Progress of laser additive manufactured high-performance metal structural materials
-
摘要: 高性能金属构件激光增材制造技术在重大高端装备制造中展现出巨大发展潜力和广阔的应用前景,北京航空航天大学在大型金属构件激光增材制造方面开展了深入研究,取得了许多突破性研究成果。文中综述了该团队在高性能金属结构材料激光增材制造技术方面的研究进展,揭示了激光增材制造非平衡凝固形核生长机理,建立了钛合金和镍基高温合金晶粒形态主动控制方法,提出了激光增材制造材料强韧化新机理,开发出高性能增材制造钛合金和超高强度钢。未来研究热点仍聚焦于激光/金属交互作用行为、材料凝固相变规律等基础问题研究,以及基于激光增材超常冶金的高性能全新金属结构材料设计与开发,以进一步发挥激光增材制造技术在国家重大装备大型金属构件制造方面的变革性潜力。Abstract: Laser additive manufacturing technology on high-performance metallic components has shown great potential and broad application prospects in the manufacturing of key equipment. Beihang University has conducted deep research on laser additive manufactured large metallic components and achieved many research breakthroughs. In this article, the progress of laser additive manufactured high-performance metal structural materials was summarized. The non-equilibrium solidification and nucleation growth behavior were revealed, and the active control method on grain morphologies of titanium alloys and nickel-based superalloys was established. Besides, new strengthening and toughening mechanisms for laser additive manufactured materials were proposed, while titanium alloy and ultra-high strength steel specially for additive manufacturing were developed. Future research interests will continue to focus on fundamental issues such as laser/metal interaction behavior, material solidification and phase transition laws, as well as the design and development of high-performance new alloys based on extreme metallurgical conditions of laser additive manufacturing. Thus, the transformative potential of laser additive manufacturing technology in the manufacturing of large metal components for key equipments can be further unleashed.
-
0. 引言
随着现代工业的快速发展,航空、航天、电力、石化、船舶等高端装备正向大型化、高参数、高安全、长寿命、低成本的方向快速发展,对钛合金、高强钢、耐热合金等大型复杂关键金属构件的制造技术要求越来越高。采用铸锭冶金和塑性成形等传统制造技术生产上述大尺寸、复杂结构、高性能关键金属构件,需要万吨级以上的重型锻造装备及大型锻造模具,技术难度大,且材料切削量大、材料利用率低、周期长、成本高。因此,钛合金等高性能难加工金属大型关键构件制造技术已成为国家重大高端装备制造业的基础和核心关键技术。
高性能金属构件激光增材制造(Laser additive manufacturing)技术,采用高功率激光使金属粉末或丝材原位冶金熔化,快速凝固逐层堆积,能够快速完成全致密、高性能大型复杂金属构件的直接近净成形制造,是一种“变革性”的低成本、短周期、高性能、“控形/控性”一体化、绿色、数字制造技术,可为大中型难加工金属构件的制造提供一种快速、柔性、低成本、高性能、短周期的新方法。该技术在航空、航天、核电、石化、船舶等重大高端装备制造中展现出巨大发展潜力和广阔应用前景,已成为国际材料加工工程与先进制造技术学科交叉领域的前沿研究热点方向之一[1−6]。
北京航空航天大学大型金属构件增材制造国家工程实验室经过20多年的研究,在该领域取得了许多突破性研究成果,尤其是激光增材制造钛合金关键承力构件已在大型运输机、运载火箭等航空航天重大装备研制和生产中得到应用。笔者主要介绍了团队在高性能金属结构材料激光增材制造技术方面的研究进展。
1. 揭示激光增材制造非平衡凝固形核生长机理,建立晶粒形态主动控制方法
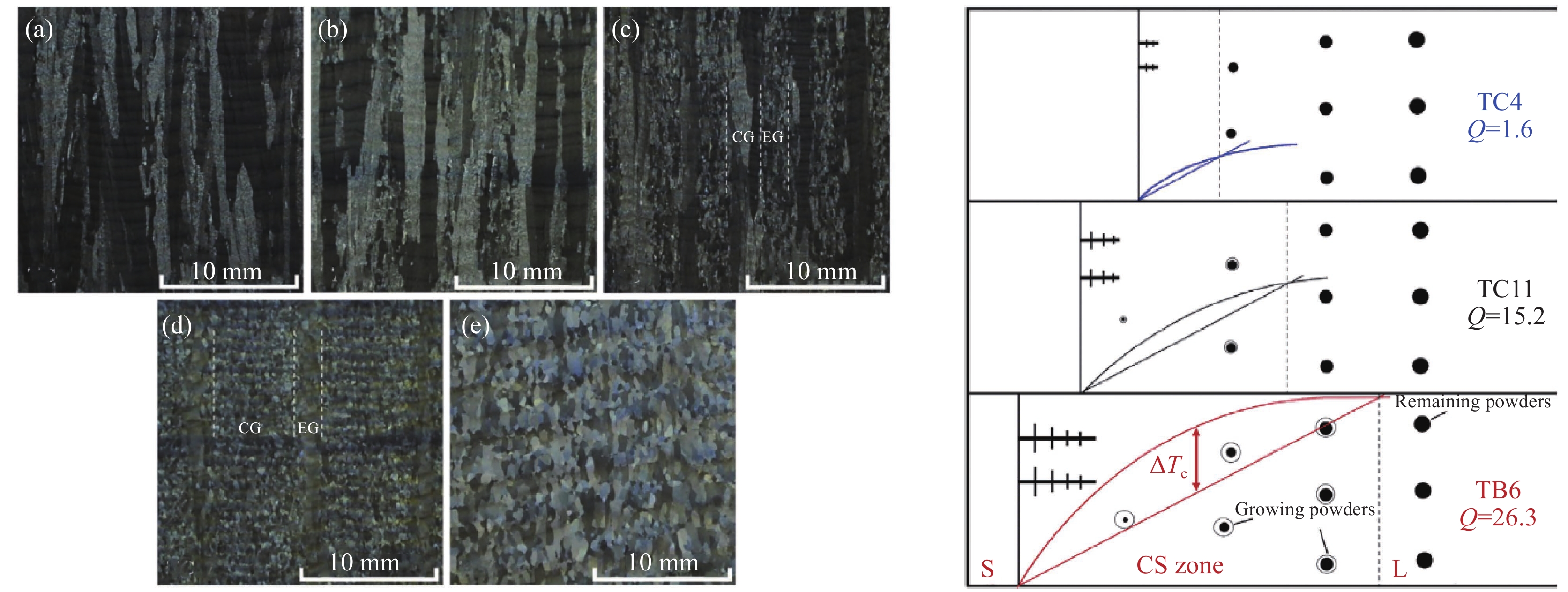
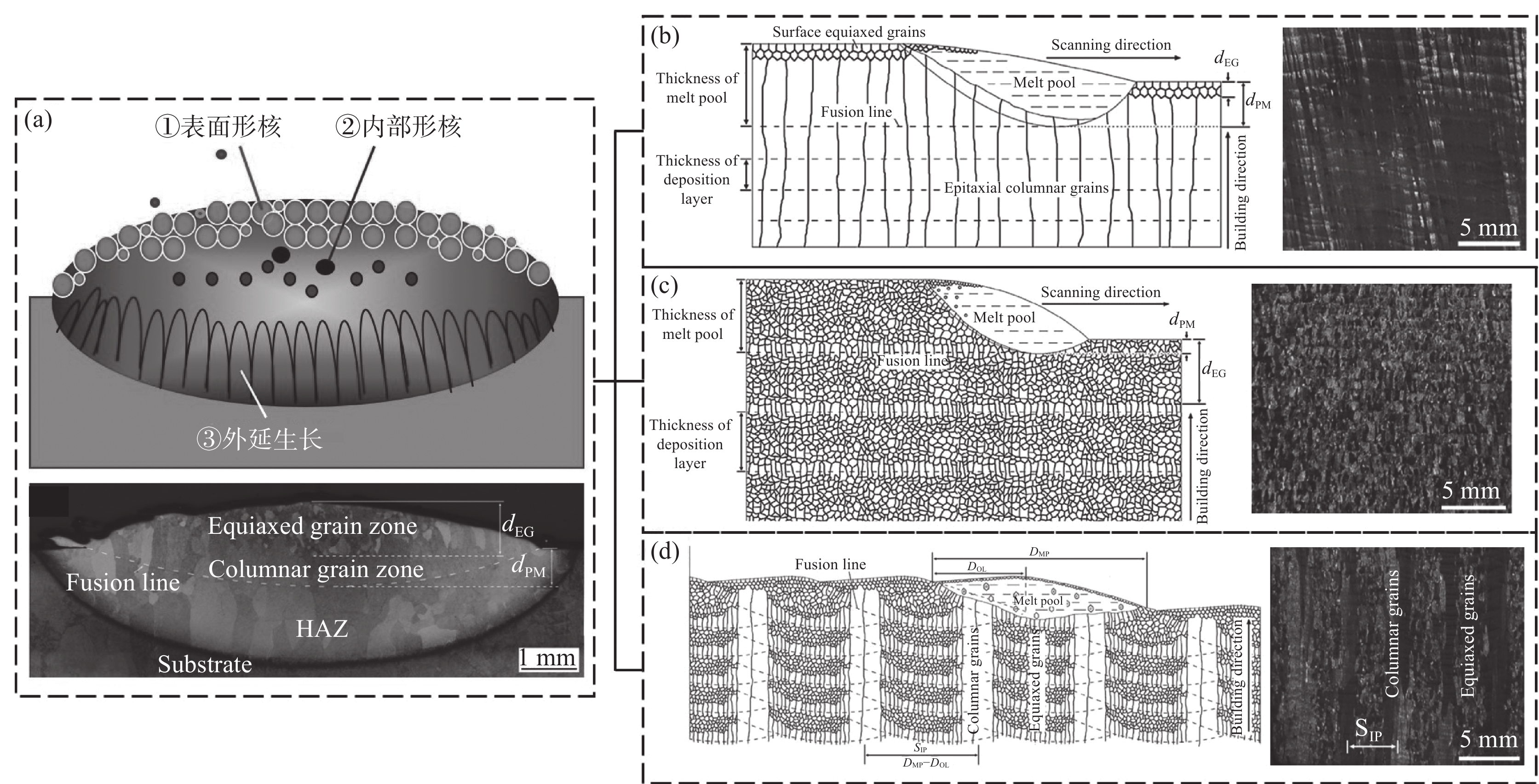
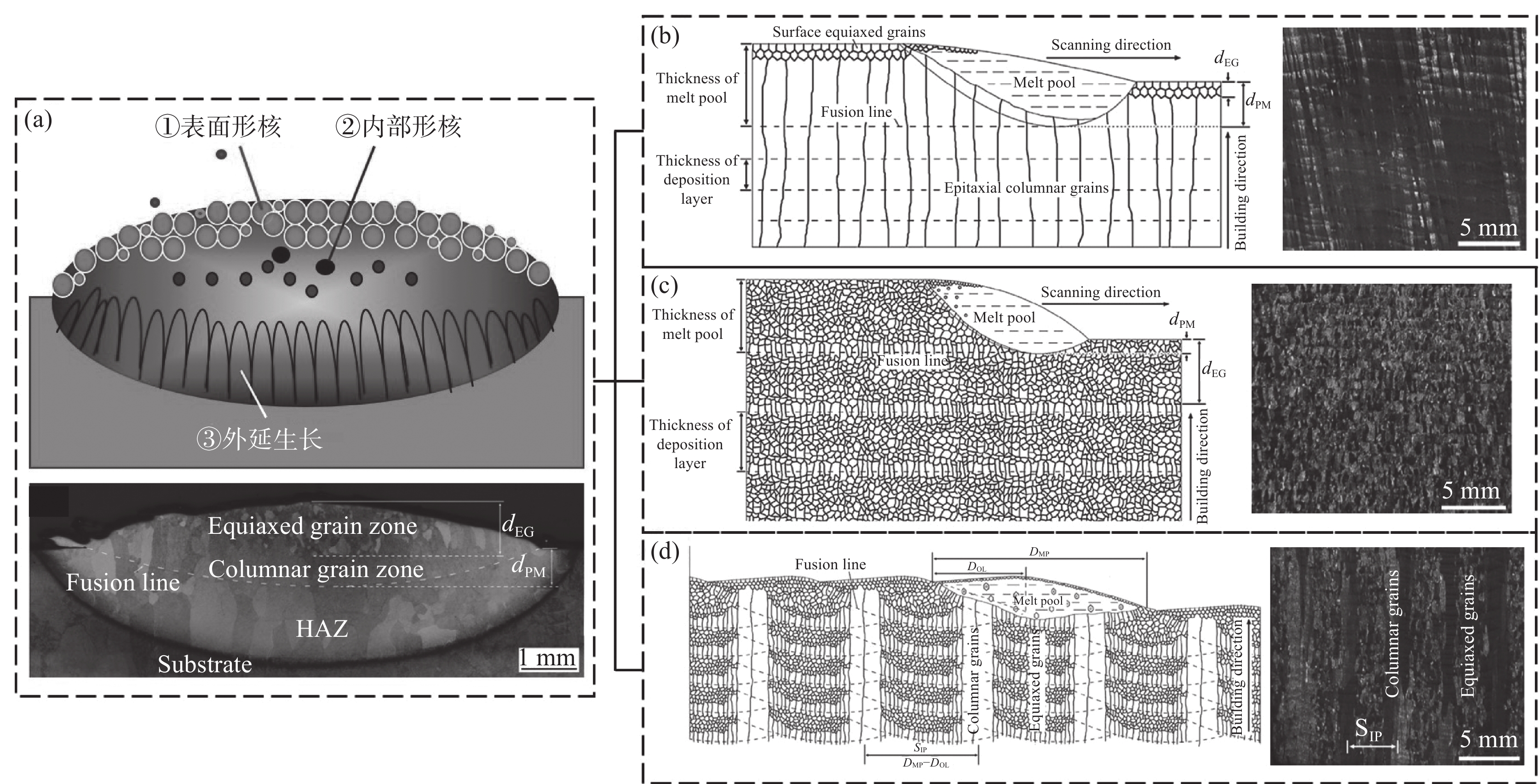
激光增材制造过程中移动熔池微区熔体的冶金动力学行为及其晶体形核和长大过程直接决定了最终增材制造构件的冶金组织(如晶粒尺寸、晶粒形态、晶体取向、晶界结构及化学成分均匀性等)和力学性能,并表现出对激光增材制造工艺参数和工艺过程状态变化的高敏感性及复杂多变性。建立一种可行的激光增材制造大型钛合金构件晶粒形貌控制方法是一项具有挑战性的研究,需要对激光逐层增材制造过程中的凝固行为有深入的了解。北航团队对激光增材制造钛合金不同工艺条件下局部熔池的凝固形核与生长机制、逐层堆积晶粒形态选择行为等进行了全面研究,为激光增材制造钛合金构件晶粒形貌控制通用方法的建立奠定了重要基础[7−9]。图1为激光增材制造TC11钛合金不同晶粒形态及形成机制[8]。
结果显示,等轴晶的非均匀形核和柱状晶的池底外延生长是两种主要凝固机制,熔池内两种凝固机制之间的竞争主导了晶粒形态选择过程,并决定了逐层沉积构件的沉积态晶粒结构。通过对熔池局部凝固温度梯度、沉积速度的控制,获得了全柱状晶、全等轴晶以及一种独特的由柱状晶和等轴晶粒交替排列组成的类“钢筋混凝土”晶粒结构,并建立了这三种代表性晶粒形态主动控制方法。
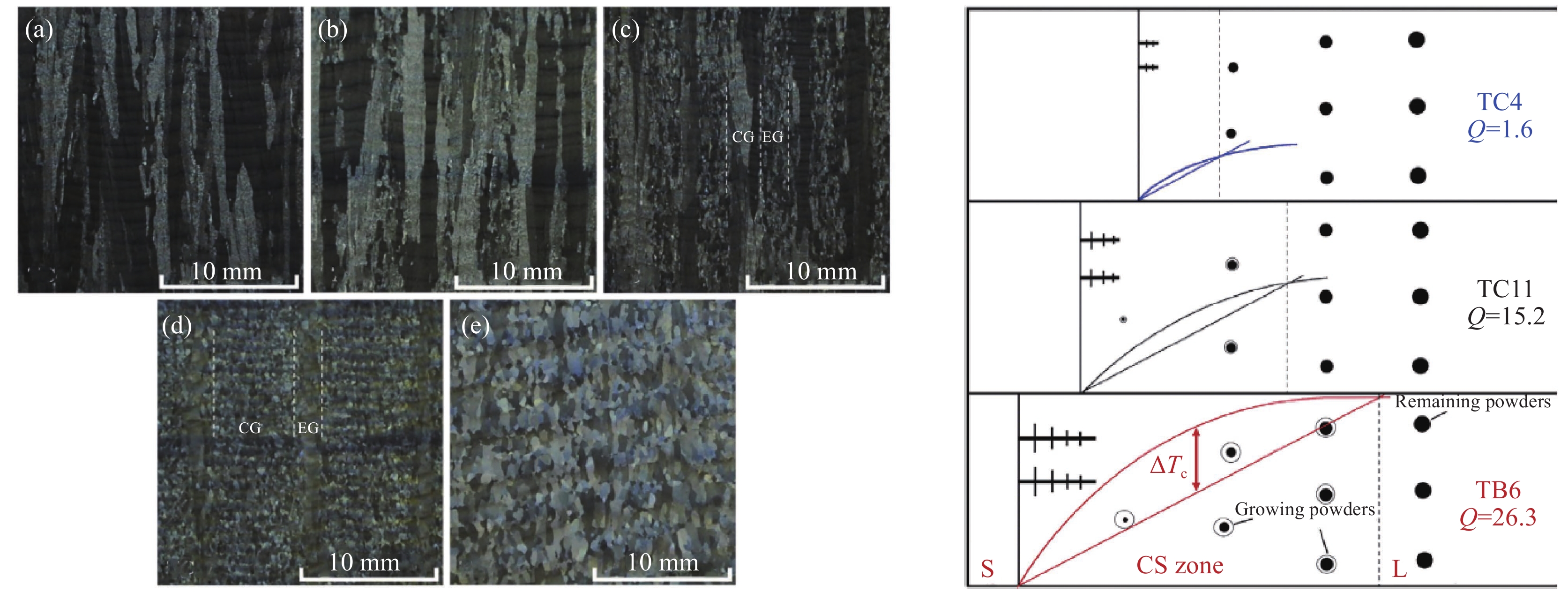
进一步研究了合金化元素含量对激光增材制造钛合金凝固行为和晶粒形态的影响(见图2)。选取具有不同Mo当量和生长限制因子Q的TC4、TA15、TC11、TC17、TB6等五种钛合金,发现在相同的工艺条件下,激光增材制造五种钛合金中等轴晶粒的形成趋势和体积分数随着合金元素含量的增加而逐渐增加,等轴晶体积分数从TC4钛合金的0(全柱状晶组织)到TC11钛合金的45%(柱-等混合组织),再到TB6钛合金的100%(全等轴晶组织)[9]。
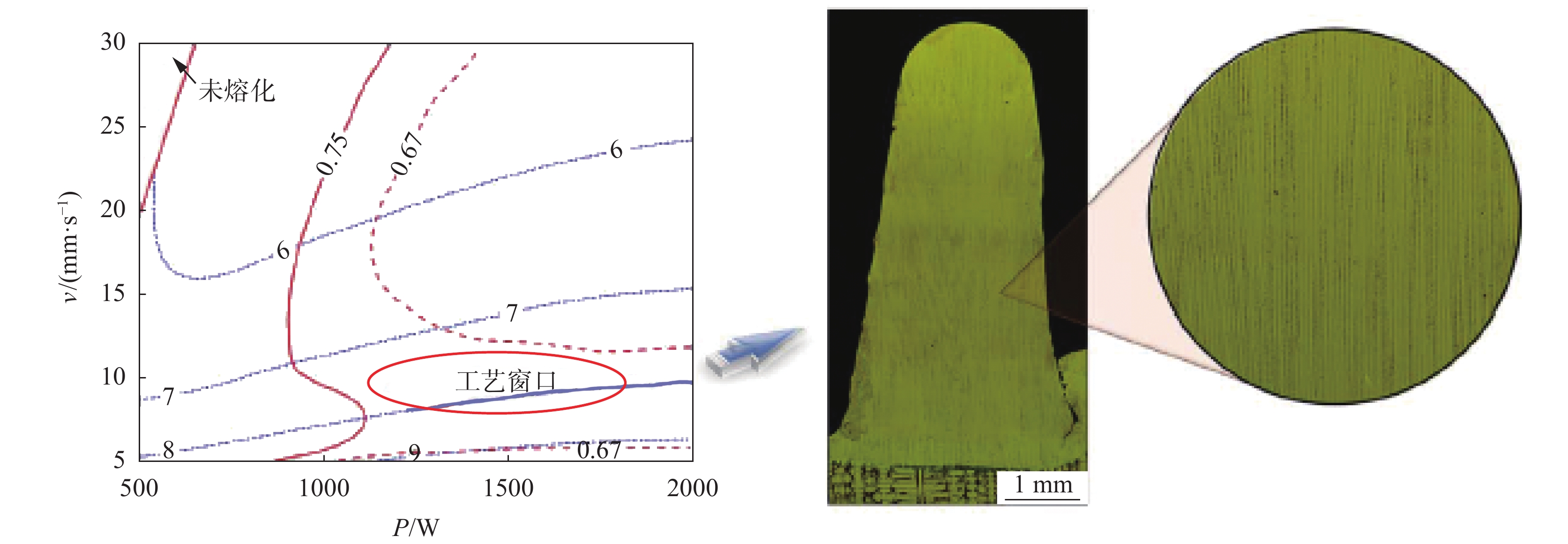
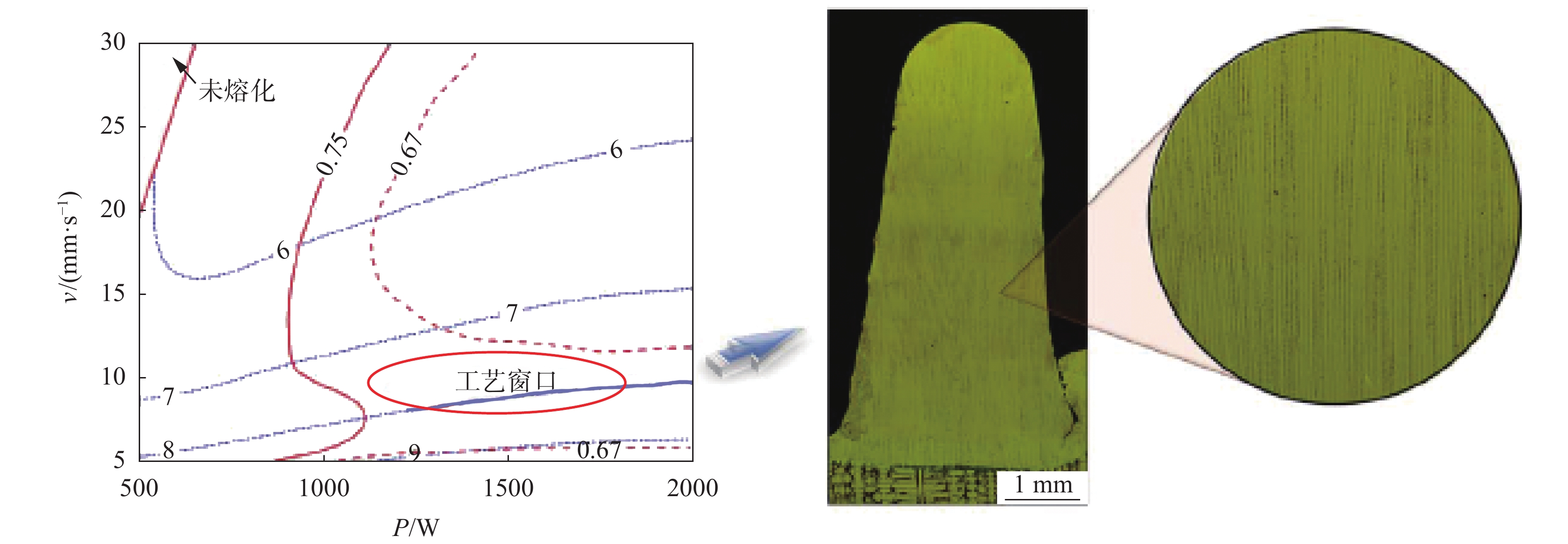
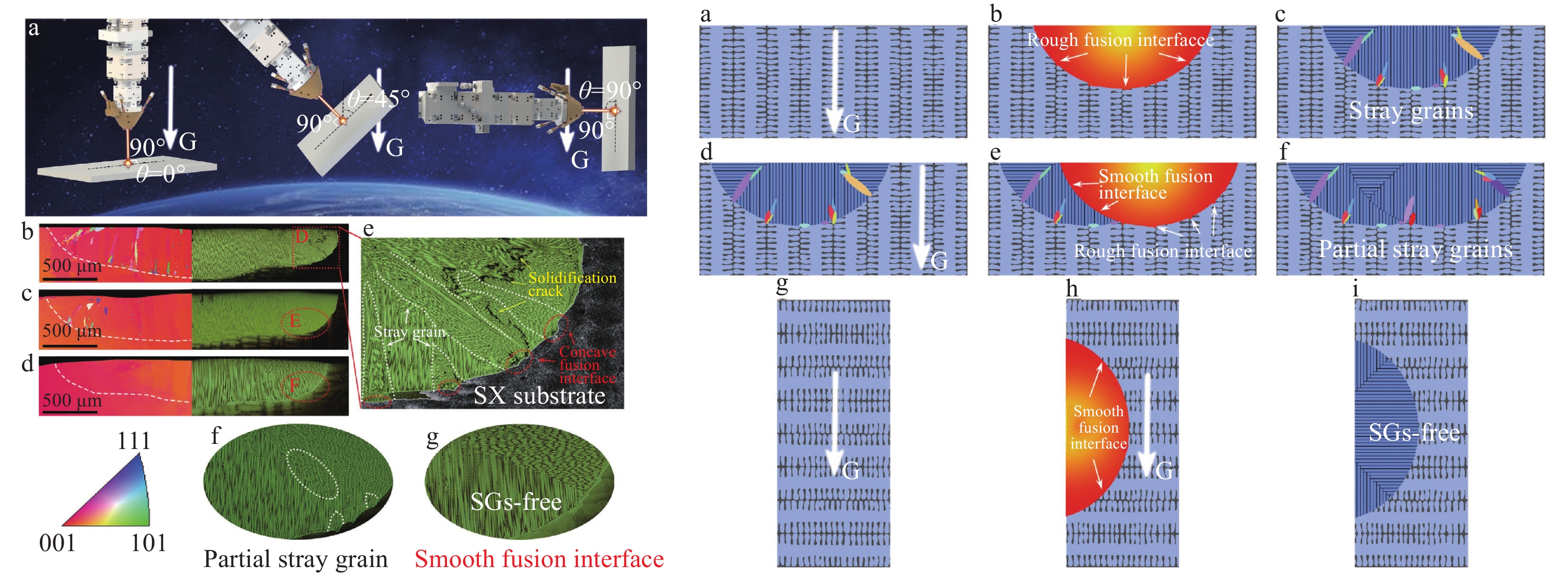
对凝固组织的控制是单晶镍基高温合金激光增材制造成功的关键,北航团队发展出微细柱晶/单晶高温合金激光约束熔化沉积增材制造技术新途径。通过试验和数值模拟,建立了激光增材制造工艺—凝固组织之间的联系,获得了合适的加工窗口,可成功制备出无裂纹、低偏析、枝晶细小的微细柱晶/单晶高温合金试样[10](见图3)。
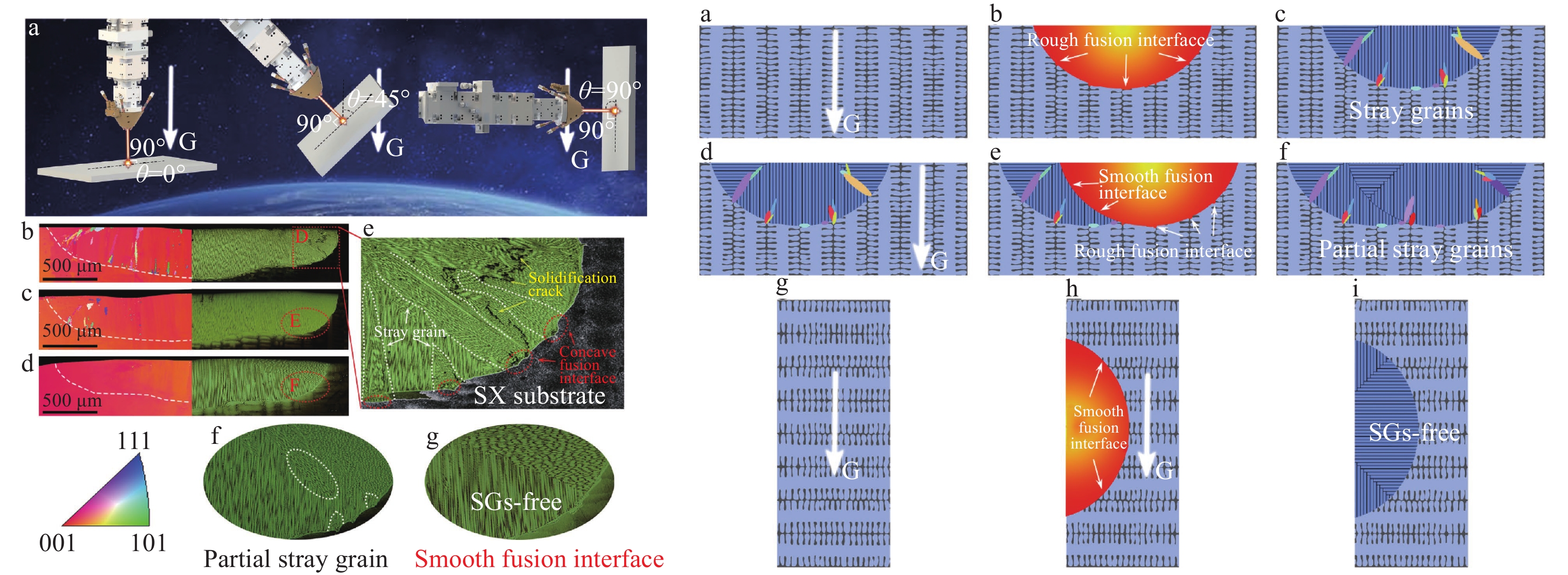
在传统定向凝固单晶基材上进行激光增材制造,发现基材枝晶间的成分偏析易使熔池底部结晶时形成非定向晶粒;基材熔化过程枝晶间区域形成的熔池轮廓凹陷,以及枝晶间区域的化学成分和未熔的析出相(大块γ′相及碳化物颗粒等)会促进熔池结晶时非定向晶粒形核;在激光快速凝固过程中,通过激光束水平照射方法增加熔池底部液体流动速度,或者采用基材均匀化处理降低其微观偏析,可以形成光滑的固液界面,能够有效抑制熔池底部结晶时非定向晶粒的形成[11](见图4)。此外,还发现基材晶体取向会影响激光增材制造凝固过程中树枝晶的生长方向,进而会影响熔池结晶时非定向晶粒的生成,基于计算模型和试验结果,获得了优化的基材取向条件((001)/[110]条件),并成功地使用激光增材制造技术在单晶基材上制备出镍基高温合金单晶试样[12]。
2. 开发出高性能激光增材制造金属结构材料,提出激光增材制造强韧化新机理
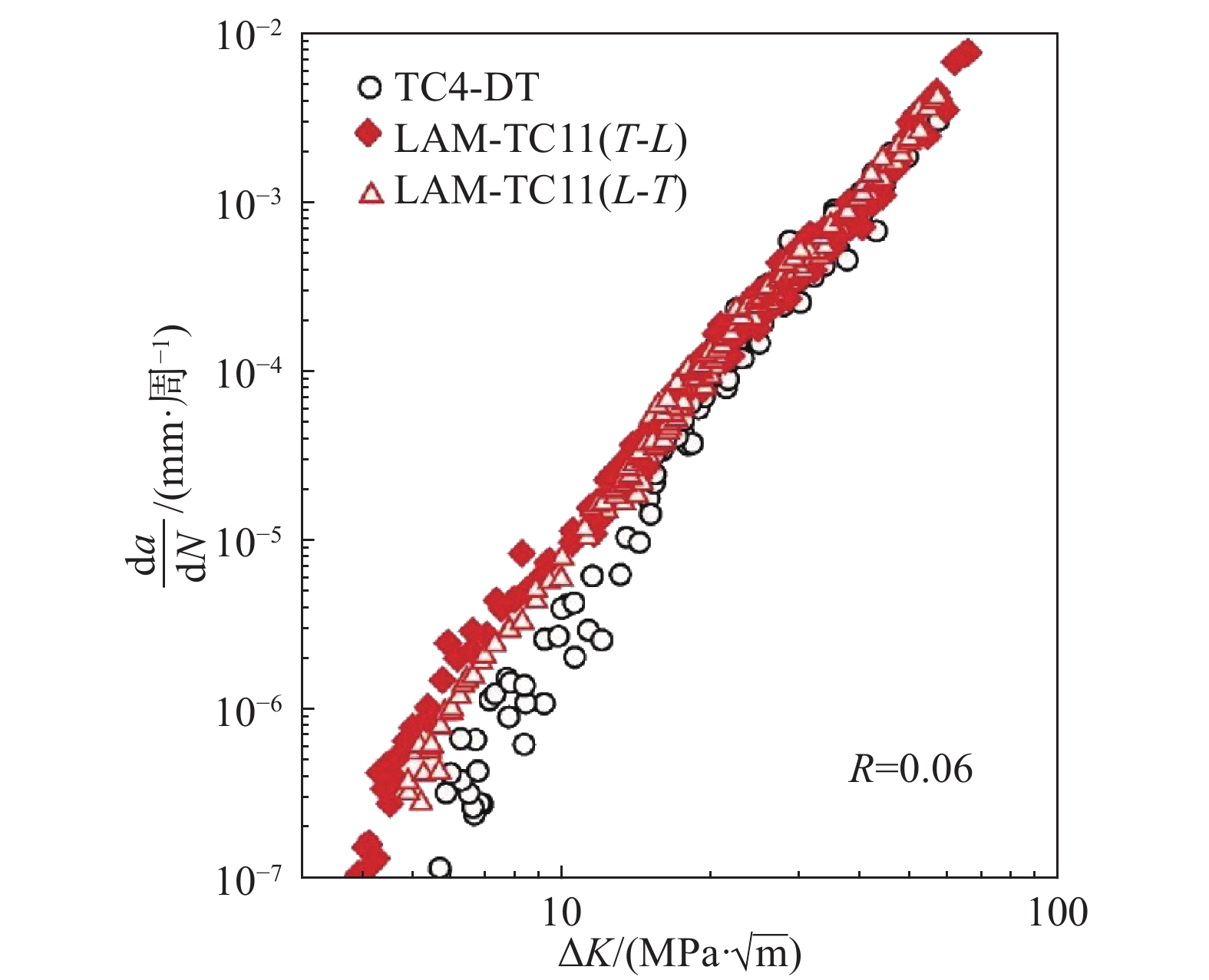
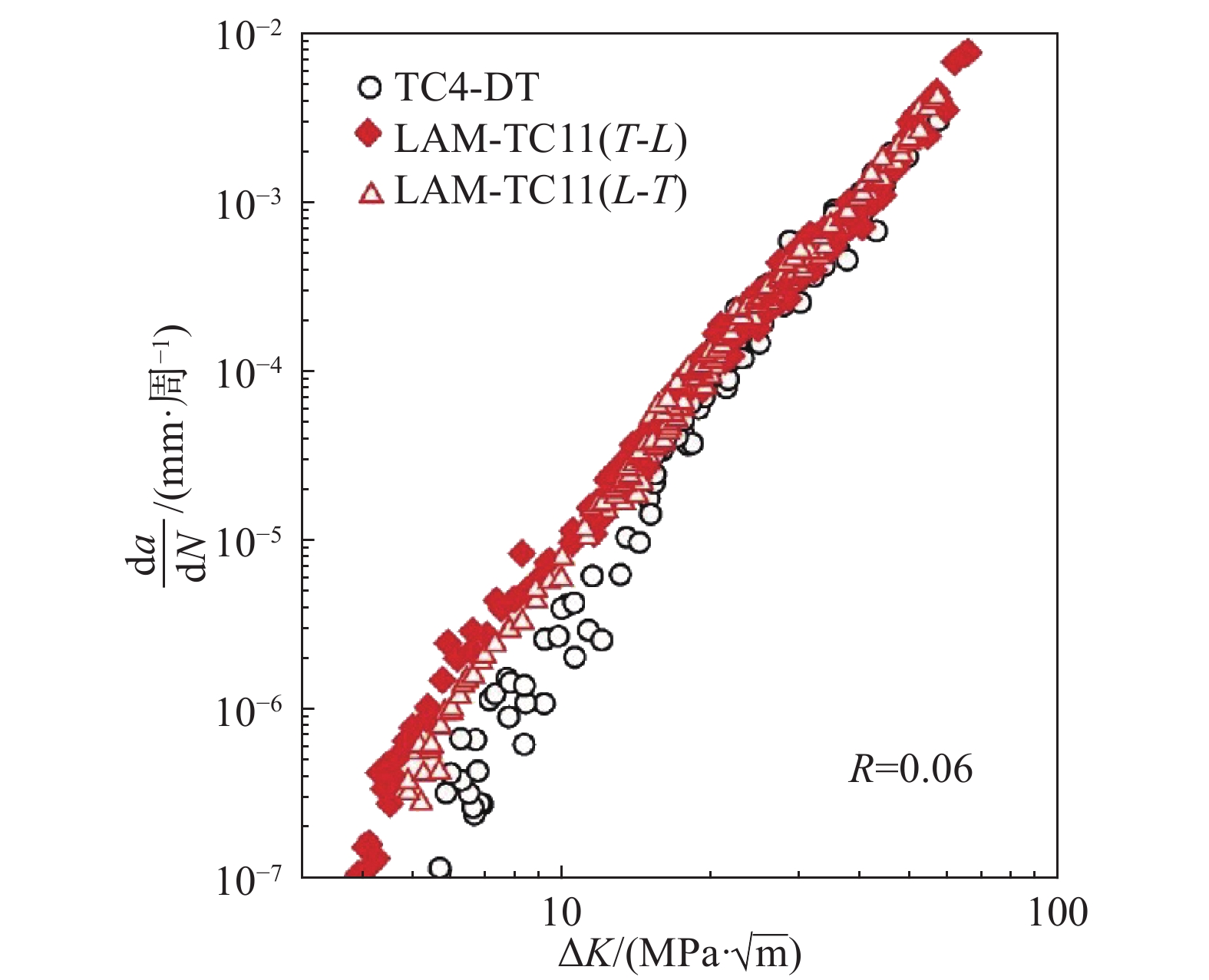
团队在国内外率先开展了基于增材制造的高性能钛合金激光超常冶金制备研究。激光增材制造钛合金在经历了极为特殊的超高温度/温度梯度、瞬时小尺寸熔池快速熔化—快速凝固过程以及逐层沉积反复剧烈温度热循环后,形成了特殊的超细网篮组织,进一步通过专用热处理工艺得到与传统制造技术完全不同的特种双态组织,由端部带有触须状形貌的片层初生α相和超细α+β转变组织构成,该特种双态组织的“α/β比界面积”极高,能够阻碍位错滑移而具有较高的静强度,同时在塑性变形过程中能够更加有效地阻碍裂纹扩展,从而提高综合力学性能[13−15]。据此通过钛合金化学成分的精确调控、激光增材制造成形工艺和专用热处理工艺的全流程控制,突破了激光增材制造高强韧钛合金材料制备关键技术,开发出激光增材制造高强高韧钛合金材料LAM-TC11,与目前主承力结构采用的TC4-DT钛合金相比,损伤容限性能相当,疲劳性能有所改善,许用应力提高23%,其高强韧性、低疲劳缺口敏感性和优异的抗裂纹扩展特性对大型整体主承力结构减重、服役安全具有重要意义[16]。其中,LAM-TC11与锻件TC4-DT钛合金的疲劳裂纹扩展速率见图5,LAM-TC11、TC11锻件、TC4-DT和TC4钛合金强度和断裂韧性对比见表1。
 图 5 LAM-TC11与锻件TC4-DT钛合金的疲劳裂纹扩展速率相当[16]Figure 5. Comparison of fatigue crack growth rate of LAM-TC11 titanium alloy and forged TC4-DT
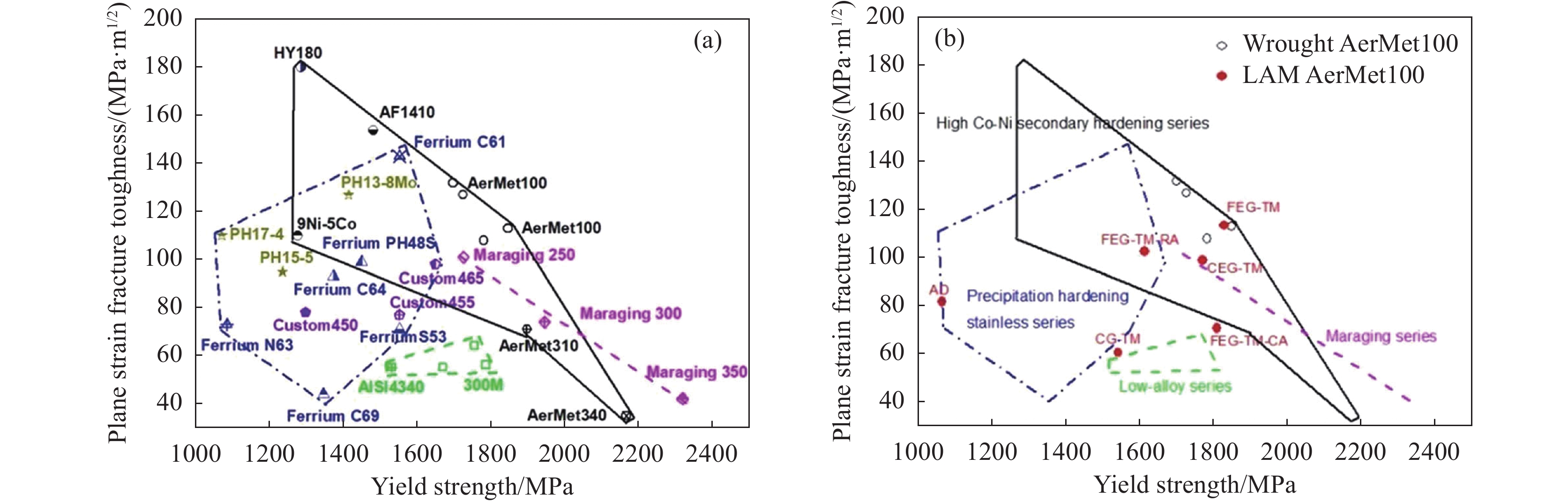
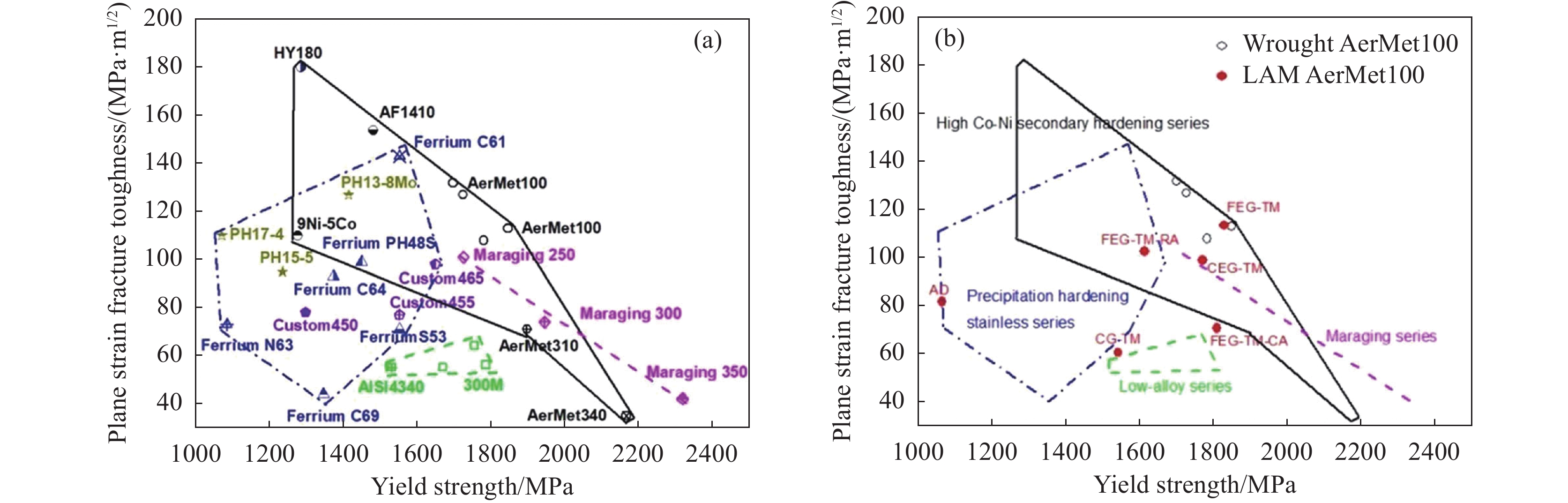
图 5 LAM-TC11与锻件TC4-DT钛合金的疲劳裂纹扩展速率相当[16]Figure 5. Comparison of fatigue crack growth rate of LAM-TC11 titanium alloy and forged TC4-DT开发出激光增材制造AerMet100超高强度钢材料,揭示了激光增材制造高合金超高强韧钢的组织演化机制和热处理强韧化机制,激光增材制造AerMet100钢的拉伸性能、断裂韧性、疲劳性能等综合力学性能及耐蚀性能达到了锻件水平[17−19],激光增材制造AerMet100钢的屈服强度和断裂韧性及其与典型商用超高强度钢的性能对比见图6。团队与航空工业沈阳飞机设计研究所合作,试制了激光增材制造AerMet100钢飞机起落架零件,通过了结构综合验证试验,并已在飞机上实现了领先试用[20]。
表 1 LAM-TC11、TC11锻件、TC4-DT和TC4钛合金强度和断裂韧性对比[16]Table 1. Comparison of ultimate strength and fracture toughness of LAM-TC11, forged TC11, TC4-DT and TC4 titanium alloys[16]试样 极限强度
σb/MPa屈服强度
σ0.2/MPa断裂韧性
KIC/(MPa·m1/2)屈强比
σ0.2/σb(KIC/σb)/(mm)1/2 许用应力
[σ]=(σb/1.5)/MPa(KIC/σ0.2)2/mm LAM-TC11 1056 902 116 0.85 3.47 704 16.54 TC11锻件 1076 980 76 0.91 2.23 717 6.01 TC4-DT(锻造) 858 794 106 0.93 3.92 572 17.82 TC4(锻造) 922 885 64 0.96 2.19 614 5.23 3. 未来研究热点及趋势
尽管金属结构材料激光增材制造技术已取得了一定的研究成效,但仍有大量全新前沿基础性问题和核心技术需要潜心研究,主要的研究热点及趋势如下:
1)高性能金属结构材料激光增材制造基础问题研究。包括激光/金属交互作用行为及能量吸收利用机制、内部冶金缺陷形成机制及力学行为、移动熔池约束凝固行为及构件晶粒形态演化规律、非稳态循环固态相变行为及显微组织形成规律、内应力演化规律及构件变形开裂预防方法等方面,持续系统深入的研究,以及新的测试手段和理论方法的出现有望进一步加深对上述基础问题的理解,实现对激光增材制造高性能金属结构材料质量性能的更加精细控制。
2)基于激光增材超常冶金的高性能全新金属结构材料设计与开发。传统材料大多基于铸造或锻造技术开发,其材料成分并不能充分匹配激光增材制造技术优势,在对高性能金属结构材料激光增材制造基础问题深入理解的基础上,开发增材制造专用的钛合金、高温合金、高强钢、铝合金、镁合金等新型金属结构材料。
3)面向国家重大装备研制生产亟需,开发大型/超大型金属构件高沉积效率、高质量、高性能、低成本、智能化激光增材制造技术。
-
图 5 LAM-TC11与锻件TC4-DT钛合金的疲劳裂纹扩展速率相当[16]
Figure 5. Comparison of fatigue crack growth rate of LAM-TC11 titanium alloy and forged TC4-DT
表 1 LAM-TC11、TC11锻件、TC4-DT和TC4钛合金强度和断裂韧性对比[16]
Table 1. Comparison of ultimate strength and fracture toughness of LAM-TC11, forged TC11, TC4-DT and TC4 titanium alloys[16]
试样 极限强度
σb/MPa屈服强度
σ0.2/MPa断裂韧性
KIC/(MPa·m1/2)屈强比
σ0.2/σb(KIC/σb)/(mm)1/2 许用应力
[σ]=(σb/1.5)/MPa(KIC/σ0.2)2/mm LAM-TC11 1056 902 116 0.85 3.47 704 16.54 TC11锻件 1076 980 76 0.91 2.23 717 6.01 TC4-DT(锻造) 858 794 106 0.93 3.92 572 17.82 TC4(锻造) 922 885 64 0.96 2.19 614 5.23 -
[1] Arcella F G, Froes F H. Producing titanium aerospace components from powder using laser forming[J]. JOM, 2000,52(5):28-30. doi: 10.1007/s11837-000-0028-x [2] Wang Huaming. Materials’ fundamental issues of laser additive manufacturing for high-performance large metallic components[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014,35(10):2690-2698. (王华明. 高性能大型金属构件激光增材制造: 若干材料基础问题[J]. 航空学报, 2014,35(10):2690-2698.Wang Huaming. Materials’ fundamental issues of laser additive manufacturing for high-performance large metallic components[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(10): 2690-2698. [3] Wang Xiangming, Su Yadong, Wu Bin. Application of additive manufacturing technology on aircraft structure development[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2014(22):16-20. (王向明, 苏亚东, 吴斌. 增材技术在飞机结构研制中的应用[J]. 航空制造技术, 2014(22):16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2014.22.002Wang Xiangming, Su Yadong, Wu Bin. Application of additive manufacturing technology on aircraft structure development[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2014(22): 16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-833X.2014.22.002 [4] Lu Bingheng. Additive manufacturing——Current situation and future[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020,31(1):19-23. (卢秉恒. 增材制造技术——现状与未来[J]. 中国机械工程, 2020,31(1):19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.01.003Lu Bingheng. Additive manufacturing——Current situation and future[J]. China Mechanical Engineering, 2020, 31(1): 19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2020.01.003 [5] Tang Haibo, Wu Ning, Zhang Shuquan, et al. Research status and development trend of high performance large metallic components by laser additive manufacturing technique[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2019,11(4):58-63. (汤海波, 吴宇, 张述泉, 等. 高性能大型金属构件激光增材制造技术研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 精密成形工程, 2019,11(4):58-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6457.2019.04.008Tang Haibo, Wu Ning, Zhang Shuquan, et al. Research status and development trend of high performance large metallic components by laser additive manufacturing technique[J]. Journal of Netshape Forming Engineering, 2019, 11(4): 58-63. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-6457.2019.04.008 [6] Gu Dongdong, Zhang Hongmei, Chen Hongyu, et al. Laser additive manufacturing of high-performance metallic aerospace components[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020,47(5):32-55. (顾冬冬, 张红梅, 陈洪宇, 等. 航空航天高性能金属材料构件激光增材制造[J]. 中国激光, 2020,47(5):32-55.Gu Dongdong, Zhang Hongmei, Chen Hongyu, et al. Laser additive manufacturing of high-performance metallic aerospace components[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers, 2020, 47(5): 32-55. [7] Wang Huaming, Zhang Shuquan, Wang Tao, et al. Progress on solidification grain morphology and microstructure control of laser additively manufactured large titanium components[J]. Journal of Xihua University(Natural Science Edition), 2018,37(4):9-14. (王华明, 张述泉, 王韬, 等. 激光增材制造高性能大型钛合金构件凝固晶粒形态及显微组织控制研究进展[J]. 西华大学学报(自然科学版), 2018,37(4):9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-159X.2018.04.002Wang Huaming, Zhang Shuquan, Wang Tao, et al. Progress on solidification grain morphology and microstructure control of laser additively manufactured large titanium components[J]. Journal of Xihua University(Natural Science Edition), 2018, 37(4): 9-14. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-159X.2018.04.002 [8] Wang T, Zhu Y Y, Zhang S Q, et al. Grain morphology evolution behavior of titanium alloy components during laser melting deposition additive manufacturing[J]. Journal of Alloy and Compounds, 2015,632:505-513. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2015.01.256 [9] Zhu Yanyan, Tang Haibo, Li Zhuo, et al. Solidification behavior and grain morphology of laser additive manufacturing titanium alloys[J]. Journal of Alloy and Compounds, 2019,777:712-716. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.11.055 [10] Liang Yaojian, Cheng Xu, Li Jia, et al. Microstructural control during laser additive manufacturing of single-crystal nickel-base superalloys: New processing–microstructure maps involving powder feeding[J]. Materials & Design, 2017,130:197-207. [11] Wang Jiawei, Wang Huaming, Li Kangjie, et al. A new strategy to inhibit stray grain formation during laser directed solidification of single crystal superalloys[J]. Journal of Alloy and Compounds, 2022,906:163852. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2022.163852 [12] Wang Jiawei, Wang Huaming, Gao Hongwei, et al. Crystal growth for different substrate orientations during laser directed solidification of single crystal superalloys[J]. Journal of Alloy and Compounds, 2023,957:170219. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2023.170219 [13] Zhu Yanyan, Li Jia, Tian Xiangjun, et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of hybrid fabricated Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si titanium alloy by laser additive manufacturing[J]. Materials Science and Engineering A, 2014,607:427-434. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2014.04.019 [14] Zhu Yanyan, Liu Dong, Tian Xiangjun, et al. Characterization of microstructure and mechanical properties of laser melting deposited Ti-6.5Al-3.5Mo-1.5Zr-0.3Si titanium alloy[J]. Materials and Design, 2014,56:445-453. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2013.11.044 [15] Wang Yafei, Chen Rui, Cheng Xu, et al. Effects of microstructure on fatigue crack propagation behavior in a bi-modal TC11 titanium alloy fabricated via laser additive manufacturing[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2019,35:403-408. [16] Zhang Jikui, Kong Xiangyi, Ma Shaojun, et al. Laser additive manufactured high strength-toughness TC11 titanium alloy: Mechanical properties and application in airframe load-bearing structure[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021,42(10):467-477. (张纪奎, 孔祥艺, 马少俊, 等. 激光增材制造高强高韧TC11钛合金力学性能及航空主承力结构应用分析[J]. 航空学报, 2021,42(10):467-477.Zhang Jikui, Kong Xiangyi, Ma Shaojun, et al. Laser additive manufactured high strength-toughness TC11 titanium alloy: Mechanical properties and application in airframe load-bearing structure[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2021, 42(10): 467-477. [17] Ran Xianzhe, Cheng Hao, Wang Huaming, et al. Corrosion properties of laser melting-deposited corrosion-resistant ultrahigh strength steel AerMet100[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2012,33(12):126-131. (冉先喆, 程昊, 王华明, 等. 激光熔化沉积AerMet100耐蚀超高强度钢的耐蚀性[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2012,33(12):126-131.Ran Xianzhe, Cheng Hao, Wang Huaming, et al. Corrosion properties of laser melting-deposited corrosion-resistant ultrahigh strength steel AerMet100[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment, 2012, 33(12): 126-131. [18] Ran Xianzhe, Liu Dong, Li Jia, et al. Effects of post homogeneity heat treatment processes on microstructure evolution behavior and tensile mechanical properties of laser additive manufactured ultrahigh-strength AerMet100 steel[J]. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2018,723:8-21. [19] Ran Xianzhe, Zhang Shuquan, Liu Dong, et al. Role of microstructural characteristics in combination of strength and fracture toughness of laser additively manufactured ultrahigh-strength AerMet100 steel[J]. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A, 2021,52:1248-1259. doi: 10.1007/s11661-021-06148-1 [20] Cui Can, Wang Xiangming, Wu Bin, et al. Study on application of laser deposited additive manufacturing technology on aircraft undercarriage[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2018,61(10):74-79. (崔灿, 王向明, 吴斌, 等. 激光直接沉积成形增材制造技术在飞机起落架上的应用研究[J]. 航空制造技术, 2018,61(10):74-79.Cui Can, Wang Xiangming, Wu Bin, et al. Study on application of laser deposited additive manufacturing technology on aircraft undercarriage[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2018, 61(10): 74-79. -






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载: