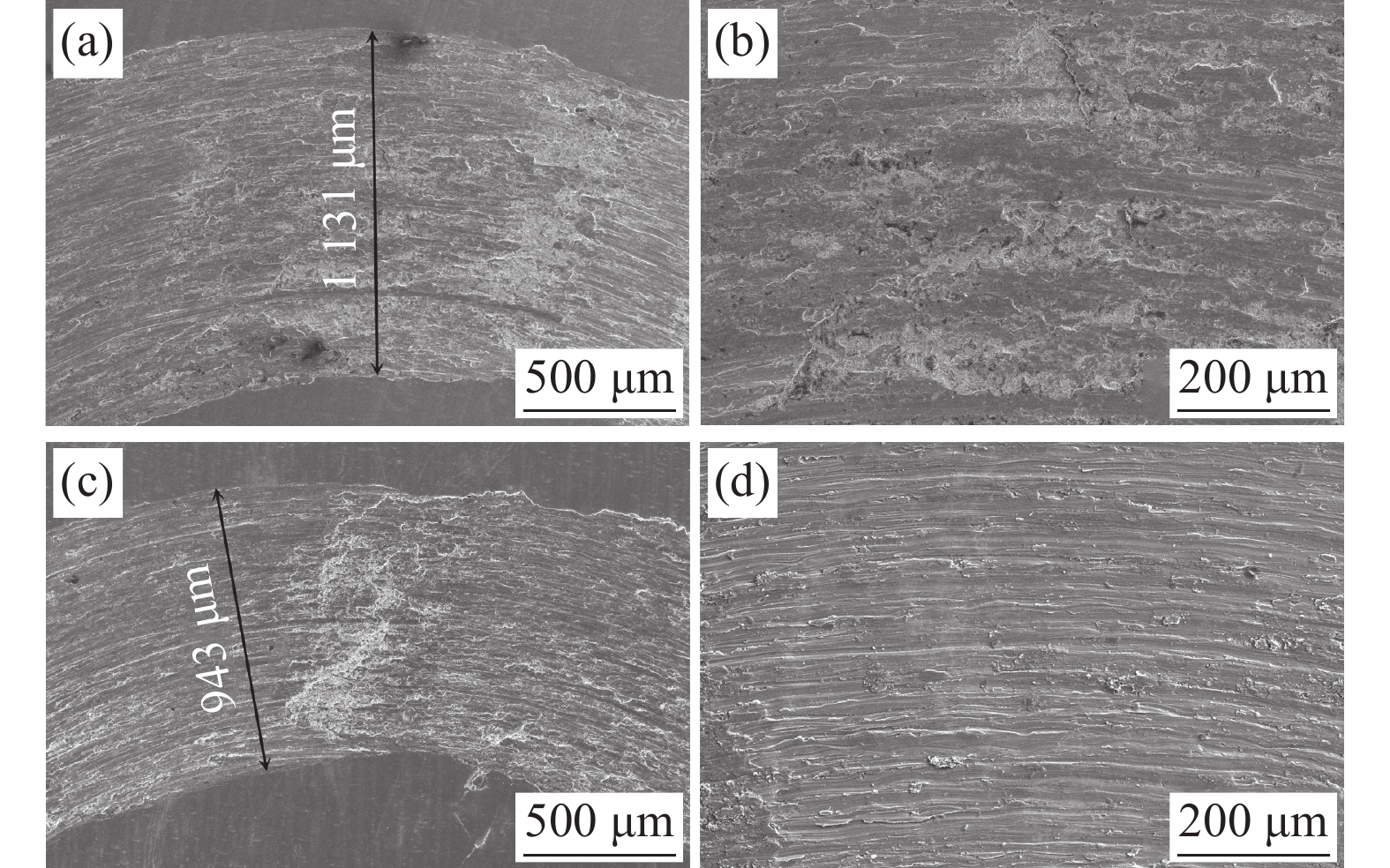
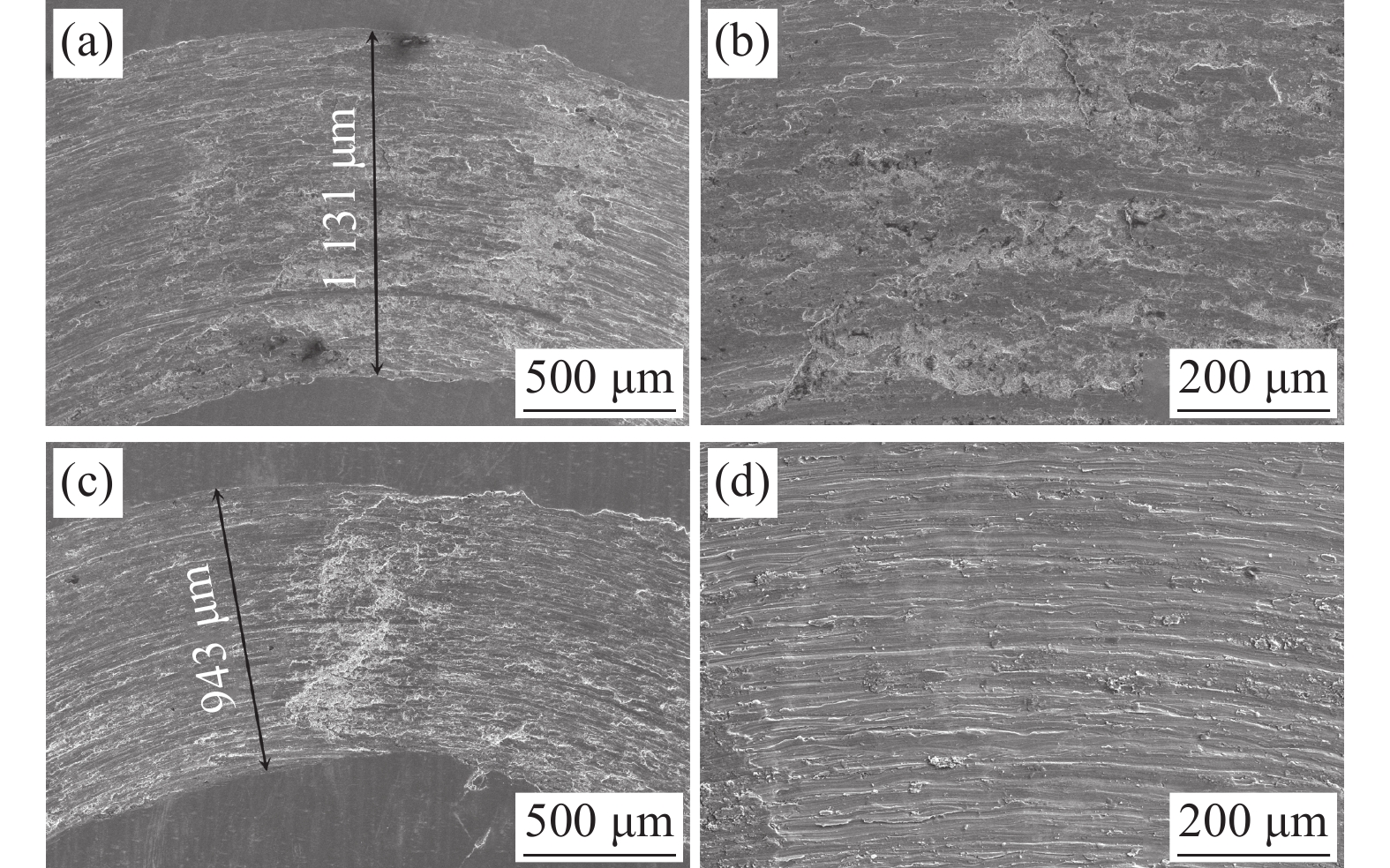
图8(a)和图8(b)所示为不同放大倍数下纯钛试样摩擦磨损后的表面形貌;图8(c)和图8((d)所示为不同放大倍数下改性层试样摩擦磨损后的表面形貌。钛及钛合金磨损机制主要是粘着磨损、磨粒磨损和氧化磨损,Farnoush等人[19]研究表明,对钛进行搅拌摩擦改性后其磨损机制由以粘着磨损为主转变为磨粒磨损。分析图8(a)和图8(c)磨痕宽度,可知纯钛试样磨痕宽度约
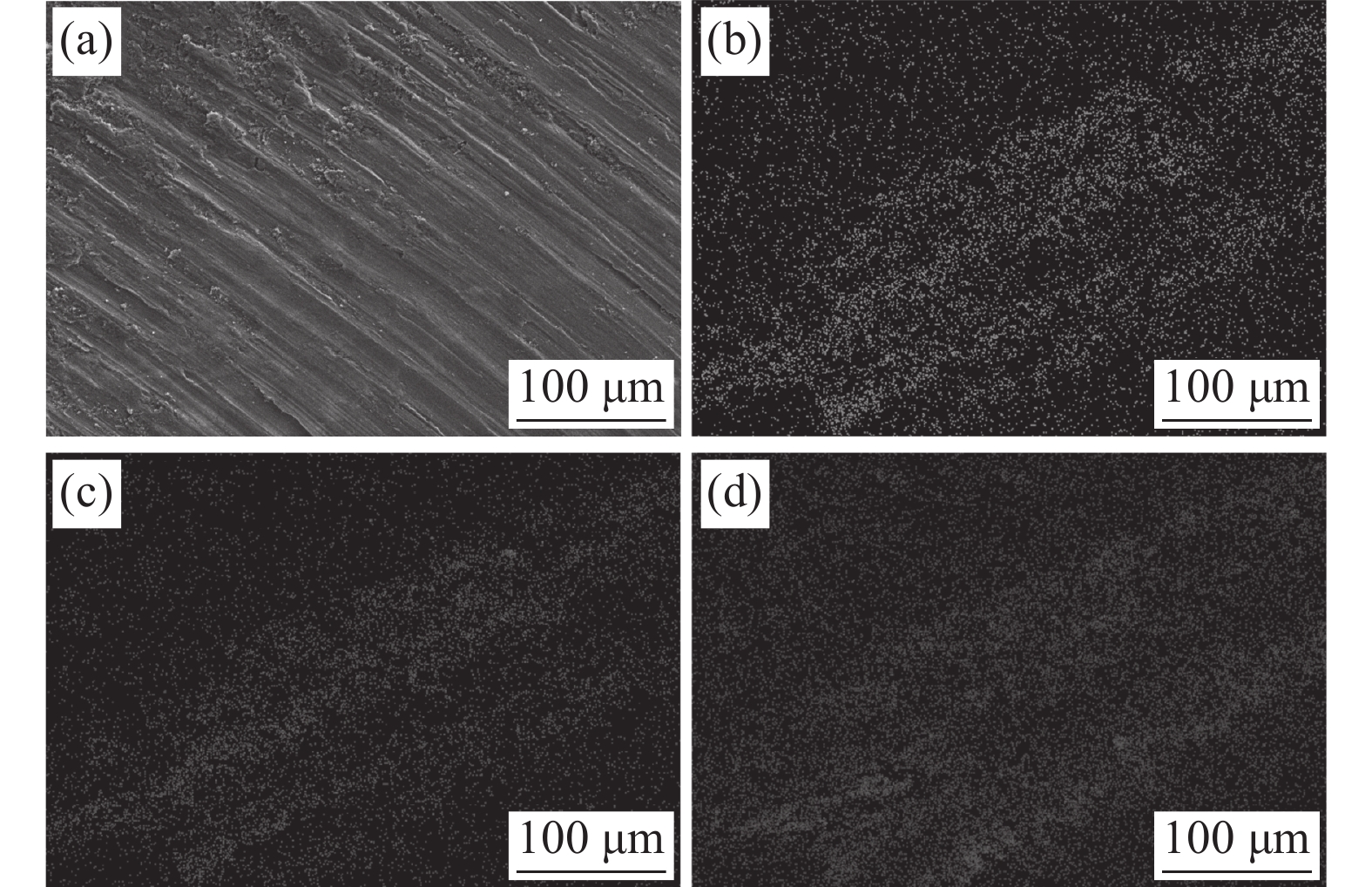
1131 μm,表面改性试样磨痕宽度约943 μm。从图8(b)和图8(d)可以看出,纯钛摩擦磨损面呈剥层撕裂形貌,磨屑尺寸较大;表面改性层试样摩擦磨损面呈“犁沟”磨损形貌,“犁沟”两侧金属产生剧烈塑性变形而翻起,属于磨粒磨损典型特征,犁削屑尺寸较小,磨损量小。为了进一步分析钛表面改性TiCuZnSn合金层的摩擦磨损行为,采用扫描电镜对摩擦磨损表面进行了面扫描,结果如图9所示。从图9(b)~(d)可以看出,合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn分布较多的区域摩擦磨损表面更光滑,该区域组织未发生明显破裂现象和存在较多犁削屑。这进一步说明合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn的存在对提高改性层的摩擦磨损性能是有利的。3. 结论
1)在TA2纯钛表面预置金属粉末TiCuZnSn,通过搅拌摩擦加工技术进行表面改性,可获得内部无缺陷、与钛基体结合良好的生物医用TiCuZnSn表面合金层,该改性合金层最大深度约2.5 mm。
2)合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn提高了钛表面改性层的杨氏模量和硬度,相较于合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn对改性层杨氏模量的提高,对改性层硬度的提升幅度更显著。
3)预置合金元素TiCuZnSn的搅拌摩擦改性层磨损机制主要为磨粒磨损。合金元素Cu、Zn、Sn有助于提高钛表面改性层的摩擦磨损性能,相较于纯钛,该改性层平均磨损率降低约28.95%。
-
表 1 改性层不同微区纳米压痕测试数值
Table 1. Nano-indentation test values of different micro-regions of modified layer
位置 压痕最大深度hmax/nm 简约杨氏模量Er/GPa 纳米压痕硬度H/GPa J 2545.7965 272.9590 4.4357 K 2981.7511 242.8243 3.1678 -
[1] Yi Peiyun, Peng Linfa, Huang Jiaqiang, et al. Multilayered TiAlN films on Ti6Al4V alloy for biomedical applications by closed field unbalanced magnetron sputter ion plating process[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C, 2016,59:669-676. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.10.071 [2] Finke B, Polak M, Hempel F, et al. Antimicrobial potential of copper‐containing titanium surfaces generated by ion implantation and dual high power impulse magnetron sputtering[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials, 2012,14(5):224-230. [3] Xu Ying, Wang Huanhuan, He Shiyu, et al. Preparation and properties of TiO2 nanotubes[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018,39(4):52-57. (许莹, 王欢欢, 何世宇, 等. TiO2纳米管的制备及其性能研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2018,39(4):52-57.Xu Ying, Wang Huanhuan, He Shiyu, et al. Preparation and properties of TiO2 nanotubes[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2018, 39(4): 52-57. [4] Gao Ang, Hang Ruiqiang, Bai Long, et al. Electrochemical surface engineering of titanium-based alloys for biomedical application[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2018,271:699-718. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.03.180 [5] An Zhongsheng, Chen Yan, Zhao Wei. Report on China titanium industry in 2021[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022,43(4):1-9. (安仲生, 陈岩, 赵巍. 2021年中国钛工业发展报告[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2022,43(4):1-9.An Zhongsheng, Chen Yan, Zhao Wei. Report on China titanium industry in 2021[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2022, 43(4): 1-9. [6] Cheng Kaiyuan, Pagan Nicholas, Bijukumar Divya, et al. Carburized titanium as a solid lubricant on hip implants: Corrosion, tribocorrosion and biocompatibility aspects[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2018,665:148-158. doi: 10.1016/j.tsf.2018.08.048 [7] Xue Tong, Attarilar Shokouh, Liu Shifeng, et al. Surface modification techniques of titanium and its alloys to functionally optimize their biomedical properties: Thematic review[J]. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology, 2020,8:1-19. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.00001 [8] Li Jie, Zhou Peng, Attarilar Shokouh, et al. Innovative surface modification procedures to achieve micro/nano-graded Ti-based biomedical alloys and implants[J]. Coatings, 2021,11(6):647. doi: 10.3390/coatings11060647 [9] Li Bo, Shen Yifu. Recent research progress in friction stir welding and friction stir processing of titanium alloys[J]. Welding & Joining, 2016, 520(10): 22-27, 69-70. (李博, 沈以赴. 钛合金搅拌摩擦焊与搅拌摩擦加工研究进展[J]. 焊接, 2016, 520(10): 22-27, 69-70.Li Bo, Shen Yifu. Recent research progress in friction stir welding and friction stir processing of titanium alloys[J]. Welding & Joining, 2016, 520(10): 22-27, 69-70. [10] Zykova Anna P, Tarasov Sergei Yu, Chumaevskiy Andrey V, et al. A review of friction stir processing of structural metallic materials: Process, properties, and methods[J]. Metals, 2020, 10(6): 772. [11] Vikram Kumar S Jain1, James Varghese, S Muthukumaran. Effect of first and second passes on microstructure and wear properties of titanium dioxide-reinforced aluminum surface composite via friction stir processing[J]. Arabian Journal for Science and Engineering, 2018,44(2):949-957. [12] Zhang Erlin, Fu Shan, Wang Ruoxian, et al. Role of Cu element in biomedical metal alloy design[J]. Rare Metals, 2019, 38(6): 476-494. [13] Fang Yingjing, Attarilar Shokouh, Yang Zhi, et al. Toward bactericidal enhancement of additively manufactured titanium implants[J]. Coatings, 2021,11(6):668. doi: 10.3390/coatings11060668 [14] Zhang Xiangyu, Wang Huizhen, Li Jiangfang, et al. Corrosion behavior of Zn-incorporated antibacterial TiO2 porous coating on titanium[J]. Ceramics International, 2016,42(15):17095-17100. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2016.07.220 [15] Hsu Hsuehchuan, Wu Shihching, Hong Yusheng, et al. Mechanical properties and deformation behavior of as-cast Ti-Sn alloys[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009,479(1-2):390-394. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2008.12.064 [16] Singh, Abhishek Kumar, Kaushik Lalit, et al. Evolution of microstructure and texture in the stir zone of commercially pure titanium during friction stir processing[J]. International Journal of Plasticity, 2022,150:103184. doi: 10.1016/j.ijplas.2021.103184 [17] Wang Liqiang, Xie Lechun, Lü Yuting, et al. Microstructure evolution and superelastic behavior in Ti-35Nb-2Ta-3Zr alloy processed by friction stir processing[J]. Acta Materialia, 2017,131:499-510. doi: 10.1016/j.actamat.2017.03.079 [18] Guo Yongyi, Jiang Luyao, Huang Weijiu, et al. Effect of low rotation speed on tribological properties of friction stir processed commercial pure Ti[J]. Surface Technology, 2018,47(9):101-108. (郭勇义, 蒋璐瑶, 黄伟九, 等. 慢速搅拌摩擦加工对工业纯钛摩擦磨损性能的影响[J]. 表面技术, 2018,47(9):101-108.Guo Yongyi, Jiang Luyao, Huang Weijiu, et al. Effect of low rotation speed on tribological properties of friction stir processed commercial pure Ti[J]. Surface Technology, 2018, 47(9): 101-108. [19] Farnoush H, Bastami A B, Sadeghi A, et al. Tribological and corrosion behavior of friction stir processed Ti-CaP nanocomposites in simulated body fluid solution[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2013,20:90-97. doi: 10.1016/j.jmbbm.2012.12.001 -






 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载: