Analysis of factors influencing the sedimentation height of hydrolyzed metatitanic acid
-
摘要: 以某钛白粉厂生产数据为依据,统计分析了水解偏钛酸沉降高度对粒度分布和初品质量的影响规律。结果表明,随着水解偏钛酸沉降高度增加,水解偏钛酸D50呈现增加趋势,相应获得初品Tcs和Scx均呈现下降趋势,初品平均粒径呈现增加趋势,控制偏钛酸沉降高度在130 mm以下可以获得颜料性能较好的钛白粉。试验研究表明,水解钛液的TiO2浓度、F值、水解晶种加量和水解判灰时间均对水解偏钛酸的沉降高度和D50有较大影响。随水解钛液浓度增加,水解偏钛酸沉降高度呈下降趋势,随F值增加,水解偏钛酸沉降高度和D50呈现增加趋势,随水解晶种加量的增加,水解偏钛酸沉降高度呈下降趋势,随判灰时间的延长,水解偏钛酸沉降高度呈现先增加后减小的趋势。Abstract: Based on the production data of a certain titanium dioxide factory, the influence of the sedimentation height of metatitanic acid on its particle size distribution and titanium dioxide pigment properties was statistically analyzed. The results show that with the increase of sedimentation height, the D50 of metatitanate shows an increasing trend, while the Tcs and Scx of titanium dioxide pigment show a decreasing trend, and the average particle size shows an increasing trend. Controlling the sedimentation height of titanium dioxide below 130 mm can obtain titanium dioxide with better pigment properties. The experimental results show that the TiO2 concentration, F value, seed addition, and first boiling holding time of titanium liquid all have a significant impact on the sedimentation height and D50 of metatitanic acid. As the concentration of TiO2 increases, the sedimentation height and D50 of metatitanic acid show a decreasing trend. As the F value increases, the sedimentation height of metatitanic acid and D50 show an increasing trend. With the increase of seed addition, the sedimentation height of metatitanic acid shows a decreasing trend. With the extension of the first boiling insulation time, the sedimentation height of metatitanic acid shows a trend of first increasing and then decreasing.
-
Key words:
- TiO2 /
- metatitanic acid /
- hydrolysis /
- sedimentation height /
- particle size distribution
-
0. 引言
钛白粉化学性质稳定,具有折射率高、遮盖力高、着色力强、白度和光亮度高、无毒等特点,广泛应用于涂料、塑料、印刷油墨、造纸、橡胶、陶瓷和合成纤维等领域。钛白粉的粒径分布是决定其最终质量的重要因素,它对产品的遮盖力、色相均会产生很大的影响。为了获得较好粒度分布的硫酸法钛白粉初品,需要从水解到煅烧过程严格控制,其中水解过程决定了水解偏钛酸的粒度分布。为了获得较好粒度分布的水解偏钛酸,科研工作者做了大量的相关研究。李香兰研究超声处理对水解晶种和水解过程的影响,结果表明超声波作用下可得到粒径小且均匀的偏钛酸[1]。田从学等人研究了偏钛酸结构演变过程对硫含量的影响及水解偏钛酸的性质结构 (晶体结构、粒度分布、杂质含量等) 对金红石型钛白的结构与颜料性能的影响[2−3]。于康等人[4]对比了外加晶种加压水解、微加压水解、常压水解的差异,并通过控制水解工艺获得满足偏钛酸粒度要求的产品。周强等[5]通过优化水解晶种加量和变灰时间得到适合生产装饰纸用钛白粉的偏钛酸。曾小义等[6]通过中心响应面法建立了水解温度、初始钛液浓度、钛液 F值对平均粒径与水解率的耦合数学模型,通过方差分析及失真分析,验证了所建立的数学模型的适用性。王焜等人[7]利用聚焦光束反射测量仪(FBRM)、原位拉曼光谱考察了晶种形成过程中溶液组成和粒子的变化,得到了有效的晶种表征手段,考察了晶种加量和保温时间对水解反应动力学的影响。
水解偏钛酸的沉降高度是其粒度分布的宏观体现,也是生产过程中少数现场操作人员可以自己直接快速检测的指标,各个钛白粉厂家根据自身产品质量控制要求和生产经验对水解偏钛酸的沉降高度作了不同的要求。由于缺乏确定沉降高度指标范围的有力依据,各钛白粉厂沉降高度控制范围对产品质量控制上存在一定的缺陷,同时由于对沉降高度影响因素不够明确,生产过程中调控沉降高度的手段也比较缺乏。目前未见水解偏钛酸沉降高度与产品质量的相关性报道,也未见对偏钛酸沉降高度影响因素进行分析的相关报道。针对上述问题,有必要对沉降高度与初品性能的相关性进行研究,以便为钛白粉质量控制提供有力支撑。
1. 试验部分
1.1 试验原料及设备
试验所需主要原料:TiO2浓度为160~215 g/L的工业钛液,8%~10%氢氧化钠溶液。碳酸氢钠:饱和溶液,铝片:纯度99.5%以上,硫氰酸铵: 50 g/L水溶液,硫酸高铁铵: $C_{[{\mathrm{NH}}_4\;{\mathrm{Fe}}({\mathrm{SO}}_4)_2]} $=0.1 mol/L。试验所用其他煅烧晶种、硫酸锌、磷酸、氢氧化钠均为攀枝花某钛白粉厂提供的工业级原料。
1.2 试验设备
试验所用主要仪器如下:激光粒度仪(型号马尔文3000)、扫描电镜(型号JSM-7001F,日本电子株式会社)、马弗炉(型号KF1200,洛阳科炬炉业有限公司)、电加热套(型号ZNHW,郑州卓成仪器科技有限公司)、四口烧瓶。
1.3 试验方法
1)现场数据统计:使用某钛白粉厂生产大数据进行统计分析,考察沉降高度与钛液指标及产品初品质量的相关性,从而根据初品质量要求反推沉降高度的控制范围要求及对应钛液指标控制要求。
2)实验室水解验证:采用外加晶种水解工艺,晶种钛液和稀碱液均预热到85 ℃左右,然后将晶种钛液快速加入到稀碱液中,在96 ℃保温一段时间,直到稳定性(以10 mL计)达到110~130 mL。然后快速把水解晶种加入到预热到96 ℃的钛液中,预混5~10 min后升温到第一次沸腾,保温一段时间(判灰),停止加热,30 min后二次升温至沸腾,保温90 min后,缓慢加入稀释水将体系浓度稀释到165 g/L,继续保沸2 h后,水解结束。通过调整水解钛液的浓度、钛液F值、水解晶种加量、判灰时间(第一次沸腾保温时间)等方式获得不同水解偏钛酸。
3) 沉降高度的检测方法:将加热到90 ℃的水解浆料样品搅拌均匀,量取100 mL到已盛有900 mL 20 ℃水的
1000 mL具塞量筒中,塞上塞子,上下倒转量筒3次,使筒内浆液充分混匀,静置并记录起始时间,静置沉降到30 min时,用直尺量上层清液柱的高度(单位:mm)。2. 试验结果与讨论
2.1 沉降高度与钛白初品性能相关性分析
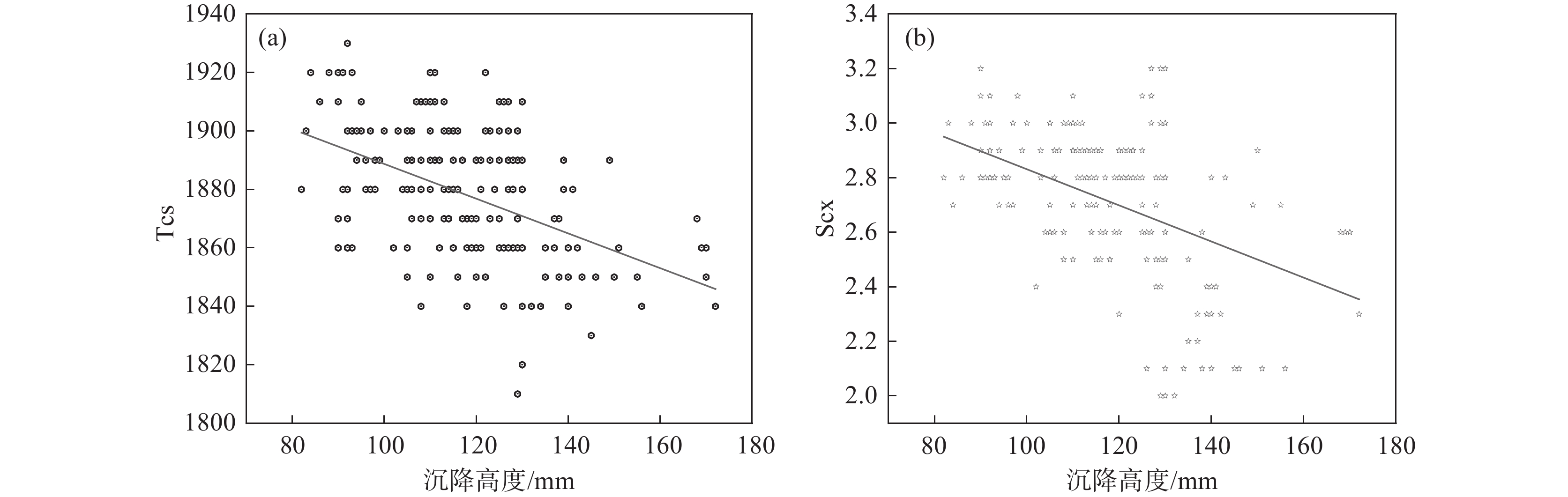
统计某钛白粉厂某年中控数据,将水解偏钛酸沉降高度与水解结束延时30 h后的初品Tcs(消色力)和Scx(蓝相)进行分析,其散点图见图1,将连续批次出现沉降高度<100、100~110、110~120、120~130 mm和130 mm以上的不同沉降高度范围的偏钛酸与当期初品质量均值进行对比分析,结果见表1,对应水解钛液指标见表2。
表 1 沉降高度与初品颜料性能均值对应Table 1. Settlement height and mean performance of primary pigments沉降高度/mm Tcs Scx L a b 亮度 范围 均值 <100 92.97 1890.0 2.81 97.34 −0.49 3.23 95.16 100~110 105.65 1871.5 2.65 97.57 −0.49 3.37 95.03 110~120 113.60 1876.0 2.72 97.53 −0.52 3.35 95.35 120~130 126.78 1880.8 2.70 97.46 −0.47 3.55 95.25 130~150 142.63 1861.3 2.35 97.51 −0.47 3.70 95.30 >150 161.90 1841.0 2.41 97.33 −0.31 3.20 95.30 表 2 沉降高度均值与钛液指标的关系Table 2. Relationship between mean settlement height and titanium liquid index沉降高度/mm F值 总钛/
(g·L−1)铁钛比 固含量
×106稳定性/
mLD50/
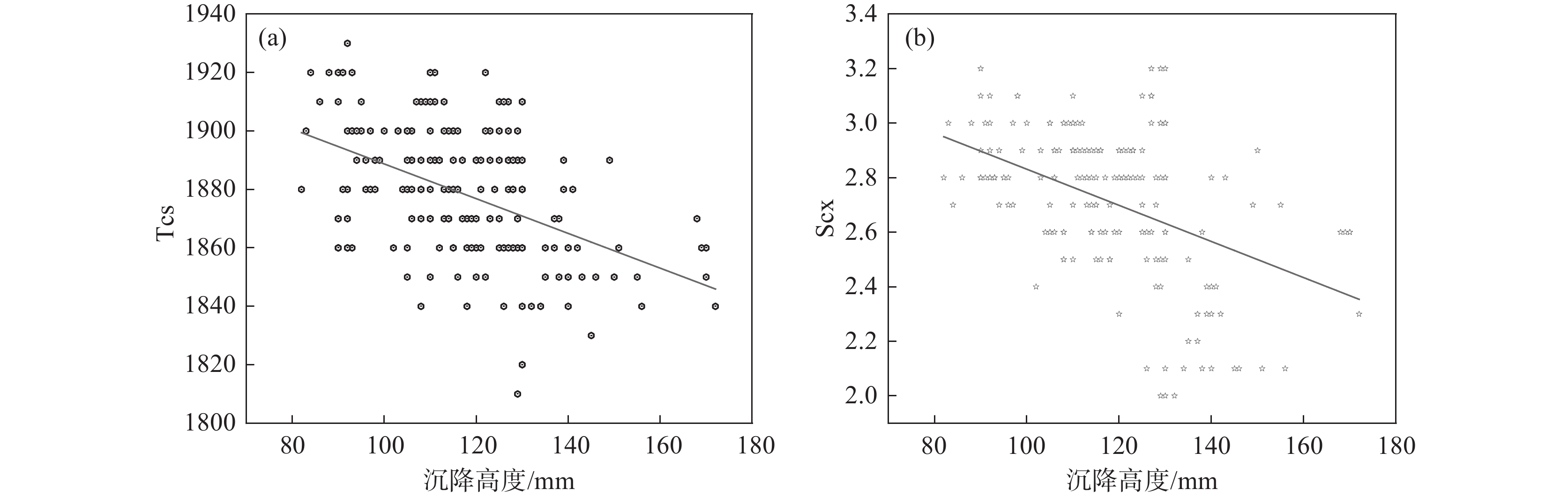
μm范围 均值 <100 92.97 2.02 196.7 0.28 26 500 1.85 100~110 105.65 1.98 196.2 0.30 26 500 1.91 110~120 113.60 2.06 195.1 0.29 26 500 1.83 120~130 126.78 2.00 193.5 0.30 25 500 2.00 130~150 142.63 2.02 191.6 0.31 25 500 2.28 >150 161.90 1.98 189.9 0.31 26 500 2.33 从图1可见,总体上Tcs和Scx均随沉降高度的增加而降低,Tcs与沉降高度的相关系数为
−0.43014 ,Scx与沉降高度的相关系数为−0.44696 ,这样得出的结论就是沉降高度和Tcs、Scx有中等强度相关性。由表1可知,初品性能和沉降高度有较强的对应关系。消色力Tcs随沉降高度增加呈现下降趋势,沉降高度小于130 mm之前消色力下降较小,大于140 mm以后下降较多。Scx也随沉降高度增加呈现下降趋势,b值随沉降高度呈现上升趋势。亮度与沉降高度对应关系不强。为了保证Tcs和Scx处于较高的水平,控制沉降高度在130 mm以下较好。
由表2可知,在该钛白粉厂钛液指标控制范围内,沉降高度和水解结束偏钛酸D50均随钛液总钛(TiO2)浓度的减少呈较为明显的上升趋势,其它F值、铁钛比、固含量和稳定性无明显差异。这表明该厂F值、铁钛比、固含量和稳定性的控制范围较为合理,其控制内的波动范围对水解偏钛酸质量影响较小,但该厂二氧化钛浓度控制范围偏大,其波动范围已经严重影响到了偏钛酸的沉降高度和D50的波动,有必要将其控制范围进一步缩小,以控制沉降高度到130 mm以下为目标,该厂的钛液总钛指标控制范围可由190~200 g/L调整到194~200 g/L。
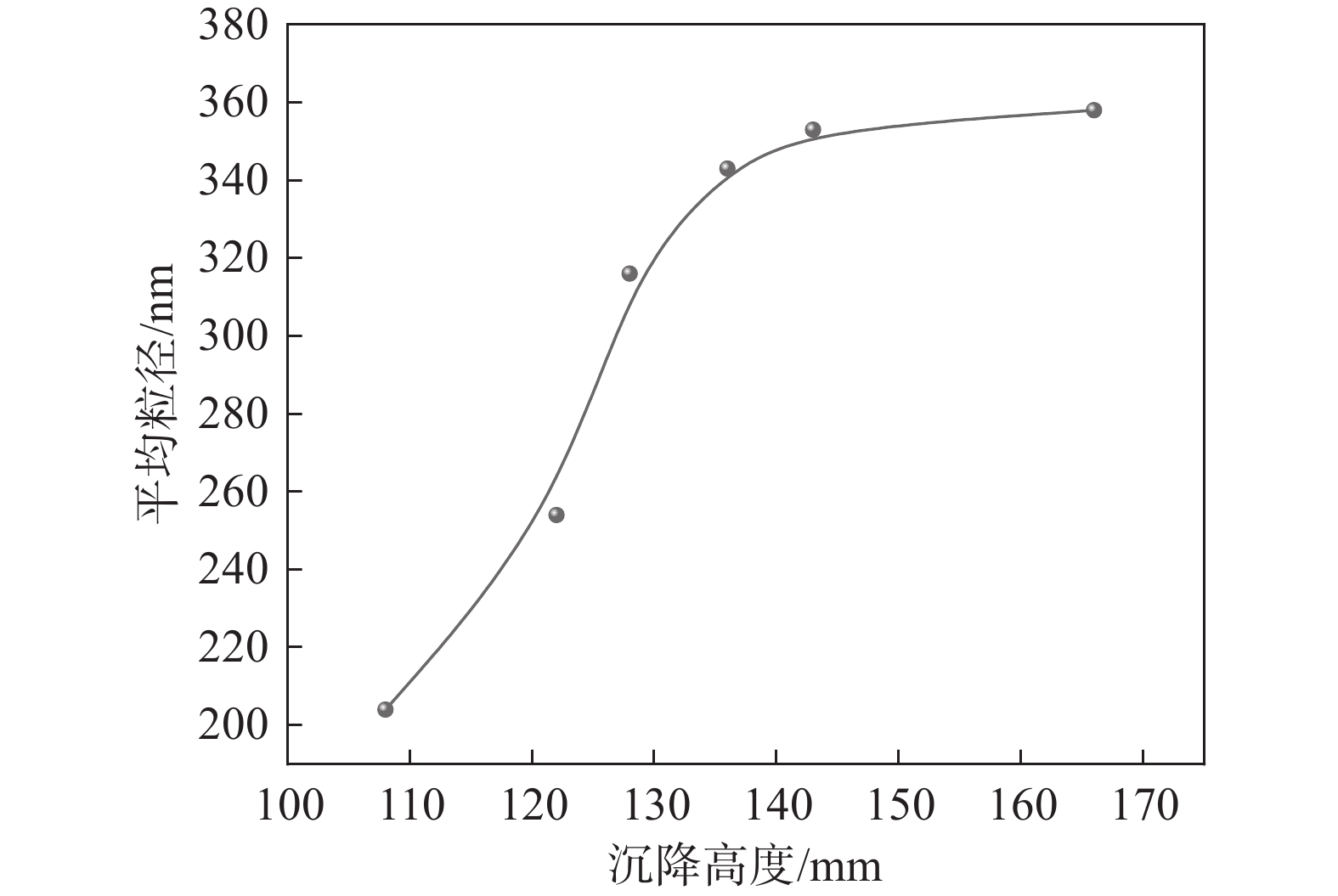
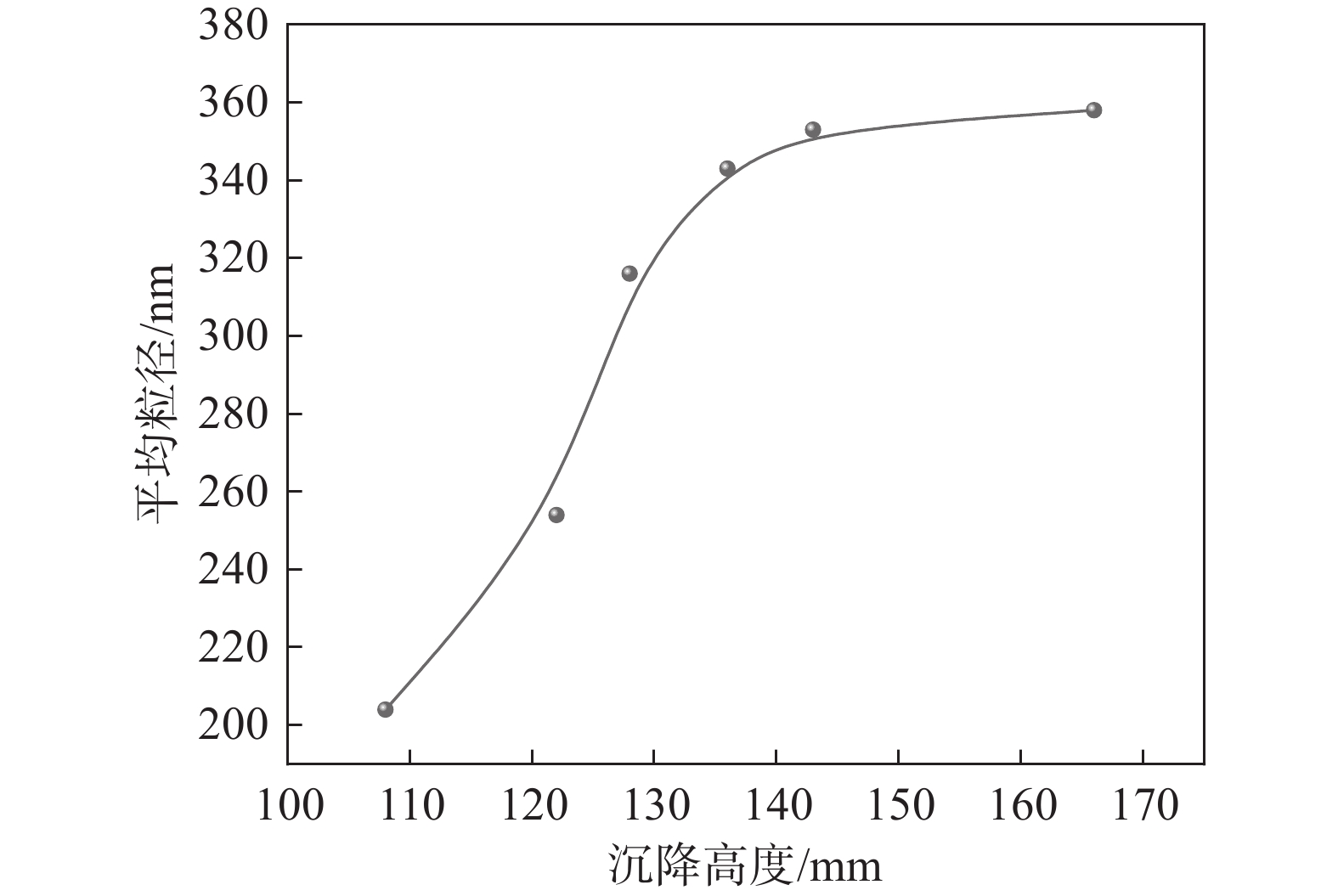
取不同沉降高度的偏钛酸在实验室进行盐处理后煅烧到金红石含量达到98%~99%,统计初品的平均粒径,结果见图2。由图2可知,随着偏钛酸沉降高度提高,初品粒度有逐渐变大的趋势。由此可见,在相同盐处理条件下水解偏钛酸的沉降高度对初品的平均粒径有较大影响,为了得到预定的平均粒径的初品,需要对水解偏钛酸沉降高度范围做出相应的控制。
2.2 沉降高度与偏钛酸粒径相关性分析
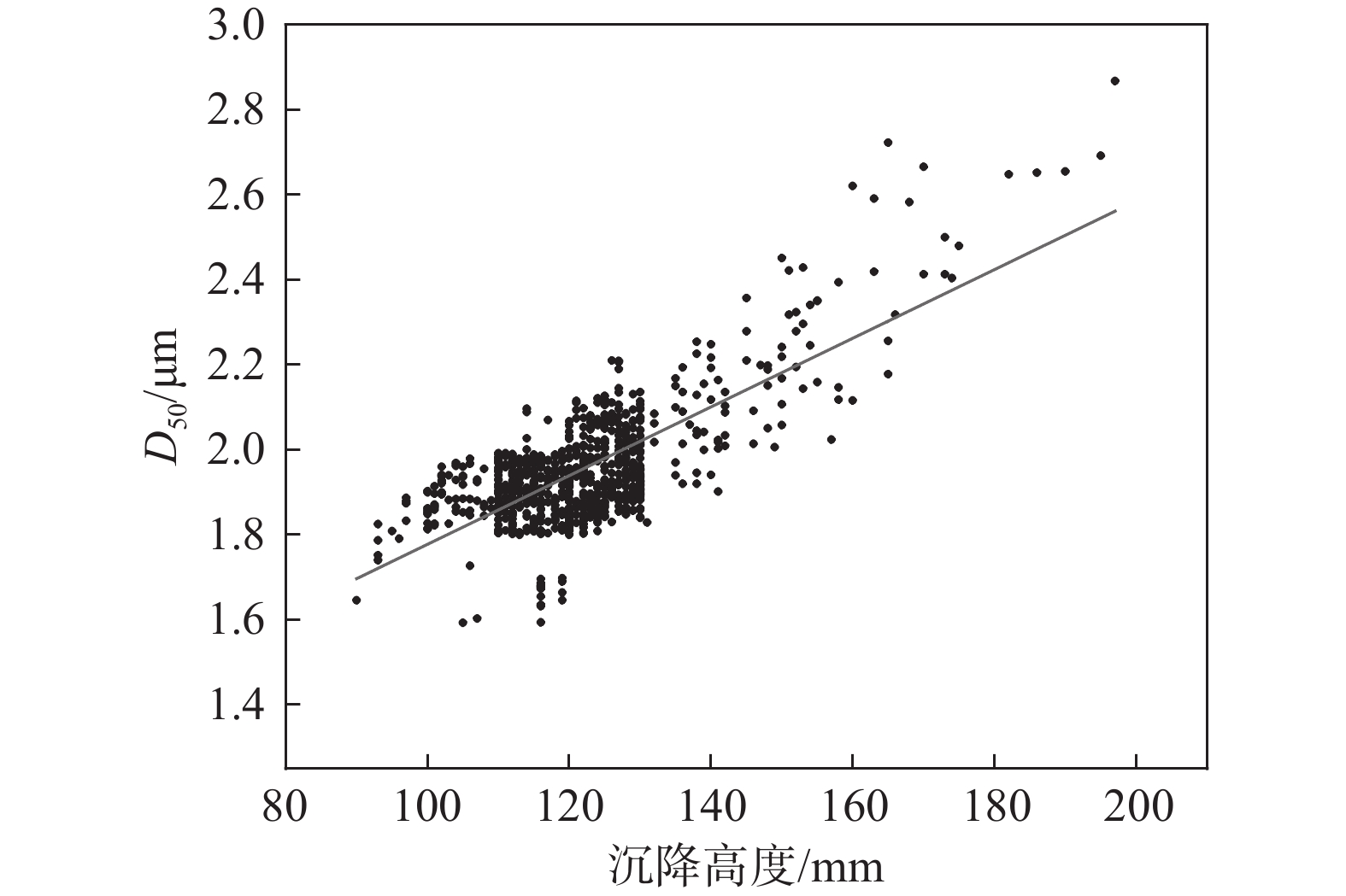
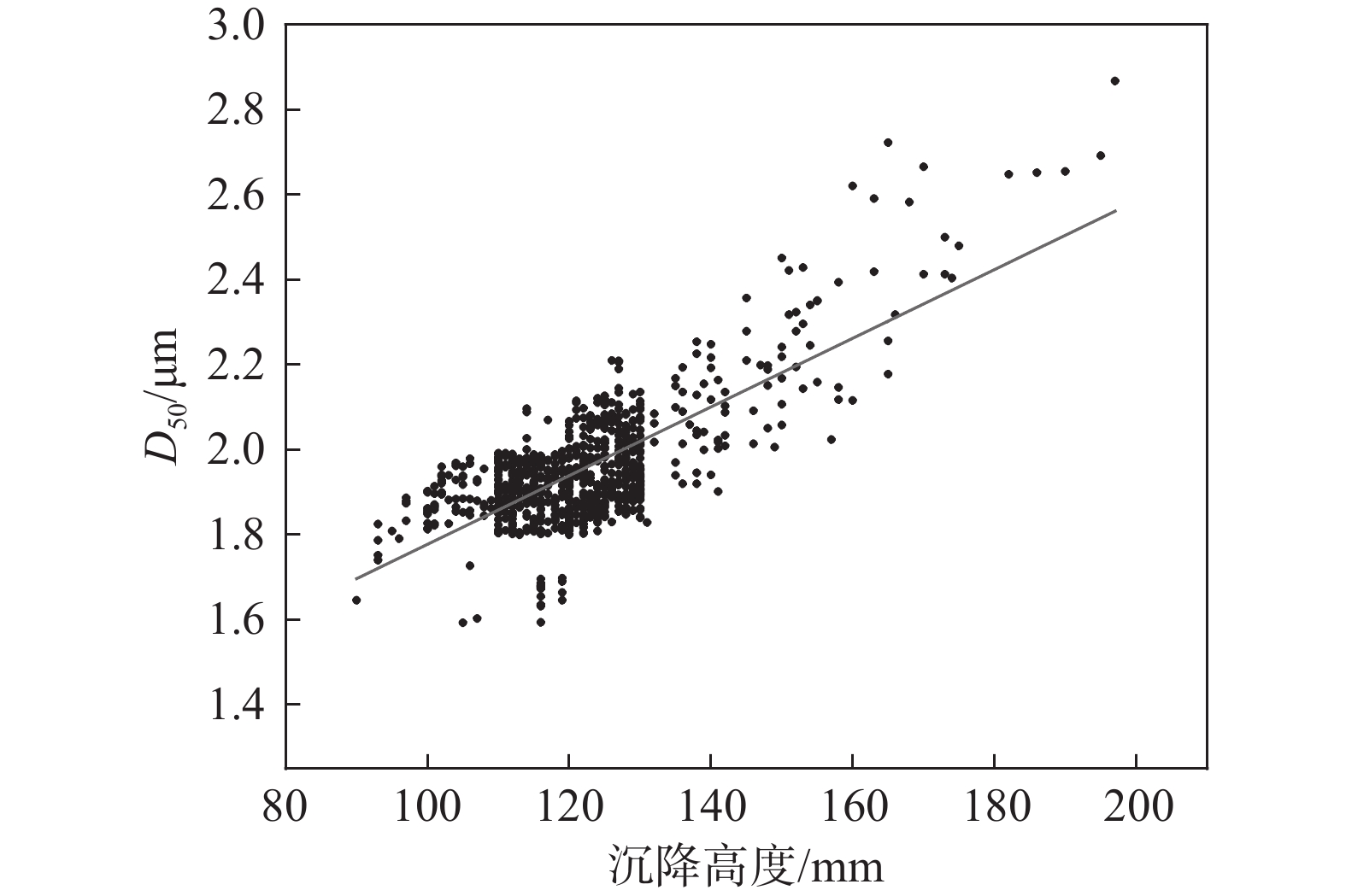
将生产数据中水解偏钛酸的沉降高度与对应激光粒度D50绘制成散点图,结果见图3。
由图3可知,整体上随沉降高度的增加,D50呈现明显的增加趋势,计算二者的皮尔逊相关系数为
0.75056 ,表明两者具有较强的正相关性。由此可见,可以通过快速检测水解偏钛酸的沉降高度来间接表征其平均粒径。对于静止的悬浮液颗粒沉降速度由粒子重力、所受浮力和液体阻力决定,初始颗粒速度为0,因而液体阻力为0,由于偏钛酸密度大于水的密度,颗粒在重力与浮力作用下向下做加速运动,随着颗粒速度增加,液体阻力随之增加,最终重力、浮力和液体阻力达到平衡,这时颗粒速度达到最大并保持匀速运动,直到颗粒达到底部沉积区,速度开始下降,并最终沉积在容器底部。若颗粒为球形,最大速度μ满足式(1)[8]。$$ \mathrm{\mu }=\sqrt{\frac{4\left(\mathrm{\rho }-{\mathrm{\rho }}_{\mathrm{I}}\right){g}{d}}{3{\mathrm{\rho }}_{\mathrm{I}}\mathrm{\xi }}} \mathrm{\mu } $$ (1) 式中, ρ为颗粒密度,kg/m³;ρI为液体密度,kg/m³;d为颗粒直径,m;ζ为液体的阻力系数(无单位)。
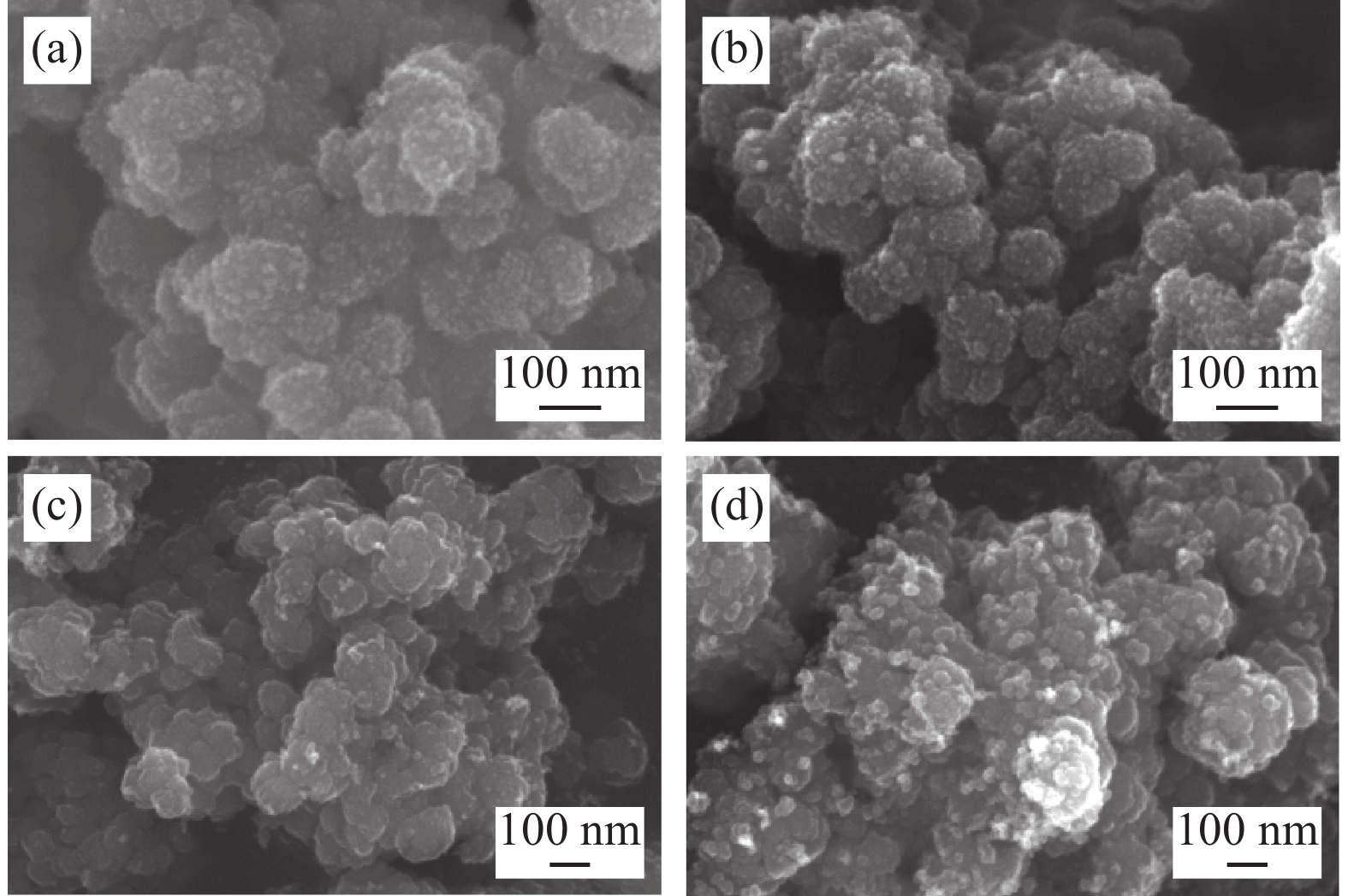
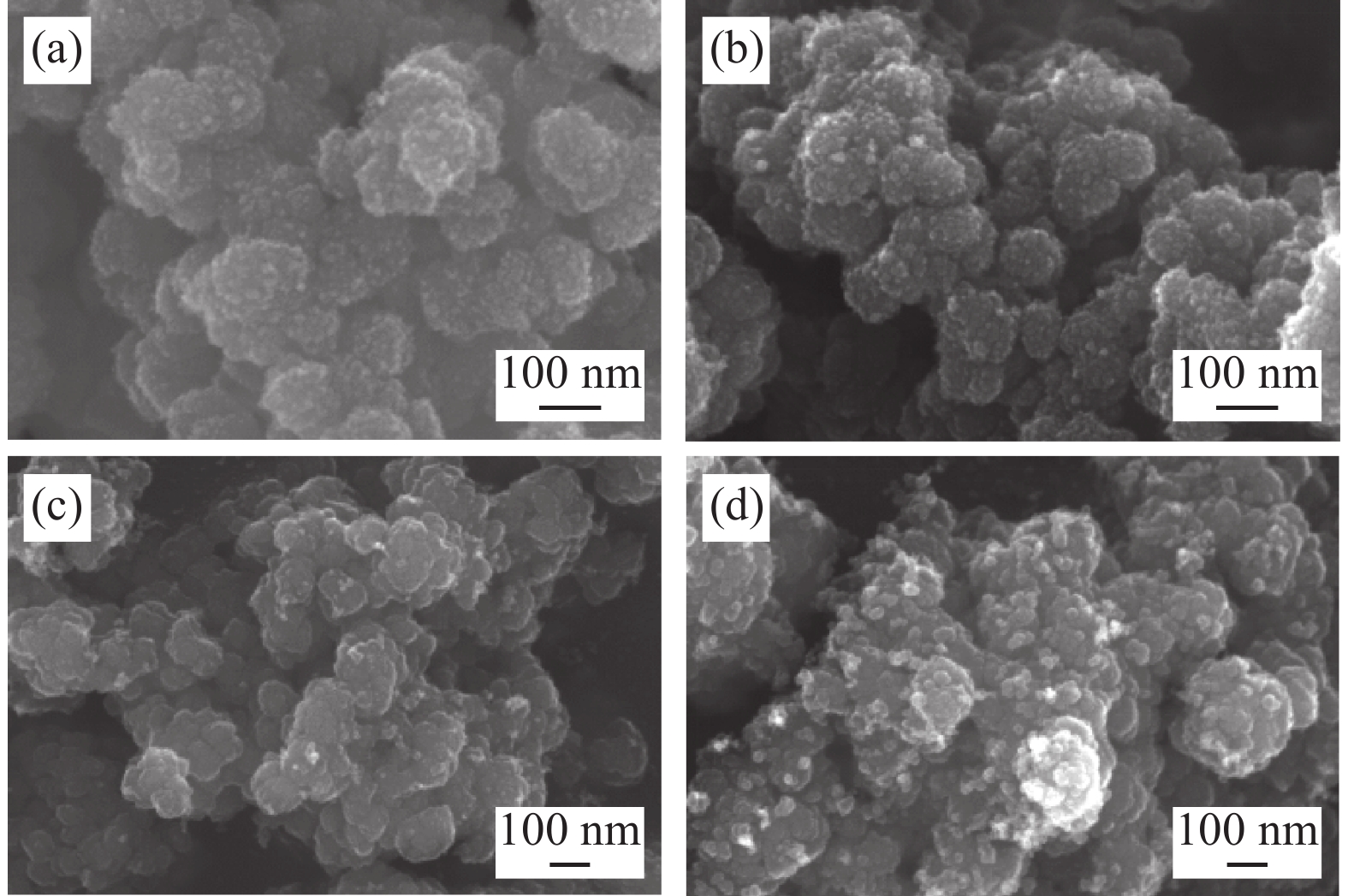
由式(1)可见,颗粒越大颗粒下降的最大速度越大,这与统计结果相符合。为进一步验证该结论,对低温烘干后的不同沉降高度的水解偏钛酸进行SEM检测,如图4所示,水解偏钛酸均为团聚颗粒,沉降高度大的样品偏钛酸的团聚颗粒相对较大。
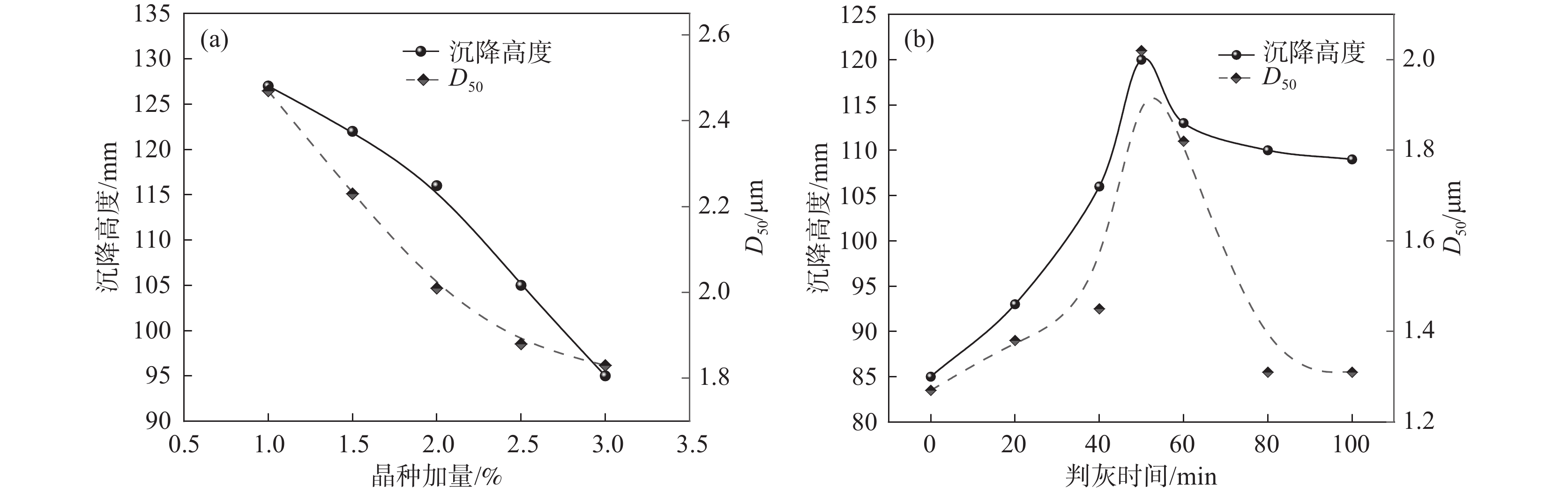
2.3 沉降高度影响因素分析
2.3.1 钛液指标对偏钛酸沉降高度的影响
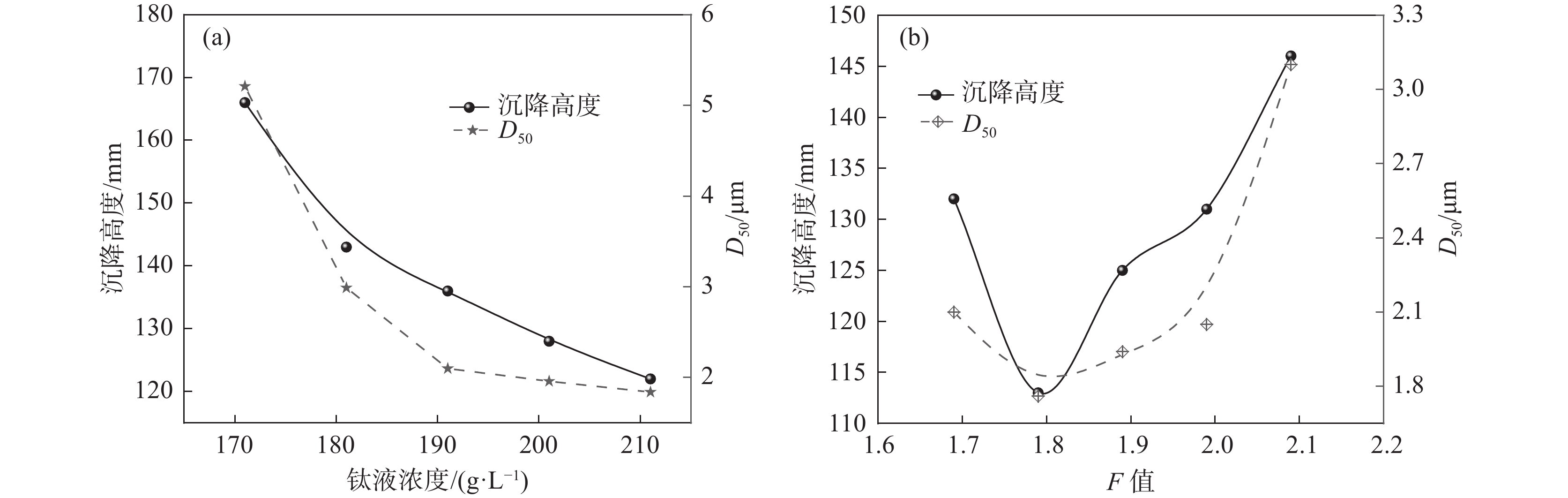
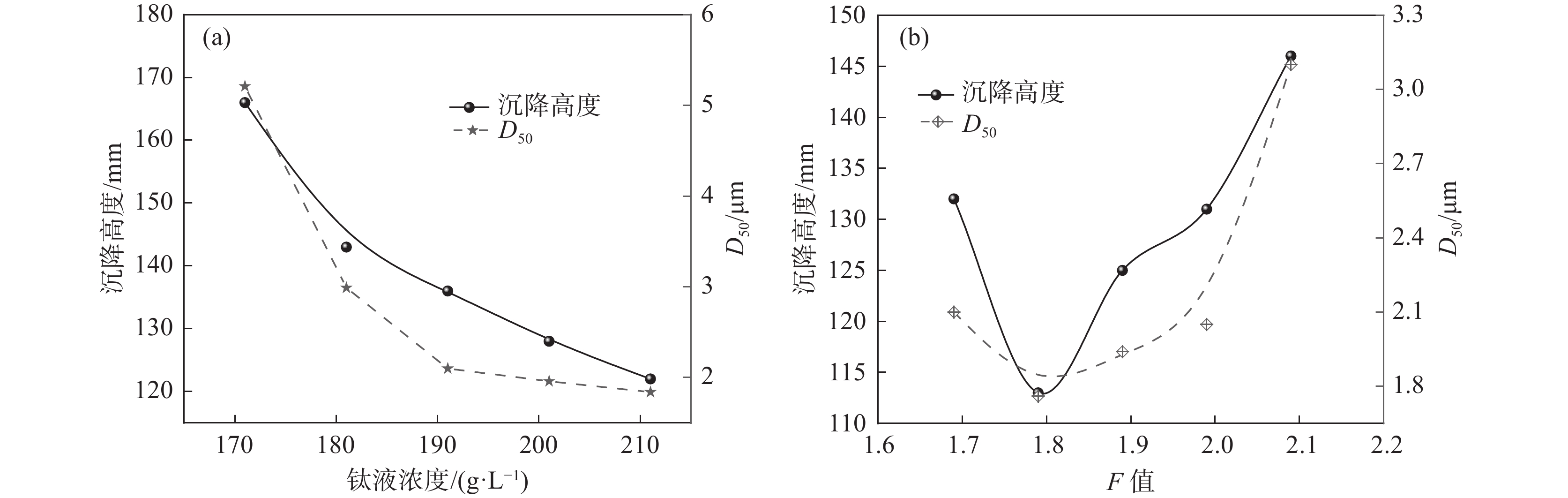
实验室采用不同钛液浓度、F值进行水解试验,考察其对水解偏钛酸沉降高度的影响。由图5(a)可知,随着钛液浓度的增加,沉降高度和D50均呈下降趋势。钛液浓度越高,其稳定性越高,相同条件下的水解速率越慢,形成的一次粒子越粗,团聚粒径相对较小,相应D50和沉降高度也越小。由图5(b)可知,随着钛液F值的增加,沉降高度和D50均呈先下降后增加的趋势。钛液F值越高体系H+浓度越高,水解向正方向进行的难度越大,因而水解速度越慢。当F值很小时,水解速度很快,短时间可形成大量的小颗粒,这些小颗粒由于粒径小、表面能大而极易团聚成粗颗粒,导致沉降高度较大,随着F值增加水解速率逐渐下降,相应形成的水解偏钛酸原始粒径逐渐增加,团聚减弱,从而导致水解偏钛酸D50下降,相应沉降高度也下降,F值进一步增加时,水解速率进一步下降,形成的初始颗粒越来越大,沉降高度也相应增加。
2.3.2 水解工艺对偏钛酸沉降高度的影响
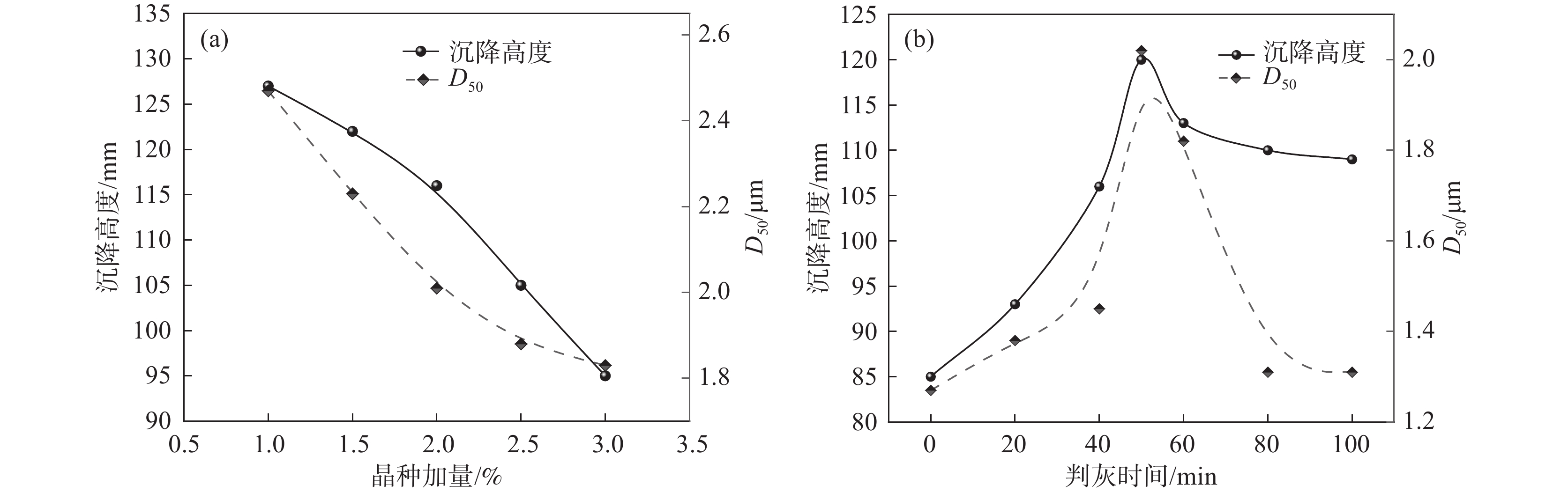
采用同一批钛液,不同的晶种加量和不同判灰时间进行水解试验,水解试验结果见图6。由图6(a)可知,晶种加量在1%~3%范围时,随着晶种加量增加,水解沉降高度呈下降趋势,偏钛酸粒径也呈相似规律。由图6(b)可知,随着第一次沸腾保温时间(判灰时间)延长,沉降高度和D50均呈现先增大后降低的规律。水解晶种加量的增加会导致水解速率的增加,水解速率越快获得的偏钛酸颗粒就越小,相应沉降高度也越小。水解过程是一个形核、晶核长大、团聚、团聚颗粒破碎形成更多晶核的过程,随着第一次沸腾保温时间(判灰时间)的延长,产生晶核数量先逐步增加,然后团聚形成不同大小的团聚体,团聚颗粒增加到一定数量后,在搅拌剪切力的作用下,大团聚颗粒破碎成更多的小团聚颗粒,直到达到相对平衡,这个过程就导致水解偏钛酸平均粒径先逐渐增加,然后再缓慢下降,最终达到相对稳定的平衡状态,相应的水解沉降高度也表现出同样的规律。
3. 结论
1)水解偏钛酸沉降高度与水解偏钛酸D50具有正相关性,和初品Tcs和Scx具有负相关性;水解偏钛酸的沉降高度增加,所得初品的平均粒径呈增加趋势。
2)水解钛液的浓度、F值、水解晶种加量和水解判灰时间均对水解偏钛酸的沉降高度和D50有较大影响。随水解钛液浓度增加,水解偏钛酸沉降高度呈下降趋势,随F值增加,水解偏钛酸沉降高度和D50呈现增加趋势,随水解晶种加量的增加,水解偏钛酸沉降高度呈下降趋势,随判灰时间的延长,水解偏钛酸沉降高度呈现先增加后减小的趋势。
3)生产中控制水解偏钛酸沉降高度范围≤130 mm可得到颜料性能较好的初品。
-
表 1 沉降高度与初品颜料性能均值对应
Table 1. Settlement height and mean performance of primary pigments
沉降高度/mm Tcs Scx L a b 亮度 范围 均值 <100 92.97 1890.0 2.81 97.34 −0.49 3.23 95.16 100~110 105.65 1871.5 2.65 97.57 −0.49 3.37 95.03 110~120 113.60 1876.0 2.72 97.53 −0.52 3.35 95.35 120~130 126.78 1880.8 2.70 97.46 −0.47 3.55 95.25 130~150 142.63 1861.3 2.35 97.51 −0.47 3.70 95.30 >150 161.90 1841.0 2.41 97.33 −0.31 3.20 95.30 表 2 沉降高度均值与钛液指标的关系
Table 2. Relationship between mean settlement height and titanium liquid index
沉降高度/mm F值 总钛/
(g·L−1)铁钛比 固含量
×106稳定性/
mLD50/
μm范围 均值 <100 92.97 2.02 196.7 0.28 26 500 1.85 100~110 105.65 1.98 196.2 0.30 26 500 1.91 110~120 113.60 2.06 195.1 0.29 26 500 1.83 120~130 126.78 2.00 193.5 0.30 25 500 2.00 130~150 142.63 2.02 191.6 0.31 25 500 2.28 >150 161.90 1.98 189.9 0.31 26 500 2.33 -
[1] Li Xianglan. Ultrasonic-assisted titanyl sulfate hydrolysis seed preparation and hydrolysis of titanium sulfate solution[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing University, 2022. (李香兰. 超声辅助硫酸氧钛水解晶种制备和钛液水解研究[D]. 重庆:重庆大学, 2022.Li Xianglan. Ultrasonic-assisted titanyl sulfate hydrolysis seed preparation and hydrolysis of titanium sulfate solution[D]. Chongqing:Chongqing University, 2022. [2] Tian Congxue. Effects of properties and structure of metatitanic acid on rutile white pigment via short sulfate process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019,40(1):1-6. (田从学. 偏钛酸性质结构对颜料钛白的影响[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2019,40(1):1-6. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.01.001Tian Congxue. Effects of properties and structure of metatitanic acid on rutile white pigment via short sulfate process[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium, 2019, 40(1): 1-6. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2019.01.001 [3] Tian Congxue, Wang Qinghong, Lian Zongxin, et al. Effect of structural evolution of metatitanic acid on sulfur content during hydrolysis of industrial TiOSO4 solution[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium , 2023, 44(1): 4-9. (田从学, 王青鸿, 练宗鑫, 等. 钛液水解过程中偏钛酸的结构演变对硫含量的影响研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2023, 44(1): 4-9.Tian Congxue, Wang Qinghong, Lian Zongxin, et al. Effect of structural evolution of metatitanic acid on sulfur content during hydrolysis of industrial TiOSO4 solution[J]. Iron Steel Vanadium Titanium , 2023, 44(1): 4-9. [4] Yu Kang, Li Qing, Gan Ying. Optimization of hydrolysis process in production of titanium dioxide sulfate[J]. China's High-tech Industry, 2023, (16): 87-89. (于康, 李庆, 甘影. 硫酸钛白粉生产中水解工艺优化研究[J]. 中国高新科技, 2023, (16): 87-89.Yu Kang, Li Qing, Gan Ying. Optimization of hydrolysis process in production of titanium dioxide sulfate[J]. China's High-tech Industry, 2023, (16): 87-89. [5] Zhou Qiang, Zhang Xiuzhen, Li Qing, et al. Research and application of rutile titanium dioxide powder for decorative paper of reinforced wood flooring[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2023, 13(26): 74-77. (周强, 张修臻, 李庆, 等. 强化木地板装饰纸用金红石型钛白粉的研究及应用[J]. 科技创新与应用, 2023, 13(26): 74-77.Zhou Qiang, Zhang Xiuzhen, Li Qing, et al. Research and application of rutile titanium dioxide powder for decorative paper of reinforced wood flooring[J]. Technology Innovation and Application, 2023, 13(26): 74-77. [6] Zeng Xiaoyi, Ma Dan, Mei Qizheng, et al. Modeling analysis and optimization of hydrolysis process parameters of metatitanic acid[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2022,36(12):281-288. (曾小义, 马丹, 梅其政, 等. 偏钛酸水解工艺参数建模分析与优化[J]. 重庆理工大学学报(自然科学), 2022,36(12):281-288.Zeng Xiaoyi, Ma Dan, Mei Qizheng, et al. Modeling analysis and optimization of hydrolysis process parameters of metatitanic acid[J]. Journal of Chongqing University of Technology (Natural Science), 2022, 36(12): 281-288. [7] Wang Kun, Lu Ruifang, Dang Leping, et al. Online characterization of seed preparation and investigation on hydrolysis kinetics of TiSO4 solution[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2022, 39(4): 50-56. (王焜, 路瑞芳, 党乐平, 等. 晶种制备的在线表征及钛液水解动力学研究[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2022, 39(4): 50-56.Wang Kun, Lu Ruifang, Dang Leping, et al. Online characterization of seed preparation and investigation on hydrolysis kinetics of TiSO4 solution[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering, 2022, 39(4): 50-56. [8] Chen Minheng, Cong Dezi, Fang Tunan, et al. Principle of chemical engineering(second edition volume 1)[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1999. (陈敏恒,丛德滋,方图南,等;化工原理(第二版上册).北京:化学工业出版社,1999.Chen Minheng, Cong Dezi, Fang Tunan, et al. Principle of chemical engineering(second edition volume 1)[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1999. -






 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载: