Effect of V content on microstructure and properties of laser cladding Fe-Cr alloy coatings
-
摘要: 采用激光熔覆技术制备了不同V含量的铁铬合金涂层,结合金相观察、SEM & EDS、X-射线衍射等分析方法研究了V含量变化时激光熔覆铁铬合金涂层的显微组织与性能的变化规律。结果表明,V含量较低时铁铬合金涂层以树枝晶生长模式为主,涂层界面的树枝晶生长过程中Cr元素来不及完全固溶到基体中,引起基体衍射峰向高角度处偏移。增加V含量能够促进树枝晶向胞状晶转变,有效改善了Cr元素在基体中不能完全固溶的现象。VC的形成促进了凝固过程中γ-Fe向马氏体的转变,涂层硬度提升,但当V含量增加到2%时,原料中高熔点钒铁含量增加,导致涂层中气孔缺陷增加,引起涂层耐磨性能降低。当V含量为1%时涂层性能最佳。Abstract: Iron-chromium alloy coatings with varying V content were fabricated using laser cladding. The microstructural and performance variations of the laser-cladded iron-chromium alloy coatings with different V contents were investigated using metallographic observation, SEM & EDS, and X-ray diffraction analysis. The results indicate that at lower V content, the iron-chromium alloy coating predominantly exhibits a dendritic growth mode. At the coating interface, the dendritic grew rapidly, Cr elements do not have sufficient time to completely dissolve into the matrix, causing the matrix diffraction peaks to shift to higher angles. Increasing V content promotes the transition from dendritic to cellular growth, effectively improving the incomplete dissolution of Cr elements in the matrix and leading to a more uniform coating structure. The formation of VC promotes the transformation of γ-Fe to martensite during solidification, and the hardness of the coating increases. However, when the V content increases to 2%, the ferrovanadium content with a higher melting point increases, resulting in an increase in pore defects, which makes the wear resistance of the coating decrease. When the V content in the coating is 1 %, the hardness and wear resistance are the best.
-
Key words:
- laser cladding /
- VC /
- iron-chromium alloy coating /
- microstructure /
- performance
-
0. 引言
激光熔覆技术具有加工精度高、熔池热影响区小、基材热变形程度小等优异特性,使得基材能够最大限度地保留其结构和性能[1−5]。激光熔覆的原材料可根据基材成分的变化选择和基材物性参数匹配的合金材料,材料选择性广,成为轨道交通、钢铁冶金关键部件的重要修复手段[6−9]。
基于冶金关键部件的材质以不同类型的合金钢为主,铁基合金与基材的物性参数匹配好,降低了对稀释率的严格要求,钝化了稀释率对涂层力学性能的影响[10],特别是Fe-Cr-C体系以其硬度高、耐磨性能好成为激光熔覆铁基涂层广泛应用的选材体系[11−12]。然而,Fe-Cr-C硬面涂层中的铬碳化物初生相脆性大,以大块形式存在时严重影响涂层的使用性能[13−14]。通过加入V、Ti、Nb等强碳化物形成元素可有效改善铬碳化物的形貌和分布,提高涂层综合性能[15−16]。V作为重要的合金元素具有调节晶粒生长、提高材料硬度和耐磨性等诸多优点[17−20]。聂辉文等人[1]在激光熔覆Fe50Mn30Cr10Co高熵合金涂层中加入了不同含量的V,发现随着V含量的增加,高熵合金的组织细化,且显微硬度、耐磨和耐腐蚀性能同步提升。Wang 等人[21]以Cr3C2和FeV50为原料制备了激光熔覆铁基合金涂层,发现V含量的增加有效改善了涂层中铬碳化物的微观形貌,涂层硬度和耐磨性能提高。然而目前报道的试验研究基材以低碳钢为主,基材的C含量增加会极大地影响涂层的微观组织和性能,高碳含量为基材时V含量对激光熔覆铁基合金涂层的影响研究报道较少。为此,笔者以60CrMnMo为基材研究了V含量对激光熔覆铁铬合金涂层组织结构和性能的影响,旨在为V强化铁铬合金涂层的应用研究提供理论支撑。
1. 试验材料和方法
激光熔覆铁铬合金涂层的60CrMnMo基材尺寸为100 mm×100 mm×20 mm,基材的化学成分如表1所示。激光熔覆试验前用RFL-P300型手持式激光除锈器对基材表面进行除锈,并用酒精去除表面污垢。
表 1 60CrMnMo基材成分Table 1. Elemental composition of 60CrMnMo basic materials% Ni C Si Mn Cr Mo Fe 0.3 0.56 0.25 0.75 1.12 0.25 余量 激光熔覆粉末原料为60低碳铬铁(w[C]=0.23%)、69高碳铬铁(w[C]=8.51%)、50钒铁(w[C]=0.26%)、72硅铁粉、球形铁粉,涂层合金元素的成分设计如表2所示。利用ZX型双锥高效混合机将粉末混合均匀,在120 ℃干燥箱中烘干备用。
表 2 各种混合粉末的元素组成Table 2. Elemental compositions of various mixed powders% 试验样品 Fe V Si Cr C V-0.5 87.80 0.50 1.00 9.70 1.00 V-1 87.30 1.00 1.00 9.70 1.00 V-2 86.30 2.00 1.00 9.70 1.00 本试验设备为LDF
6000 -60型同轴激光熔覆系统,具体试验参数如下:激光功率为2200 W,保护气体氩气的气体流量为10 L/min,激光光斑直径为4 mm,扫描速度为10 mm/s。试验结束后沿基材纵向剖面分别切割成尺寸为10 mm× 10 mm × 10 mm和30 mm× 30 mm × 5 mm的样品,用于涂层组织结构和硬度、摩擦磨损性能分析。采用X’Pert Powder型X射线衍射仪进行物相分析,试验参数如下:Cu靶、测试电压40 kV、步长0.02°、扫描速度6°/s、扫描角度30°~100°。采用Hv-
1000 STA型维氏硬度仪进行显微硬度分析,测试压力为1.96 N,加载时间为10 s。采用MVF-1A型摩擦磨损试验机进行摩擦磨损试验,压力为80 N,转速为200 r/min,加载时间为30 min。采用盐酸和硝酸体积分数比为1∶4的腐蚀液对抛光后的样品进行腐蚀,在ZEISS Axiocam-506型金相显微镜上观察金相组织,在ZEISS Sigma 500型场发射扫描电镜上进行显微形貌和能谱分析。2. 结果及讨论
2.1 涂层显微组织
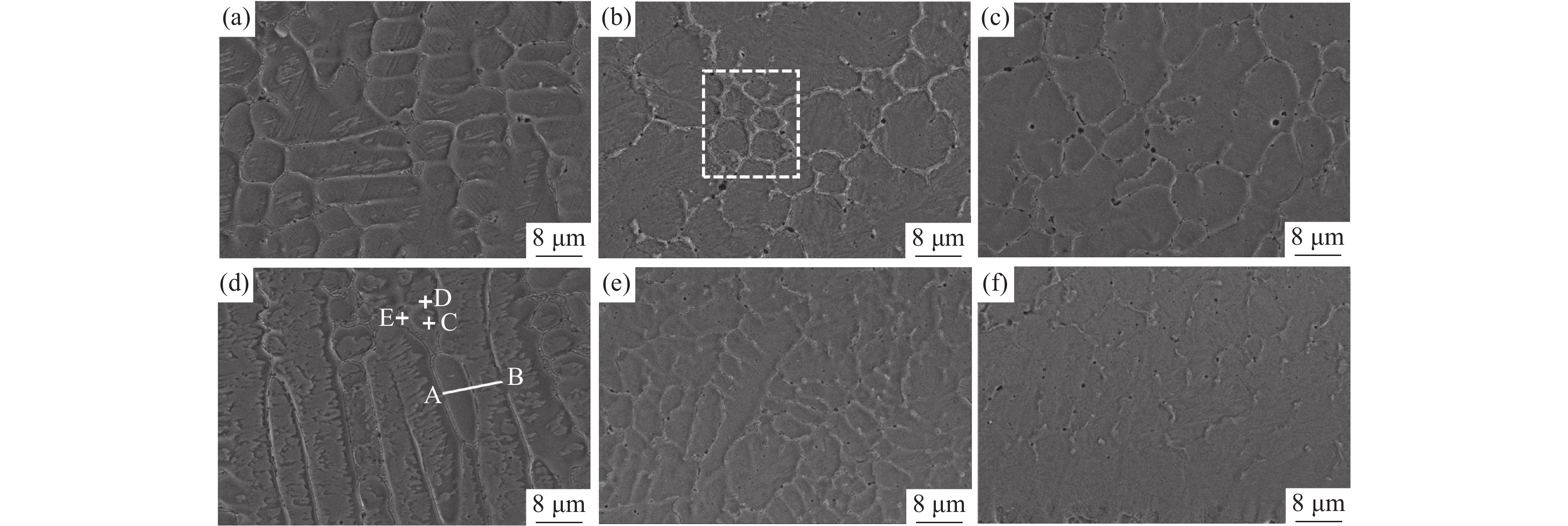
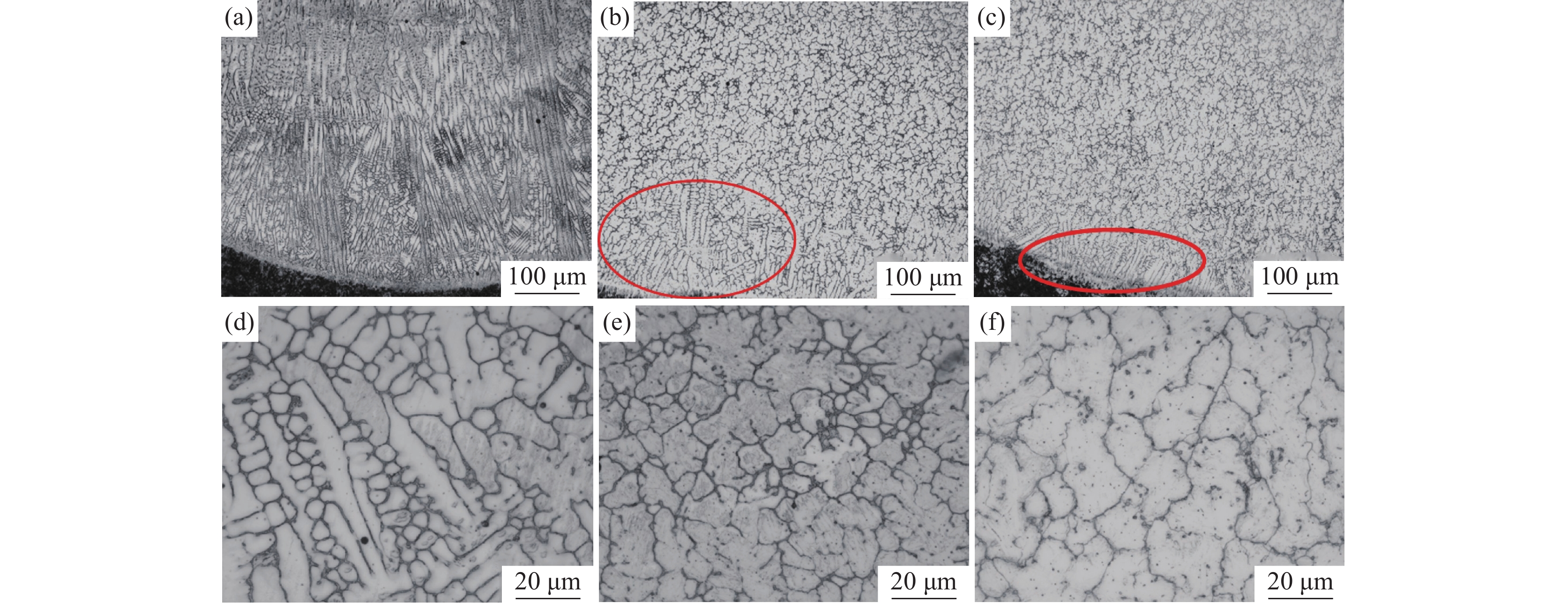
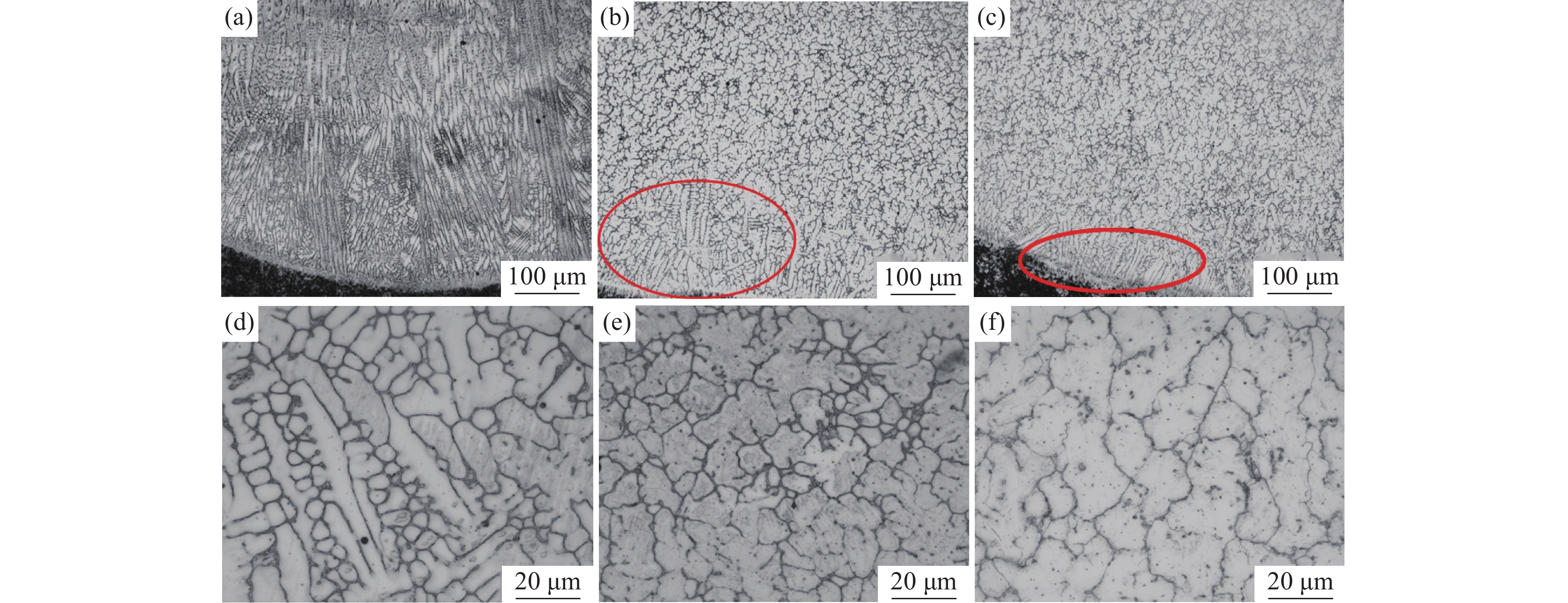
图1为不同V含量的激光熔覆铁铬合金涂层金相组织。图1(a)~(c)为200倍时涂层中下部的宏观组织,图1(d)~(f)为
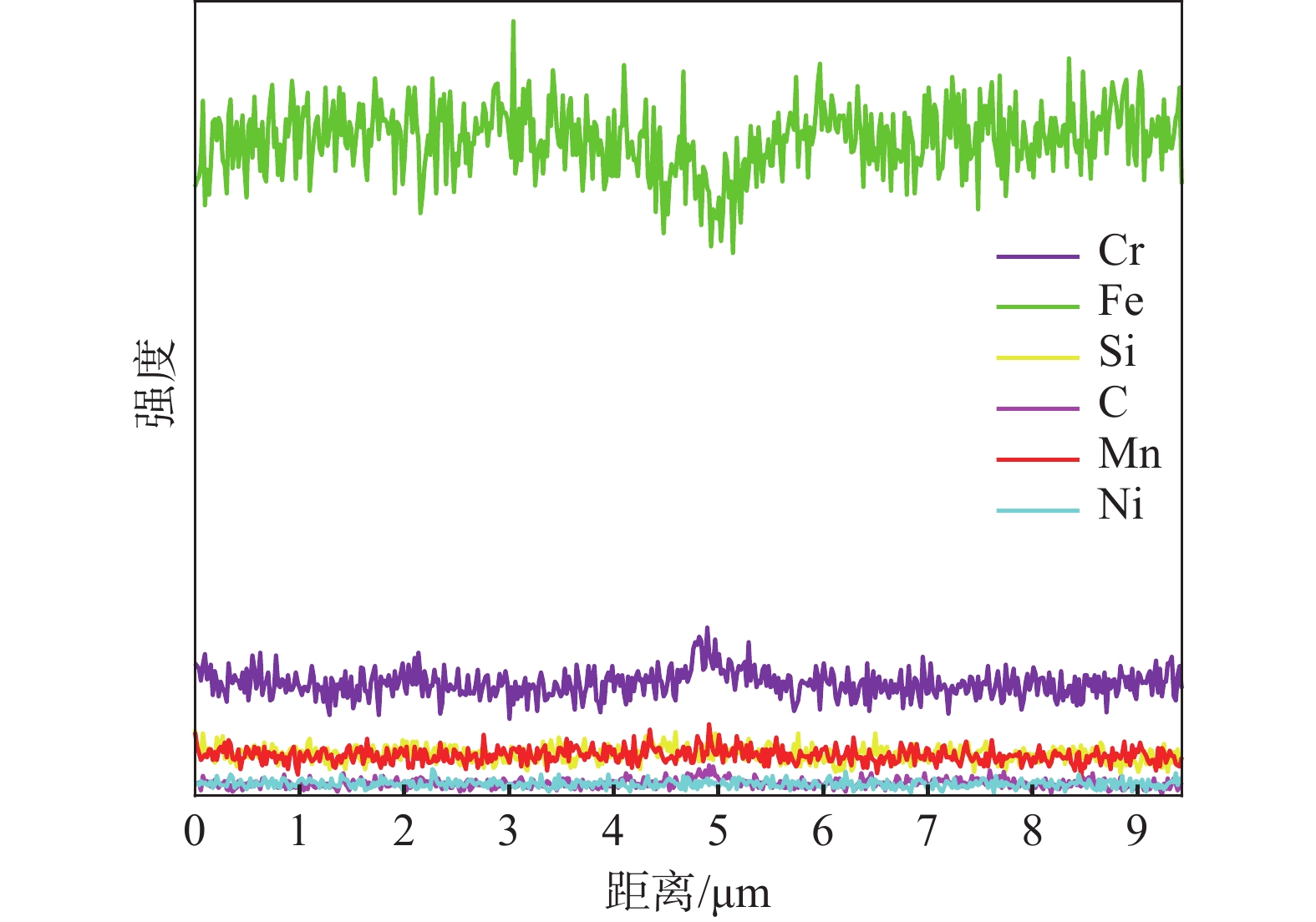
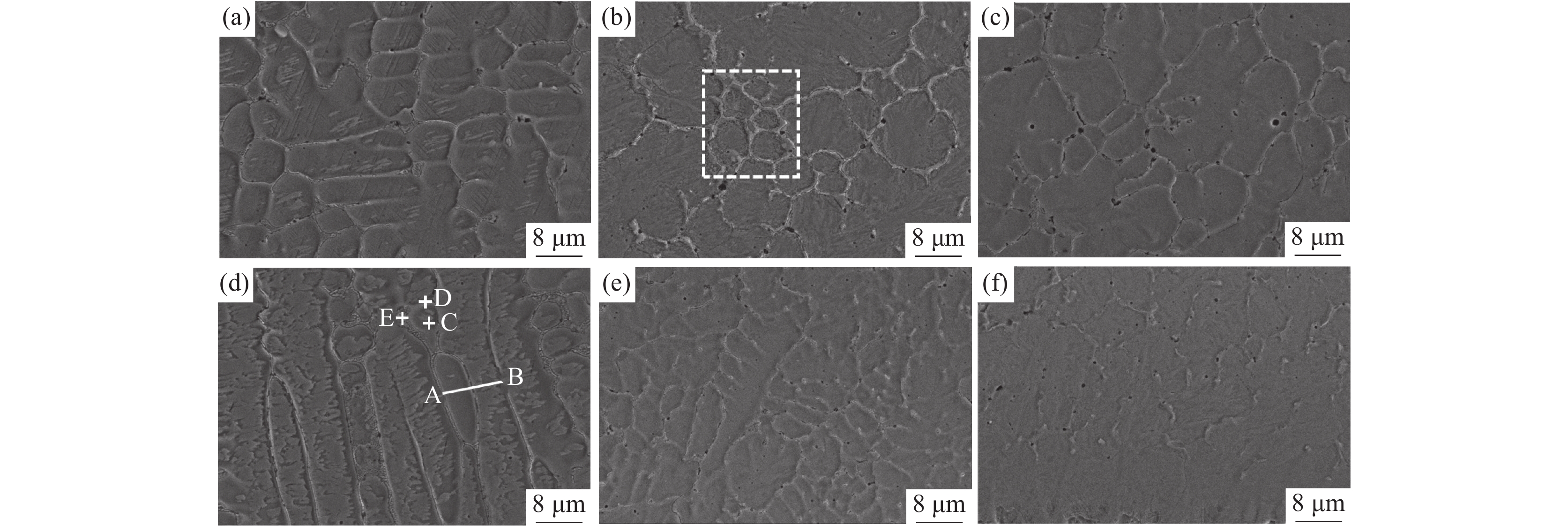
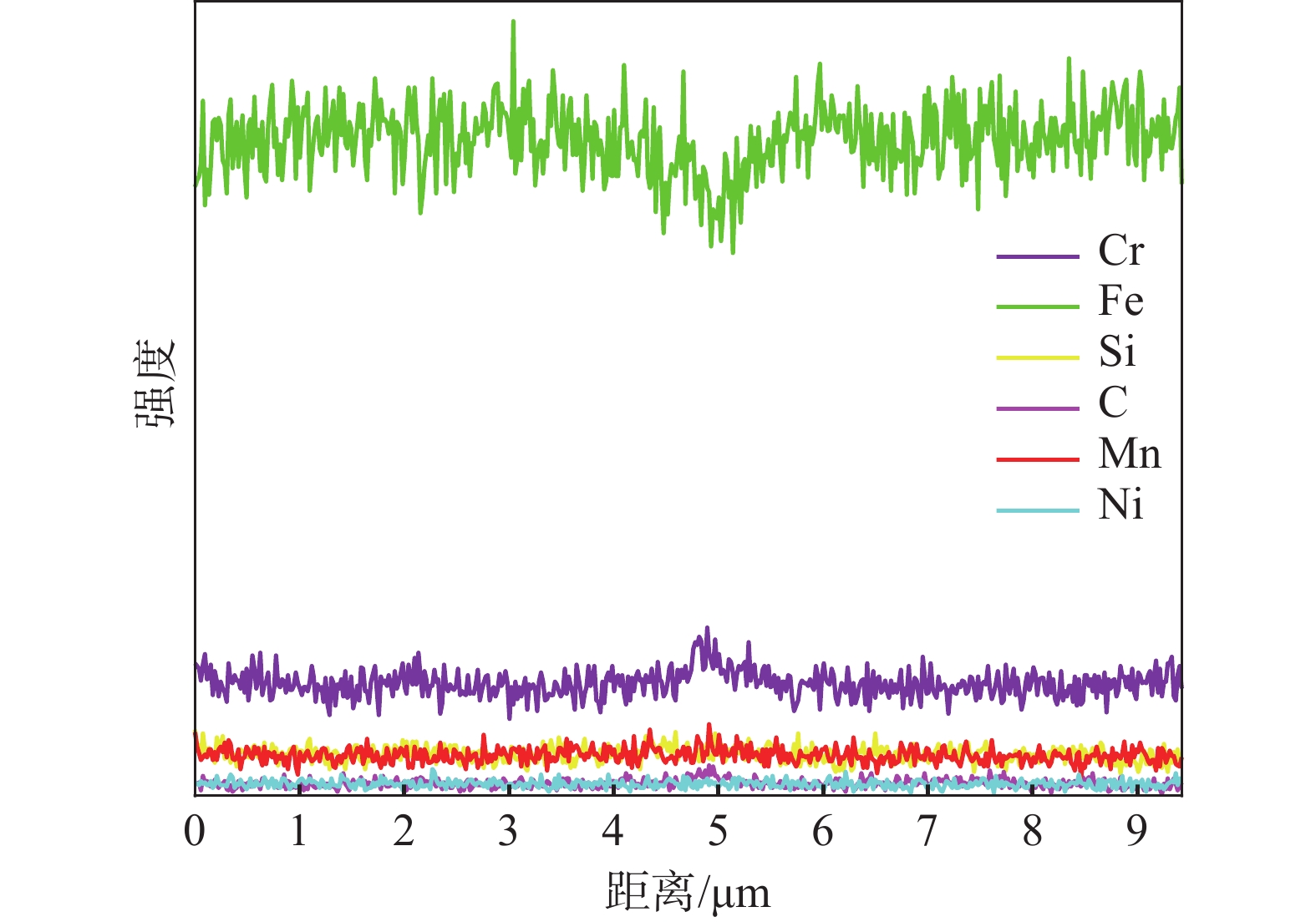
1000 倍时涂层中部的金相组织。由于激光熔覆凝固过程冷却速度快,涂层和基材界面呈现典型的树枝晶结构。随着V含量的增加,涂层界面区树枝晶的生长受到抑制,且树枝晶向胞状晶转变的生长距离显著缩短。V-0.5铁铬合金涂层中V含量较低,V元素主要固溶到基体中,铬碳化物在晶界附近富集,可以提供树枝晶生长所需的碳源,促进树枝晶的生长和分支,因此,V-0.5铁铬合金涂层以树枝晶生长模式为主。当V含量增加到1%以上时,VC形成后晶界附近的碳含量降低至胞状晶形成的临界浓度以下,促进了树枝晶向胞状晶转变,V-1和V-2铁铬合金涂层中部的金相组织为胞状晶。图2为不同V含量的激光熔覆铁铬合金涂层下部和涂层上部的微观形貌。由图2可知,V-0.5铁铬合金涂层下部的树枝晶内基体组织分布不均匀,对AB微区进行线扫描分析结果如图3所示。
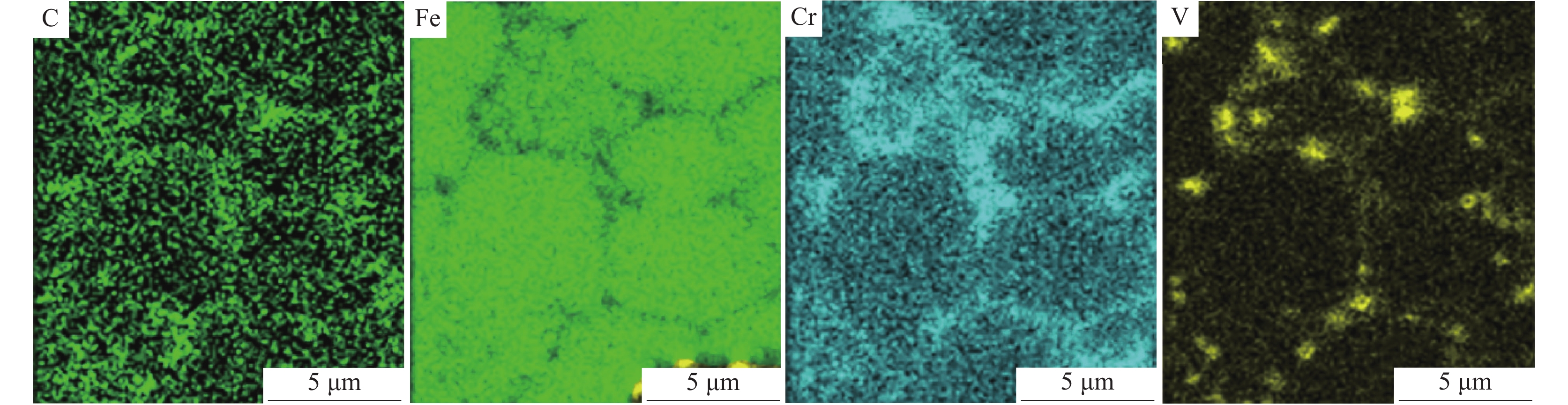
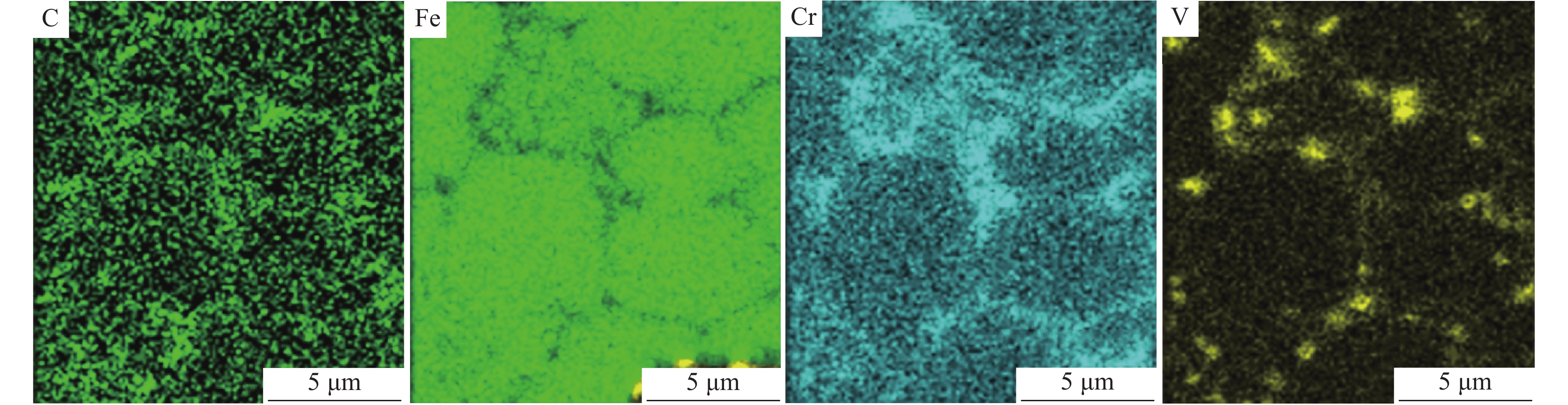
除晶界处Cr元素含量偏高外,晶界两侧基体组织的元素分布一致。说明当V含量较低时,涂层下部过冷度较大,涂层快速凝固,合金元素来不及均匀固溶到基体中,影响了基体组织的均匀性。当晶粒生长到涂层上部时过冷度减小,合金元素在基体中的固溶度增加,基体的均匀性得到明显改善。当涂层中V含量增加到1%以上时,VC富集在晶界附近,促进了Cr元素在基体中均匀分布,当涂层中V含量增加到2%时,则以胞状晶生长模式为主,V-1和V-2铁铬合金涂层中的基体偏析现象消失,组织均匀。对V-1涂层微区进行面扫描观察元素分布,结果如图4所示。V元素以VC形式均匀分布在晶界处,Cr元素在基体中均匀分布,部分铬碳化物在晶界处富集。随着V含量的增加,晶界处气孔比例增加。由于原料中钒铁熔点较高,随着原料中钒铁含量的增加,VC在晶界处形成时熔池中的气孔来不及排出,导致V含量较高时涂层中气孔缺陷增加[22]。
2.2 涂层物相组成
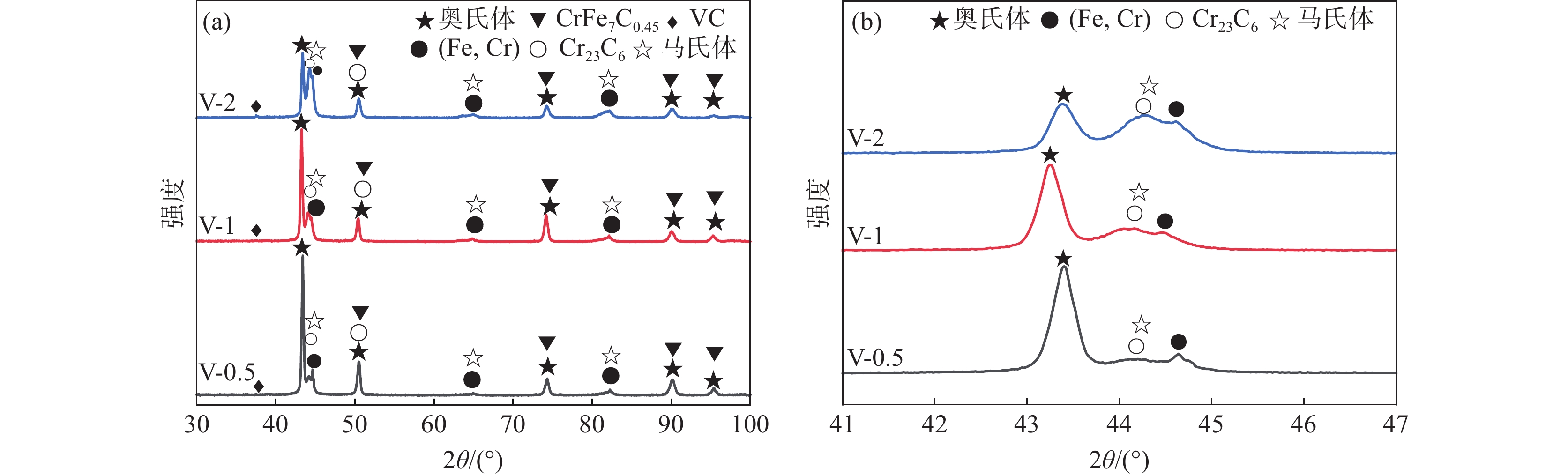
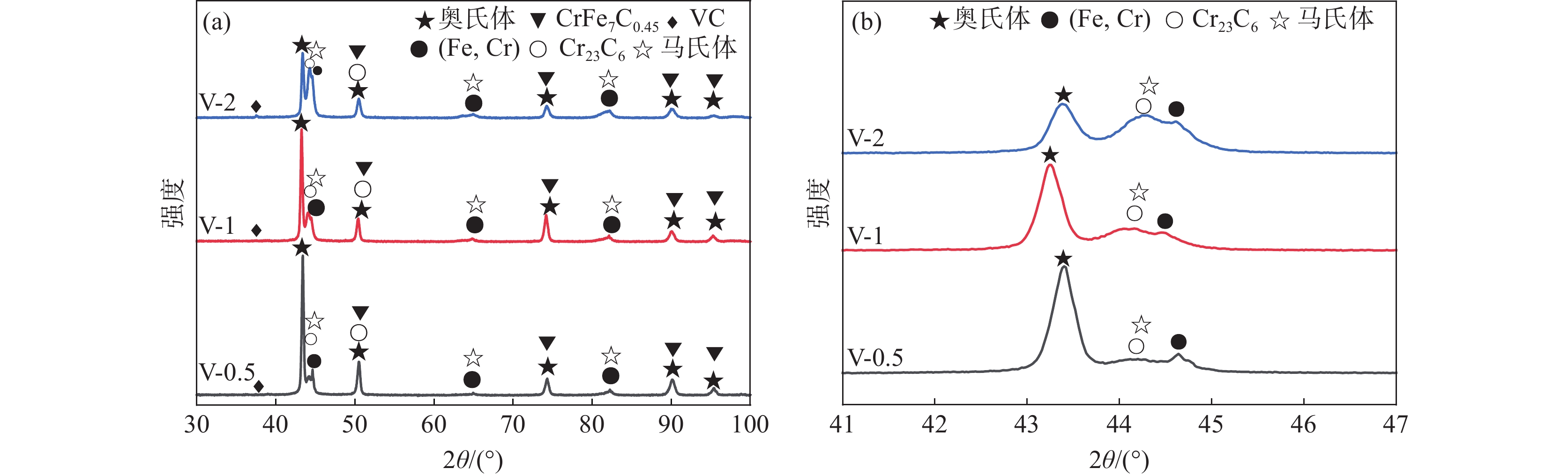
不同V含量的铁铬合金涂层区物相分析结果如图5所示。Cr元素主要以碳化物和(Fe,Cr)固溶体形式存在。V含量较低时,涂层中V元素主要固溶到基体中,未检测到VC衍射峰。基体为γ-Fe且随着V含量的增加衍射峰强度下降。γ-Fe存在原因如下:V和Cr元素在铁素体中的扩散速度低于奥氏体和马氏体,阻碍了C元素的扩散,形成了富碳区域,马氏体相变温度点降低,奥氏体表现出更高的稳定性。将主相区局部放大,可以发现VC形成后一方面促进Cr元素均匀地固溶到基体中,引起γ-Fe衍射峰向低角度方向偏移,和显微组织观察结果一致。另一方面VC形成后降低了奥氏体中的碳浓度,促进了γ-Fe向马氏体转变,引起马氏体相衍射峰增强[21,23]。
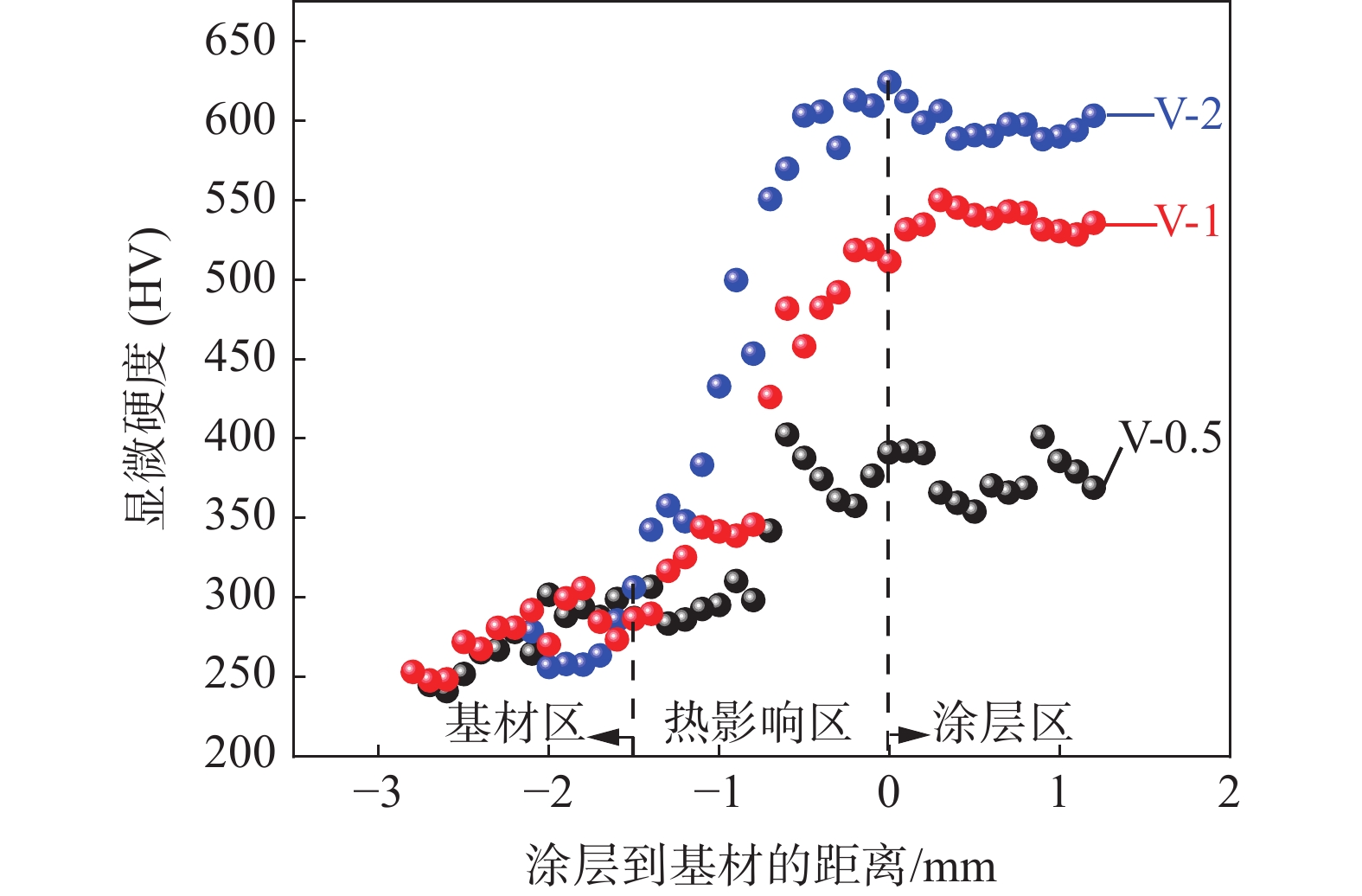
2.3 涂层性能
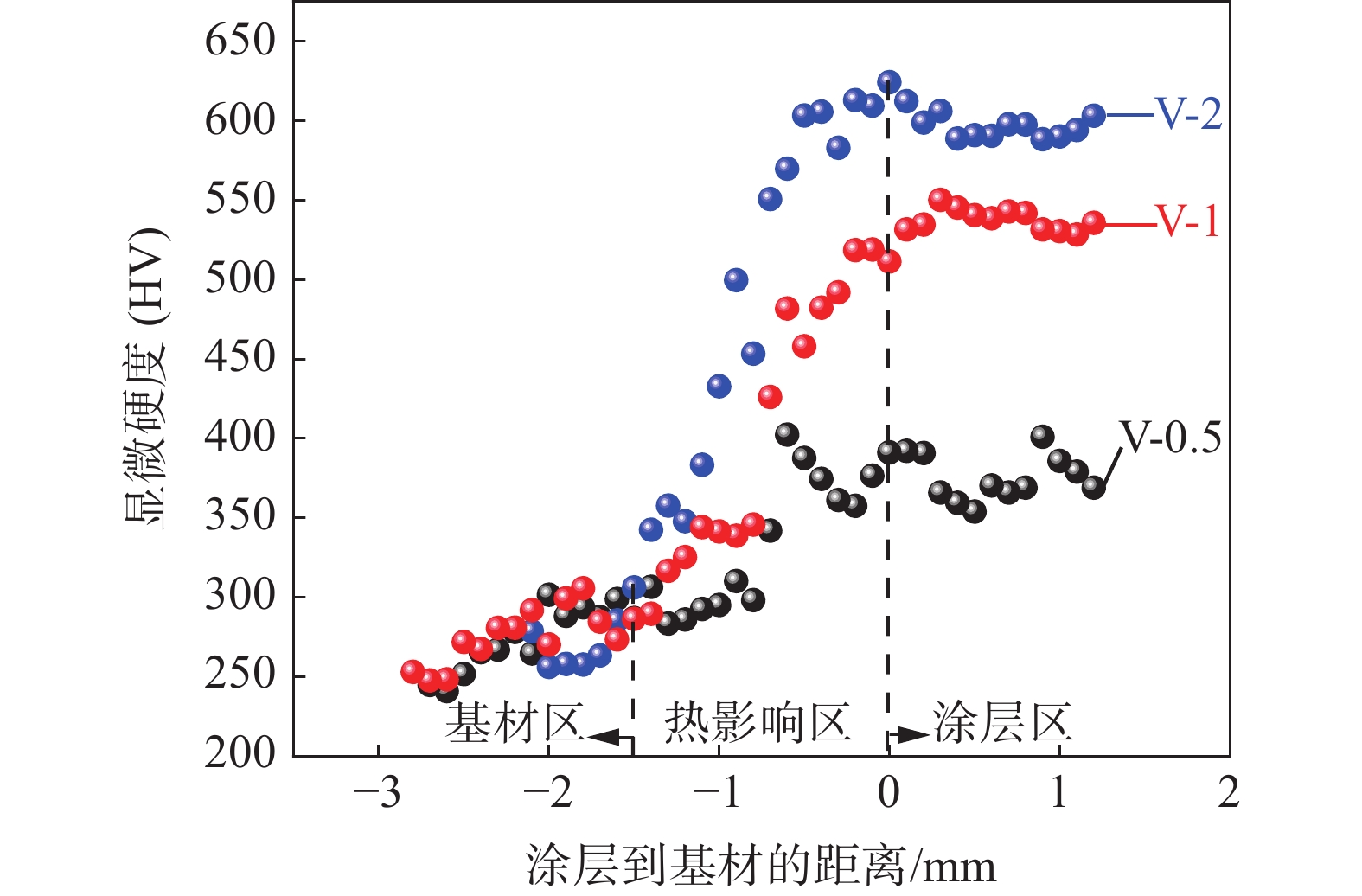
不同V含量的铁铬合金涂层显微硬度如图6所示。在高能量密度的激光束作用下基材表面熔化,快速凝固后熔池底部成分受基材稀释的影响,热影响区的硬度逐渐递增,到达涂层区后趋于稳定。随着V含量的增加,VC和马氏体相的含量增加,涂层硬度逐渐提高。
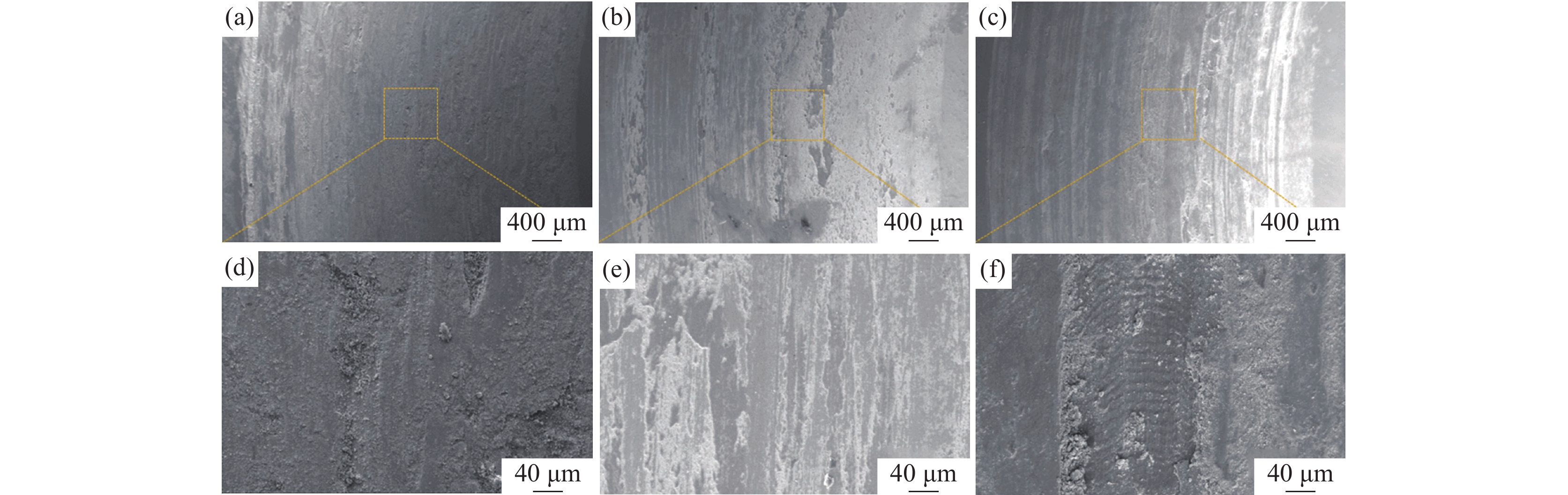
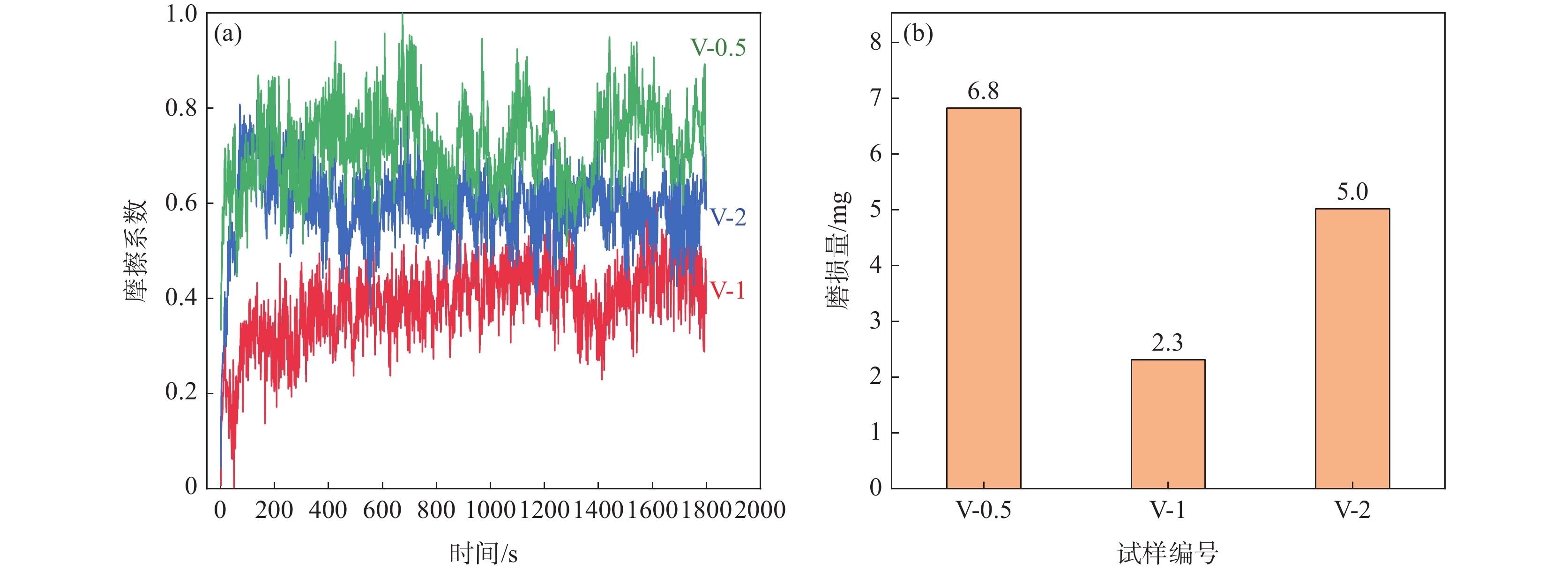
不同V含量的激光熔覆铁铬合金涂层摩擦系数和磨损量如图7所示,对比V-0.5到V-2铁铬合金涂层的摩擦系数和磨损量可知,当涂层中的V含量从0.5%增加到1%时,即V-1铁铬合金涂层的摩擦系数和磨损量显著降低,耐磨性能提升。但是继续增加V含量至2%时,即V-2铁铬合金涂层的摩擦系数和磨损量没有进一步降低,并且耐磨性能低于V-1铁铬合金涂层。
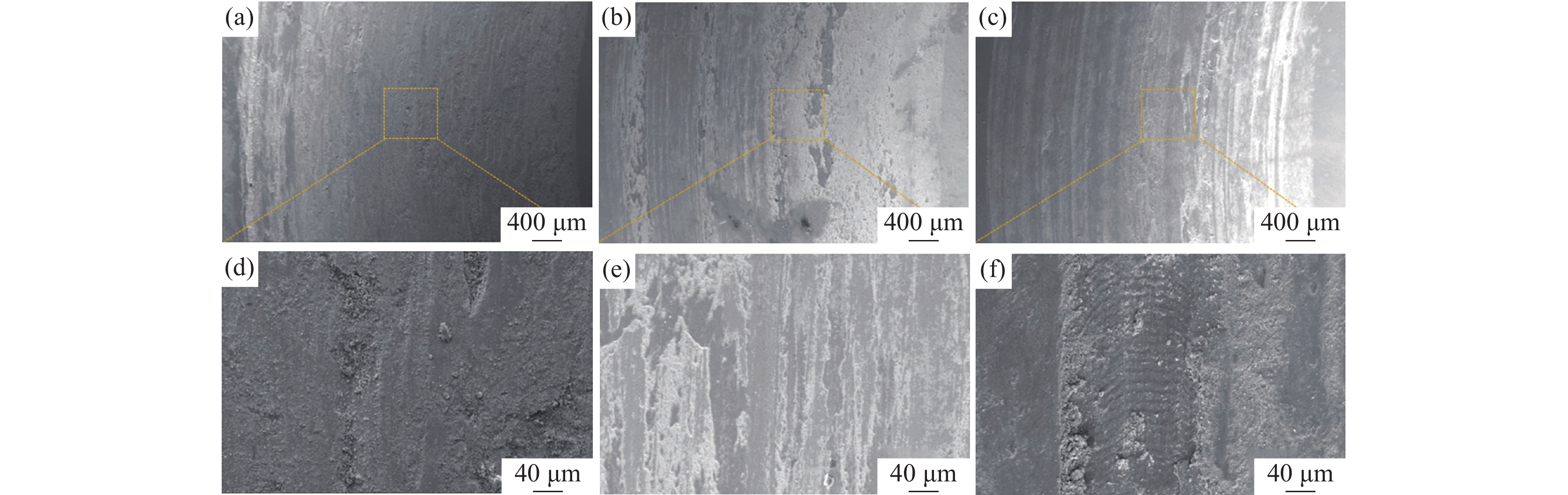
图8为不同V含量激光熔覆涂层的摩擦磨损形貌以及典型区域的微观形貌。在摩擦副的对磨作用下,样品表面局部温度升高且应力增大,易于产生粘着磨损,同时样品表面Fe、Cr等金属元素与O接触会生成氧化物,形成氧化磨损[23-24]。粘着磨损会在样品表面留下较浅的剥落坑,而氧化磨损则会生成细小的氧化物分散在涂层的表面形成氧化层,氧化层中的氧化物尺寸细小且硬度高,能够起到良好的润滑作用,减弱后续的粘着磨损。V-0.5铁铬合金涂层中Cr元素固溶不充分,涂层硬度低,整体磨痕较深。V-1铁铬合金涂层中固溶强化和晶界处分布碳化物协同提升涂层硬度,磨痕较浅,磨损形式为粘着磨损和氧化磨损。结合物相分析结果可知,V-2铁铬合金涂层中晶界处的铬碳化物和VC含量增加,虽然涂层硬度提高,但脆性增加,碳化物在对磨过程中脱落,导致涂层表面不均匀,且脱落的碳化物加剧了涂层磨损,引起磨损量增加。另一方面涂层中的气孔缺陷较V-0.5和V-1明显增多,这些气孔缺陷在晶界处聚集,降低了有效承载能力,引起局部应力集中,导致涂层磨损量增加。
3. 结论
1) 激光熔覆铁铬合金涂层中的V含量较低时,即V-0.5铁铬合金涂层以树枝晶生长模式为主,Cr元素在凝固过程中来不及完全固溶到基体中,涂层界面区的γ-Fe基体组织分布不均匀,涂层硬度和耐磨性能较低。
2) 当激光熔覆铁铬合金涂层中的V含量超过1%时,涂层界面区树枝晶的生长受到抑制,树枝晶向胞状晶转变的生长距离缩短,V-2铁铬合金涂层以胞状晶生长模式为主。凝固过程中Cr元素充分固溶到基体中,涂层组织分布均匀,硬度和耐磨性能最佳。
3)激光熔覆铁铬合金涂层中的V含量增加后促进了γ-Fe向马氏体转变,引起涂层硬度和耐磨性能提升。当V含量增加到2%时,涂层中晶界处的气孔缺陷增加,引起耐磨性能下降。
-
表 1 60CrMnMo基材成分
Table 1. Elemental composition of 60CrMnMo basic materials
% Ni C Si Mn Cr Mo Fe 0.3 0.56 0.25 0.75 1.12 0.25 余量 表 2 各种混合粉末的元素组成
Table 2. Elemental compositions of various mixed powders
% 试验样品 Fe V Si Cr C V-0.5 87.80 0.50 1.00 9.70 1.00 V-1 87.30 1.00 1.00 9.70 1.00 V-2 86.30 2.00 1.00 9.70 1.00 -
[1] Nie Huiwen, Zeng Songsheng, Nie Junhong, et al. Influence of VC addition amount on microstructure and properties of laser clad Fe50Mn30Cr10Co10 high-entropy alloy coating[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Materials, 2023,47(4):7-11, 27. (聂辉文, 曾松盛, 聂俊红, 等. VC添加量对激光熔覆Fe50Mn30Cr10Co10高熵合金涂层组织和性能的影响[J]. 机械工程材料, 2023,47(4):7-11, 27. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202304002Nie Huiwen, Zeng Songsheng, Nie Junhong, et al. Influence of VC addition amount on microstructure and properties of laser clad Fe50Mn30Cr10Co10 high-entropy alloy coating[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering Materials, 2023, 47(4): 7-11, 27. doi: 10.11973/jxgccl202304002 [2] Wang Haomin, Wang Guoqing, Xiong Yangkai, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser cladded VC-Cr7C3 composite cladding layer[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2022,47(11):245-252. (王皓民, 汪国庆, 熊杨凯, 等. 激光熔覆VC-Cr7C3复合熔覆层的组织与力学性能[J]. 金属热处理, 2022,47(11):245-252.Wang Haomin, Wang Guoqing, Xiong Yangkai, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of laser cladded VC-Cr7C3 composite cladding layer[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2022, 47(11): 245-252. [3] Zhang Wei, Feng Qiuhong, Wang Eryi, et al. Microstructure and hardness of laser cladded in-situ synthesized VC reinforced Fe-Ni based composite coating[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019,44(7):190-193. (张伟, 冯秋红, 王尔亦, 等. 激光熔覆原位生成VC增强Fe-Ni基复合涂层的组织与硬度[J]. 金属热处理, 2019,44(7):190-193.Zhang Wei, Feng Qiuhong, Wang Eryi, et al. Microstructure and hardness of laser cladded in-situ synthesized VC reinforced Fe-Ni based composite coating[J]. Heat Treatment of Metals, 2019, 44(7): 190-193. [4] Lü Yufang, Xu Peng, Liang Rou, et al. Corrosion resistance of VC-reinforced Fe-based SMA coatings by laser cladding[J]. Surface Coatings Technology, 2024,478(2024):130457. [5] Rahman U N, Capuano L, Cabeza S, et al. Directed energy deposition and characterization of high-carbon high speed steels[J]. Additive Manufacturing, 2019, 30(2019): 1-12. [6] Cheng Heng, Liu Shuai, Jiang Shaoteng, et al. Effect of CeO2 on the Microstructure and properties of in situ nano-VC reinforced sub-micron Fe-based laser cladding layers[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2024,33:1-11. [7] Shi Kao, Zhou Wenqian, Sun Yufu, et al. Effect of vanadium carbide reinforced particles on wear resistance of laser cladding Fe-Co duplex coating[J]. Journal of Thermal Spray Technology, 2023,32(1):124-134. doi: 10.1007/s11666-022-01477-y [8] Zhang Hui, Wu Dongting, Luan Tao, et al. Effects of graphite particle size on microstructure and properties of in-situ Ti-V carbides reinforced Fe-based laser cladding layers[J]. International Journal of Electrochemical Science, 2019, 14(3): 2208-2215. [9] Zhuo Yan, Li Chengxiang, Shi Xin, et al. Evaluation model of electromagnetic pulse welding effect based on Vc-β trajectory curve[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2022,20:616-626. [10] Li Xuejun, Liu Ying, Zhou Tingchuan. Improvement in microstructure and wear-resistance of high chromium cast iron/medium carbon steel bimetal with high vanadium[J]. Materials Research Express, 2021, 8(4): 1-9. [11] Ren Yiqun, Li Liqun, Zhou Yuandong, et al. In situ synthesized VC reinforced Fe-based coating by using extreme high-speed laser cladding[J]. Materials Letters, 2022, 315: 131962. [12] Peng Zhiliang, Zhang Jian, Zhang Mingjun, et al. Laser in-situ preparation and mechanical properties of VC reinforced Fe-based wear-resistant composite cladding[J]. Ceramics International, 2022, 48(19): 28240-28249. [13] Gao Yu, Liu Ying, Wang Lu, et al. Microstructure evolution and wear resistance of laser cladded 316L stainless steel reinforced with in-situ VC-Cr7C3[J]. Surface Coatings Technology, 2022, 435: 128264. [14] Kirchgaßner M, Badisch E, Franek F. Behaviour of iron-based hardfacing alloys under abrasion and impact[J]. Wear, 2008,265(5):772-779. [15] Liang Z G, Zhan J M, Shi W Q, et al. Parameters optimization of the laser cladding of a Fe-based VC composite coating using response surface methodology (RSM)[J]. Lasers in Engineering, 2021,49:179-203. [16] Liu Changyu, Xu Peng, Pang Chi, et al. Phase transformation in Fe–Mn–Si SMA/WC composite coating developed by laser cladding[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2021,267:124595. [17] Chung R J, Tang X, Li D Y, et al. Microstructure refinement of hypereutectic high Cr cast irons using hard carbide-forming elements for improved wear resistance[J]. Wear, 2013, 301(1-2): 695-706. [18] Eremin E N, Losev A, Ponomarev I A, et al. Structure and properties of the weld metal N8G6M3FTB after aging[J]. AIP Conference Proceedings, 2019, 214: 40004. [19] Yang Xiong, Chen Yarong, Zhang Zhenlin, et al. Study on microstructure and properties of laser-clad Fe-based (Ti, V)C composite coatings[J]. Surface Coatings Technology, 2023,464:129552. [20] Kannan Rajesh G, Sathiya P, Bharathi D T K, et al. Welding parameter optimization by whale optimization algorithm and experimental investigation on microstructure and mechanical properties of spin arc welded 15CDV6 HSLA steel[J]. Metals and Materials International, 2023,29(9):2743-2759. doi: 10.1007/s12540-023-01406-w [21] Wang Haiyang, Zhang Song, Zhang Chunhua, et al. Effects of V and Cr on laser cladded Fe-based coatings[J]. Coatings, 2018,8(3):107-118. doi: 10.3390/coatings8030107 [22] Cao Yabin, Ma Zeming, Zhu Hao, et al. Evolution behavior regulation of carbide in Fe-based laser cladding coating[J]. Materials Research Express, 2019,6(11):116590-116590. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/ab4c5f [23] Zong Weian, Zhang Song, Zhang Chunhua, et al. Preparation and characterization of in situ carbide particle reinforced Fe-based gradient materials by laser melt deposition[J]. Coatings, 2019,9(8):467-481. doi: 10.3390/coatings9080467 [24] Wang Yanfang, Zhou Xuejing, Song Zihan, et al. Microstructure and tribocorrosion properties of Cr-W-Mo-V coating fabricated via laser hot-wire cladding[J]. China Surface Engineering 2024, 37(3): 1-12. (王彦芳, 周雪景, 宋子翰, 等. 热丝激光熔覆Cr-W-Mo-V钢涂层组织与腐蚀磨损性能[J]. 中国表面工程, 2024, 37(3): 1-12.Wang Yanfang, Zhou Xuejing, Song Zihan, et al. Microstructure and tribocorrosion properties of Cr-W-Mo-V coating fabricated via laser hot-wire cladding[J]. China Surface Engineering 2024, 37(3): 1-12. -





 下载:
下载:








 下载:
下载: