Preparation of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode material from vanadium tailings
-
摘要: 以钒渣提钒过程中产生的富含铁锰的浸出液为原料,通过共沉淀法制备了二水草酸铁锰Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4∙2H2O,以此为前驱体,通过高温固相法成功合成了磷酸锰铁锂LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4正极材料,实现了钒渣浸出液中铁锰资源的综合利用。结果表明,在初始pH值为3.5,温度25 ℃,反应时间90 min,草酸铵加料量为理论值的1.1倍,加料方式为正加的条件下,铁和锰的沉淀率分别为99.5%和99.4%,与其他杂质实现深度分离,Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4·2H2O的纯度达99.97%,且粒径较小,分散性良好。可将其作为合成磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的前驱体,为磷酸锰铁锂的工业化生产提供了思路。Abstract: Using the iron-manganese-rich leaching solution generated during vanadium extraction from vanadium slag was used as the raw material, and ferromanganese oxalate dihydrate Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4∙2H2O was prepared by co-precipitation, and lithium ferromanganese iron phosphate LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 anode material was successfully synthesized by the high-temperature solid-phase method using this precursor, which achieved the comprehensive utilization of the iron-manganese resources in the vanadium slag leaching solution. The results showed that under the conditions of initial pH 3.5, temperature 25 ℃, reaction time 90 min, ammonium oxalate addition 1.1 times of the theoretical value, and the addition mode of positive addition, the precipitation efficiency of Fe and Mn were 99.5% and 99.4%, respectively. The depth separation from other impurities was achieved, and the purity of Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4·2H2O reached 99.97% with small particle sizes and good dispersion. It can be used as a precursor for synthesizing lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials, which provides the idea for the industrial production of lithium iron manganese phosphate.
-
0. 引言
为实现“双碳目标”,电化学储能技术的高质量发展尤为重要。而开发一种安全稳定、环境友好、高能量密度、低成本的锂离子电池正极材料,符合当下发展电化学储能技术的要求。磷酸铁锂凭借高安全性和低成本的优势,近年来作为锂离子电池正极材料被广泛应用于电动车和储能领域;然而,磷酸铁锂较低的电化学工作平台(3.4 V)限制了其能量密度上限(580 Wh/kg),难以适应当下新能源电车对长续航里程电池的需求[1]。磷酸锰锂最初被认为是磷酸铁锂的替代品,其电化学工作平台能达到4.1 V,能量密度可达701 Wh/kg[2]。然而,在磷酸锰锂中,锰元素的Jahn-Teller效应可能会导致晶格变形,导致磷酸锰锂极低的锂离子扩散系数[3]。研究发现,由于磷酸锰锂与磷酸铁锂空间构型相同,锰和铁离子能够互掺杂形成均匀的铁锰固溶体,铁对锰的取代能有效抑制磷酸锰锂中Mn3+产生的Jahn-Teller效应[4]。磷酸锰铁锂结合了磷酸铁锂和磷酸锰锂的优点,在显著提升能量密度的同时保证了材料的高安全性,三者具有相似的理论比容量[5](约170 mAh/g),被认为是具有广阔应用前景的正极材料。
磷酸铁锂有着成熟的磷酸铁作为前驱体和主流的固相法合成工艺,而磷酸锰铁锂没有标准前驱体。目前制备磷酸锰铁锂的主要方法有高温固相法、溶胶凝胶法、水热法和共沉淀法等。李晶等[6]采用高温固相法,以磷酸二氢铵、碳酸锰、磷酸铁、碳酸锂和葡萄糖为原料,合成了LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4/C正极材料,该材料在0.1C倍率下,放电比容量为165 mAh/g,在20C倍率下,放电比容量为85 mAh/g,呈现出优异的循环稳定性和倍率特性。Liu等人[7]以氢氧化锂、草酸亚铁、磷酸二氢铵、磷酸锰和葡萄糖为原料,采用固相法得到LiMn1-xFexPO4/C(x = 0.1,0.3,0.5),当x = 0.5时,在0.1C倍率下,放电比容量为140 mAh/g。朱波等[8]将水和乙二醇以1∶15比例混合作为溶剂热反应介质,以磷酸、氢氧化锂、硫酸锰、和硫酸亚铁为原料,溶剂热法合成了LiMn1-xFexPO4 (x = 0,0.1,0.1.5,0.2,0.3)正极材料。研究表明,当x = 0.3时,在2C的倍率下,放电容量为138 mAh/g,且具备良好的循环稳定性。Lü等[9]以一定量的磷酸二氢锂、草酸锰和草酸亚铁为原料,以葡萄糖为碳源,使用溶胶凝胶法,合成了不同比例的LiMn1-xFexPO4/C正极材料,其中LiMn0.5 Fe0.5PO4/C材料具有良好的有序晶体结构。Yue等[10]以硝酸锰、硝酸铁、磷酸为原料,使用共沉淀法制备得到前驱体Mn0.85Fe0.15PO4·H2O,将制备得到的前驱体以碳酸锂和葡萄糖为锂源和碳源,采用高温固相法,合成了LiMn0.85Fe0.15PO4/C正极材料,该材料性能优异,在0.1C的倍率下,放电比容量达152.5 mAh/g。
在上述研究中,试验所采用的锰源和铁源主要是分析纯级的锰盐和铁盐,原料成本较高。钒渣选择性氧化得到的提钒尾液[11−12]中含有大量的铁和较多的锰,倘若以其为合成磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的原料,不仅可以减少成本,缩短流程,同时也能实现资源的有效回收与利用。此外,钒渣浸出液为液态,各元素在溶液中分散性好,可使用工艺简单的共沉淀法,通过铁锰共沉淀进行形貌调控,最终通过高温固相法合成分散性和均一性更好的磷酸锰铁锂正极材料。
因此,以钒渣直接浸出提取低价钒过程[13−15]中得到的富含铁锰的浸出液为原料,通过草酸盐共沉淀制备Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4∙2H2O,以此作为前驱体合成了磷酸锰铁锂正极材料,实现资源的有效回收与利用。主要考察了pH值、温度、时间、沉淀剂加料量、加料方式等因素对铁锰共沉淀过程的影响,为规模化生产磷酸锰铁锂正极材料提供理论基础。
1. 试验部分
1.1 试验原料及试剂
试验中所用钒渣由某公司提供,经由钒渣加压浸出液分离钒铬与其他杂质元素后产生的富含铁锰溶液,主要含铁、锰以及少量的钒和铬,各元素浓度见表1。
表 1 溶液中主要元素及其含量Table 1. Major elemental contents in the solutiong·L−1 Fe Mn V Cr 25.21 5.13 0.26 0.24 试验中所用试剂有:草酸铵、硫酸锰、硫酸、氨水、碳酸锂、磷酸二氢铵、无水乙醇、N-甲基吡咯烷酮(NMP)、聚偏二氟乙烯(PVDF)、乙炔黑,均为分析纯;金属锂片、聚丙烯隔膜、1 mol/L LiPF6(碳酸乙烯酯(EC)): 碳酸二甲酯(DMC)体积比为1∶1,均为电池级。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4∙2H2O前驱体的制备
取适量上述富含铁锰的浸出液,加入一定量的硫酸锰搅拌至完全溶解,使溶液中铁锰的浓度比为1: 1。然后加入一定量的草酸铵,用2 mol·L−1硫酸和浓氨水调节pH值,密封后置于恒温水浴锅中,调节水浴温度和搅拌速率,搅拌一定时间后停止,静置陈化后进行真空抽滤,得到共沉淀产物和滤液,将共沉淀产物放入真空干燥箱中,保持在120 ℃进行真空恒温干燥,干燥后得到共沉淀前驱体,最后对前驱体和滤液进行分析表征。
1.2.2 LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4正极材料的合成
采用高温固相法,取一定量的前驱体产物,按照物质的量比为n前驱体∶n碳酸锂∶n磷酸二氢铵=1∶1.05∶1称取一定量的碳酸锂和磷酸二氢铵混合加入到球磨罐中,以无水乙醇作为分散介质湿球磨4 h。将研磨好的物料在管式炉中以氩气为保护气,700 ℃焙烧10 h,冷却至室温,即可得到LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4正极材料。
1.3 分析与表征
使用pH计(PHSJ-4F)测量pH值;采用ICP-OES(ICAP7400)分析溶液中各元素含量;采用X射线衍射仪(DX2700)测定共沉淀产物和焙烧产物的晶体物相组成;采用扫描电子显微镜(JSM 7610F)对样品进行表面样貌分析;采用激光粒度分析仪(JL-6100)对共沉淀产物的粒度大小与颗粒尺寸分布进行分析。
1.4 电化学测试
将所合成的材料、乙炔黑、PVDF以质量比为8:1:1的比例混合后置于球磨罐中,加入适量NMP作为溶剂,球磨30 min后取出料浆,均匀涂抹在铝箔上,涂层厚度为14 μm。将涂抹好的铝箔放置于120 ℃烘箱中,真空干燥12 h,干燥结束后,用切片机切为直径为13 mm的圆形极片作为工作电极,锂片作为对电极,直径为19 mm的聚丙烯膜作为隔膜,LiPF6(碳酸乙烯酯(EC))作为电解液,在充满氩气的手套箱中,组装为CR2025型扣式半电池。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 各因素对前驱体合成的影响
2.1.1 初始pH值的影响
在反应温度为25 ℃、时间为2 h、草酸铵加料量为理论值(铁和锰的理论加入摩尔量之和)、搅拌速率为
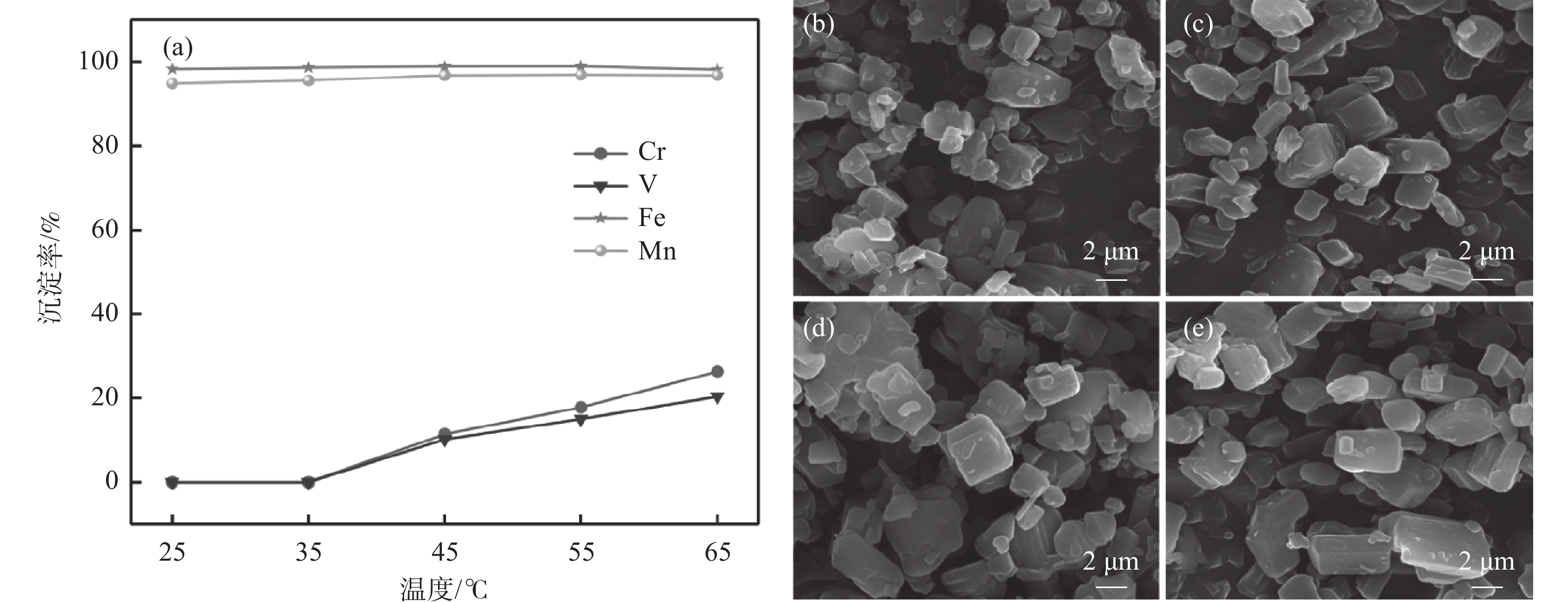
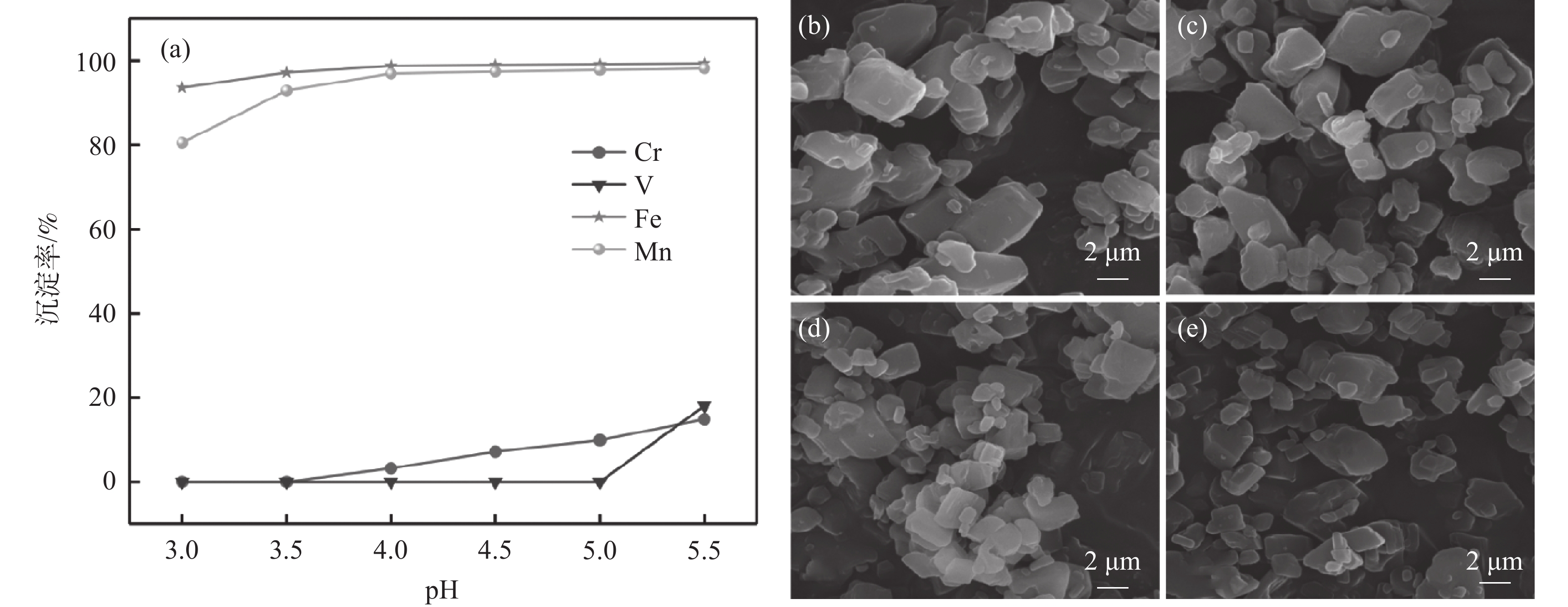
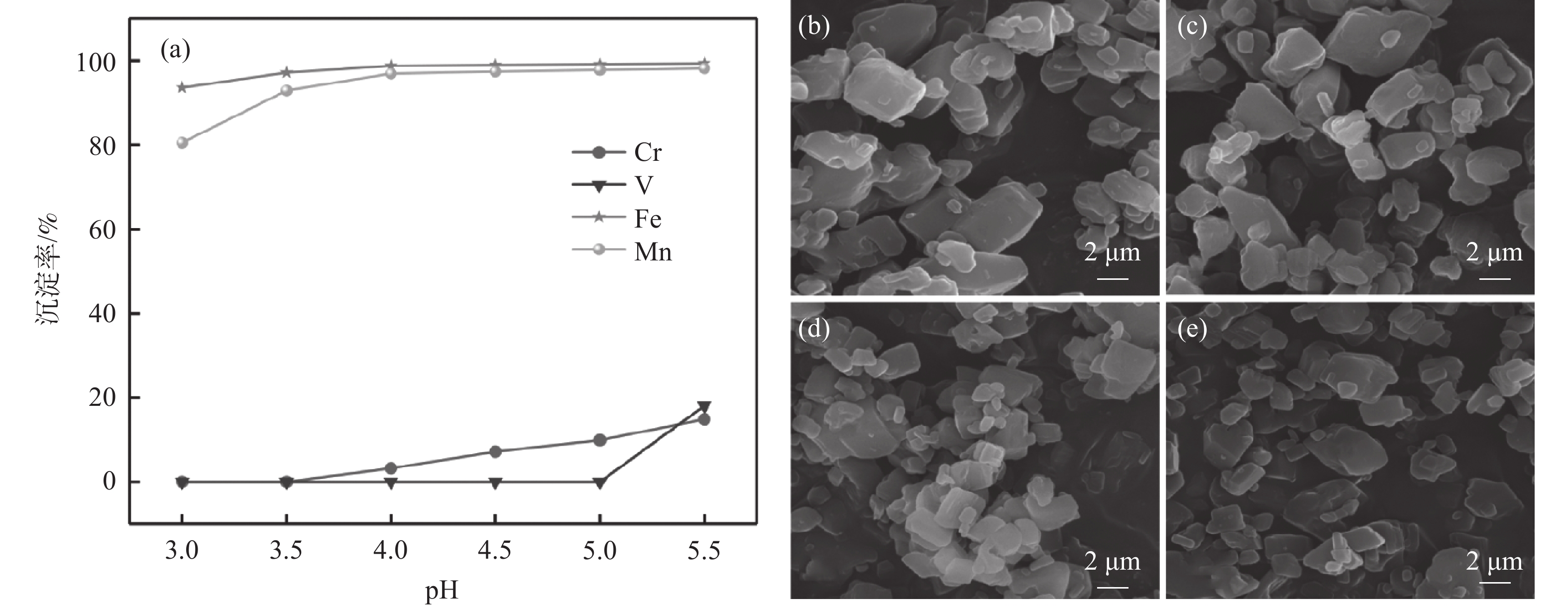
1200 r/min的条件下,探索了溶液初始pH值对铁、锰、钒、铬沉淀率的影响。结果如图1(a)所示,在pH值为3.0时,铁和锰的沉淀率分别为93.5%和80.4%,随着pH值的升高,铁和锰的沉淀率逐渐增加。在pH值为3.5时,铁和锰的沉淀率分别为97.1%和92.2%。再继续增加沉淀pH值,铁锰的沉淀率继续上升,但当pH值高于3.5时,铬开始产生沉淀,钒在pH值为5.0到5.5之间开始产生沉淀。主要是因为当溶液的pH值过高时,溶液中的其他金属离子容易水解,进入共沉淀前驱体中,对后续制备的磷酸锰铁锂的电化学性能造成影响。由图1(b)~(e)可以看出,随着pH值的升高,共沉淀产物的粒径有所下降,颗粒间存在团聚现象。主要原因是pH值较低时,金属离子配合速度较快,易形成大粒径前驱体,形貌难以控制[16];随着pH值升高,沉淀速率逐渐减慢,有利于晶核的生长。因此,综合考虑杂质离子的分离与沉淀率影响,确定初始pH值为3.5。2.1.2 温度的影响
在初始pH值为3.5、反应时间为2 h、草酸铵加料量为理论值、搅拌速率为
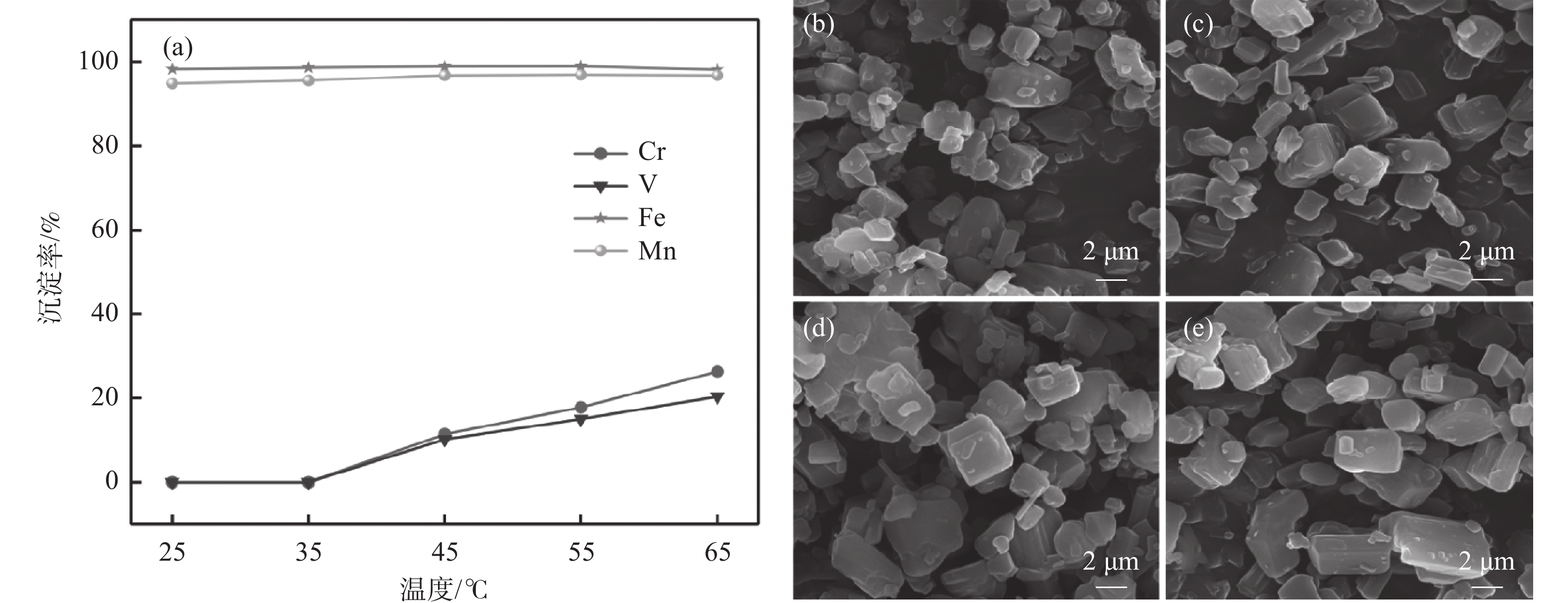
1200 r/min 的条件下,探索了温度对铁、锰、钒、铬沉淀率的影响。结果如图2(a)所示,在25 ℃时,铁和锰的沉淀率分别为97.2%和92.2%,随着温度的升高,铁锰的沉淀率略有增加,但整体变化不大。当温度高于35 ℃时,钒和铬开始沉淀,且温度越高,沉淀率越大。由图2(b)~(e)可以看出,随着温度的升高,共沉淀产物的粒径逐渐变大,主要原因是温度升高使得共沉淀反应体系动能增加,从而促进前驱体颗粒生长;但温度过高,锰的氧化物会优先生产,直接影响前驱体纯度[17]。同时,在后续制备磷酸锰铁锂正极材料时,前驱体的粒度大小直接影响混料过程、焙烧过程中的反应活性以及材料的粒度大小[18],最终影响材料性能。因此,确定共沉淀温度为25 ℃。2.1.3 反应时间的影响
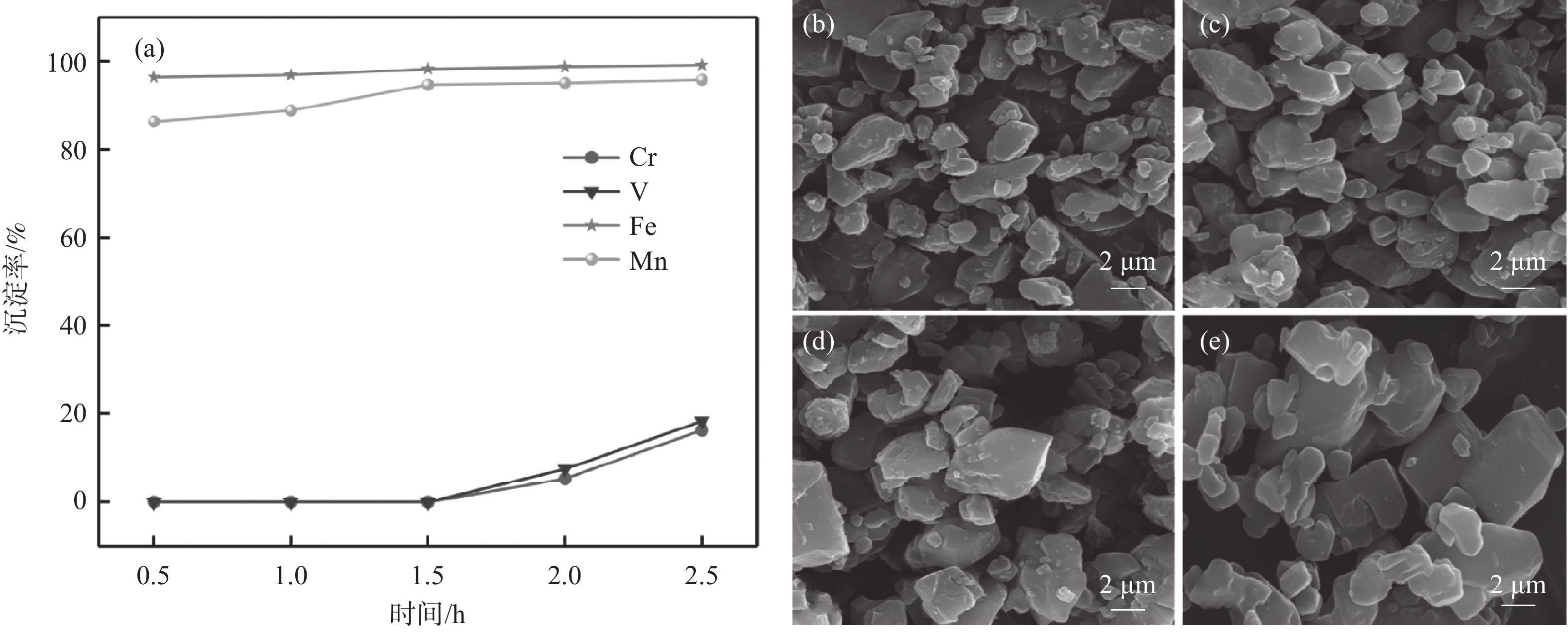
在初始pH值为3.5、温度为25 ℃、草酸铵添加量为理论值、搅拌速率为
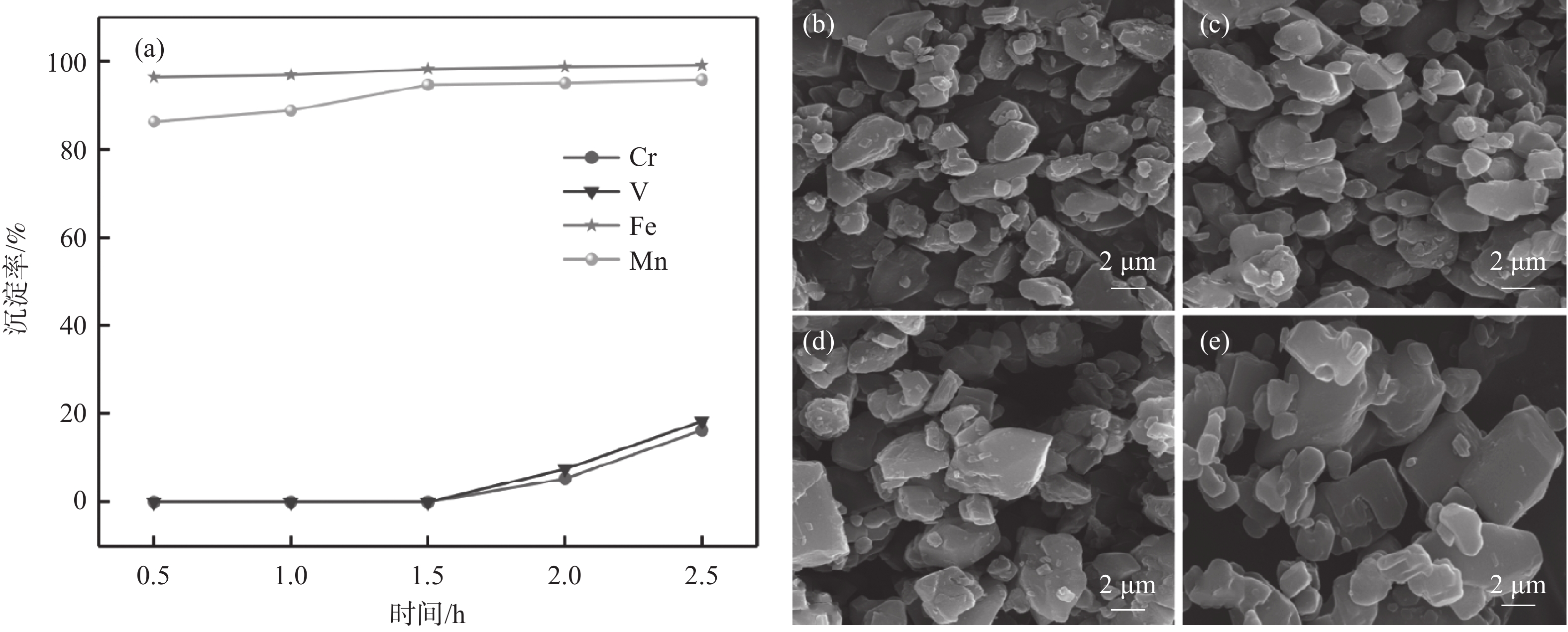
1200 r/min的条件下,研究了反应时间对铁、锰、钒、铬沉淀率的影响,结果如图3(a)所示。由图可知,随着反应时间的增加,铁和锰的沉淀率逐渐升高,反应1.5 h,铁和锰的沉淀率分别达到97.3%和92.3%,钒和铬基本不沉淀。之后,随着反应时间的延长,铁和锰的沉淀率基本保持不变。由图3(b)~(e)可以看出,随着反应时间的延长,长方体型的草酸铁锰形貌更加规整[19],表面更为光滑,更有利于制备出具有良好形貌的磷酸锰铁锂正极材料。但反应时间过长,铁锰共沉淀产物会夹杂部分钒铬金属离子,所以反应时间不宜过长。因此,确定反应时间为1.5 h。2.1.4 草酸铵加料量的影响
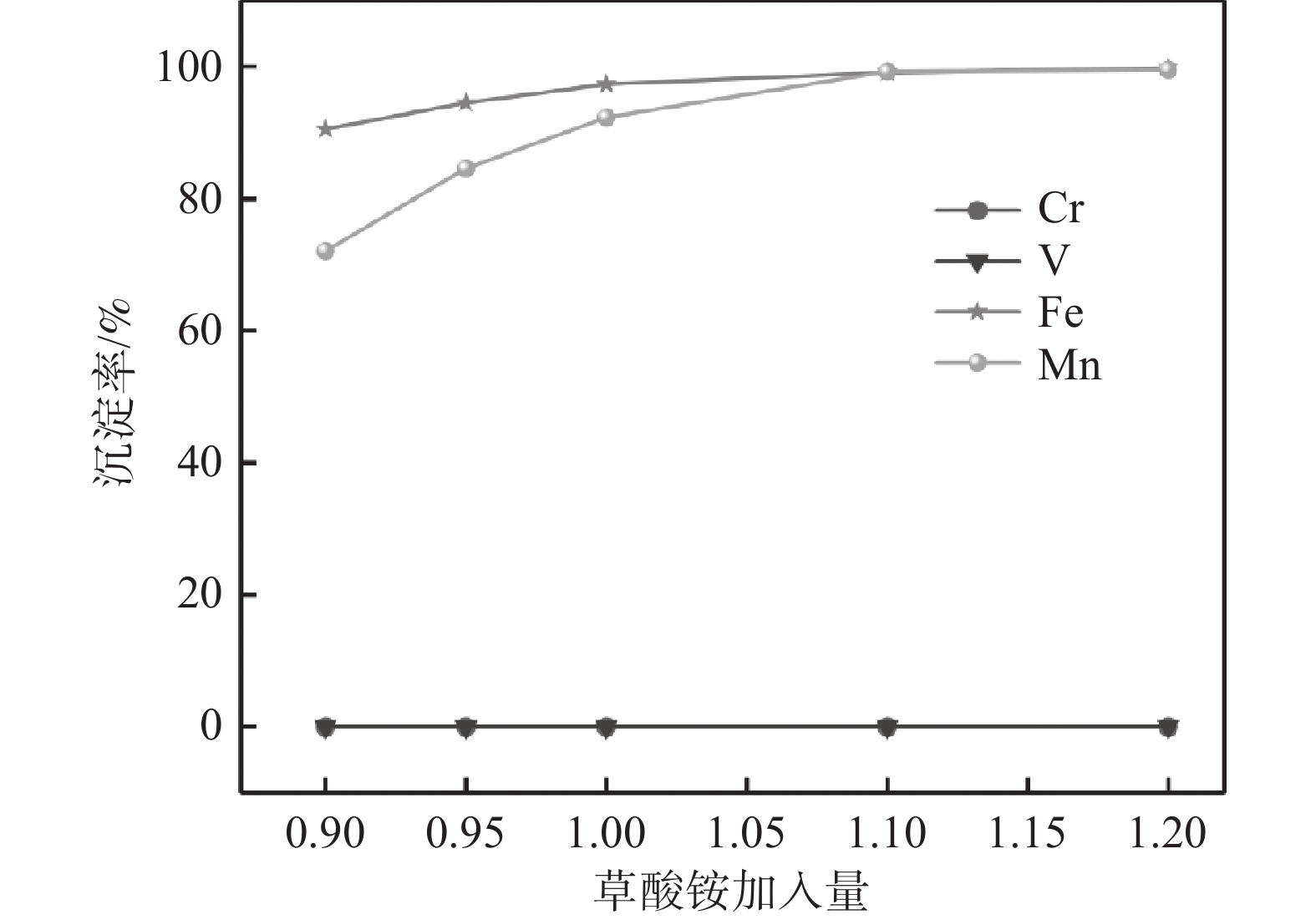
在初始pH值为3.5、温度为25 ℃、反应时间为1.5 h、搅拌速率为
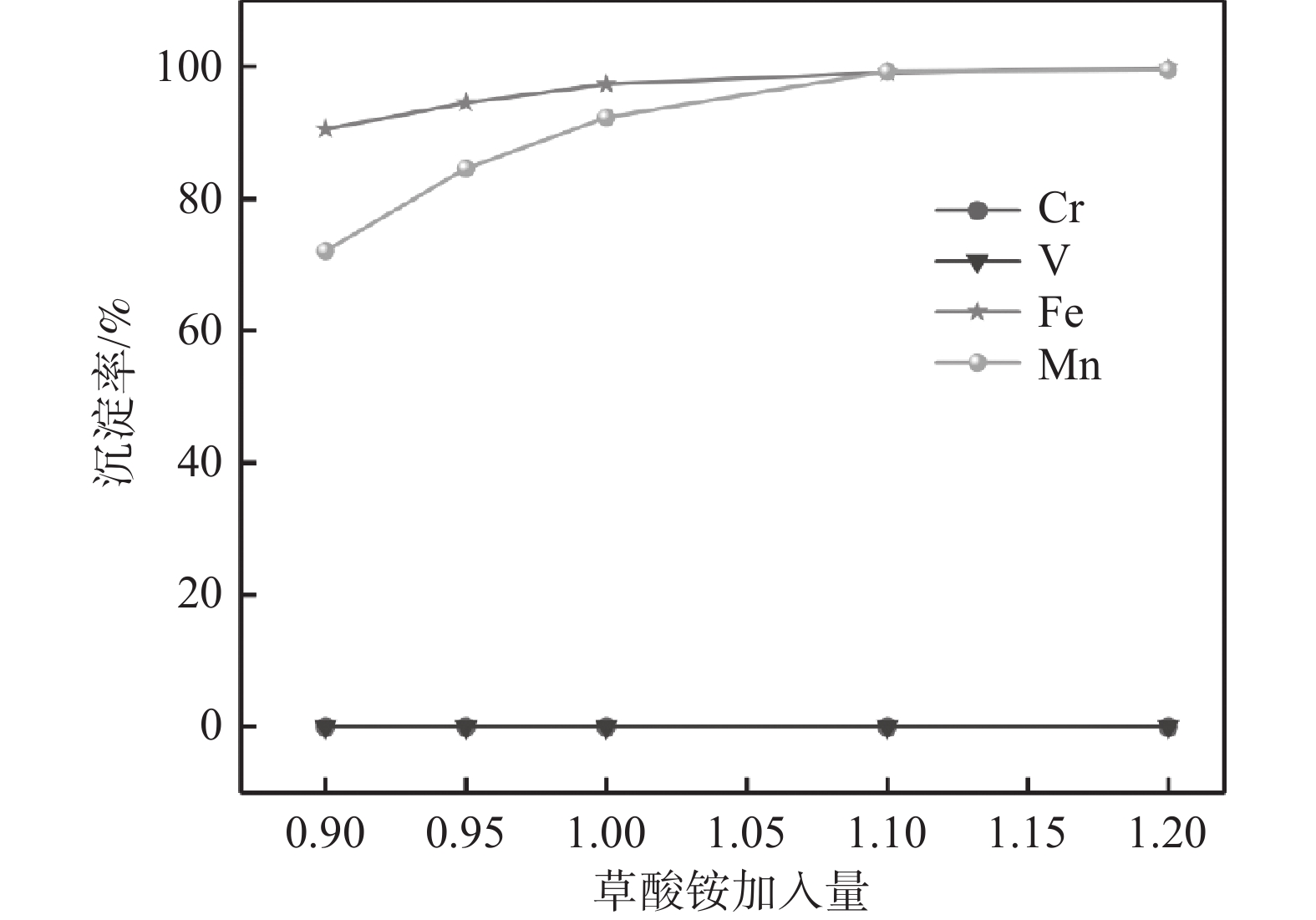
1200 r/min 的条件下,探索了沉淀剂草酸铵的加料量(分别为理论值的0.90、0.95、1.00、1.05、1.10、1.20倍)对铁、锰、钒、铬沉淀率的影响,结果如图4所示。由图可知,在理论的草酸铵用量下,铁和锰的沉淀率分别为98.2%和92.3%,此时铁和锰并未沉淀完全,主要是因为部分的草酸根与钒铬结合,消耗了部分草酸。进一步增加草酸铵的用量至1.1倍,铁和锰的沉淀率分别增加到了99.5%和99.4%,基本可以实现铁锰完全共沉淀。因此,确定草酸铵的加料量为理论值的1.1倍。2.1.5 草酸铵加料方式的影响
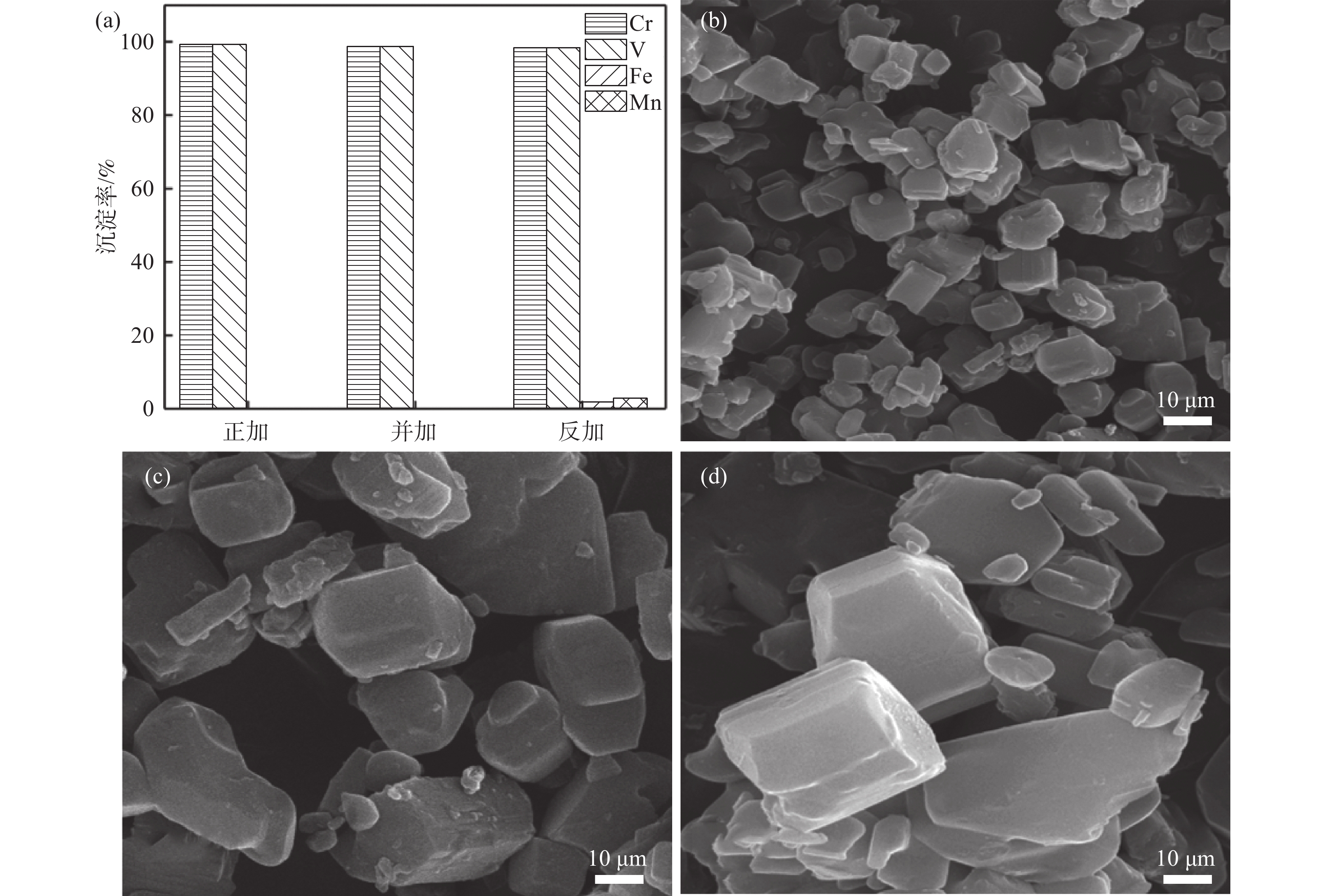
在初始pH值为3.5、反应时间为1.5 h、温度为25 ℃、草酸铵加料量为理论值的1.1倍、搅拌速率为
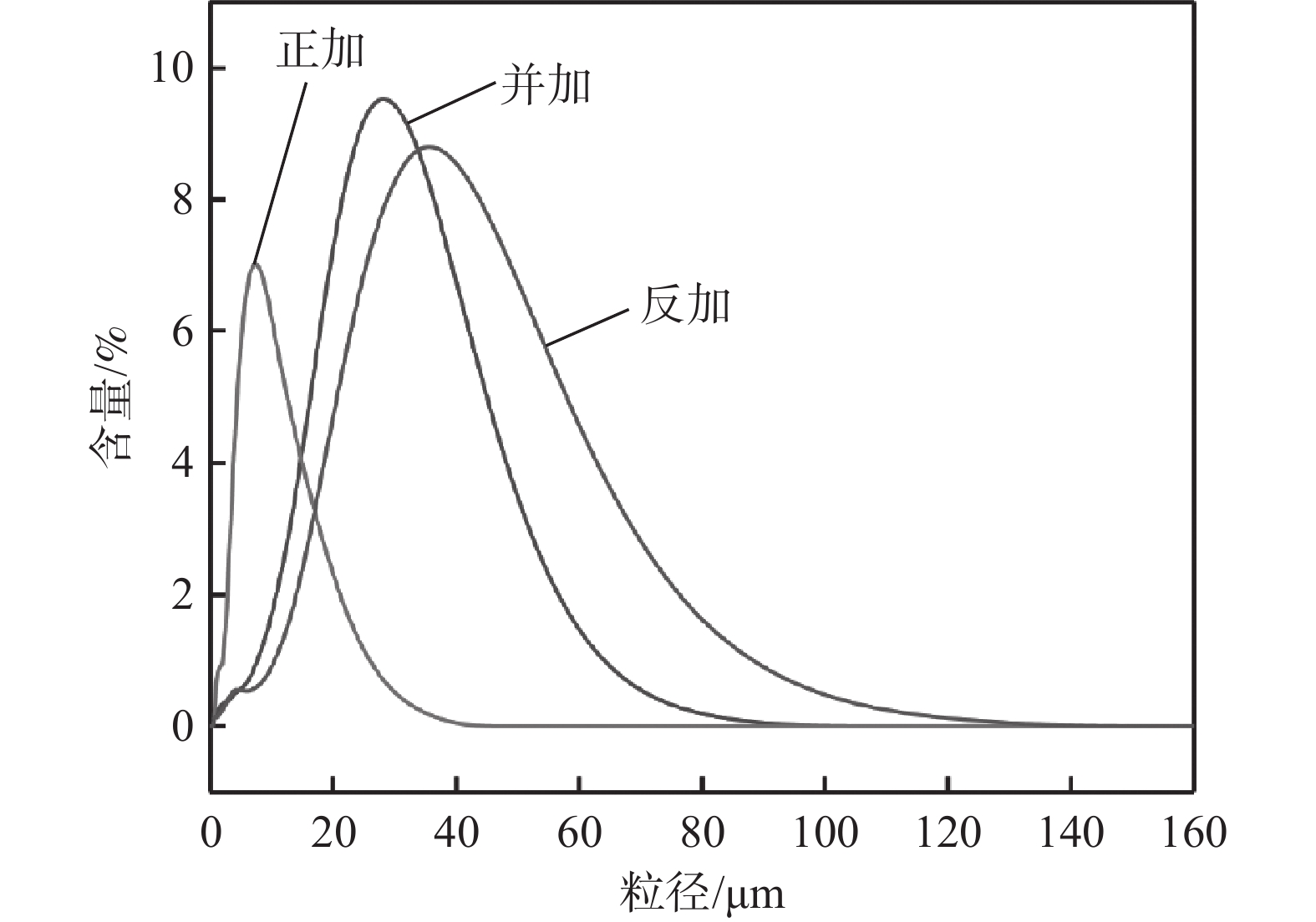
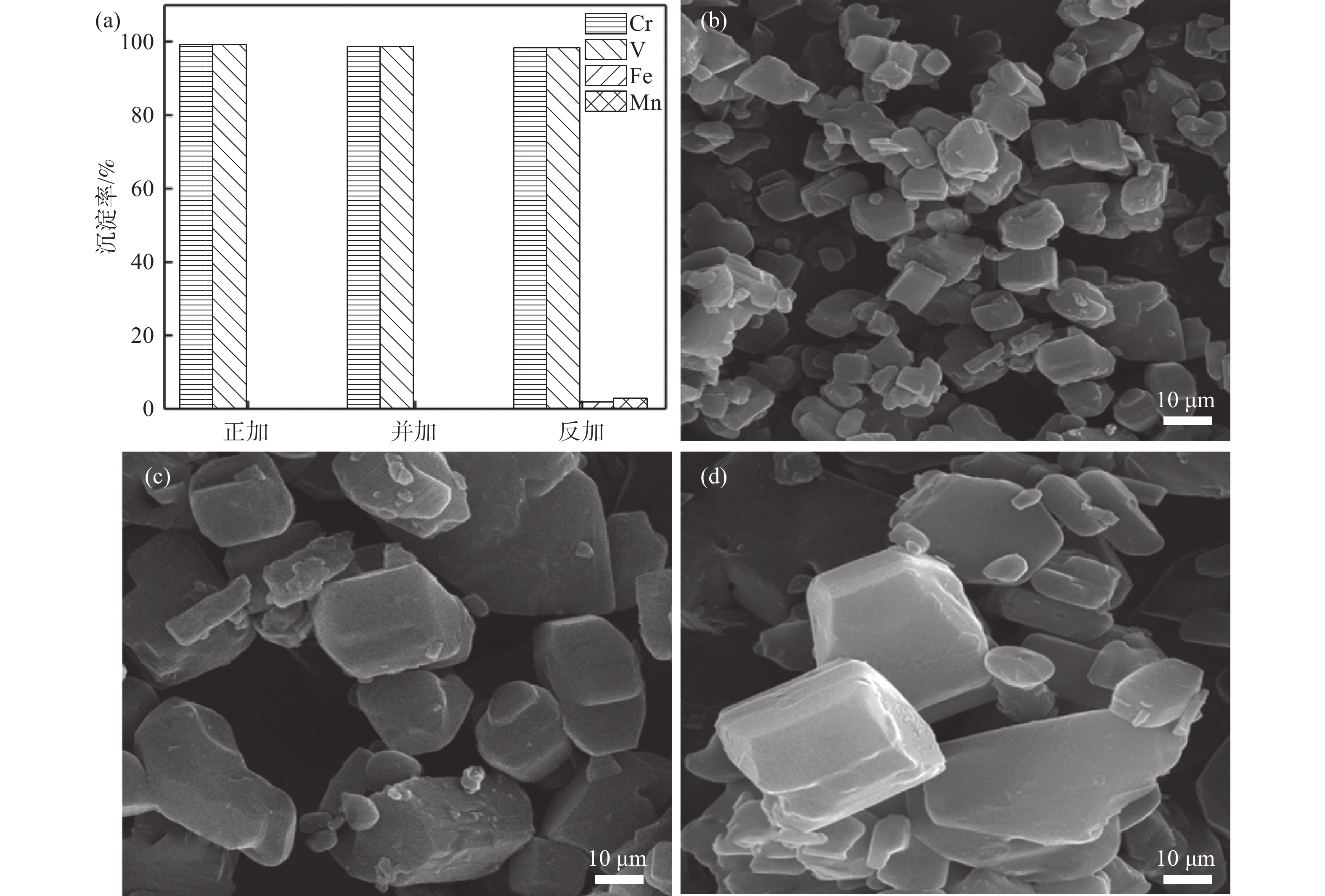
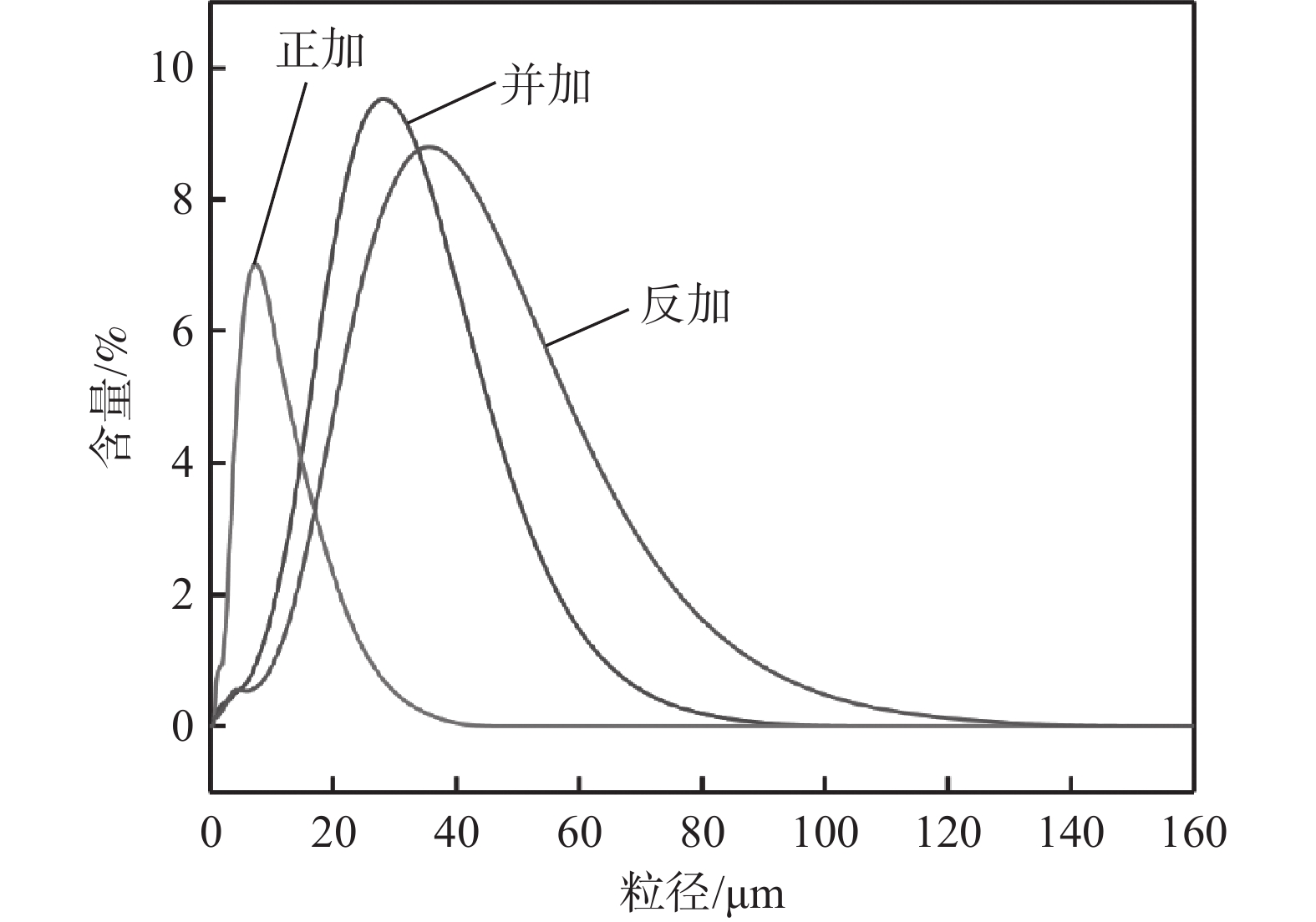
1200 r/min的条件下,控制加料方式分别为草酸铵溶液通过蠕动泵以一定的流速逐滴加入到浸出液中(正加);浸出液通过蠕动泵以一定的流速逐滴加入到草酸铵溶液中(反加);浸出液与草酸铵溶液同时通过蠕动泵以一定流速逐滴加入到空置烧杯中(并加),研究了三种不同加料方式对铁、锰、钒、铬沉淀过程的影响,结果如图5(a)所示。从图5(a)可以看出,三种加料方式中铁和锰的沉淀率都在98%以上,加料方式为正加和并加时,钒和铬不会产生沉淀。而加料方式为反加的过程中,钒和铬会产生部分沉淀,这主要是因为反加的过程中,由于草酸根的水解,在局部产生较多的氢氧根离子,会造成局部pH值较高,部分钒和铬水解,产生沉淀。通过扫描电子显微镜进一步对三种不同加料方式的产物形貌进行分析,结果如图5(b)~(d)所示,可以看出,加料方式为正加时,沉淀产物的粒径最小,分散更均匀。而加料方式为反加时,可以观察到沉淀产物中有较大粒径的颗粒存在。进一步对三种不同加料方式下的共沉淀产物的粒径进行分析,结果如图6和表2所示。可以看出,不同的加料方式对于共沉淀产物的颗粒尺寸有显著影响,正加共沉淀产物的粒度最小,D50为7.56 μm;反加共沉淀产物的粒度最大,D50达到41.87 μm;有研究表明,前驱体的粒度越小,越有利于提高磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的电化学性能[20]。因此,选择加料方式为正加,此时钒铬不会产生沉淀,并且共沉淀产物的粒度也最小。
表 2 不同加料方式共沉淀产物的粒度Table 2. Particle sizes of co-precipitation products with different addition methods加料方式 D10/μm D50/μm D90/μm 正加 2.89 7.57 17.32 并加 10.57 26.66 46.31 反加 12.14 41.87 62.46 2.2 铁锰共沉淀前驱体表征
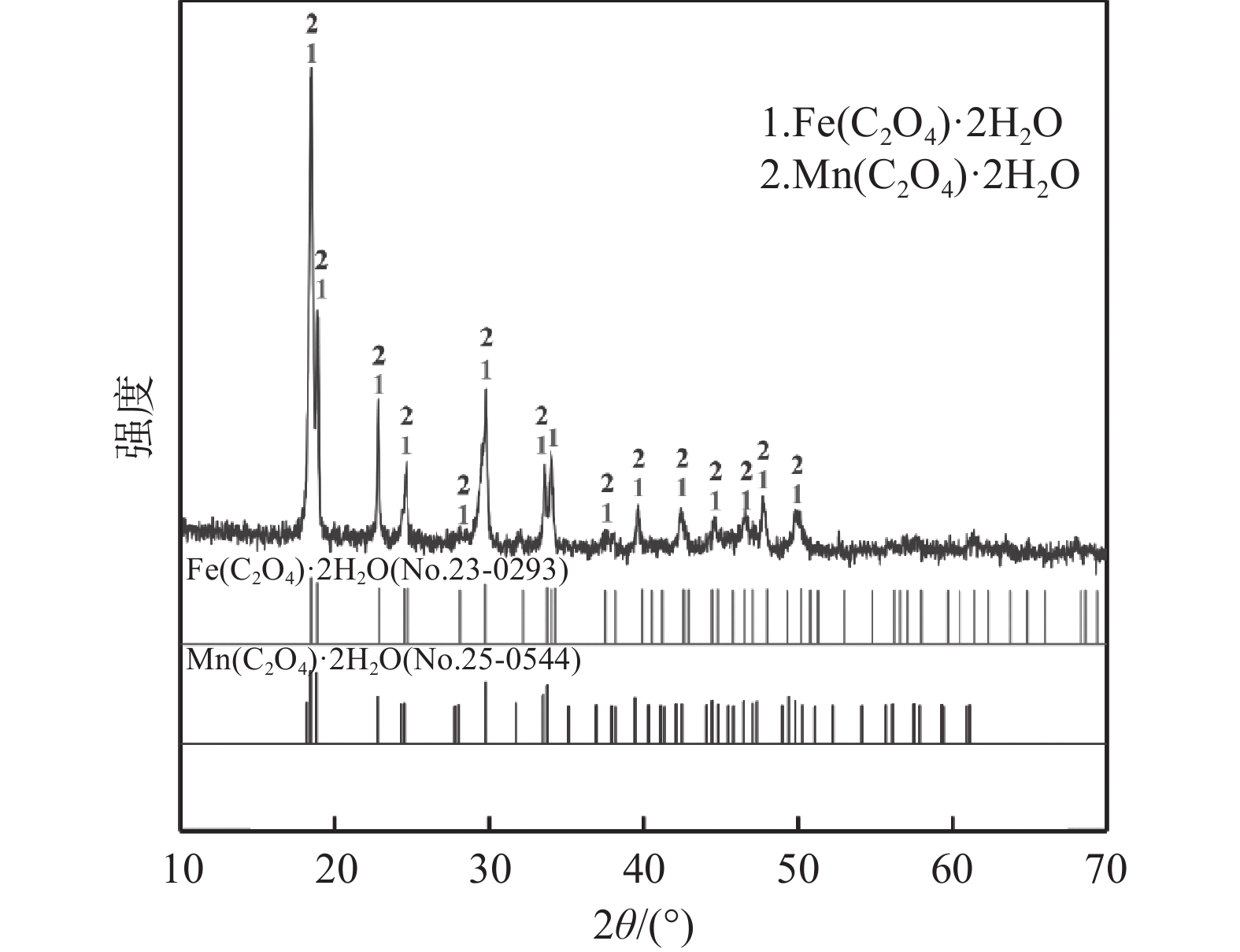
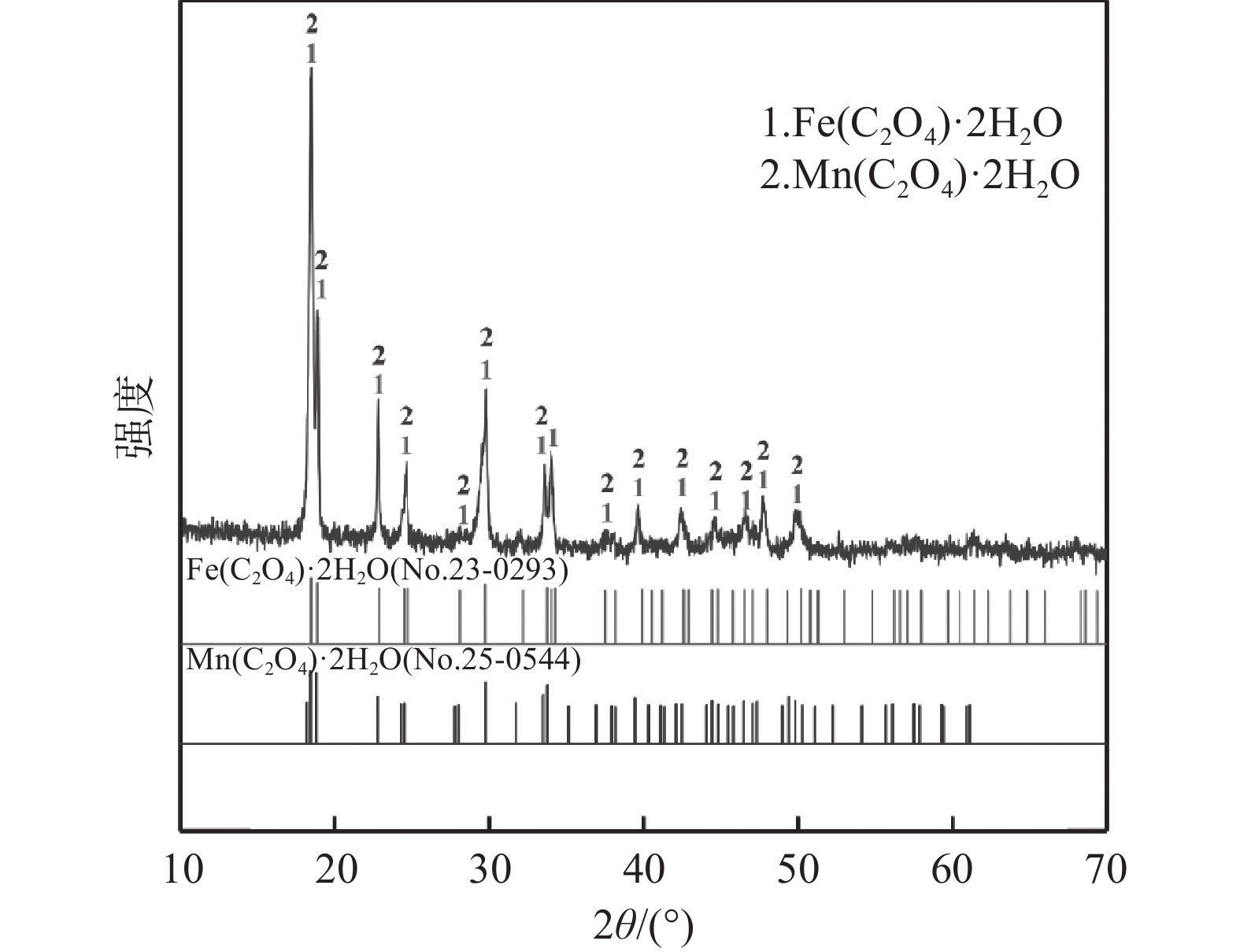
将沉淀产物用去离子水进行三次洗涤后,在真空烘箱中120 ℃真空干燥24 h,并采用ICP和XRD对沉淀产物的元素组成和物相结构进行了分析,结果如表3和图7所示。沉淀产物中FeC2O4·2H2O和MnC2O4·2H2O的纯度达99.97%,含有0.03%的V和小于0.01%的Cr,这是因为草酸沉淀产物的大量产生会夹带微量的杂质。从图7中可以看出,沉淀产物的衍射峰强度大,而且尖锐,表面沉淀结晶好,结晶度高。沉淀产物由FeC2O4·2H2O和MnC2O4·2H2O组成,没有杂质峰出现,证明产品纯度高。
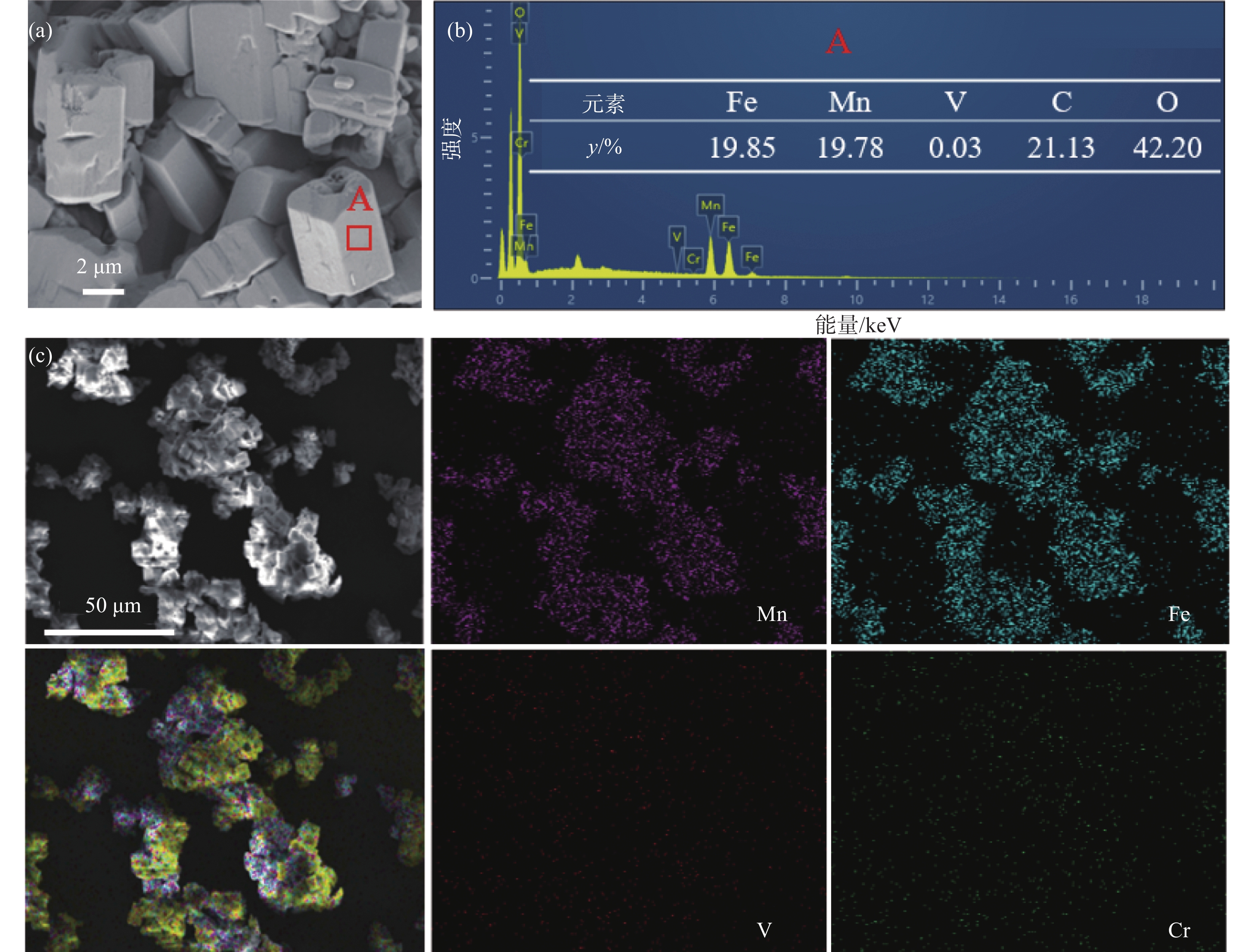
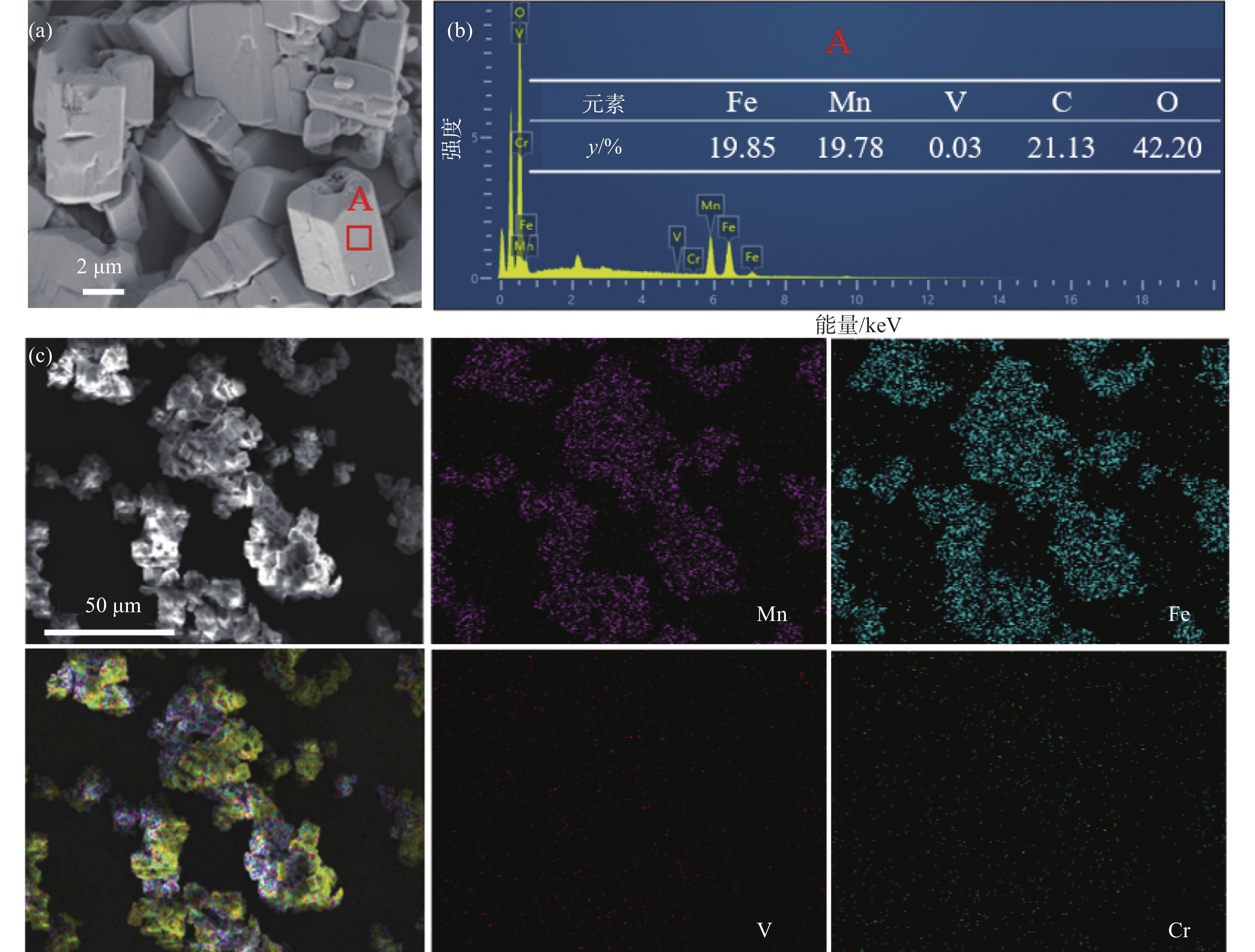
表 3 沉淀产物的组成Table 3. Compositions of the precipitation product% Fe Mn V Cr 49.94 50.03 0.03 <0.01 通过SEM-EDS确定了沉淀产物的形貌和元素含量,如图8所示。沉淀产物为长方体状,颗粒大小不一,沉淀颗粒表面光滑,而截面上有一些孔隙。EDS结果表明,铁和锰的含量基本相同,只含有0.03%的V,没有检测到其他杂质元素的衍射峰。此外,在沉淀产物中,Fe和Mn均相分布,表明前驱体中Fe和Mn混合均匀。
2.3 磷酸锰铁锂的制备与电化学性能测试
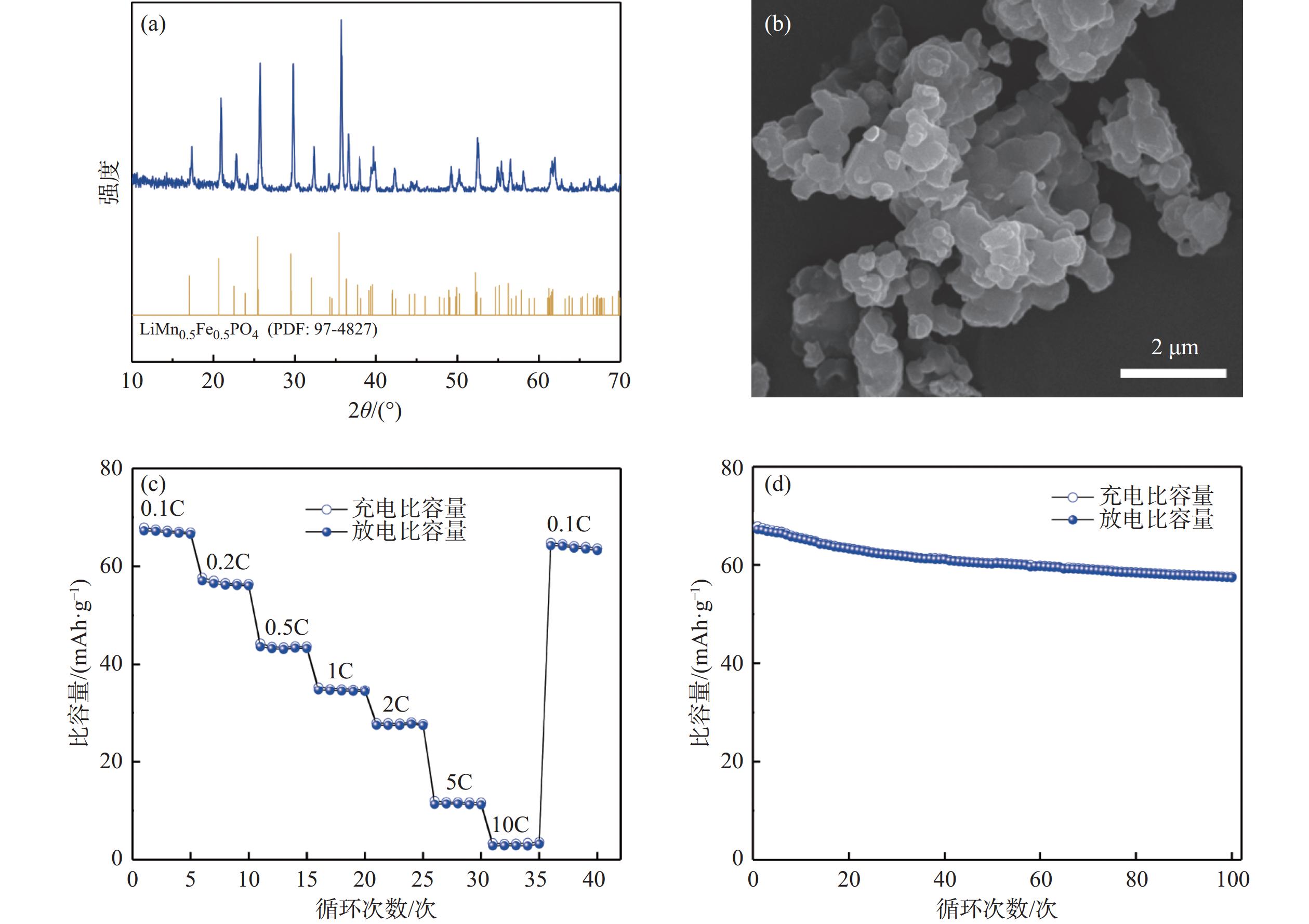
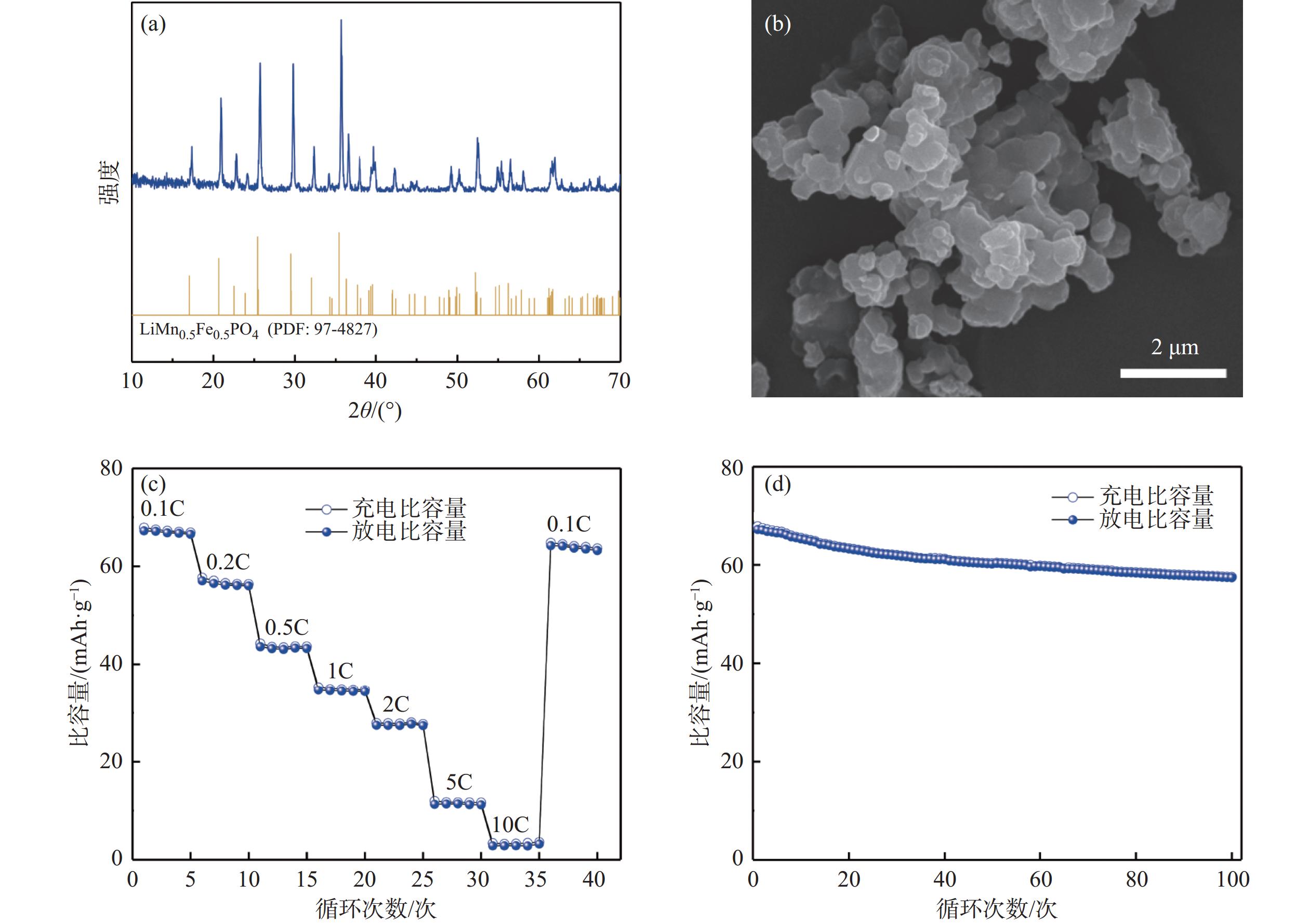
以共沉淀法制备的Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4·2H2O为前驱体,按照物质的量之比加入其他原料,利用高温固相法制备得到的磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的XRD图谱如图9(a)所示。可以看出合成材料的主要物相组成为LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4,其XRD的衍射峰与对应的标准卡片相对应,并且衍射峰较为尖锐,表明晶体结构形成较为良好。图9(b)为LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4材料的微观形貌,可以看出材料在焙烧过程中,立方体型的晶粒相熔合,出现片层状堆叠的现象。
图9(c)为所制备的LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4的倍率性能图。LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4在0.1C的电流密度进行充放电时,首周放电比容量为66.7 mAh/g。随着电流密度增加至0.2C、1C、2C、5C和10C时,首周放电比容量分别下降到57.1、43.6、34.7、27.4 mAh/g和2.8 mAh/g。各循环5次后,将电流密度调回至0.1C时,没有观察到明显的容量损失,说明该材料的结构较为稳定。图9(d)为LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4在电流密度为0.1C时的充放电循环性能图。其首次放电比容量为66.7 mAh/g,循环100次后放电比容量降到了58.8 mAh/g,容量保持率为88.2%。其电化学性能还有待提高,主要的原因是磷酸盐体系材料的导电性较差,但其倍率和循环性能与文献中未经改性的材料相比具有一定的优势[21−24],后续可通过碳包覆、掺杂等方式[25]进一步提高材料的电化学性能,以满足电池产品需求。
3. 结论
1)通过草酸盐共沉淀法,可从富含铁锰的钒渣浸出液制备Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4·2H2O。在初始pH值为3.5、温度25 ℃、反应时间90 min、草酸铵加料量为理论值的1.1倍、加料方式为正加的条件下,铁和锰的沉淀率分别达99.5%和99.4%。
2)所制备的Mn0.5Fe0.5C2O4·2H2O纯度达99.97%,且粒径较小,分散性良好,可将其作为合成磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的前驱体。该工艺实现了低价钒浸出液中铁锰资源的有效利用,为磷酸锰铁锂正极材料的规模化生产提供了思路。
致谢
本研究得到了国家自然科学基金(批准号:51774205)的资助以及四川大学后续能源材料与器件教育部工程研究中心开放课题资助。感谢四川大学新能源与低碳技术研究院提供的XRD技术协助,感谢四川大学化工学院工程实验教学中心提供的ICP-OES和SEM技术协助。
-
表 1 溶液中主要元素及其含量
Table 1. Major elemental contents in the solution
g·L−1 Fe Mn V Cr 25.21 5.13 0.26 0.24 表 2 不同加料方式共沉淀产物的粒度
Table 2. Particle sizes of co-precipitation products with different addition methods
加料方式 D10/μm D50/μm D90/μm 正加 2.89 7.57 17.32 并加 10.57 26.66 46.31 反加 12.14 41.87 62.46 表 3 沉淀产物的组成
Table 3. Compositions of the precipitation product
% Fe Mn V Cr 49.94 50.03 0.03 <0.01 -
[1] Schmuch Richard, Wagner Ralf, Hörpel Gerhard, et al. Performance and cost of materials for lithium-based rechargeable automotive batteries[J]. Nature Energy, 2018,3(4):267-278. doi: 10.1038/s41560-018-0107-2 [2] Wang Yanqiang, Ke Junxiong, Wang Biao, et al. Research progress of ferromanganese phosphate precursors[J]. Chemical Management, 2023(25):138-141. (王彦强, 柯君雄, 王镖, 等. 磷酸锰铁前驱体的研究进展[J]. 化工管理, 2023(25):138-141.Wang Yanqiang, Ke Junxiong, Wang Biao, et al. Research progress of ferromanganese phosphate precursors[J]. Chemical Management, 2023(25): 138-141. [3] Franky E, Lora Bedoya, Victoria Salgado, et al. Stable V-doped LiMnPO4/C cathode material for Li-ion batteries produced by a fast and facile microwave-assisted synthesis[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2023,938:53-61. [4] Said Oukahou, Mohammad Maymoun, Abdelali Elomrani, et al. Enhancing the electrochemical performance of olivine LiMnPO4 as cathode materials for Li-ion batteries by Ni-Fe codoping[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2022, 5(9): 10591-10603. [5] Du Hao, Kang Yuqiong, Li Chenglei, et al. Easily recyclable lithium-ion batteries: Recycling-oriented cathode design using highly soluble LiFeMnPO4 with a water-soluble binder[J]. Battery Energy, 2023,2(4):20230011. [6] Li Jing, Qin Yuanbin, Ning Xiaohui, et al. Improved preparation of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials by high-temperature solid-phase method[J]. Materials Guide, 2020,34(16):16001-16005. (李晶, 秦元斌, 宁晓辉, 等. 改进高温固相法制备磷酸锰铁锂正极材料[J]. 材料导报, 2020,34(16):16001-16005. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19070270Li Jing, Qin Yuanbin, Ning Xiaohui, et al. Improved preparation of lithium manganese iron phosphate cathode materials by high-temperature solid-phase method[J]. Materials Guide, 2020, 34(16): 16001-16005. doi: 10.11896/cldb.19070270 [7] Liu Hongyu, Ren Li, Li Jiashen, et al. Iron-assisted carbon coating strategy for improved electrochemical LiMn0.8Fe0.2PO4 cathodes[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2016,212:800-807. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2016.07.049 [8] Zhu Bo, Wang Yajing, Wang Yanming, et al. Synthesis of LiMn1- xFe xPO4 nanosheets by solvothermal method and their electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Artificial Crystals, 2016,45(7):1826-1831. (朱波, 王雅静, 汪燕鸣, 等. 溶剂热法合成LiMn1- xFe xPO4纳米片及其电化学性能[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2016,45(7):1826-1831. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2016.07.020Zhu Bo, Wang Yajing, Wang Yanming, et al. Synthesis of LiMn1-xFexPO4 nanosheets by solvothermal method and their electrochemical properties[J]. Journal of Artificial Crystals, 2016, 45(7): 1826-1831. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-985X.2016.07.020 [9] Lü Wei, Cai Wenlong, Wang Tuan, et al. Thermodynamic equilibrium theory-guided design and synthesis of Mg-doped LiFe0.4Mn0.6PO4/C cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2023,9(1):619-627. [10] Yue Yang, Sun Miaomiao, Yu Wenhao, et al. Recovering Fe, Mn and Li from LiMn1- xFe xPO4 cathode material of spent lithium-ion battery by gradient precipitation[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2023,36:1016-1026. [11] Wang Zhenghao, Chen Liang, Yang Ke, et al. Exploration of a novel vanadium source for the synthesis of a Na3V2(PO4)3 cathode of sodium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2024,12(5):1973-1983. [12] Wang Zhenghao, Chen Liang, Qin Zhifeng, et al. A green and efficient route for simultaneous recovery of low valence of vanadium and chromium, titanium and iron from vanadium slag[J]. Resources, Conservation Recycling, 2022,178:106046. doi: 10.1016/j.resconrec.2021.106046 [13] Yin Rentao, Chen Liang, Qin Zhifeng, et al. A novel complexation method for separation and recovery of low valence vanadium, iron and chromium from sulfuric acid solution[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022,373:133640. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2022.133640 [14] Wang Zhenghao, Chen Liang, Yin Rentao, et al. Preparation of vanadyl sulfate electrolyte for vanadium flow battery from vanadium slag using calcium salt precipitation, sodium carbonate leaching and solvent extraction[J]. Hydrometallurgy, 2023,222:106146. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2023.106146 [15] Zhou Weihua, Li Zhenqin, Duan Meng, et al. Study on complexation and iron removal in vanadium slag leach solution[J]. Iron and Steel Vanadium and Titanium, 2016,37(5):20-24. (周维华, 李振溱, 段猛, 等. 钒渣浸出液中络合除铁的研究[J]. 钢铁钒钛, 2016,37(5):20-24. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.05.004Zhou Weihua, Li Zhenqin, Duan Meng, et al. Study on complexation and iron removal in vanadium slag leach solution[J]. Iron and Steel Vanadium and Titanium, 2016, 37(5): 20-24. doi: 10.7513/j.issn.1004-7638.2016.05.004 [16] Ding Dong, Yuta Maeysohi, Masaaki Kubota, et al. A facile way to synthesize carbon-coated LiMn0.7Fe0.3PO4/reduced graphene oxide sandwich-structured composite for lithium-ion batteries[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019,2(3):1727-1733. doi: 10.1021/acsaem.8b01821 [17] Yu Songmin, Jin Hongbo, Yang Minghu, et al. Fluorine-doped modified LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode materials and their electrochemical properties[J]. Advances in Chemical Engineering, 2023,43(1):302-309. (于松民, 金洪波, 杨明虎, 等. 氟掺杂改性LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4正极材料及其电化学性能[J]. 化工进展, 2023,43(1):302-309.Yu Songmin, Jin Hongbo, Yang Minghu, et al. Fluorine-doped modified LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 cathode materials and their electrochemical properties[J]. Advances in Chemical Engineering, 2023, 43(1): 302-309. [18] Li Gang, Dai Zhongjia, Yang Wensheng, et al. Influence of precursor particle size on the performance of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 lithium ternary material[J]. Power Supply Technology, 2020,44(2):145-148. (李刚, 戴仲葭, 杨文胜, 等. 前驱体粒径对锂电三元材料LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2性能的影响[J]. 电源技术, 2020,44(2):145-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2020.02.001Li Gang, Dai Zhongjia, Yang Wensheng, et al. Influence of precursor particle size on the performance of LiNi0.8Co0.1Mn0.1O2 lithium ternary material[J]. Power Supply Technology, 2020, 44(2): 145-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2020.02.001 [19] Yang Hao, Fu Cuimei, Sun Yijian, et al. Fe-doped LiMnPO4@C nanofibers with high Li-ion diffusion coefficient[J]. Carbon, 2020,158:102-109. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.11.067 [20] Lin Chengliang, Zhao Meiju, Yuan Yunquan, et al. Research on the performance regulation of LiMn0.75Fe0.25PO4-based hybrid cathode materials[J]. Power Supply Technology, 2023,48(1):45-50. (蔺成良, 赵美菊, 袁云泉, 等. LiMn0.75Fe0.25PO4基混合正极材料性能调控研究[J]. 电源技术, 2023,48(1):45-50.Lin Chengliang, Zhao Meiju, Yuan Yunquan, et al. Research on the performance regulation of LiMn0.75Fe0.25PO4-based hybrid cathode materials[J]. Power Supply Technology, 2023, 48(1): 45-50. [21] Kosova Nina, Podgornova Olga, Gutakovskii Anton. Different electrochemical responses of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4 prepared by mechanochemical and solvothermal methods[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,742:454-465. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.242 [22] Deng Yuanfu, Yang Chunxiang, Zou Kaixiang, et al. Recent advances of Mn-rich LiFe1- yMn yPO4 (0.5 ≤ y ≤ 1.0) cathode materials for high energy density lithium ion batteries[J]. Advanced Energy Materials, 2017,7(13):10-16. [23] Xiao F P, Ding B, Lai O M, et al. High performance LiMn1- xFe xPO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1) synthesized via a facile polymer[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2017,160(6):918-926. [24] Wei Xiang, Yan Junzhong, Jun Yiji, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis, evolution, and electrochemical performance of LiMn0.5Fe0.5PO4 nanostructures[J]. Physical chemistry chemical physics, 2019,17(28):29-37. [25] Zhou Xue, Xie Ye, Deng Yuanfu, et al. The enhanced rate performance of LiFe0.5Mn0.5PO4/C cathode material via synergistic strategies of surfactant-assisted solid state method and carbon coating[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014,3(3):996-1004. -





 下载:
下载:









 下载:
下载: